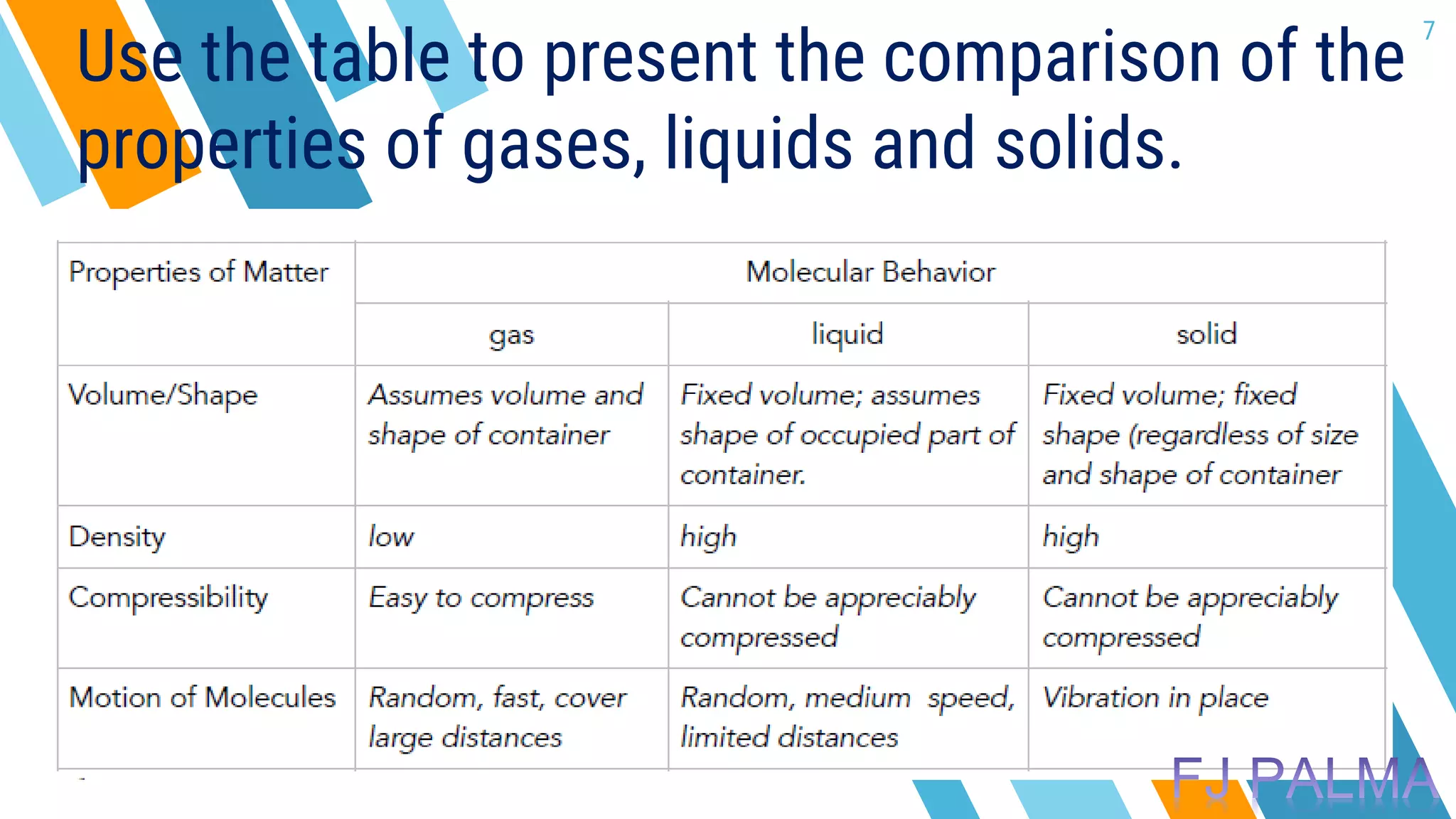
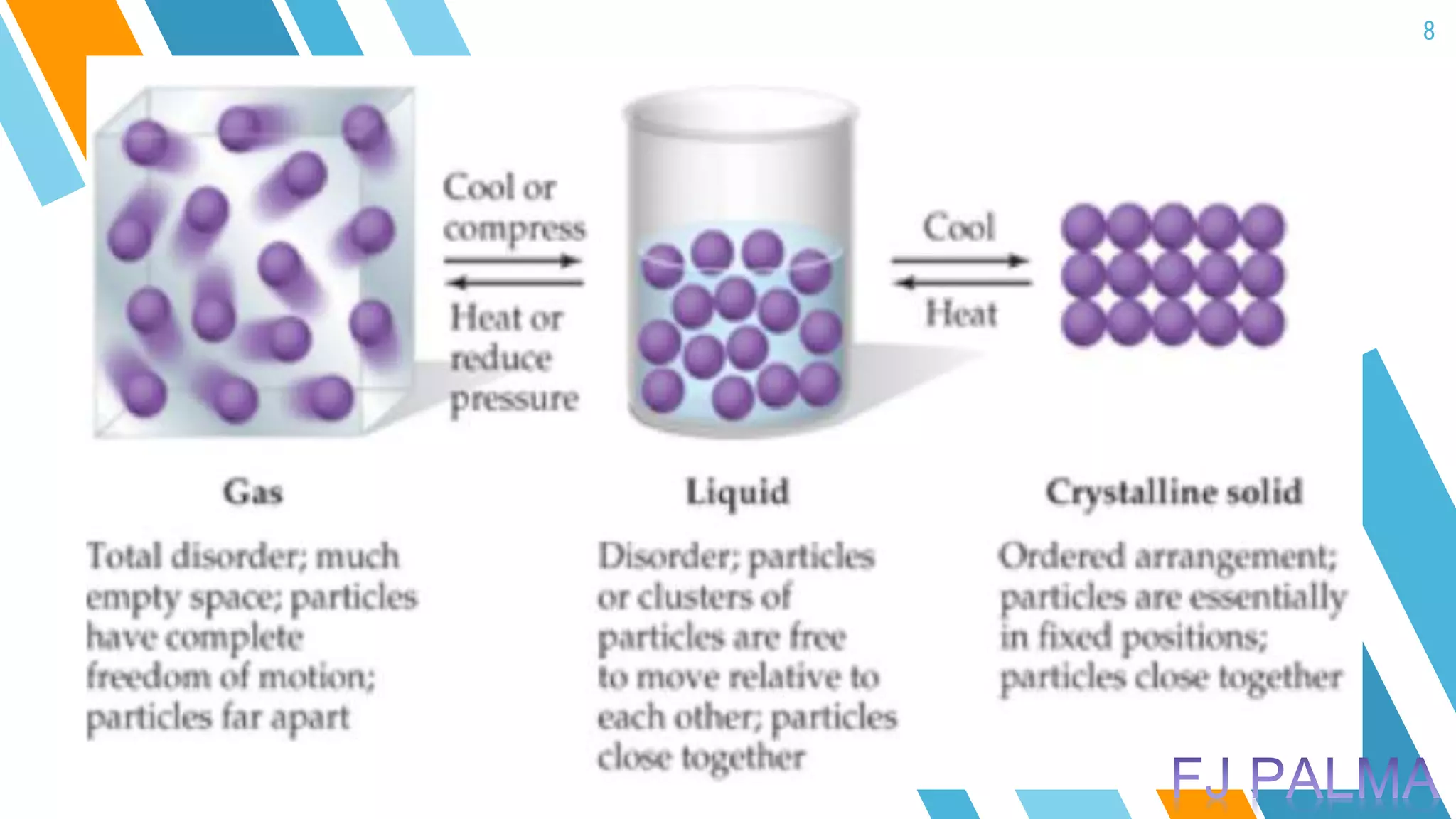
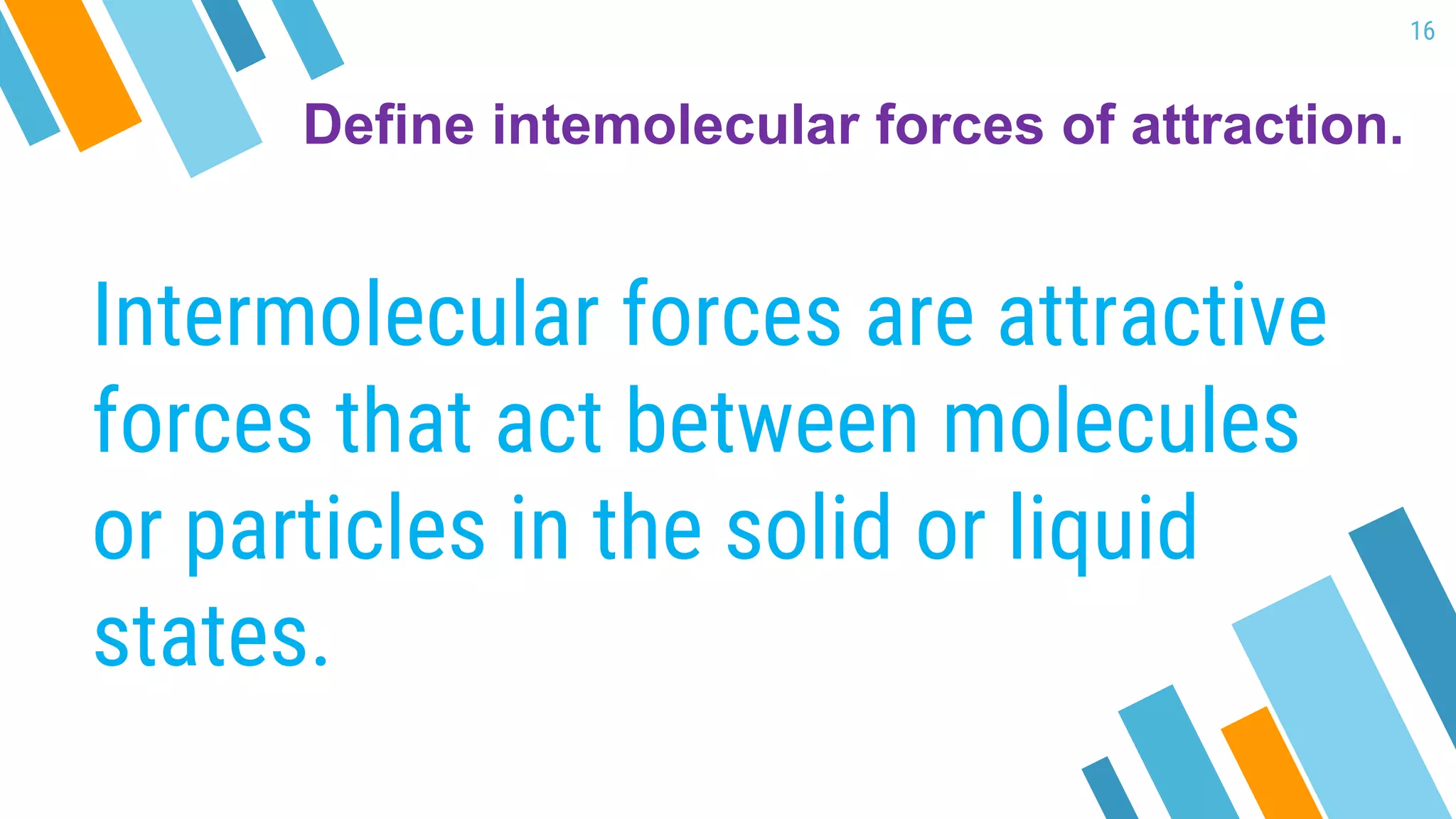
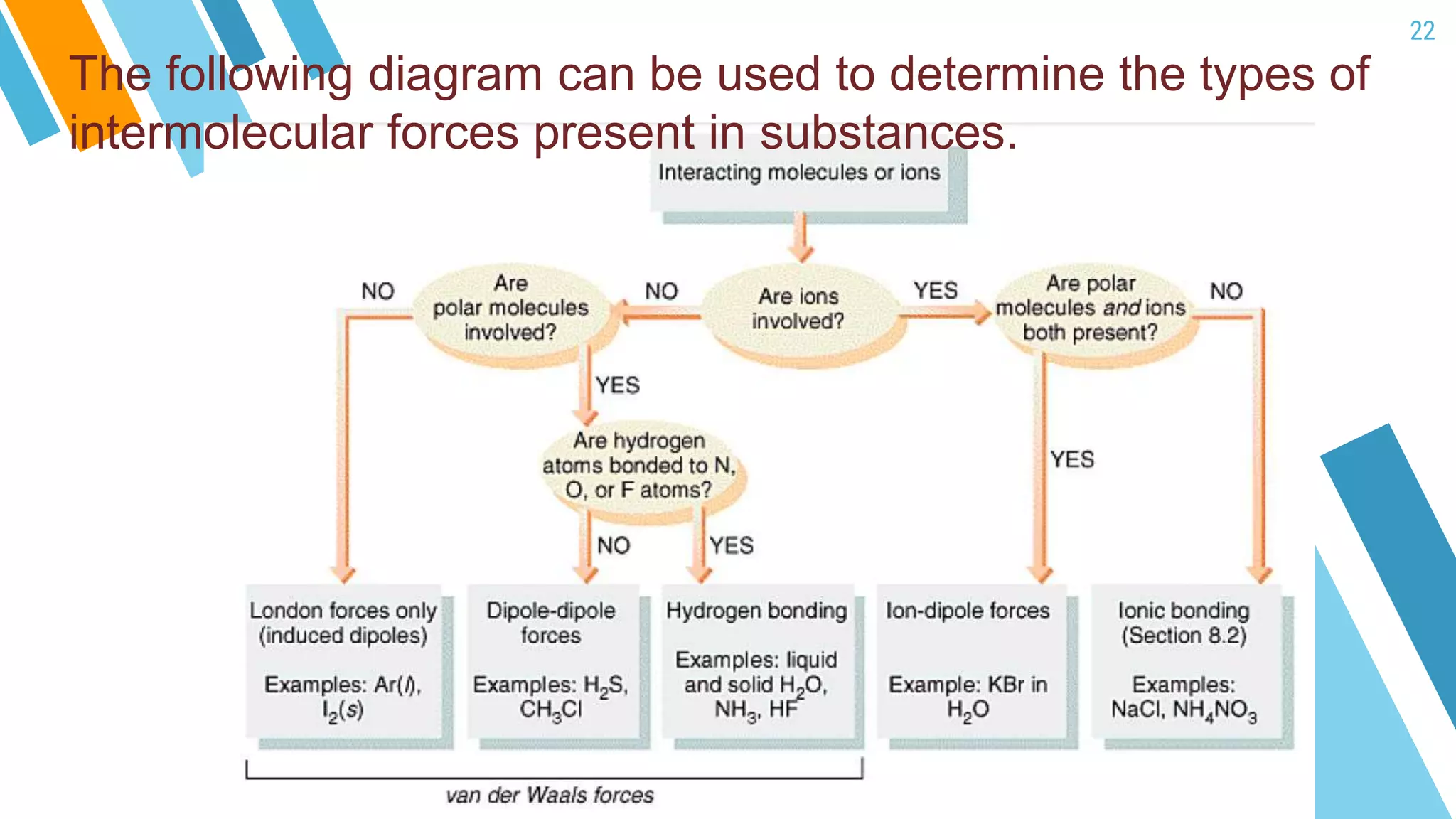
This document provides an overview of a lesson on the kinetic molecular theory of liquids and gases. The specific learning outcomes include comparing the properties of liquids, solids, and gases and describing intermolecular forces. The lesson includes activities where students act out different states of matter and compare the distances, arrangements, and volumes of particles in gases, liquids, and solids. It also involves an activity where students observe the evaporation rates of different liquids on coins to analyze intermolecular forces. The document defines intermolecular forces and describes different types including London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding.