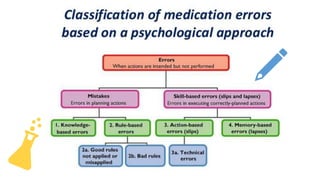
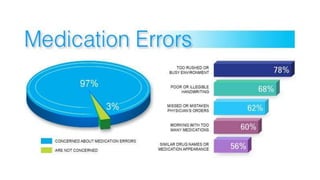
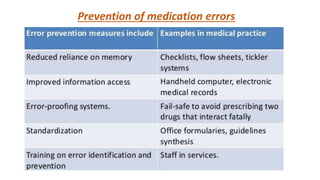
Medication errors can occur at any point during the medication use process and can cause patient harm if not prevented. This presentation defines medication errors as any preventable event that may cause inappropriate medication use or patient harm. It then describes common types of medication errors such as prescribing errors, omission errors, wrong time errors, unauthorized drug errors, and more. The presentation emphasizes that medication errors are a particular problem in low and middle income countries. It concludes by stating that prevention of medication errors is important but does not provide specifics on prevention strategies.