F.sc. Chemistry Part 2. (inorganic portion tests & solved - Malik Xufyan
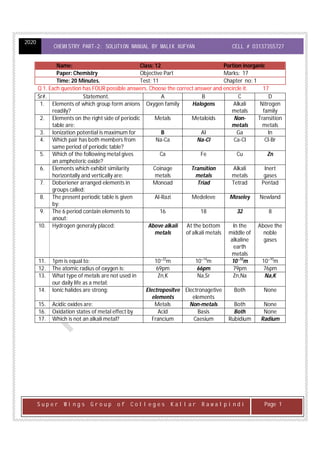
- 1. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 1 Name: Class: 12 Portion inorganic Paper: Chemistry Objective Part Marks: 17 Time: 20 Minutes. Test: 11 Chapter no: 1 Q 1. Each question has FOUR possible answers. Choose the correct answer and encircle it. 17 Sr#. Statement. A B C D 1. Elements of which group form anions readily? Oxygen family Halogens Alkali metals Nitrogen family 2. Elements on the right side of periodic table are: Metals Metaloids Non- metals Transition metals 3. Ionization potential is maximum for B Al Ga In 4. Which pair has both members from same period of periodic table? Na-Ca Na-Cl Ca-Cl Cl-Br 5. Which of the following metal gives an amphoteric oxide? Ca Fe Cu Zn 6. Elements which exhibit similarity horizontally and vertically are: Coinage metals Transition metals Alkali metals Inert gases 7. Doberiener arranged elements in groups called: Monoad Triad Tetrad Pentad 8. The present periodic table is given by: Al-Razi Medeleve Moseley Newland 9. The 6 period contain elements to anout: 16 18 32 8 10. Hydrogen generaly placed: Above alkali metals At the bottom of alkali metals In the middle of alkaline earth metals Above the noble gases 11. 1pm is equal to: 10⁻22 m 10⁻14 m 10⁻12 m 10⁻10 m 12. The atomic radius of oxygen is: 69pm 66pm 79pm 76pm 13. What type of metals are not used in our daily life as a metal: Zn,K Na,Sr Zn,Na Na,K 14. Ionic halides are strong: Electropositve elements Electronagetive elements Both None 15. Acidic oxides are: Metals Non-metals Both None 16. Oxidation states of metal effect by Acid Basis Both None 17. Which is not an alkali metal? Francium Caesium Rubidium Radium
- 2. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 2 Name: Class: 12 Portion Inorganic Paper: Chemistry Subjective Part Marks: 68 Time: 2:40 Test: 11 Chapter no: 1 SECTON –I Q 2. Give the short answers of the following EIGHT questions. 16 i. Define perodic table. ii. What is newland’s law of octates? iii. Why d and f- block elements are tarsition elements? iv. Why the size of cation is smaller than parent atom? v. Why the ionic radii of negative ions are larger than the size of their parent atom? vi. Why ionization energy decreases down the group and increases along the period? vii. Why the second value of electron affinity of an element is shown with a positive sign? viii. Why the metalic character increses from top to bottomin a group of metal? Q 3.Give the answers of the following EIGHT questions. 16 i. Why the oxidation state of noble gases is ysually zero? ii. Why diamond is a non-conductor and graphite is fairly a good conductor? iii. Differentiate b/w acid oxides basic and amphotaric oxides. iv. Define oxidation states and hydration energy. v. What is meant by the electrical conductivity ? This property depends upon different factors also write down. vi. How blocks help to differentiate the different elements?Explain. vii. Give some property which are similar to the IVA group elements. viii. Define atomic radius and ionic radii. Q 4.Give the answers of the following SIX questions. 12 i. Why atomic radius increases down the group? Explain. ii. What factors effecting on ionization energy along period and group? Explain. iii. What is meant by the metallic character? What do you know about this? iv. Give the behavior of melting and boiling points along behavior. v. Differentiate b/w ionic and covalent halides. vi. Differentiate b/w ionic and intermediate halides. SECTION-ll Give the answers of the following THREE questions.Each question is of FOUR marks. 24 Q 5.A) What type of improvements is made in Mandeleve’s periodic table? A) Classify the oxides on the basis of their acidic and basic character. Q 6.A) What problems that faced the chemists in placing the hydrogen atom in the periodic table ? Explain. B) Discuss the periodic trends of melting and boiling points. Q 7.A) Define and explain hydration energy. B) Discuss about the position of hydrides and oxides.
- 3. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 3
- 4. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 4 Name: Class: 12 Portion Inorganic Paper: Chemistry Subjective Part Marks: 68 Time: 2:40 Test: 11 Chapter no: 1 SECTON –I Q 2. Give the short answers of the following EIGHT questions. 16 ix. Define perodic table. The arrangement of elements in a systematic manner, in order to correlate their properties is called periodic classification. The resulting table is called periodic table. x. What is newland’s law of octates? In 1864, an English chemist, Newland arranged elements in order of their increasing atomic masses. He found that “Every eight elements had properties in common with first one.” For example: first two octaves of Newland’s are Li Be B C N O F Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Li resembles Na, Be resembles Mg etc. xi. Why d and f- block elements are transition elements? d and f block elements have variable oxidation states. They have different chemical and physical properties. They have different number of electrons in their valance orbit. Therefore, d and f block elements are also called transition elements. xii. Why the size of cation is smaller than parent atom? The size of cation is smaller than parent atom due to these following reasons. Many atoms lost their valance or outermost shell due to the removal of one or more electrons. In positive ions number of electrons are reduced but positive charge on nucleus is same. Therefore, nucleus powerfully attracts outer electrons inward resulting in decrease of ionic radius. xiii. Why the ionic radii of negative ions are larger than the size of their parent atom? Ionic radii of negative ions are larger due to increase in number of electrons in valance shell. The size of parent atom is decreased , it is because number of electrons are less in parent atom than negative ion. When an atom accepts an electron, it takes a negative charge and its size is increased. Its ionic radius also increased but its positive charge on electron remains same. xiv. Why ionization energy decreases down the group and increases along the period? Ionization energy decreases down the group due to increase in the size of atom. Number of shells increases down the group. Therefore, the size of atom increases and the attraction b/w the nucleus and valance electrons is decreased. An eletron can easily be removed from the atom due to increase the atomic radius and small amount of energy is required. Therefore, ionization energy decreases down the group. Ionization energy is increased along the period due to the strong attraction of nucleus to their electrons and atomic radius is also decreased. An electron cannot be removed from
- 5. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 5 the atom due to the strong attraction of nucleus to their electrons. A large amount of energy is required to remove electron from atom. Therefore, ionization energy increases along the period. xv. Why the second value of electron affinity of an element is shown with a positive sign? When a second electron is added in a un-negative ion, the incoming electron is repelled by the negative ion and energy is absorbedin the process indicated by the positive figure. e.g; O(g) + eˉ Oˉ E.A1 = -141kJmol-1 O(g) + eˉ O2 ˉ E.A2 = +780kJmol-1 xvi. Why the metalic character increases from top to bottom in a group of metal? Metalic character increases from top to bottom due to increase in atomic size. e.g; in halogens, metallic character increases from top to bottom. Thus, the iodine is most metallic. Q 3.Give the answers of the following EIGHT questions. 16 ix. Why the oxidation state of noble gases is usually zero? Oxidation state of noble gases is usually zero. It is because no vacancy is present in their valance shell. No electron will be added in the noble gases. All the shells in noble gass is completed. Therefore, noble gases are also called zero group elements. x. Why diamond is a non-conductor and graphite is fairly a good conductor? In diamond, C in the form of diamond is non-conductor. It is because all its valance electrons are used up in making tetrahedral structure and no free electron is present in it. But C in the form of graphite is a good conductor. It is because it has free valance electrons. xi. Differentiate b/w acid oxides basic and amphotaric oxides. Acid Oxides Basic Oxides Amphotaric oxides i) Oxides of non-metals are i) Oxides of metals are i) Oxides of relatively less generally acidic. generally basic. electropositive elements. E.g; BeO. ii) These form acids in ii) These form bases in ii) They show properties of both water. water. acidic and basic oxides. xii. Define oxidation states and hydration energy. Oxidation state is defined as: “It is apparent charge with sign, which an atom has in a compound.” e.g; In ionic compounds, It is usually the number of electrons gain or lost. In NaCl, oxidaion state of Na is +1 and that of chlorine is -1. Hydration energy is defined as: “it is the amount of heat evolved or absorbed when 1 mole of ions dissolve in H2O to give infinetly dilute charge.” e.g; when 1 mole of gaseous hydrogen ions are dissolved in water, 1075 kj energy is released. H⁺ + H2O H3O⁺(aq) ∆H h = -1075kmol-1 xiii. What is meant by the electrical conductivity? This property depends upon different factors also write down.
