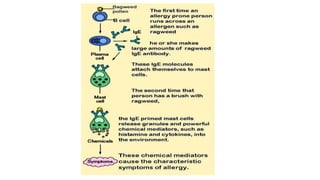
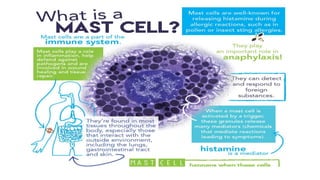
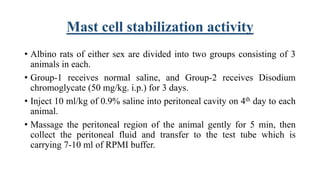
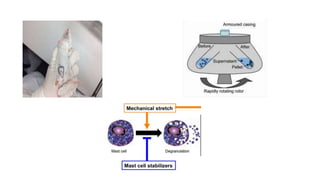
This document describes procedures for evaluating the antiallergic and mast cell stabilizing activity of drugs. It involves using guinea pigs to test if drugs can prevent bronchoconstriction induced by histamine aerosol exposure. It also involves collecting mast cells from rat peritoneal fluid and observing if drugs can prevent degranulation when exposed to egg albumin. The procedures provide a way to test if drugs can stabilize mast cell membranes and prevent the release of inflammatory mediators associated with allergic responses.