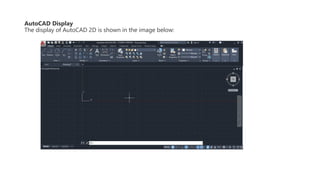
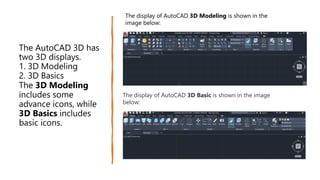
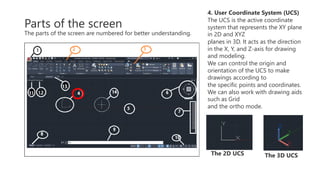
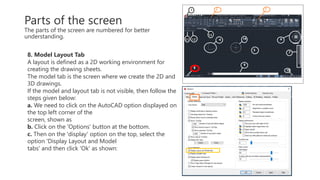
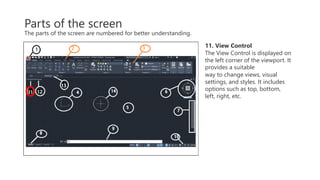
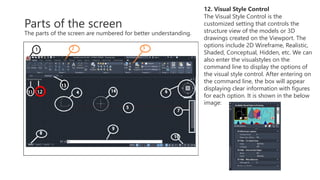
This document provides an overview of the basic parts of the AutoCAD screen interface. It describes 14 key parts of the screen for both 2D and 3D displays, including the application menu, ribbon panels, user coordinate system, model space, view cube, navigation bar, command line, status bar, view controls, visual style controls, file tabs, and mouse cursor. The document numbers and provides images for each part, and gives brief descriptions of their functions in AutoCAD.