- 6. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 6 Electrical conductivity is a property of elements that causes the electricity. This property is due to the free electrons in elements. Free electrons are present in metals. Therefore, metals are the good conductor of electricity. This property depends upon: Presence of loose electrons in valance shell of elements. Easy removal of loose electrons. xiv. How blocks help to differentiate the different elements? Explain. Modern periodic table is divided into four blocks on the basis of valance shell electronic configuration.these blocks are: i) s-block ii) p-block iii) d-block iv) f-block These blocks tells about the valance shell of electrons of elements and their properties especially valancy and oxidation state. s-block elements are the elements in which valance electrons are present in s-orbital. p-block elements are the elements in which valance electrons are present in p-orbital. d-block elements are the elements in which valance electrons are present in d-orbital. f-block elements are the elements in which valance electrons are present in f-orbital. xv. Give some properties if hydrogen which are similar to the IVA group elements. There are following properties are present in IVA group elements which is similar to hydrogen atom. Valance shell of hydrogen is half filled like group IVA elements. Both hydrogen and group IVA members combine with other elements through covalent bonds. Like carbon, hydrogen has strong reducing properties. e.g. CuO + H2 Cu + H2O xvi. Define atomic radius and ionic radii. The average distance b/w the nucleus of an atom and the outermost orbit is called atomic radius, while considering atom as spherical. The atomic radii are usually measured in picometer (pm). 1 pm = 10-12 m The radius of ion while considering it spherical is called ionic radius. It is also measured in picometer (pm). Q 4.Give the answers of the following SIX questions. 12 vii. Why atomic radius increases down the group? Explain. Atomic radius increases down the group due to three two factors. i) Increase in number of shell ii) Shielding effect From up to down number of shell increases and the size of atom is also increased. Therefore, atomic radius is also increased. It is the decrease in force of attraction b/w outermost shell and nucleus due to the inner shell electrons. Shielding effect increases due to increase in size of atom. Therefore, atomic radius is also increased. viii. What factors effecting on ionization energy along period and group? Explain. Following factors effecting on ionization energy along period.
- 7. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 7 From left to right in the periodic table magnitude of nuclear charge increases and I.E is also increased. Following factors effecting on ionizatin energy along group. Along group, atomic radii increased and the I.E decreased. Greater the shielding effect of inner shell of electrons lower will be the I.E and vice verca. ix. What is meant by the metallic character? What do you know about this? Elements those have the tendency to give or gain electrons, form positive or negative ions and also forms basic or acidic oxides which dissolve in water to form bases or acids. E.g. Na2O + H2O 2NaOH SO3 + H2O H2SO4 Metals are the good conductors of heat and electricity. While non-metals are the bad conductors of heat and electricity. Metallic character decreases from left to right due to decrease in atomic size. Metallic character increases from up to down due to increase in atomic size. x. Give the behavior of melting and boiling points along period. In short periods, melting points increases up to middle with the increase in valance electrons and then decreases up to noble gases. Group IA elements have lowest melting points because they provide one electron per atom for binding. Group IIA elements have slightly higher melting points because they provide two electrons for binding. Carbon provides maximum number of binding electrons. Thus, it has highest melting point. Melting point decreases from group IVA to noble gases. It is because members of the last groups, exist as single, small covalent molecules. These have weak intermolecular forces. Thus, their melting points are low. xi. Define ionic and covalent halides. 1. Strong electropositive elements form ionic halide. it is because they have strong electronegativity difference with halogens. Halides of group IA elements are purely ionic. These have 3D crystal lattic. In ionic halides, strong intermolecular forces are present. They are present high melting solids. 2. Covalent halides: In covalent halides, weak intermolecular forces are present. These are generally present as gases, liquids or low melting solids. Physical properties of covalent halides depend upon the size and polarizability of halogen atom. xii. Differentiate b/w ionic and intermediate hydrides. Ionic hydrides Intermediate hydrides i) These are ionic in nature. i) These are covalent in nature. ii) They form basic solution with water. ii) They form acidic or basic solution with
- 8. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 8 water. iii) These are crystalline solids. iii) They may be in the form of gases or liquids or low melting solids. iv) Elements of group IA and heavier iv) hydrides of Be, Mg etc are members of IIA form ionic hydrides. Intermediate. SECTION-ll Give the answers of the following THREE questions.Each question is of FOUR marks. 24 Q 5.A) What type of improvements is made in Mandeleev’s periodic table? See the topic of improvements in Mandeleevs’ periodic table. B) Classify the oxides on the basis of their acidic and basic character. See the topic of oxides. Q 6.A) What problems that faced the chemists in placing the hydrogen atom in the periodic table ? Explain. See the topic of position of hydrogen in the periodic table. C) Discuss the periodic trends of melting and boiling points. See the topic of Melting and boiling points. Q 7.A) Define and explain hydration energy. See the topic f hydration energy. C) Discuss about the classification of hydrides and oxides. See the topic of hydrides and oxides.
- 9. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 9 Name: Class: 12 Portion inorganic Paper: Chemistry Objective Part Marks: 17 Time: 20 Minutes. Test: 12 Chapter no: 2 Q 1. Each question has FOUR possible answers. Choose the correct answer and encircle it. 17 Sr#. Statement. A B C D 1. The hydroxide which is most soluble in water is: Ba(OH)2 Mg(OH)2 Sr(OH)2 Ca(OH)2 2. Dolomite is an ore of: Strontium Magnesium Barium Potassium 3. Down’s cell is used to prepare: Na2CO3 Na metal NaOH NaHCO3 4. Which metal is resistant to complete oxidation? Na K Be None 5. Which metal is not present abundantly in earth crust? Si Al Na O 6. Na metal cannot be stored under: Benzene Kerosene Alcohol Toluene 7. NaOH is prepared by the hydrolysis of: Molten NaCl Aqueous NaCl Aqueous Na2CO3 Molten Na2CO3 8. In manufacturing of caustic soda ,which is formed as a by-product? O2 Cl2 NaCl N2 9. Which one of the following is most basic? Al2O3 SiO2 P2O5 MgO 10. Which mineral is used in isolation of sodium? Lime stone Natron Halite Barite 11. Which ion will have the maximum value of heat of hydrogenation? Na⁺ Cs⁺ Ba2 ⁺ Mg2⁺ 12. Which is not alkaline earth metal? Be Ra Ba Rn 13. The oxides of baryllium are: Acidic Basic Amphoteric None 14. The mineral CaSO4.2H2O has the general name: Gypsum Dolomite Calcite Epsom salt 15. The element Cs bears resemblance with: Ca Cr All None 16. Chile saltpeter had chemical formula: NaNO3 KNO3 Na2B4O7 Na2CO3.H2O 17. Gypsum is an important source of Na,K Na,Cl Ca,S Na,S
- 10. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 10 Name: Class: 12 Portion Inorganic Paper: Chemistry Subjective Part Marks: 68 Time: 2:40 Test: 12 Chapter no: 2 SECTON –I Q 2. Give the short answers of the following EIGHT questions. 16 i. Give the occurrence of alkali metals. ii. Define alkaline earth metals. iii. What is meant by the peculiar behavior of lithium? iv. What is meant by solubilities and lactic energies of alkal metals? v. Give some reaction of oxygen with alkali metals. vi. How alkali metals react with water?Give some reactions. vii. How hydrogen and sulphur react with alklain earth metals? viii. Why the aqueos solution of Na2 CO3 is alkaline in nature? Q 2. Give the short answers of the following EIGHT questions. 16 i. What happened when lithium is heated and lithium hydroxide is heated with water? ii. Why lime water turns milky with CO2 but become clear with excess CO2? iii. How gypsum is converted into plaster of paris? iv. How lime mortar is prepared? v. How lime and sand are used to make glass? vi. Give formulas of following ores: vii. Dolomite ii) Asbestos iii) sylvite iv) Beryl viii. Describe the role of lime in agricalture. ix. What is meant by slacked lime? Q 4. Give the short answers of the following SIX questions. 12 i. What is the function of Ca in plant growth? ii. What is meant by the setting of plater of paris? iii. Give the some uses of plaster of paris. iv. Describe the role of gypsum in agriculture. v. What is meant by the carbonates of alkaline earth metals? vi. What do you know about the reactivity of alkaline earth metals? SECTION-ll Give the answers of the following three questions.Each question is of FOUR marks. 24 Q 5. Explain in detail about the peculiar behavior of following: A) Lithium B) Berylium Q 6. A) Give the commercial preparation of sodium by Down’s cell in detail. B) Give commercial preparation of NaOH by the diaphragm cell in detail. Q 7. A) Describe the role of gypsum in industry. B) Describe the role of lime in industry.
