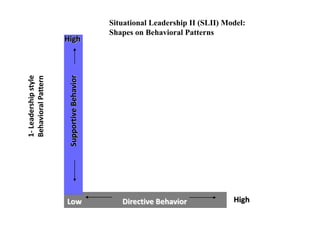
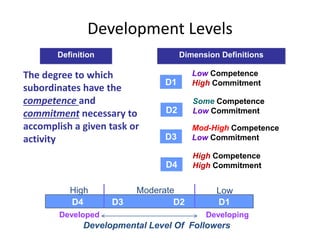
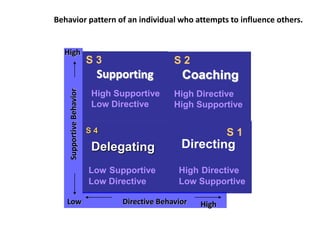
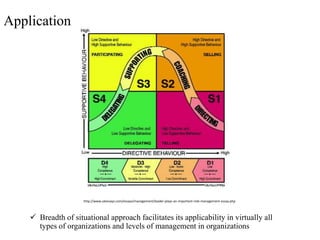
Situational leadership theory proposes that leaders should adapt their leadership style to fit the development level of their followers. It identifies four development levels that followers can be at based on their competence and commitment. The theory also outlines four leadership styles that range from directing/telling to delegating. Effective leaders will diagnose which style is appropriate based on where followers fall on the development scale. The approach aims to match leadership style with follower readiness to perform tasks. Critics argue that more research is needed to validate situational leadership's prescriptions. However, supporters note its flexibility makes it practical for managers to apply in different organizational contexts.