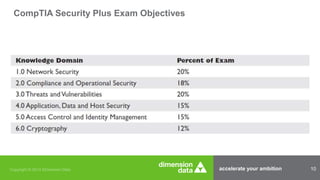
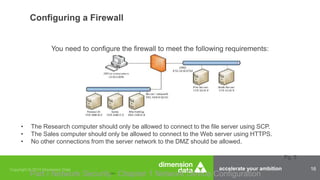
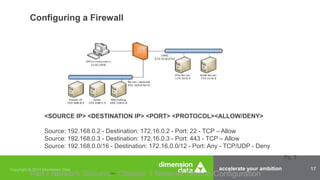
The document outlines the necessity of obtaining a security certification, such as CompTIA Security+, for IT professionals, particularly within the military and government sectors due to mandates like DOD 8570.01-M, which requires certified personnel for information assurance roles. It details various security devices, including firewalls, routers, and switches, and emphasizes the importance of their configuration to maintain network security. Additionally, it mentions available training programs and resources for preparing for the CompTIA Security+ examination.