- 11. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 11 Name: Class: 12 Portion Inorganic Paper: Chemistry Subjective Part Marks: 68 Time: 2:40 Test: 12 Chapter no: 2 SECTON –I Q 2. Give the short answers of the following EIGHT questions. 16 ix. Give the occurrence of alkali metals. Alkali metals are highly reactive. Therefore, they do not occur free in nature. They are found in combined state. Most of earth crust is made up of insoluble alumino silicates of alkali metals. Na and K are more abundant and constitute to about 2.4% of earth crust. Li is found as complex mineral which are widely distributed. An important commercial source of Li is the mineral spodumene i.e. LiAl(SiO3)2. Small amounts of Rb and Cs are found in K salts deposits. Fr is not occur in nature. it is radioactive element. It is produced in laboratory by nuclear reaction. It is very unstable, therefore, its chemistry is not well known. x. Define alkaline earth metals. Elements of group llA elements are called alklaine earth metals. They form ionic compounds. they show +2 oxidation state. They have two electrons in ‘s’ orbital of their valance shell. xi. What is meant by the peculiar behavior of lithium? First member of each main group of periodic table does not follow the regular trends of the group. Similarly Li shows difference from its family members. This behavior is due to the following reasons. Both Li and Li+ ions have very small size. Li+ has high charge density. Li has less electropositivity than sodium. xii. What is meant by solubilities and lattice energies of alkali metals? Cations of alkali metals have low charge and large radii than the radius of any cations from the same period. Thus lattice energies of their salts are low. Hence, most of the simple salts of alkali metals are water-soluble. Most of the salts are ionized completely in aqueous solution. xiii. Give some reaction of oxygen with alkali metals. Some reactions of oxygen with alkali metals are: 4Li + O2 2Li2O Li2O + CO2 Li2CO3 4Na + O2 2Na2O Rb + O2 RbO2 xiv. How alkali metals react with water? Give some reactions. Alkali metals react with water rapidly. A small piece of sodium or potassium or lithium floats on water and it reacts vigorously with water to liberate hydrogen and form metal hydroxide. The reaction is highly exothermic. The heat is released may ignite the hydrogen. 2Na + 2H2O 2NaOH + H2 xv. How hydrogen and sulphur react with alklain earth metals?
- 12. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 12 Reaction with Hydrogen: Mg + H2 Pressure MgI2 MgH2 Ca + H2 CaH2 Reaction with sulpher: Mg + S MgS xvi. Why the aqueos solution of Na2 CO3 is alkaline in nature? Na2CO3 is hydrolyzed by water to give alkaline solution. In water, Na2CO3 ionized to give carbonate anions. Na2CO3 2Na⁺ + CO3 2ˉ Hydrolysis of carbonate anion gives strong alkaline NaOH, which is greatly ionized. While carbonic acid produced, is a weak acid and is not greatly ionized. Thus, solution of Na2CO3 shows alkaline nature. CO3 2ˉ + 2H2O H2CO3 + 2OHˉ Overall reaction is Na2CO3 +2H2O 2NaOH + H2CO3 Strong alkali weaker acid Q 2. Give the short answers of the following EIGHT questions. 16 x. What happened when lithium hydroxide is treated with water? Lithium hydroxide produced hydrogen when it is treated with water. LiH + H2O LiOH + H2 xi. Why lime water turns milky with CO2 but become clear with excess CO2? Lime water is solution of lime CaO in water. When CaO is dissolved in water, it reacts with water to produced Ca(OH)2. When CO2 is passed through lime water it reacts with Ca(OH)2 and produced CaCO3. Ca(OH)2 + CO2 CaCO3 + H2O The milkyness disappears when excess CO2 is passed through it due to the formation of Ca(HCO3)2, which is soluble in water. Ca(OH)2 + CO2 CaCO3 + H2O CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O Ca(HCO3)2 xii. How gypsum is converted into plaster of paris? When gypsum is heated at 100˚C it loses 3/4th of its water and changes to plaster of paris. 2CaSO4.2H2O CaSO4)2.H2O + 3H2O Or CaSO4 .H2O CaSO4.⅟2H2O + H2O xiii. How lime mortar is prepared? Ordinary mortar is also called lime mortar, is prepared by mixing freshly slaked lime with sand and water to form a thick paste. Mortar is made by mixing freshly slaked lime (one volume), sand (three
- 13. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 13 or four volumes) and water to make thick paste. This material is hardened or sets when placed b/w stones and bricks. Thus, it binds the blocks firmly together. The reactions for this process are CaO + H2O Ca(OH)2 Ca(OH)2 + CO2 CaCO3 + H2O Ca(OH)2 + SiO2 CaSiO3 + H2O xiv. How lime and sand are used to make glass? Lime and sand react at high temperature to form calcium silicate (CaSiO3). Calcium silicate is firther used in the formation of glass. xv. Give formulas of following ores: i) Dolomite ii) Asbestos iii) sylvite iv) Natron The formula of dolomite is MgCO3.CaCO3. The formula of asbestos is CaMg3(SiO3)4. The formula of sylvite is KCl. The formula of natron is Na2CO3.H2O. xvi. Describe the role of lime in agriculture. The roles of lime in agriculture are: i) CaO is used for neutralizing acidic soils. ii) Application of lime to acidic soil increases the amount of readily soluble phosphorous. iii) CaO is used for making lime sulpher sprays which have a strong fungicidal action. xvii. What is meant by slacked lime? When lime is mixed with water it form calcium hydroxide called slaked lime. This process is called slaking of lime. It is an exothermic process. CaO + H2O Ca(OH)2 Q 4. Give the short answers of the following SIX questions. 12 vii. What is the function of Ca in plant growth? The functions of Ca in plant growth are: i) Ca is essential for the normal growth of plant. Different plants required different amount of Ca. ii) Soils containing Ca are alkaline in nature. iii) Presence of Ca in soil controls the availability of phosphorous in soil. iv) Ca is also necessary for normal development of leaves. Sufficient Ca accumulates in leaves and barks. viii. What is meant by the setting of plaster of paris? When plaster of paris is mixed with half of its weight of water, it forms a plastic type of viscous mass which then sets to a hard porous mass. This process completes in 10 to 15 mins. During this process, solid mass expand 1% by volume and fills the mould completely. Thus, it gives a sharp impression. this is called setting of plaster of paris. ix. Give the some uses of plaster of Paris. It is used
- 14. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 14 For making plaster walls. For casts of statuary, coins etc. In surgery. Its bandages are used to keep fractured bone in place after setting. x. Describe the role of gypsum in agriculture. The roles of gypsum in agriculture is Gypsum is an important source of Ca and S. S is also an important element for plant growth. S is also an important constituent of protein. In fertilizers, gypsum supplied Ca to the soil for crop production. It is particularly important where soils are subject to extensive leaching. xi. What is meant by the carbonates of alkaline earth metals? Alkaline earth metal carbonates are the only slightly soluble in water. The solubility decreases down the group. They decompose on heating. CaCO3 CaO + CO2 MgCO3 MgO + CO2 BaCO3 BaO + CO2 xii. What do you know about the reactivity of alkaline earth metals? Alkaline earth metals are very reactive due to low ionization energies. The reactivity increases down the group. However, alkaline earth metals are less reactive than alkali metals. SECTION-ll Give the answers of the following three questions.Each question is of FOUR marks. 24 Q 5. Explain in detail about the peculiar behavior of following: A) Lithium B) Berylium See the topics of peculiar behavior of lithium of beryllium. Q 6. A) Give the commercial preparation of sodium by Down’s cell in detail. See the topic of commercial preparation of sodium by Down’s cell. B) Give commercial preparation of NaOH by the diaphragm cell in detail. See the topic of commercial preparation of NaOH by the diaphragm cell. Q 7. A) Describe the role of gypsum in industry. See the topic of role of gypsum in industry. B) Describe the role of lime in industry. See the topic of role of lime in industry.
