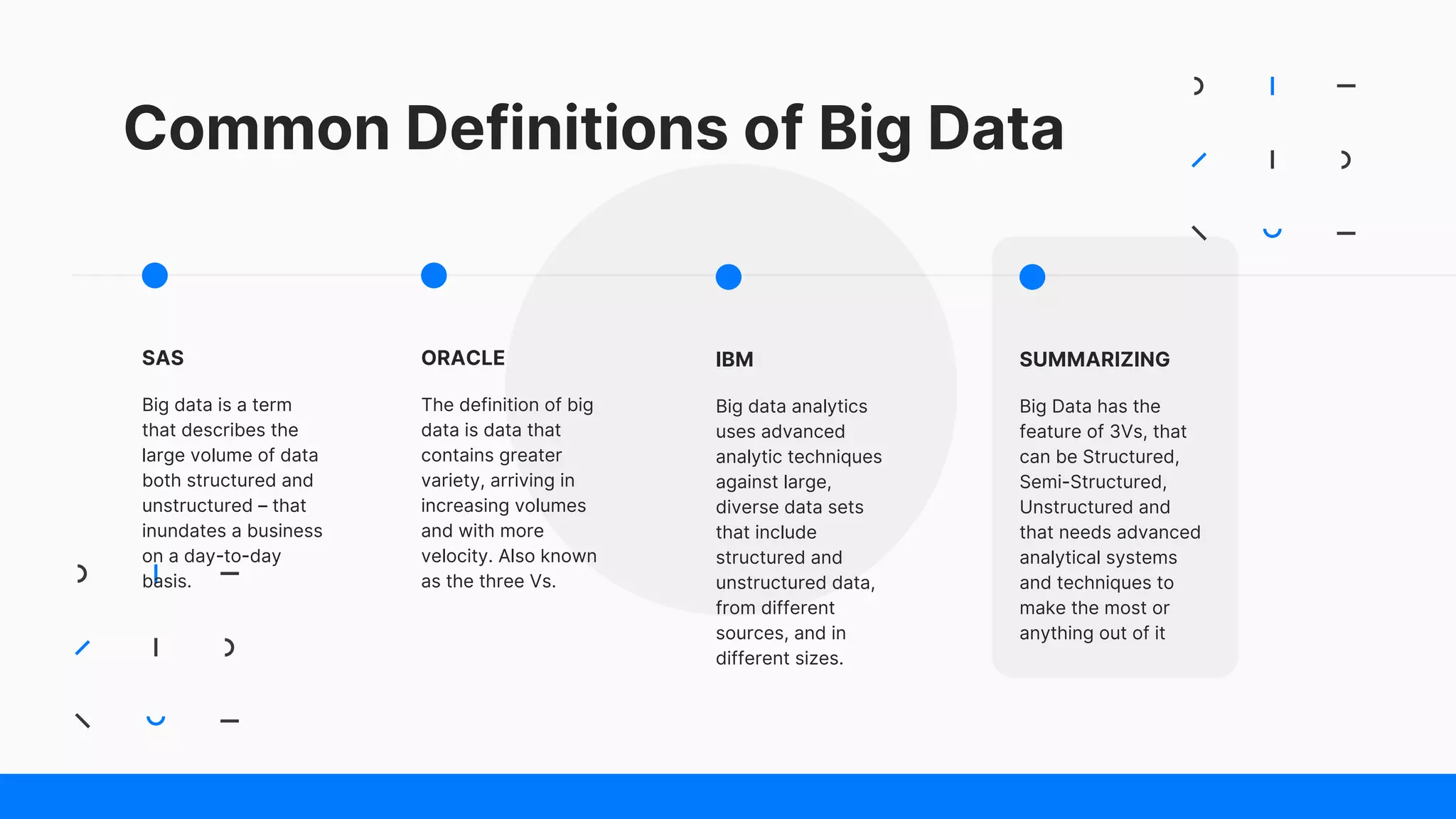
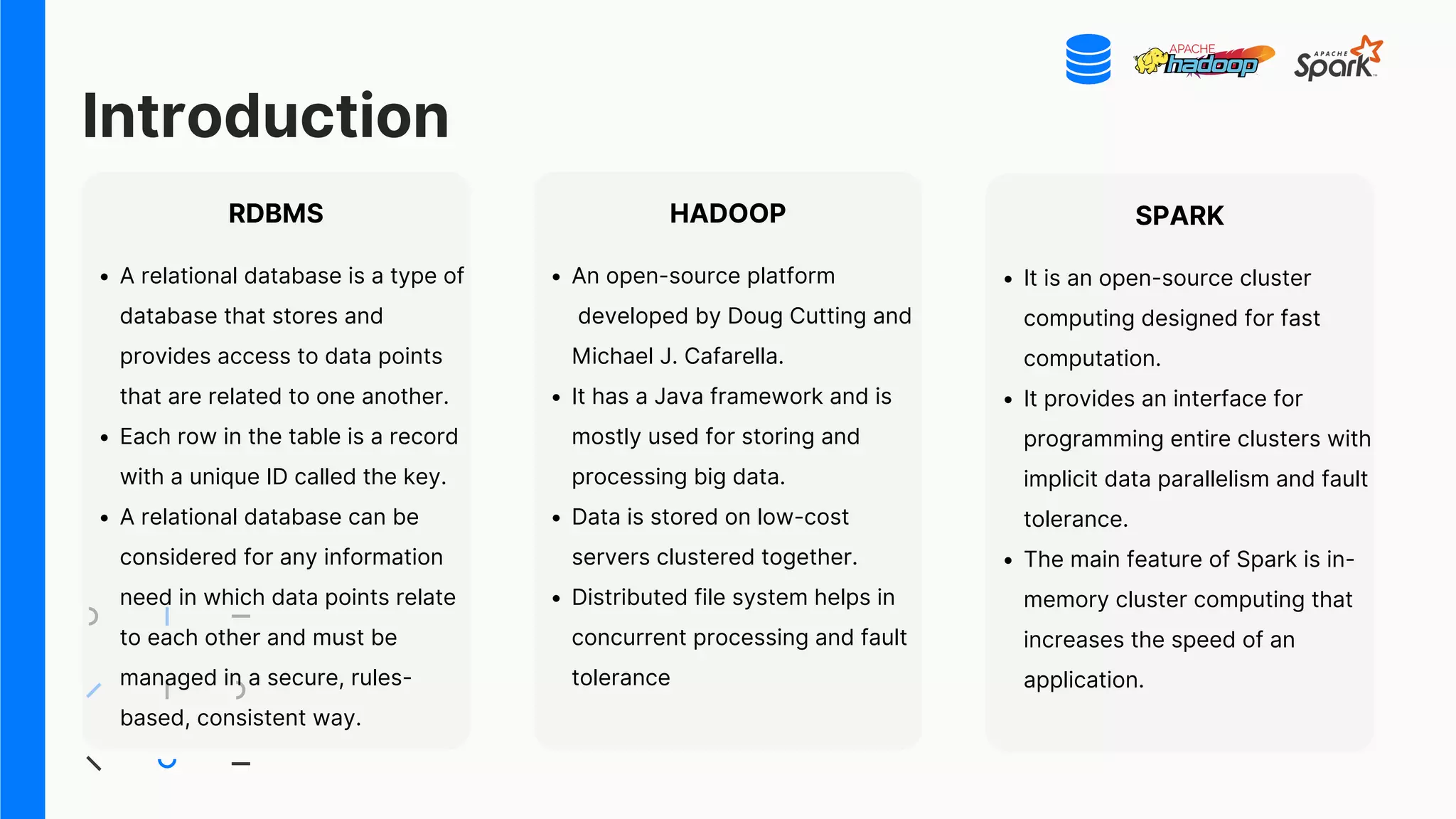
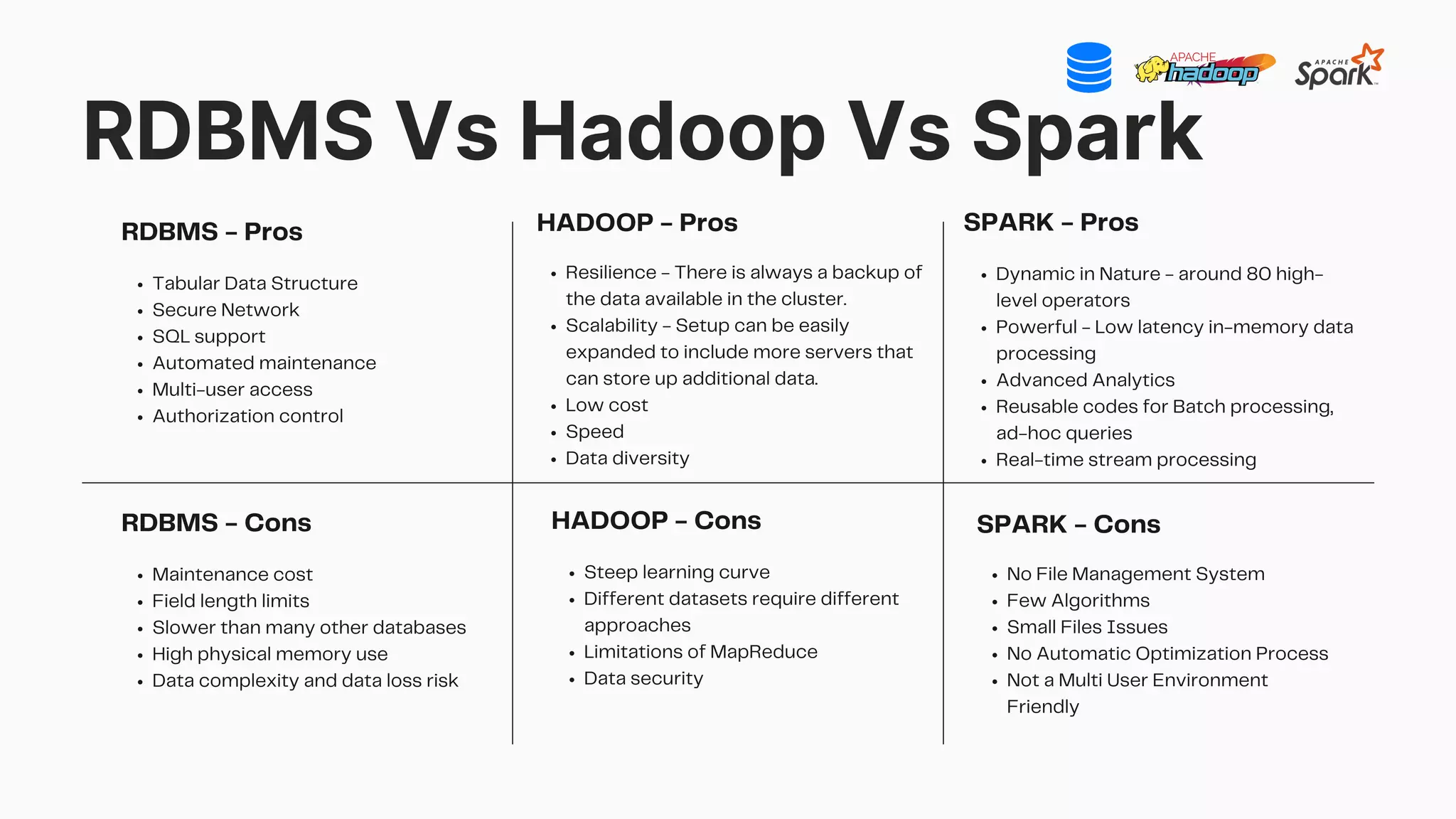
The document compares RDBMS, Hadoop, and Spark, outlining their definitions, core competencies, and functional differences in handling big data. It discusses applications of each system across various industries and highlights the benefits and drawbacks of each framework in terms of scalability, performance, and security. The presentation emphasizes the importance of selecting the right technology based on specific business needs and data characteristics.