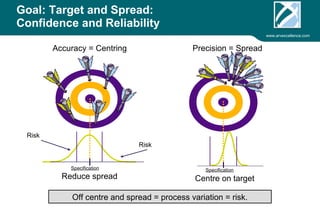
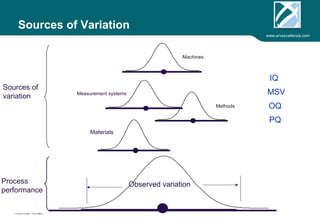
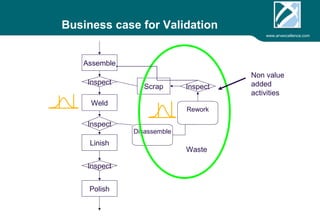
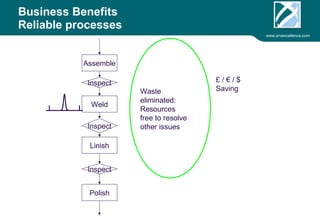
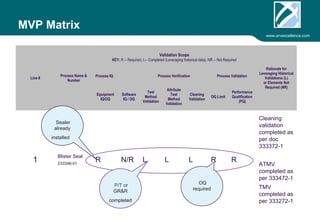
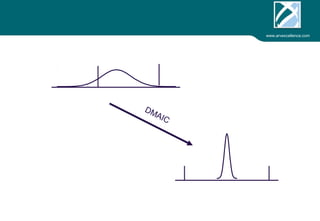
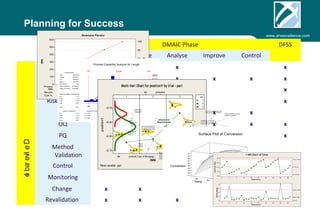
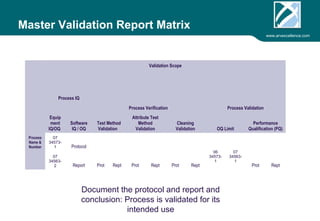
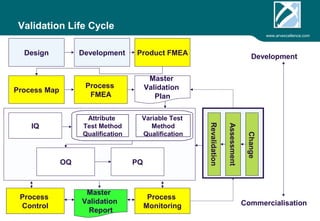
ARV Excellence is a consulting firm specializing in process validation for medical devices, focusing on regulatory compliance, risk management, and process improvement. The document outlines the validation lifecycle, including risk management strategies based on ISO 14971, as well as the importance of a Master Validation Plan (MVP) to ensure reliable processes. It emphasizes the need for evidence-based documentation to assure consistent product quality and regulatory adherence.




![www.arvexcellence.com
Validation
• Requirement:
“establish documented evidence which provides a high degree of assurance
that a specific process will consistently produce a product meeting its
predetermined specifications and quality attributes.” [1]QSR 820.3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/validationmasterplanning2-141103091702-conversion-gate01/85/Process-Validation-Master-Planning-DMAIC-Fusion-7-320.jpg)