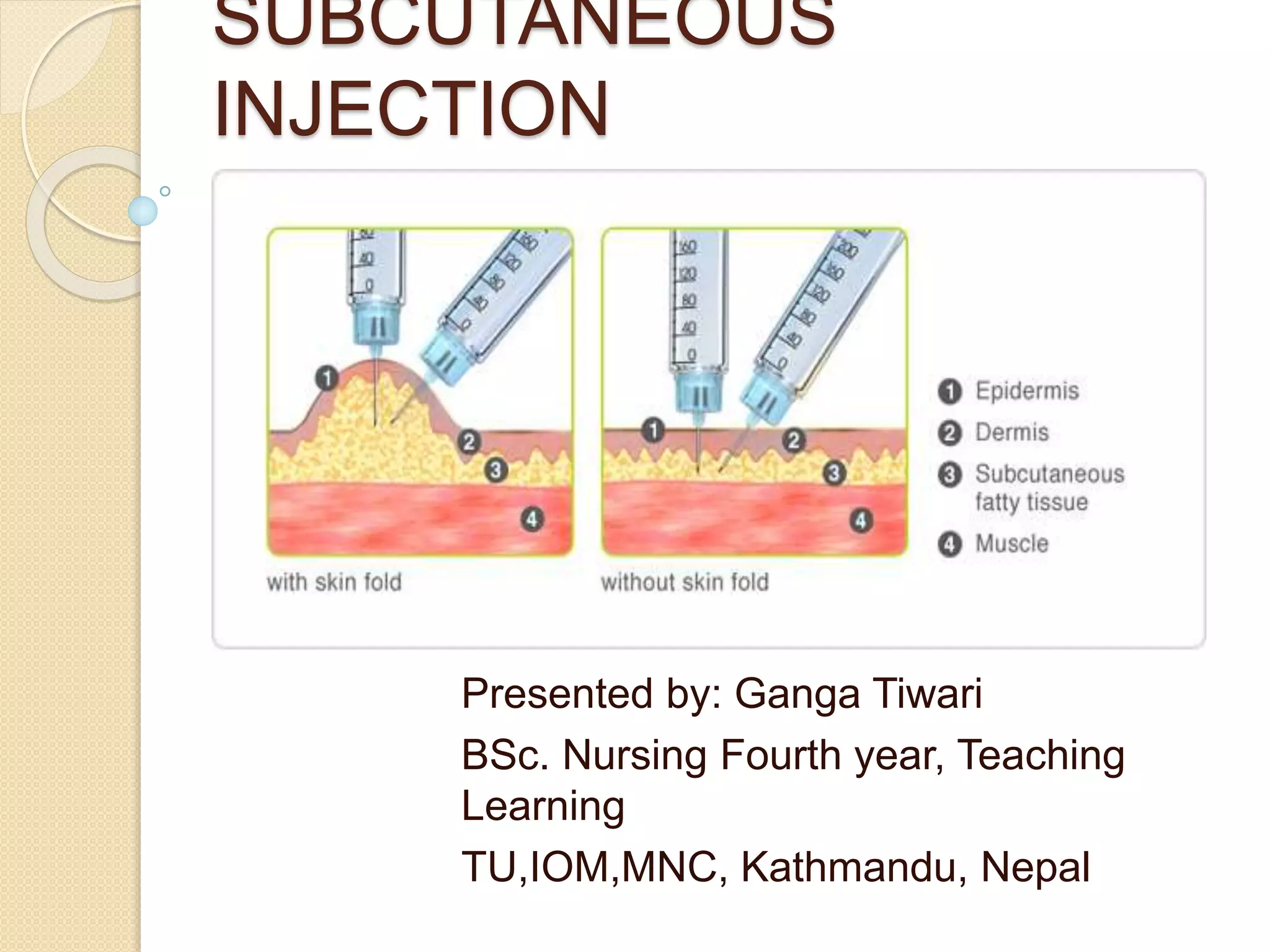
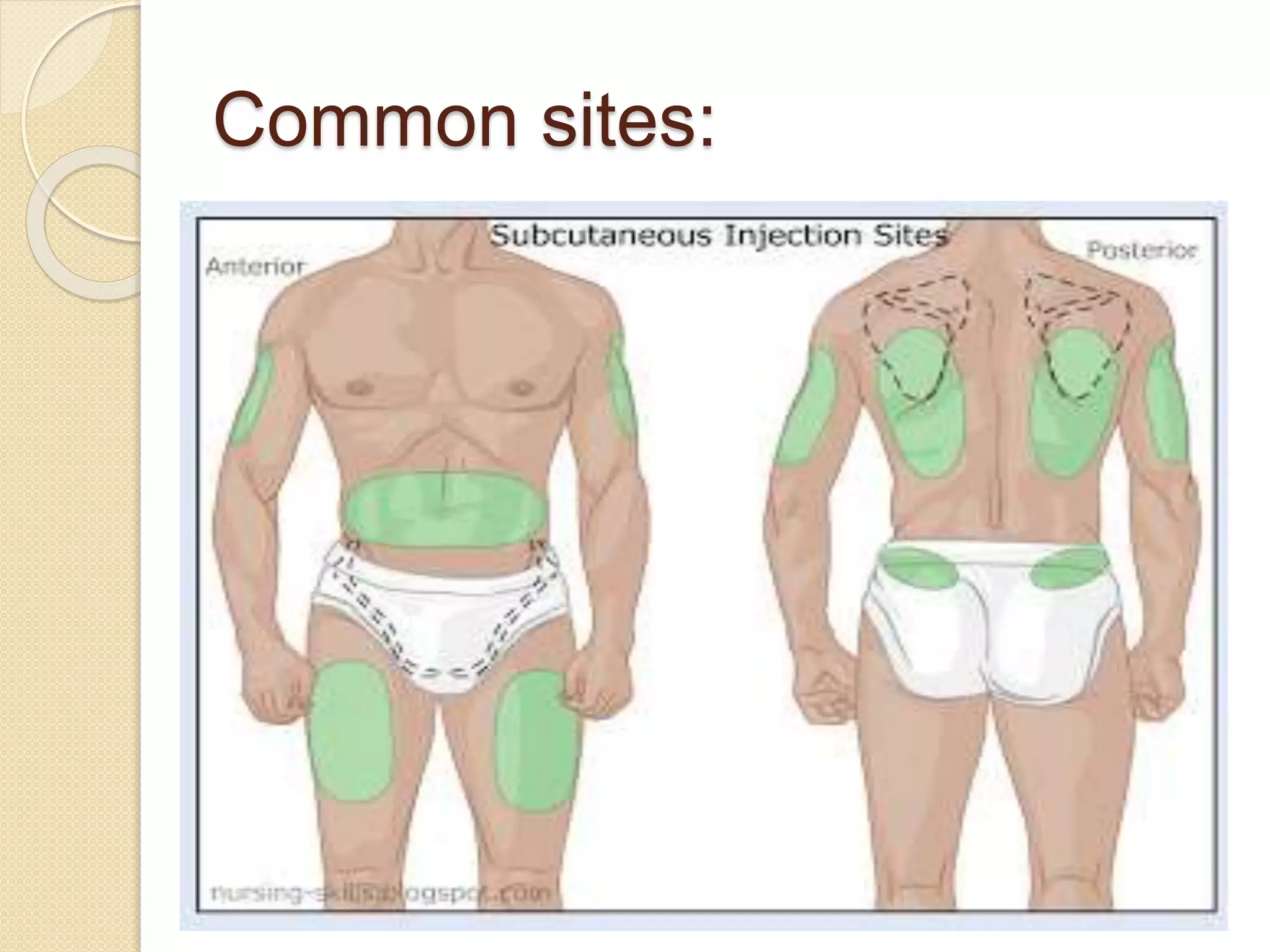
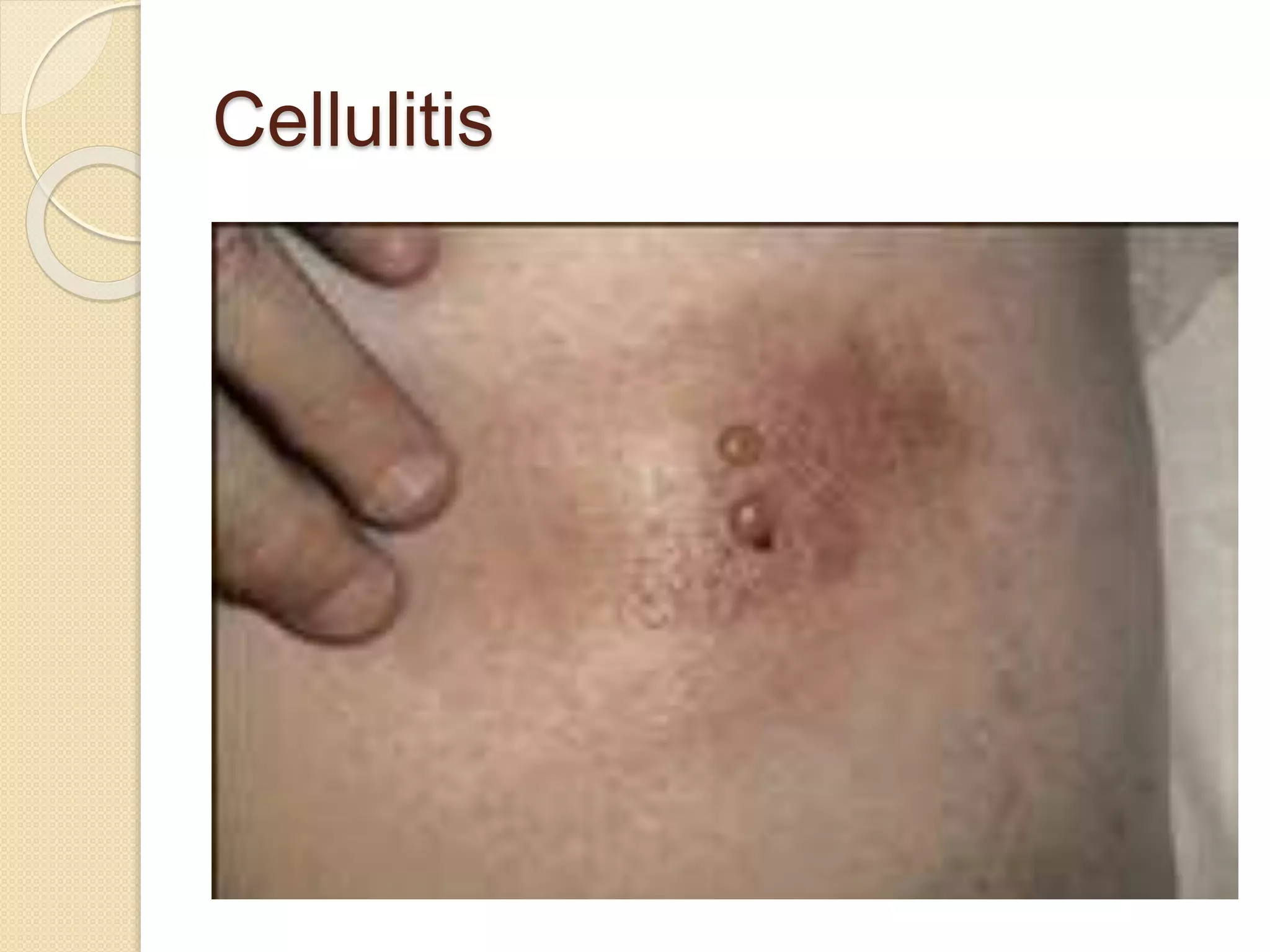
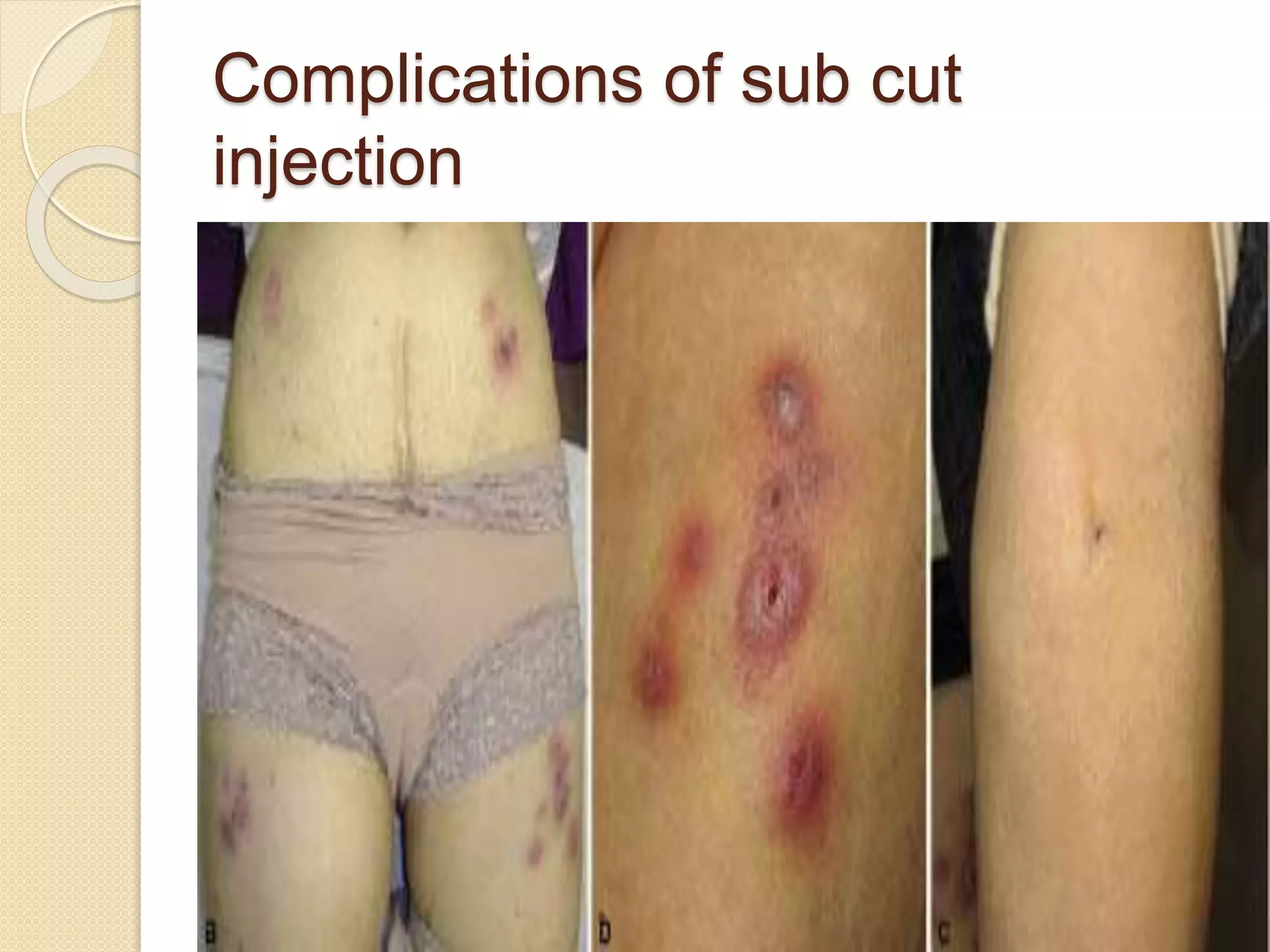
Subcutaneous injections involve injecting medication into the subcutaneous fat layer just below the dermis. Only small doses of water-soluble medications are given this way due to the tissue's sensitivity. Common sites for subcutaneous injections include the outer arm, back, abdomen, and thighs. The procedure involves preparing medications and supplies, positioning the patient, cleaning the injection site, quickly inserting the needle at a 45-90 degree angle, injecting the medication slowly, withdrawing the needle, and applying pressure. Potential complications include fat necrosis, erythema, abscess formation, cellulitis, and nodule formation.