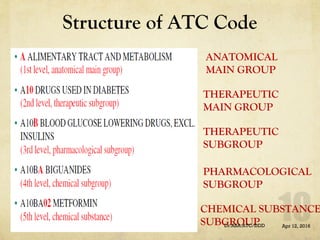
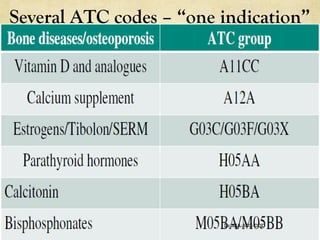
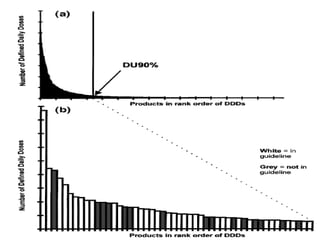
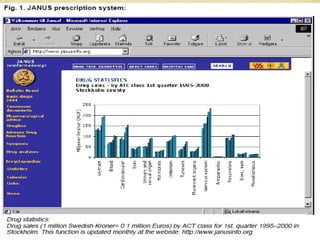
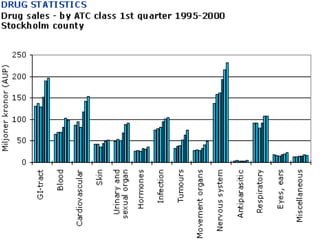
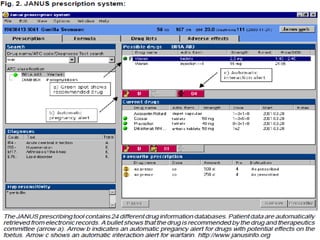
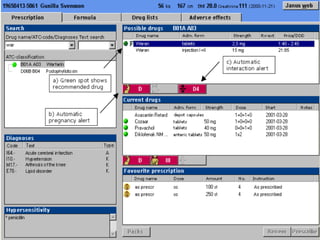
The ATC/DDD system provides an international standard for drug utilization research, assisting in the comparison and presentation of drug consumption statistics across various levels. It classifies drugs based on their main therapeutic use and assigns defined daily doses (DDD) to facilitate the measurement of drug use, though it is not intended for decisions regarding pricing or reimbursement. Additionally, the system includes general principles for classification, suggests methods for expressing drug exposure, and acknowledges limitations in pediatric dosing assignment.