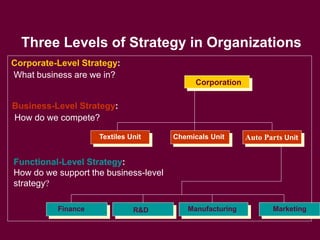
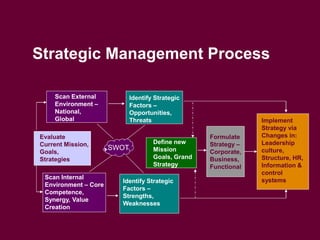
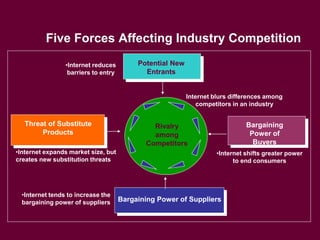
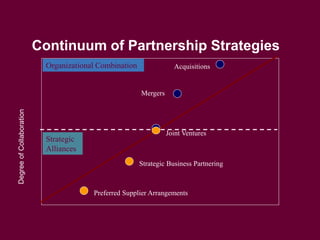
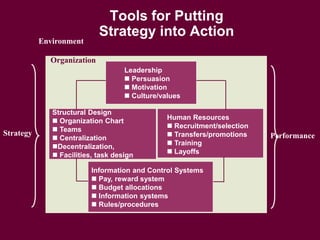
The document discusses strategic management and planning, including defining strategy formulation as establishing goals and plans and strategy implementation as using tools to achieve strategic outcomes. It covers topics such as analyzing organizational strengths and weaknesses, developing grand strategies for growth, stability, or retrenchment, and implementing strategies through leadership, structural design, information and control systems, and human resources. Key models and frameworks are presented for strategic management processes, global corporate strategies, and competitive strategies.