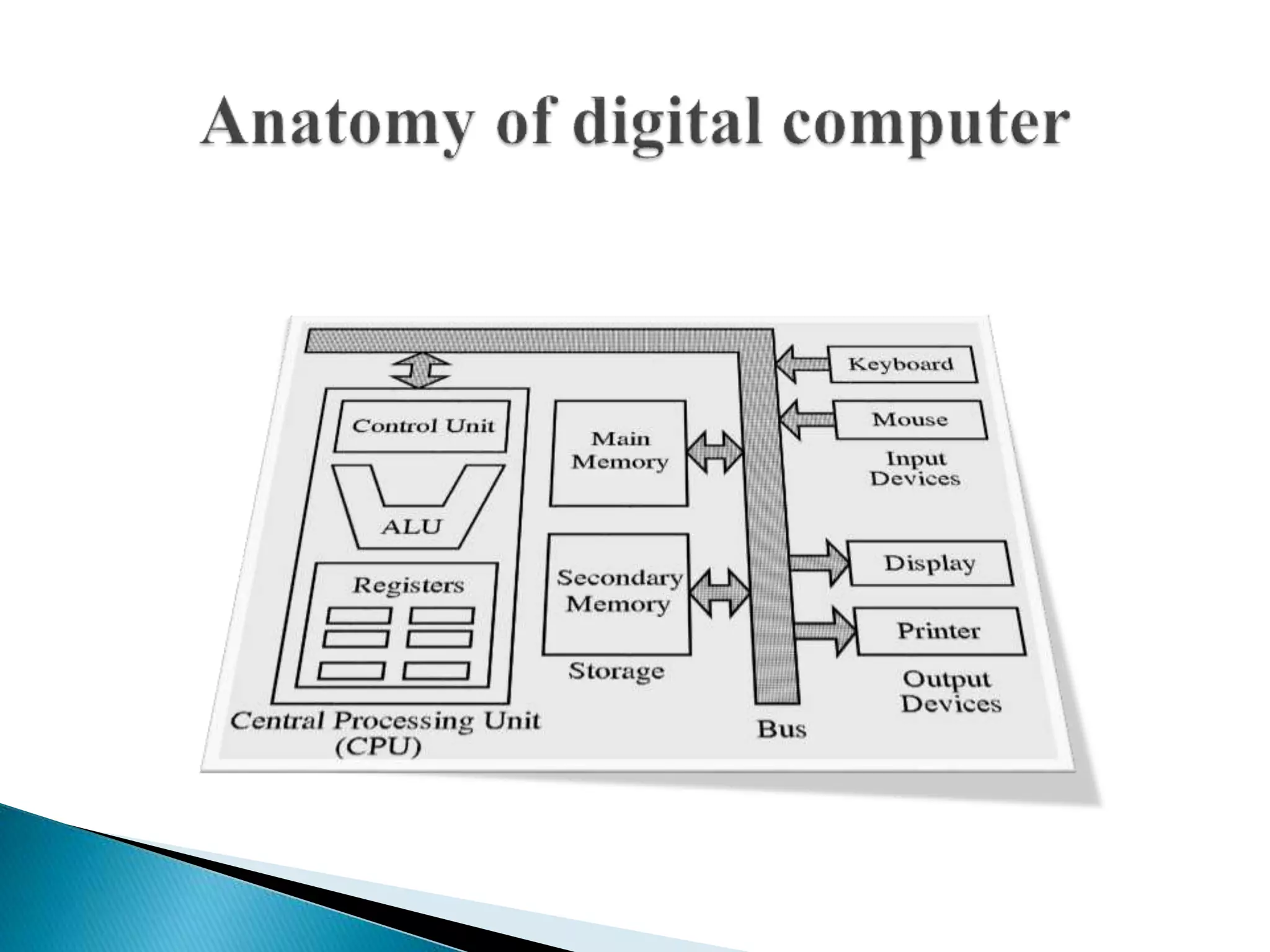
Information technology encompasses various areas such as computer support, network management, and information security. It involves different types of computers and storage devices, alongside input and output devices, and requires a programming language and operating system to function effectively. Additionally, cybersecurity is crucial for protecting information systems across various applications, including business, education, and entertainment.