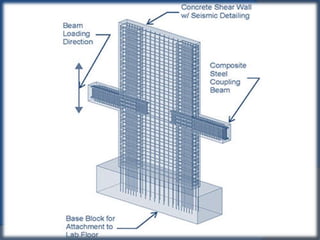
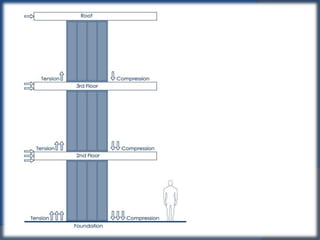
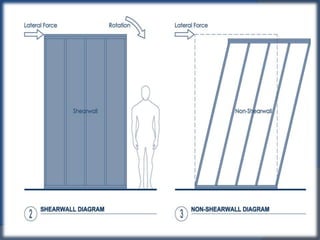
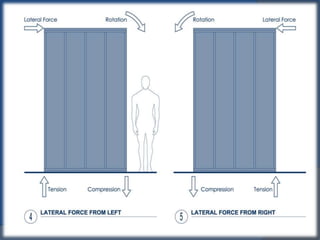
Shear walls are structural elements found in buildings that provide strength and stiffness to resist lateral forces like wind and earthquakes. They run continuously from the foundation to the top of the building and can range in thickness from 150mm to 400mm. Shear walls carry large horizontal loads during earthquakes and work together with beams, columns, and moment frames to resist seismic forces in different directions. Reinforcing concrete structures with external steel shear walls is an effective technique for strengthening existing buildings by improving seismic capacity, base shear capacity, and stiffness while also reducing costs and construction time compared to other methods.