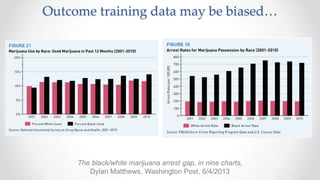
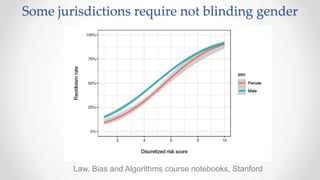
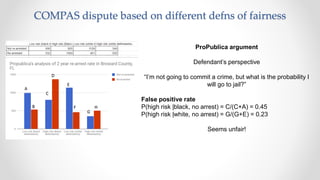
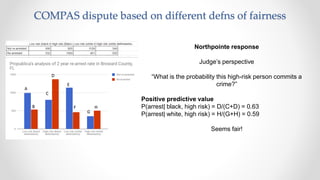
The document discusses frameworks for assessing algorithmic bias and fairness, focusing on how algorithms influence outcomes based on protected classes such as race, gender, and age. It examines various legal and ethical concepts of fairness in machine learning, including allocative fairness, demographic parity, and disparate impact, highlighting both the potential and limitations of algorithmic decision-making in contexts like sentencing and lending. The text also emphasizes that achieving fairness is complex, requiring careful consideration of the data, systems, and societal impacts involved.











![Notation for fairness properties
Observable features of each case are a vector X
The class or group membership of each case is A
Model outputs a numeric “score” R
R = r(X,A) ∊ [0,1]
We turn the score into a binary classification C by thresholding at t
C = r > t
The true outcome (this is a prediction) is the binary variable Y
A perfect predictor would have
C = Y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfa2019algorithmicbias3-190704174445/85/Frameworks-for-Algorithmic-Bias-19-320.jpg)