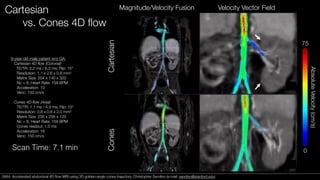
This document presents a method for accelerated 4D flow MRI of the abdomen using a 3D golden-angle cones trajectory. Preliminary studies in pediatric patients show this approach can achieve high spatial and temporal resolution with scan times under 5 minutes and be robust to high acceleration rates. Compared to Cartesian 4D flow, the cones trajectory results in more diffuse motion artifacts that are better suited for imaging near the bowels and allows for shorter echo times and smaller velocity encodings. Reconstruction using compressed sensing with soft-gating further reduces artifacts from respiratory motion.


![Cartesian 4D flow1,2 in the abdomen
Many challenges…
• Low Venc
• Respiratory & bowel motion
• High spatiotemporal resolution
required for simultaneous
DCE+4D Flow (XD Flow3)
• Long scan times
11-year-old female patient w/ ferumoxytol
TE/TR: 2.16 ms / 6.16 ms; Flip: 20°
Resolution: 1.0 x 1.4 x 1.0 mm3
Nc = 10, Heart Rate: 100 BPM
Acceleration: 4.0 x 2.5
Venc: 100 cm/s
Scan Time: 9.4 minutes
[1] M Markl, et al. Time-resolved 3DPC MRI. JMRI, 2003.
[2] JY Cheng, et al. Comprehensive 4D flow MRI. JMRI, 2016.
[3] JY Cheng, et al. XD Flow. Scientific reports, 2017.
0684. Accelerated abdominal 4D flow MRI using 3D golden-angle cones trajectory. Christopher Sandino (e-mail: sandino@stanford.edu)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cones-200327183025/85/Accelerated-abdominal-4D-flow-MRI-using-3D-golden-angle-cones-trajectory-3-320.jpg)
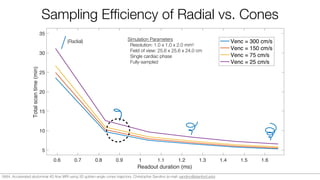
![kz
kx
Non-Cartesian 4D Flow
• Previous work: 3D radial4,5 and
stack-of-spirals6,7
• 3D cones trajectory8,9 combines
advantages of both:
• Short echo times
• Motion robust
• High sampling efficiency
[4] T Gu, et al. PC-VIPR. Am J Neuroradiology, 2005.
[5] KM Johnson, et al. Renal PC-VIPR. JCMR, 2008.
[6] A Sigfridsson, et al. Spiral 4D flow. MRM, 2012.
[7] H Dyvorne, et al. Abdominal spiral 4D flow. Radiology, 2014.
[8] PT Gurney, et al. 3D cones. MRM, 2006.
[9] EJ Zucker, et al. Pediatric chest MRI w/ cones. JMRI, 2017.
0684. Accelerated abdominal 4D flow MRI using 3D golden-angle cones trajectory. Christopher Sandino (e-mail: sandino@stanford.edu)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cones-200327183025/85/Accelerated-abdominal-4D-flow-MRI-using-3D-golden-angle-cones-trajectory-4-320.jpg)
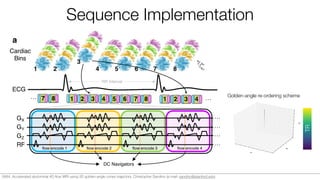
![Estimation of respiratory motion
[10] T Zhang, et al. Robust body MRI with dense coil arrays. MRM, 2016.
Multi-channel DC navigators Respiratory signal
filtering,
clustering10,
etc.
0684. Accelerated abdominal 4D flow MRI using 3D golden-angle cones trajectory. Christopher Sandino (e-mail: sandino@stanford.edu)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cones-200327183025/85/Accelerated-abdominal-4D-flow-MRI-using-3D-golden-angle-cones-trajectory-7-320.jpg)
![PI/CS Reconstruction
• CPU reconstruction time: 4-5 hours (implemented using BART12)
• Initially intractable due to memory required for oversampling in all 3 spatial dimensions
➡ PCA coil compression13 (32->16 channels)
➡ Tradeoffs with temporal resolution
m = argminm
1
2
kW(Am y)k2
2 +
X
i
i|Ri(m)|1
Forward model A includes:
• Coil sensitivities (ESPIRiT)
• Non-uniform FFT
Weighting matrix W includes:
• Density compensation
• Respiratory motion state
consistency (soft-gating11)
Sparsity promoters Ri include:
• 3D spatial Wavelet
• Temporal finite differences
m = reconstructed images
y = acquired k-space data
x = spatial domain
c = cardiac phase
r = respiratory phase
t = temporal phase
[11] KM Johnson, et al. Improved least squares recon. MRM, 2012.
[12] M Uecker, et al. BART. ISMRM, 2015.
[13] F Huang, et al. Coil compression. MRM, 2007.
0684. Accelerated abdominal 4D flow MRI using 3D golden-angle cones trajectory. Christopher Sandino (e-mail: sandino@stanford.edu)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cones-200327183025/85/Accelerated-abdominal-4D-flow-MRI-using-3D-golden-angle-cones-trajectory-8-320.jpg)

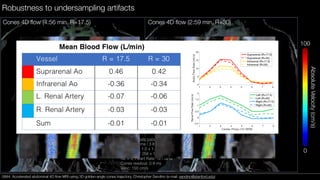
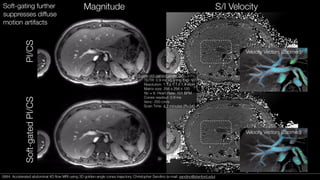
![Limitations
• Spatiotemporal resolution currently limited by reconstruction
• Eddy current-related phase errors appeared to be worse in cones before
phase correction14
• Off-resonance effects not observed in short readout reconstructions, but
will need to be corrected for extended readouts
[14] PG Walker, et al. Semi-automatic phase error correction. JMRI, 1993.
0684. Accelerated abdominal 4D flow MRI using 3D golden-angle cones trajectory. Christopher Sandino (e-mail: sandino@stanford.edu)0684. Accelerated abdominal 4D flow MRI using 3D golden-angle cones trajectory. Christopher Sandino (e-mail: sandino@stanford.edu)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cones-200327183025/85/Accelerated-abdominal-4D-flow-MRI-using-3D-golden-angle-cones-trajectory-13-320.jpg)

