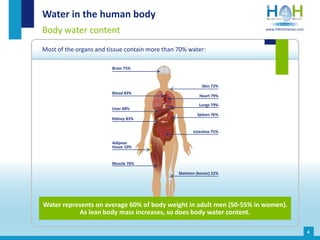
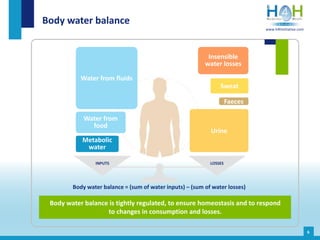
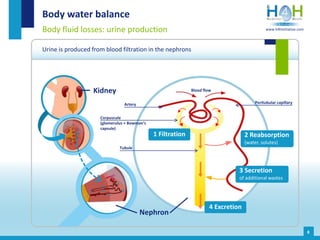
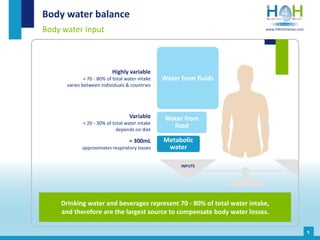
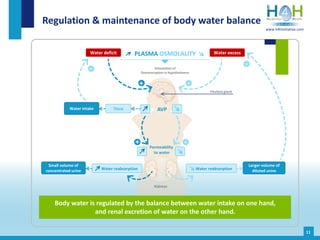
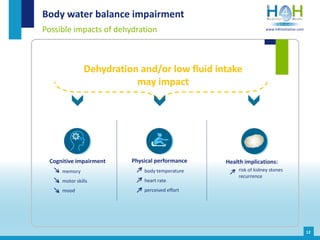
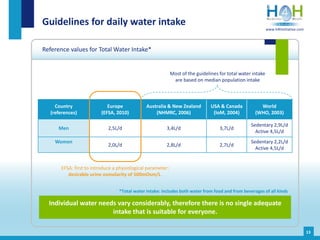
The document covers the physiological basis of hydration and water balance in the human body, detailing body water distribution, absorption, and regulation mechanisms. It emphasizes the importance of adequate water intake to maintain cognitive and physical functions and provides guidelines for daily water consumption for both men and women. Additionally, it highlights the health impacts of dehydration, including risks to kidney function and overall physical performance.