- 15. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 15 Name: Class: 12 Portion inorganic Paper: Chemistry Objective Part Marks: 17 Time: 20 Minutes. Test: 13 Chapter no: 3 Q 1. Each question has FOUR possible answers. Choose the correct answer and encircle it. 17 Sr#. Statement. A B C D 1. The aquous solution of borax is Acidic Basic Nutral Corrosive 2. Which is most abundant in earth crust? Al In B Ga 3. In SiO2, Si atoms are hybridized sp sp2 sp3 None 4. Which metal that show allotropyi is: Sn Pb Bi B 5. Tincal is a mineral of: Al B Si C 6. Which element forms an ion with charge 3+: Berilium Iodine Lead Oxygen 7. Boron traces are present in: Earth crust Deep sea Soil Dried lakes 8. The formula of corundium is: Al2O3 KH2Al3(SiO4)3 Na3AlF6 Al2O3.H2O 9. Borax is used in: Pulp washing Screening Metallurgy None 10. Boric acid is also called: Orthoboric acid Metaboric acid Tirboric acid Tetraboric acid 11. The color of aluminium is: Pale yellow Sea green Dull grey Sky blue 12. Viterous silica is ___ towards many reagents. Inert Reactive Moderately Most reactive 13. Asbestos is used in making: Paints Dyes Hardboard Cosmetics 14. When semiconductor is heated,its conductivity: Increased Decreased Moderately increase Remains same 15. Semiconductor are also called: Insulator Good conductor Half conductor None 16. The color of lead chromate is: Pale yellow Chrome yellow Reddish brown Reddish yellow 17. The formula of red lead is: Pb3O4 PbO2 PbCrO4 PbO
- 16. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 16 Name: Class: 12 Portion Inorganic Paper: Chemistry Subjective Part Marks: 68 Time: 2:40 Test: 13 Chapter no: 3 SECTON –I Q 2. Give the short answers of the any EIGHT questions. 16 i. Give some chemical properties of group lllA elements. ii. Give the names of group lllA elements. iii. Give the names of some important minerals of boron. iv. What do you know about the occurrence of B and Al? v. What is borax? Also give its occurrence. vi. How you prepare the borax from boric acid? vii. Give some physical properties of borax. viii. What is meant by borax bead test? ix. What do you know about the chemistry of borax bead test? x. What is meant by lead chromate and white lead? Q 3. Give the short answers of the any EIGHT questions. 16 i. Give some uses of borax. x. Define semiconductor. ii. Give the commercial preparation of ortho boric acid. iii. Give the reaction of boric acid with caustic soda and soda ash iv. What is meant by titration? v. Give some uses of boric acid. vi. What do you know about the aluminium? vii. How aluminium react with acids and alkalis? viii. Give some uses of aluminium. ix. Give the some uses and properties of silicons. Q 4. Give the short answers of the any SIX questions. 12 i. Differentiate b/w carbon and silicon family. ii. What are silicons and silicates? iii. Give the some uses of silicon and silicates. iv. Why is CO2 a gas while SiO2 is solid at room temperature? v. What is meant by slicates?Give their preparation and uses. vi. What type of clay are present? Explain. vii. What is meant by asbestos and soap stone? viii. Give some uses of aluminium silicates. ix. How aluminium silicates are are formed? x. Give the some uses of red lead and litherage.Also give their properties.
- 17. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 17 SECTION-ll Give the answers of the following THREE questions. Each question os of EIGHT marks. 24 Q 5.Define and explain semiconductor. Q 6.Give the preperties of IIIA and IVA group elements. Q 7.What is borax and boric acid? Also give their preparation, properties and uses.
- 18. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 18 Name: Class: 12 Portion Inorganic Paper: Chemistry Subjective Part Marks: 68 Time: 2:40 Test: 13 Chapter no: 3 SECTON –I Q 2. Give the short answers of the any EIGHT questions. 16 xi. Give some chemical properties of group lllA elements. Chemical properties f group IIIA elements are They react with oxygento form oxides of the general formula M2O3. They react with halogen to form halides of the general formula MX3. xii. Give the names of group lllA elements. The names of group lllA elements are boron (B), aluminium (Al), Gallium (Ga), indium (In) and thallium (Tl). xiii. Give the names of some important minerals of boron. Some important minerals of boron are Borax or tincal (Na2B4O7.10H2O), Colemanite ( Ca2B6O11.5H2O), ortho boric acid (H3BO3). xiv. What do you know about the occurrence of B and Al? Occurrence of boron: Boron is not an abundant element. It is found in traces in soil. It is also necessary for proper growth of plants. Boron is also found in combined state with oxygen mostly as oxyborate ions. It occurs mainly as salts of polyboric acids. Occurrence of Al: Al is the third most abundant element in earth crust after O and Si. Al mainly mainly occurs as alumino-silicates mineral on rocks of outer portion of earth. xv. What is borax? Also give its occurrence. Borax is a sodium salt of tetraboric acid. It is most important of all borates. It is naturally occurs as tincal (Na2B4O7.10H2O), which is found in dried lakes of Tibet and California. xvi. How you prepare the borax from boric acid? 4H3BO3 + Na2CO3 Na2B4O7 + 6H2O + CO2 xvii. Give some physical properties of borax. Physical properties of borax are It is white crystalline solid. It is sparingly soluble in cold water but more soluble in hot water. e.g. 100g of water dissolve 3g of decahydrate at 10˚C while 99.3g at 100˚C. When its saturated solution is allowed to crystallize above 62˚C, it forms octahedral crystals of pentahydrate (Na2B4O7.5H2O). Below 62˚C it forms decahydrate crystals. xviii. What is meant by borax bead test?
