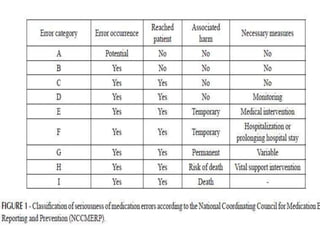
The Pune Adventist Hospital training document addresses medication errors, defining them as preventable events that can harm patients. It details contributing factors including human, system, and medication-related issues, and outlines the six rights of medication administration. Various types of errors, such as prescribing, dispensing, administration, transcription, and indent errors are also discussed, alongside common causes and risks associated with each type.