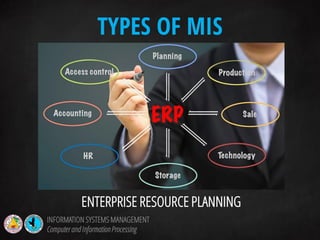
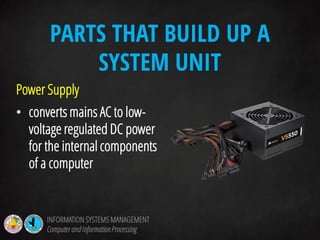
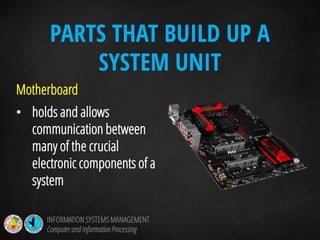
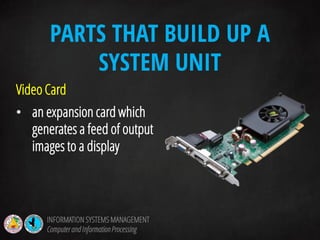
The document discusses information systems management and information processing. It defines key terms like data, information, and information processing systems. It describes the functions of an information processing system as accepting input, processing data into information, storing data and information, and presenting output. It outlines the six components of an information processing system as hardware, software, data, procedures, people, and feedback. It also discusses the evolution of management information systems and provides examples of different types of information systems used.