- 19. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 19 It is used to detect colored radicals like Cu2+ , Fe2+ , Mn2+ , Co2+ ,Cr3+ and Ni2+ . Make a loop of clean Pt wire. Heat it in a flame to remove impurities. Take a little borax on hot loop and heat again. Borax will first well up and then melts to give a colorless, glassy bead. Put some compound on the bead and heat again first in oxidizing flame and then in reducing flame. Note the color of the bead. For example: With Cu salt CuO is formed which react with B2O3 to give Cu(BO2)2. It shows blue color in oxidizing flame in cold state and give green color in hot state. CuO + B2O3 Cu(BO2)2 xix. What do you know about the chemistry of borax bead test? When borax is heated on loop, it is decomposed to give sodium metaborate and boric anhydride and a glassy bead is produced. Na2B4O7 2NaBO2 + B2O3 When given salt is heated on this bead, metallic oxides are produced which react with B2O3 to give colored metaborates of metals. Thus, metal cations can be identified. xx. What is meant by lead chromate and white lead? Lead chromate is PbCrO4. It is used as a pigment. It is also called chrome yellow. It gives red or orange basic lead chromate on boiling with dilute alkali hydroxide, which is used as a pigment. White lead is a basic lead carbonate. Its formula is 2PbCO3. Pb(OH)2.It is an amorphous white pigment. It mixes readily with linseed oil and has good covering power. It becomes crystalline and its covering power is reduced. Q 3. Give the short answers of the any EIGHT questions. 16 x. Give some uses of borax. Borax is used in softening of water. It is used in metallurgy. It is used as flux in welding and in metallurgy. It is used in leather industry for tanning and dyeing. It is used in making washing powder. xi. Give the commercial preparation of ortho boric acid. From borax: A hot concentrated solution of borax is treated with a calculated quantity of conc.H2SO4. On cooling, crystals of boric acid are formed which are separated. Na2B4O7 + H2SO4 + 5H2O Na2SO4 + 4H3BO3 xii. Give the reaction of boric acid with caustic soda and soda ash. With caustic soda: 4H3BO3 + 2NaOH Na2B4O7 + 7H2O With soda ash: 4H3BO3 + Na2CO3 Na2B4O7 + 6H2O + CO2 xiii. What do you know about the titration of boric acid?
- 20. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 20 Boric acid is a weak Acid. Therefore, it cannot be titrated with alkalies in usual manner. However, in the presence of glycerol, it can be titrated against a standard alkali using phenolphthalein as an indicator. xiv. Give some uses of boric acid. Boric acid is used in medicines as an antiseptic, e.g., dusting powder, boric ointment and boric solution is used as an eye-wash. It is also used in candle industry for stiffening of wicks. It is used in pottery as a glaze because borate glazes are more fusible than silicate glaze and have a higher coefficient of expansion. xv. What do you know about the aluminium? Al is the third most abundant element in earth crust after O and Si. Al mainly mainly occurs as alumino-silicates mineral on rocks of outer portion of earth. It is dull grey metal. It has low density. It is malleable and ductile. xvi. How aluminium react with acids and alkalis? With acids: 2Al + 6HCl 2AlCl3 + 3H2 With alkalies: 2Al + 2NaOH + 6H2O 2NaAl(OH)4 + 3H2 xvii. Give some uses of aluminium. Al is used for making cooking utensils, window frames and kitchen foil. Al is very light and have high tensile strength. It is nearly three times less dense than iron. Thus, it is used in transport industries, in making aircrafts, ships and cars etc. It is an excellent conductor of both heat and electricity. It is used for making petrol and milk storage tanks because it reflects light. Thus, it prevents overheating of petrol and milk in the sun. xviii. Give the some uses and properties of silicons. Some methyl silicones are oily liquid. The viscosity of silicon incases with increases in chain length. These are used as lubricants. These are either mixed with greases or used as oils in bearings , gear etc. Methyl silicones of high molecular mass resemble rubber and are used in making rubber tubing and sheets. They are also used in hydraulic brakes and other hydraulic systems. xix. Define semiconductor. A substance which has electrical conductivity b/w conductor and insulator is called semiconductor. For example: silicon, germanium, selenium etc. Q 4. Give the short answers of the any SIX questions. 12 i. What are silicones and silicates?
- 21. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 21 The polymers having backbone of altering Si oxygen atoms with non-polar side chain are called silicones. Derivatives of silicic acid are called silicates. ii. Give the some uses of silicates. It is used as filter for soap in soap industry. It is used in textile as a fire proof. It is used as furniture polishing. It is used in calico printing. iii. Why is CO2 a gas while SiO2 is solid at room temperature? CO2 exists as separate molecules, which have weak forces, therefore it is a gas at room temperature. SiO2 exist as polymer with altering Si and O atoms joined together to form big structure of SiO2. Therefore, it is a solid. iv. How silicates are prepared? Also give their properties. It is prepared by fusing sodium carbonate with pure sand. It is done in a furnace called reverberatory furnace. Na2CO3 + SiO2 Na2SiO3 + CO2 It is soluble in water. it’s solution is strongly alkaline due to hydrolysis. Na2SiO3 + 2H2O 2NaOH + H2SiO3 v. What types of clay are present? Explain. There are three type of clays are present. These are Pure clay has formula Al2O3.(SiO2)2.2 H2O. It is white and it is called kaolin. It is used to make porcelain and china ware. Ordinary clay is impure. It contains compounds of iron and other metals. Due to these metallic compounds it has yellow or reddish yellow color. Impure clay is easily fused because it contains impurities such as oxides of iron, calcium, magnesium and other metals. vi. What is meant by asbestos and soap stone? Asbestos: It is hydrated calcium magnesium silicate CaMg3 (SiO3)4. It is used in making incombustible fabrics and hardboards etc. Soap stone: It is magnesium silicate, Mg3H2(SiO3)4. It is greasy to touch. It is used in making cosmetics and household articles. vii. Give some uses of aluminum silicates. The uses of aluminum silicates are China wares are made from a mixture of kaolin, bone ash and feldspar. The mixture is fused on heating and fills the pores b/w grains of kaolin.
- 22. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 22 Clay forms easily fusible silicates with sand. Such clays are used to make bricks, tiles and stonewares. If iron oxide is present in clay, it it gives reddish color to the article on heating in a kiln. viii. How aluminium silicates are formed? Many silicate rocks contain Aluminum. These rocks weather and their complex silicates are decomposed. Boiling and freezing of water in rocks and chemical reaction of CO2 and H2O with these compounds convert them into potassium carbonate, sand and clay. e.g; weathering of potash feldspar occurs as K2O..Al2O3.6SiO2 + H2CO3 + H2O K2CO3 + 4SiO2 + Al2O3.(SiO2)2.2H2O. SECTION-ll Give the answers of the following THREE questions. Each question os of EIGHT marks. 24 Q 5.Define and explain semiconductor. See the topic of semiconductor. Q 6.Give the preperties of IIIA and IVA group elements. See the topic of properties of lllA and IVA group elements. Q 7.What is borax and boric acid? Also give their preparation, properties and uses. See the topic of borax and boric acid.
