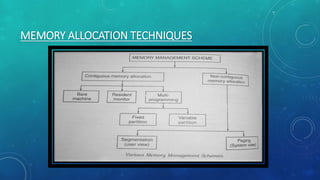
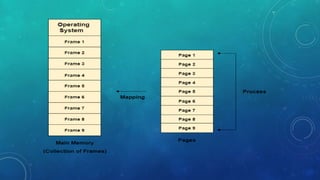
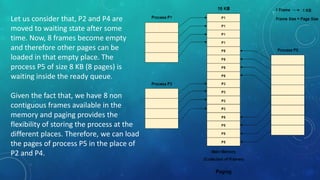
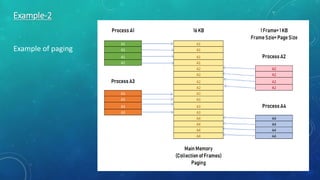
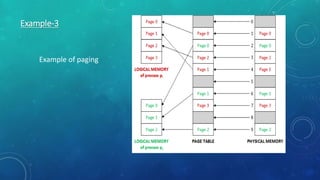
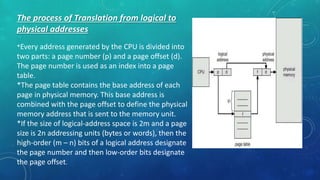
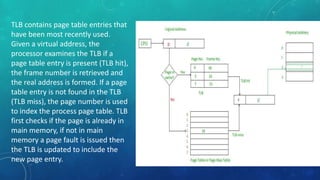
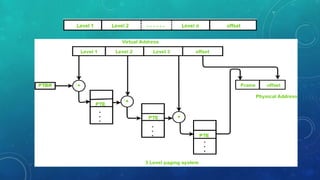
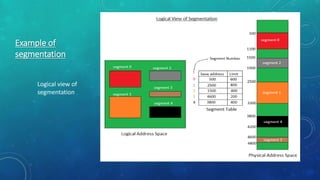
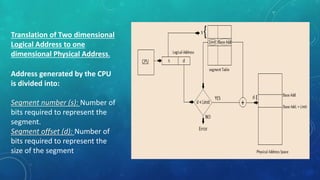
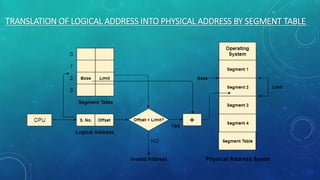
Memory management is the method by which an operating system handles and allocates primary memory. It tracks the status of memory locations as allocated or free, and determines how memory is distributed among competing processes. Memory can be allocated contiguously or non-contiguously. Contiguous allocation assigns consecutive blocks of memory to a process, while non-contiguous allocation allows a process's memory blocks to be scattered across different areas using techniques like paging or segmentation. Paging divides processes and memory into fixed-size pages and frames to allow non-contiguous allocation while reducing fragmentation.