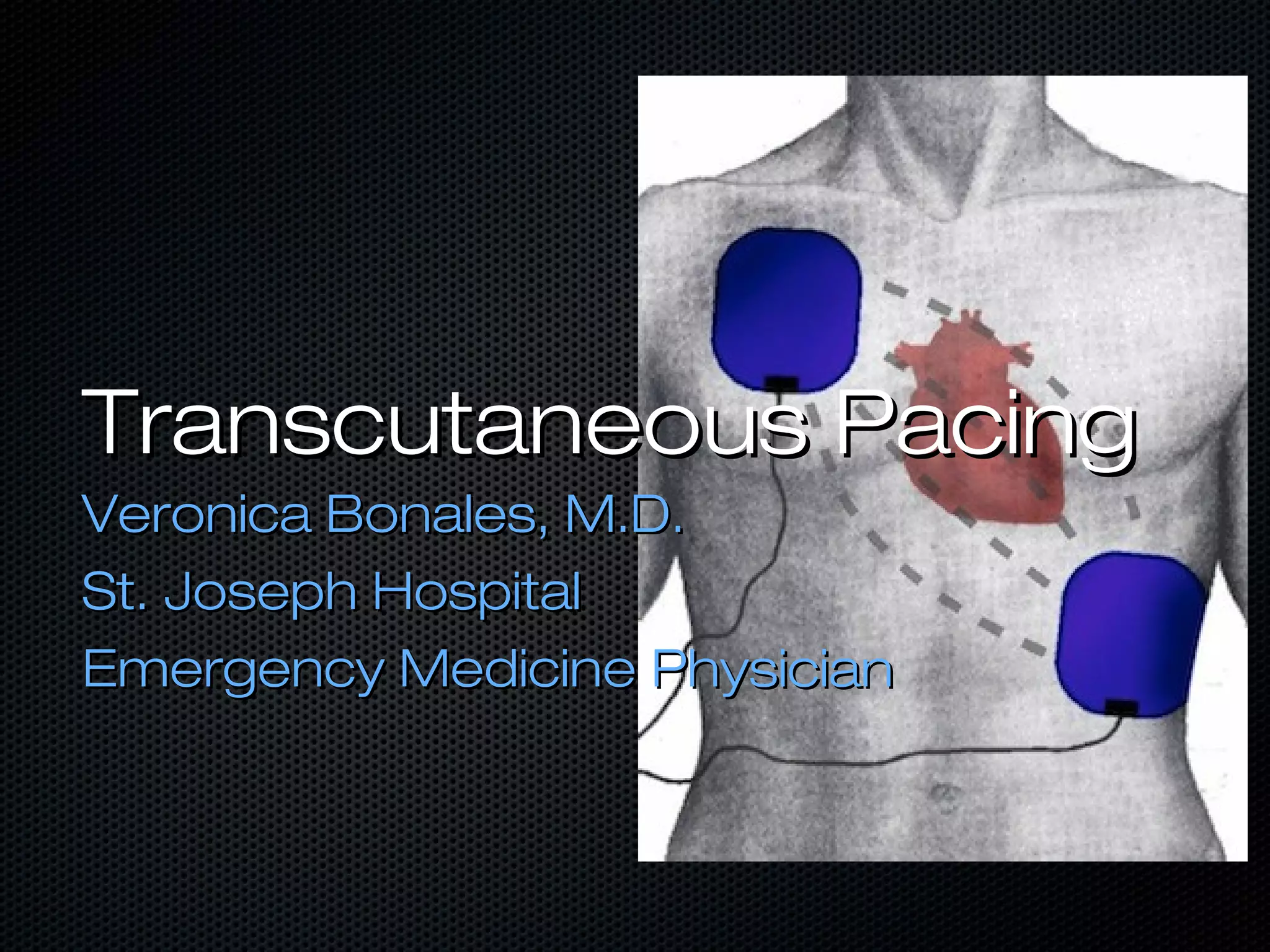
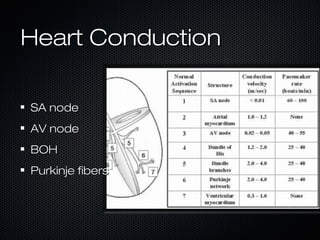
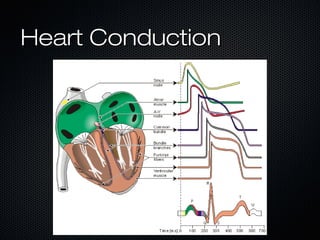
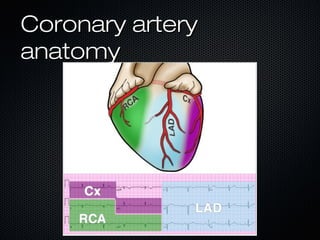
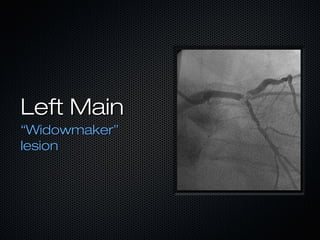
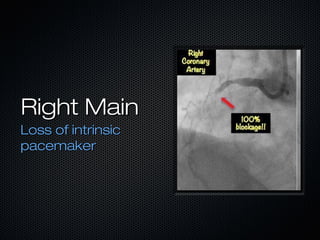
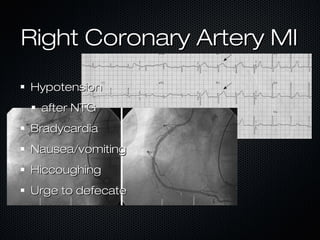
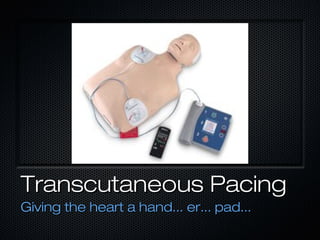
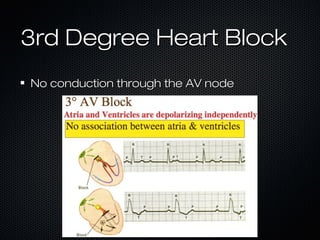
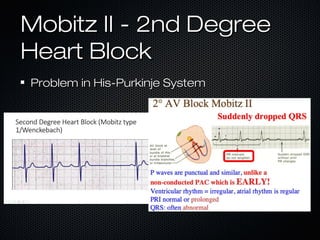
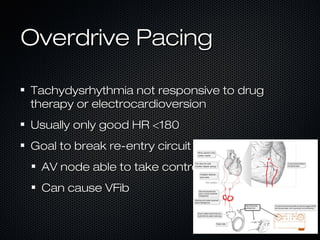
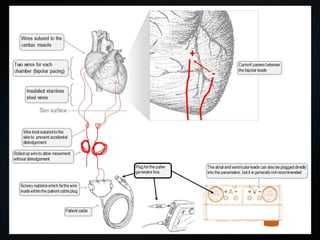
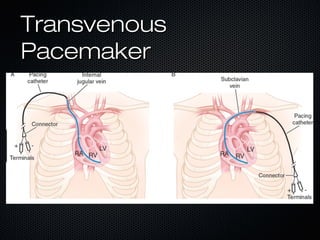
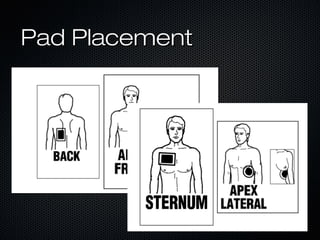
This document discusses transcutaneous pacing, which is used to treat bradycardia and heart block when the heart rate is too slow and the patient is hemodynamically unstable. It indicates transcutaneous pacing can be used for conditions like third-degree heart block, Mobitz type II second-degree heart block, asystole, and pediatric bradycardia. The document reviews how to perform transcutaneous pacing using external pads placed on the chest connected to a pacemaker, and notes potential complications like failure to pace or capture and skin burns.