- 23. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 23 Name: Class: 12 Portion inorganic Paper: Chemistry Objective Part Marks: 17 Time: 20 Minutes. Test: 14 Chapter no: 4 Q 1. Each question has FOUR possible answers. Choose the correct answer and encircle it. 17 Sr#. Statement. A B C D 1. Nitrogen is present in air to about: 98% 78% 68% 88% 2. The color of laughing gas is: yellow Blue White None 3. The smell of nitric acid is: Bad Pleasant Pungent None 4. Nitric acid does not react with: Mg Mn Cu Pt 5. Phosphorus is derived from from greek work means: Light resistant Light bearing Light absorbing Light emmiting 6. White phosphorus is: Reactive Unreactive Quite reactive Least reactive 7. Oxygen has____ allotrops. Two Three Four Five 8. The freezing point of H2SO4 is: 0◦C -11◦C 10◦C 10.5◦C 9. Oxidation of NO in air produces: N2O N2O4 NO2 N2O5 10. The formula of laughing gas is: NO N2O NO2 N2O4 11. Which catalyst is used in contact process: Fe2O3 SO3 V2O5 Ag2O 12. Which of the following specie has the maximum number of unpaired electrons? O2 O3 O2⁺ O2 2⁺ 13. Out of all the elements of group VA,the highest ionization energy is possessed by N P Sb Bi 14. The elements O,S,Se and Te are known as: Halogens Alkali metals Chalogens Coinage metals 15. Colorless gas which is paramagnetic is: NO2 NO N2O4 None 16. Which is mixed anhydried? N2O N2O5 NO2 NO 17. Which halogen is used to convert Au to produce Au3⁺ ? Br2 I2 F2 Cl2
- 24. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 24 Name: Class: 12 Portion Inorganic Paper: Chemistry Subjective Part Marks: 68 Time: 2:40 Test: 14 Chapter no: 4 SECTON –I Q 2. Give the short answers of the any EIGHT questions. 16 i. Give the occurrence of nitrogen. ii. What is meant by laughing gas?what do you know about this? iii. Give the some reactions of laughing gas with S and Cu. iv. How you prepare the lauhing gas? Give some methods of its preparation. v. How does nitrogen differs from other elements of its group? vi. Why does aqua regia dissolve gold and platinum? vii. What is meant by the fuming nitric acid? viii. Explain the brikeland and eyde’s process for the manufacturing of nitric acid. ix. Describe the methods of preparation of phosphorus pentoxide. x. Give the some reactions of phosphorus pentoxide. Q 3. Give the short answers of the any EIGHT questions. 16 i. What is meant by the “ring test” for the confirmation of presence of nitrous ions in solution? ii. Discuss the trends in physical properties of group VIA elements. iii. Give the methods for the preparation of PCl3 iv. P2O5 is a powerful dehydrating agent. Prove giving example. v. How phosphorus tri and penta chloride can be used for the preparation of other chemical compounds? vi. Give the advantages of contact process. vii. Describe the chemistry for the industrial preparation of sulphuric acid from sulphur by contact process. viii. Why is SO3dissolve in H2SO4 and not in water? ix. Prepare the nitrous acid from dinitrogen oxide and from barium nitrate. x. How nitrous acid react withorganic compounds? Q 4. Give the short answers of the any SIX questions. 12 i. Give the laboratory method for the preparation of nitric acid. ii. How nitric acid react with glycerine? iii. Give some uses of nitric aci. iv. Give the occurrence of phosphorus. v. What do you know about the allotropes of phosphorus? vi. What do you know about bone ash? Prepared the orthophosphoric acid from bone ash. vii. Give the occurrence of oxygen and sulpher. viii. Give the physical properties of sulphuric acid. ix. Give some uses of sulphuric acid. SECTION-ll
- 25. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 25 Give the answers of following three questions.Each question is of FOUR marks. 24 Q 5.A) Give the manufacturing of sulphuric acid in detail. B) Give the some reactions of sulphuric acid in detail. Q 6.A) Give the industrial manufacturing of nitric acid. B) Give the following reactions of nitric acid: i) Aqua regia ii) Magnesium iii) Water iv) FeSO4 Q 7.A) Give the preparations chemical and physical properties of phosphorus tri and petoxides B) What do you know about the oxyacids of phosphorus? Also give their preparations,physical and chemical properties.
- 26. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 26 Name: Class: 12 Portion Inorganic Paper: Chemistry Subjective Part Marks: 68 Time: 2:40 Test: 14 Chapter no: 4 SECTON –I Q 2. Give the short answers of the any EIGHT questions. 16 xi. Give the occurrence of nitrogen. Nitrogen is present in free state in air as major constituent (78% by volume). It is an inactive gas as compared to oxygen. Inorganic compounds of nitrogen are not commonly found as minerals. In combined state nitrogen is found in all living matter e.g. animals and plants. It is present in the form of proteins, urea and amino acids. xii. What is meant by laughing gas? what do you know about this? Dinitrogen oxide is also called laughing gas. Its chemical formula is N2O. it is a colorless gas. It has faint, pleasant smell. It has sweetish taste. On inhaling, its mixture with a little oxygen for sufficiently long time, a hysterical laughter is produced. Hence, it is called laughing gas. xiii. Give the some reactions of laughing gas with S and Cu. Laughing gas is not combustible. It resembles oxygen in regenerating a glowing splinter. It supports combustion of burning substances, such as sulpher and phosphorus when these are taken in the cylinder containing gas etc. S + 2N2O SO2 + 2N2 P4 + 10 N2O P4O10 + 10N2 xiv. How you prepare the laughing gas? Give some methods of its preparation. Laughing gas is prepared from Zn and ammonium nitrate. 4Zn + 10HNO3 4Zn(NO3)2 + N2O + 5H2O NH4NO3 N2O + 2H2O xv. How does nitrogen differs from other elements of its group? Nitrogen differs from other elements of its group due to the formation of its oxides. Its oxides are acidic in nature. for example, N2O, NO, N2O3, NO2 and N2O5. xvi. What do you know about aqua regia? And also explain how it is dissolved metals. When one volume of conc. HNO3 is mixed with three volumes of conc. HCl, aqua ragia is formed. It is used to dissolve gold and platinum. HNO3(conc) + 3HCl(conc) NOCl + Cl2 + 2H2O NOCl formed is composed to give NO and Cl2. 2NOCl 2NO + Cl2. The chlorine converts noble metals such as gold and platinum into their chlorides. Thus these metals are dissolved. 2Au + 3Cl2 2AuCl3 xvii. Give the names of some important ores of metallic sulpher and sulphate. Some important ores of metallic sulpher are Galena PbS
- 27. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 27 Zinc blende ZnS Cinnabar HgS Stibnite Sb2S3 Ores of sulphate are Gypsum CaSO4 Heavy spar BaSO4 xviii. Explain the brikeland and eyde’s process for the manufacturing of nitric acid. This process consists of following steps: 1. Formation of nitric oxide: An electric arc is used to combine atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen at 3000˚C to give nitric oxide. N2 + O2 ℃ ⎯⎯⎯ 2NO NO is cooled quickly at 1000˚C to avoid its decomposition. 2. Oxidation of NO to NO2: NO is oxidized with O2 at 600 ˚C to from NO2. 2NO + O2 2NO2 3. Absorption of NO2 in water: 2NO2 + H2O HNO3 + HNO2 4. Oxidation of nitrous acid: 3HNO3 HNO3 + 2NO + H2O xix. Describe the method of preparation of phosphorus pentoxide. It is prepared by burning phosphorus in excess of dry air. P4 + 5O2 2P2O5 xx. Give the some reactions of phosphorus pentoxide. Reactions of phosphorus pentoxide are With water: P2O5 + H2O (Cold) 2HPO3 As a dehydrating agent: Dehydration of HNO3: 2HNO3 + P2O5 N2O5 + 2HPO3 Dehydration of acetic acid: 2CH3COOH + P2O5 (CH3CO)2O + 2HPO3 Q 3. Give the short answers of the any EIGHT questions. 16 xi. What is meant by the “ring test” for the confirmation of presence of nitrous ions in solution? When nitrogen acid react with FeSO4, It forms a brown colored addition compound. This test is used to confirm the presence of nitrates (Ring test). FeSO4 + NO FeSO4.NO xii. Discuss the trends in physical properties of group VIA elements? Physical properties of group VIA elements are:
- 28. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 28 Physical properties O S Se Te Po Atomic number 8 16 34 52 84 Melting points (˚C) -218 113 217 450 254 Boiling points (˚C) -183 444.6 684 990 962 Atomic radius 66 104 117 137 152 xiii. Give the methods for the preparation of PCl3. 1. From white posphorus and Cl2: White phosphorus is melted in a retort in an inert atmosphere of CO2. A current of dried chlorine is passed over it. The vapours of PCl3 are collected in a flask kept in an ice bath. 2P + 3Cl2 2PCl3 2. From P and thionyl chloride: It is also prepared by reacting phosphorus with thionyl chloride. 2P + 4SOCl2 2PCl3 + 2SO2 + S2Cl2 xiv. P2O5 is a powerful dehydrating agent. Prove giving example. P2O5 is a powerful dehydrating agent. It can remove water from many substances. For example. Dehydration of HNO3: 2HNO3 + P2O5 N2O5 + 2HPO3 Dehydration of acetic acid: 2CH3COOH + P2O5 (CH3CO)2O + 2HPO3 xv. How phosphorus tri and penta chloride can be used for the preparation of other chemical compounds? Reactions of PCl3 are used for th preparation of many chemical reactions such as Reaction with Cl2, O2 and alcohol: PCl3 + Cl2 PCl5 2PCl3 + O2 2POCl3 3CH3OH + PCl3 3CH3Cl + H3PO3 Reactions of PCl5 are used for the preparation of many chemical reactions such as Reactions with metals, alcohols and water: Zn + PCl5 ZnCl2 + PCl3 C2H5OH + PCl5 C2H5Cl + POCl3 + HCl xvi. Give the advantages of contact process. It has following advantages: It gives almost pure sulphuric acid.
