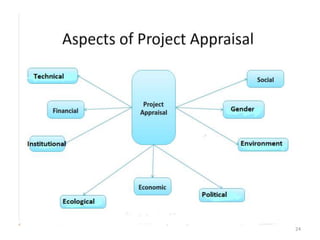
The presentation by Group No. 09 outlines the critical aspects of project appraisal necessary for successful project planning and execution. It addresses various dimensions such as social acceptability, environmental impact, technical feasibility, and financial viability, while highlighting the importance of a systematic appraisal process. Key issues discussed also include implementation strategies, risk management, and the assessment of the project's economic, social, and environmental impacts.