- 29. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 29 It is easily handled. xvii. Describe the chemistry for the industrial preparation of sulphuric acid from sulphur by contact process. SO2 is obtained by burning sulpher and iron pyrites. It is oxidized to SO3 in the presence of V2O5 catalyst. S + O2 SO2 2SO2 + O2 ℃/ ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯ 2SO3 Best yield of SO3 is obtained by using excess oxygen or air at temperature b/w 400-500˚C. SO3 formed is absorbed in conc. H2SO4 to give oleum (H2S2O7). Oleum can be converted to sulphuric acid of any strength by mixing with water. SO3 + H2SO4 H2S2O7 H2S2O7 + H2O 2H2SO4 xviii. Why is SO3 dissolve in H2SO4 and not in water? When SO3 is dissolved in water, it forms H2SO4. This reaction is highly exothermic. SO3 + H2O H2SO4 + Heat. The heat produced during the reaction vapourizes H2SO4 and a mist is formed which is not easily condensed. This causes great inconvenience to the factory workers. Hence, SO3 is dissolved first in H2SO4 to give oleum, which is then decomposed by water to give H2SO4. SO3 + H2SO4 H2S2O7 H2S2O7 + H2O 2H2SO4 xix. Prepare the nitrous acid from dinitrogen dioxide and from barium nitrate. From dinitrogen dioxide: It can be prepared by dissolving dinitrogen dioxide in water at 0˚C. N2O3 + H2O 2HNO2 From barium nitrate: Pure nitrous acid solution is obtained by reaction of ice cold barium nitrate solution with ice cold dilute sulphuric acid. Ba(NO2)2 + H2SO4 BaSO4 + 2HNO2 xx. How nitrous acid react with organic compounds? 2HNO2 + CO(NH2)2 2N2 + CO2 + 3H2O HNO2 + C6H5NH2 C6H5OH + N2 + H2O Q 4. Give the short answers of the any SIX questions. 12 i) Give the laboratory method for the preparation of nitric acid. It is prepared by heating potassium nitrate crystals with conc. H2SO4. KNO3 + H2SO4 (Conc) KHSO4 + HNO3 ii) How nitric acid react with glycerine? See the topic of reaction of nitric acid with glycerine. iii) Give some uses of nitric acid. Nitric acid used in
- 30. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 30 It is used as a laboratory agent. It is used in the manufacturing of nitrogen fertilizer. It is used in the manufacturing of explosives. It is used for making varnishes and organic dyes. iv) Give the occurrence of phosphorus. It does not occur in free state. It is found in living organism. It is necessary for normal growth of living organism. It is present in bones as calcium phosphate. It is essential constituent of bones. Bone ash (80% calcium phosphate) is an important source of phosphorus. v) What do you know about the allotropes of phosphorus? Phosphorus has three important allotrops. These allotrops are white phosphorus, red phosphorus and black phosphorus. White phosphorus is very reactive, poisonous, volatile, waxy, yellowish white substance. It is soluble in benzene and carbon disulphide. Red phosphorus is much less reactive and less poisonous than white phosphorus. Black phosphorus is most stable under ordinary conditions. It is prepared by heating red phosphorus to high temperature and pressure. vi) What do you know about bone ash? Prepared the orthophosphoric acid from bone ash. On large scale, it can be prepared by heating a mixture of phosphorite (bone ash) and sand in an electric furnace. The phosphorus pentoxide formed is treated with hot water to obtain phosphoric acid. Ca3(PO4)2 + 3SiO2 3CaSiO3 + P2O5 P2O5 + 3H2O 2H3PO4 vii) Give the occurrence of oxygen. It is most abundant element of earth crust. It forms 50% of earth crust. Water contains nearly 89% by weight oxygen. Atmospheric air contains free oxygen by ⅟4 of its by weight. viii) Give the physical properties of sulphuric acid. Physical properties of sulphuric acid are Pure sulphuric acid is a colorless oily liquid without an odour. Its specific gravity is 1.834 at 18˚C. Its freezing pint is 10.5˚C. Its boiling points are 338˚C. It is extremely corrosive to skin and causes very serious burns to all tissues. ix) Give some uses of sulphuric acid. Uses of sulphuric acid are It is used as a dehydrating agent for drying gases. It is used as a laboratory reagent. It is used in textile, iron, steel, leather and paper industries.
- 31. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 31 It is used in the manufacturing of fertilizers like ammonium sulphate and calcium superphosphate. It is used in refining of petroleum to remove nitrogen and sulpher compounds. SECTION-ll Give the answers of following three questions.Each question is of FOUR marks. 24 Q 5.A) Give the manufacturing of sulphuric acid in detail. See the topic of Contact process. B) Give the some reactions of sulphuric acid in detail. See the topic of reactions of sulphuric acid. Q 6.A) Give the industrial manufacturing of nitric acid. See the topic of Birkland and Eyde’s process. B) Give the following reactions of nitric acid: i) Aqua regia ii) Magnesium iii) Water iv) FeSO4 SEE THE TOPIC OF REACTIONS OF NITRIC ACID. Q 7.A) Give the preparations chemical and physical properties of phosphorus tri and penta chloride. See the topic of halides of phosphorus. B) What do you know about the oxyacids of phosphorus? Also give their preparations, physical and chemical properties. See the topic of oxyacids of phosphorus.
- 32. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 32 Name: Class: 12 Portion inorganic Paper: Chemistry Objective Part Marks: 17 Time: 20 Minutes. Test: 15 Chapter no: 5 Q 1. Each question has FOUR possible answers. Choose the correct answer and encircle it. 17 Sr#. Statement. A B C D 1. The color F2 is: Yellow Pale yellow Reddish yellow Greenish yellow 2. The oxidation state of F is: -1 +1 -2 +2 3. The color of HCl at room temperature is: Greenish yellow Violet Colorless Yellow 4. What type of bonding is present in HF? Ionic Covalent Dipole Hydrogen 5. The Cl2O7 is _____ liquid. Oily Concentrated Dilute All 6. The formula of bleaching powder is: CaOCl2 CaCO3 NaOH Ca(OH)2 7. Which is used to prepare chlorine? Caustic soda Baking soda Bleaching powder None of theses 8. Flourine is used to prepare: Freons Nylon Fibers PVA 9. The melting point of XeF4 is: 141◦C 146◦C 114◦C 104◦C 10. The mixture used for breathing by the sea divers contain oxygen to about: 80% 20% 40% 50% 11. Which of the following HX is the weaker acid in solution? HF HI HCl HBr 12. Which is the strongest acid? HClO HClO2 HClO3 HClO4 13. Structure of OF2 is: Linear Planer Trigonal Bent 14. Halothane is used as? Antiseptic Antipyretic Anesthetic Anti- inflammatory 15. The XeO3 is ____ . Weakly acidic Strongly acidic Basic Neutral 16. Electronegative of fluorine is: 3 2.5 4 2.58 17. Perchloric acid is ________ agent. Reducing Oxidizing Dehydrating Dehydrogenating
- 33. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 33 Name: Class: 12 Portion Inorganic Paper: Chemistry Subjective Part Marks: 68 Time: 2:40 Test: 15 Chapter no: 5 SECTON –I Q 2. Give the short answers of the any EIGHT questions. 16 i. What is bleaching powder? How it is prepared give names of different methods. ii. Discuss the oxides of chlorine. iii. What are disportionation reactions? Give an example. iv. What is iodized salt? v. What are ferons and teflons? vi. Why iodine has metalic lustre? vii. Give the various uses of halogens and their derivatives. viii. Name the gas, which is used for earthquacke peridiction. ix. What are noble gases? Explain their inertness on the basis of their electronic configuration. x. What do you know about oxyflourides of xenon? Q 3. Give the short answers of the any EIGHT questions. 16 i. Give the applications of nable gases. ii. Give the preparation of xenon oxyflourides. iii. Give the physical properties of noble gases. iv. What do you know about noble gases write down? v. What is meant by the available chlorine? Give some uses of chlorine. vi. Give general features of oxyacids of halogens. vii. What is perchloric acid ? give preparation and uses of it. viii. Discuss the preparation and properties of iodine pentoxides. ix. Write down about chlorine dioxides. x. Give the preparation of bromine monoxides. Q 4. Give the short answers of the any SIX questions. 12 i. What is meant by the bond dissociation energy of halogens? ii. What factors affecting the oxidizing power of halogens? iii. Give the trends in oxidizing power of halogens. iv. Give the properties of HF. v. Give the preparation and properties of oxides of fluorine. vi. Give some physical properties of halogens. SECTION-ll Give the answers of the following THREE questions.Each question is of FOUR marks. 24 Q 5.A) Give the similarities and dissimilarities of fluorine to their groups. B) Give the oxidizing properties of halogens.
- 34. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 34 Q 6.A) Discuss in detail of compounds of halogens. B) Give the reaction of chlorine with cold and hot NaOH. Q 7.A) How bleaching powder is manufactured on industrial scale?
- 35. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 35 Name: Class: 12 Portion Inorganic Paper: Chemistry Subjective Part Marks: 68 Time: 2:40 Test: 15 Chapter no: 5 SECTON –I Q 2. Give the short answers of the any EIGHT questions. 16 xi. What is bleaching powder? How it is prepared give names of different methods. Chemical formula of bleaching powder is CaOCl2 or Ca( OCl )Cl. It can be prepared on industrial scale. Different methods are used for the manufacturing of bleaching powder. These methods are 1. Hasenclever’s method. 2. Beckmann’s method. Hasenclever’s method is an old method while Beckmann’s method is a modern method. xii. Discuss the oxides of chlorine. Oxides of chlorine are unstable. They are not prepared by the direct reaction of chlorine aand oxygen. These are used extensively for bleaching wood, paper pulp in industry and for water treatment. There are two oxides of chlorine. These are chlorine dioxide and chlorine heptaoxide.ClO2 is prepared by the following reaction. 2ClO3ˉ + 2Clˉ + 4H⁺ 2ClO2 + Cl2 + 2H2O Chlorine heptachloride is prepared by the following reaction. 2HClO4 + P2O5 ℃ ⎯⎯⎯⎯ Cl2O7 + 2HPO3 ClO2 used as antiseptic. It is used for purification of water. it is also used to bleach cellulose material. xiii. What are disproportion reactions? Give an example. A reaction in which specie (atom, ion or molecule) is oxidized and reduced simultaneously is called disproportion reaction. For example: Reaction of Cl2 with cold and hot NaOH is an example of disproportion reaction. xiv. What is iodized salt? When some amount of iodide ions are added in common salt (NaCl) , this is called iodized salt. Usually, for this purpose NaI or KI is mixed with NaCl. Insufficient amount of iodine causes the enlargement of thyroid glands. xv. What are ferons and teflons? Flourochlorocarbons are called ferons. These are CCl2F2 (diflourodichloromethane) & CClF3 (tifluorochloromethane). These gases are used as refrigerant and aerosol poll ants. Teflon is a polymer of ( [ CF2-CF2 ]n ). It is an important plastic. xvi. Why iodine has metallic lustre? Metallic luster in iodine is due to the excitation of electrons of iodine at room temperature. Due to the bigger size of iodine the electrons of iodine at room temperature take energy and go to higher energy states. When excited electrons come back, they emit some radiations of particular wavelength. Therefore, they appears as luster grayish black solid.
- 36. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 36 xvii. Give the various uses of halogens and their derivatives. Uses of halogens or their derivatives are Fluorine is used in the preparation of ferons and teflons. Fluorides in toothpastes build a protective coating on teeth. Chlorine is used in the manufacturing of bleaching powder, PVC, CHCl3 and CCl4. Bromine is used as fungicide and as AgBr in photography. Iodine is used in pharmaceutical company. It is added as NaI or KI as a table salt. xviii. Name the gas, which is used for earthquake prediction. Radon is used for earthquake prediction. xix. What are noble gases? Explain their inertness on the basis of their electronic configuration. Elements Helium (He), Neon (Ne), Argon (Ar), Krypton (Kr), Xenon (Xe) and Radon (Ra) that are placed in zero group or VIII group or periodic table are called noble gases. These are also called inert gases or rare gases because they are chemically inert and present in very small amount in atmosphere. All noble gases have their complete octet. Therefore, they are chemically inert. xx. What do you know about oxyflourides of xenon? Oxytetraflourides are colorless volatile liquid. It can be kept in nickel vessel. it reacts with water to give XeO3. Xenon oxytetraflourides are prepared rapidly by the rapid reaction of XeF6 with silica. 2XeF6 + SiO2 2XeF4 + SiF4 Q 3. Give the short answers of the any EIGHT questions. 16 xi. Give the applications of noble gases. Application of noble gases are He is used in weather balloons, in welding and in traffic signal lights. Ne and He arc is used in making glass lasers. Xe is used in bactericidal lamps. Radon being radioactive is used in radiotherapy for cancer and for earth quack prediction. Krypton is used to fill fluorescent tubes and in flash lamps for high speed. xii. Give the preparation of xenon oxytetraflourides. 1. Xenon oxytetraflourides are prepared rapidly by the rapid reaction of XeF6 with silica. 2XeF6 + SiO2 2XeF4 + SiF4 2. Hydrolysis of XeF6 with small amount of water gives XeOF4. XeF6 + H2O XeOF4 + 2HF xiii. Give the physical properties of noble gases. All noble gases are colorless and odourless gases. They are chemically inert. Due to complete shell it is difficult to remove electrons from valance shell. Therefore, they have high ionization energy. They have low melting and boiling point and heat of vaporization. They are less soluble in water. Their solubility increases down the group due to increase in atomic size. xiv. What do you know about noble gases write down? Elements Helium (He), Neon (Ne), Argon (Ar), Krypton (Kr), Xenon (Xe) and Radon (Ra) that are placed in zero group or VIII group or periodic table are called noble gases. These are also called inert
- 37. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 37 gases or rare gases because they are chemically inert and present in very small amount in atmosphere. All noble gases have their complete octet. Therefore, they are chemically inert. All noble gases are colorless and odourless gases. They are chemically inert. Due to complete shell it is difficult to remove electrons from valance shell. Therefore, they have high ionization energy. They have low melting and boiling point and heat of vaporization. They are less soluble in water. Their solubility increases down the group due to increase in atomic size. xv. What is meant by the available chlorine? Give some uses of chlorine. The amount of chlorine which is set free during the reaction of bleaching powder with an acid, is called available chlorine. Chlorine is used in: Chlorine is used in the manufacturing of bleaching powder. It is also used in the manufacturing of HCl, which is cheapest industrial acid. It is used in the manufacturing of antiseptics and insecticides, weed killer. It is used in the manufacturing of PVC plastics. It is used as disinfectant in swimming pool and water treatment plants. xvi. Give general features of oxyacids of halogens. General features of oxyacids of halogens are Stable oxyacids of fluorine do not exist. HOF has been prepared but is highly unstable. Most of oxyacids of halogens are unstable compound. They generally exist only in aqueous solution in the form of their salts. They cannot be isolated. xvii. What do you know about decoluorization of halogens. F2 and Cl2 can oxidize colored dyes to colorless substances e.g. litmus, universal indicators etc. during bleaching Cl also act as oxidizing agent. xviii. Discuss the preparation and properties of iodine pentoxides. Iodine penta oxide is prepared by heating acidic acid at 240˚C. 2HIO3 ℃ ⎯⎯⎯⎯ I2O5 + H2O Iodine penta oxide is a white crystalline solid. It is stable up to 300˚C. It has polymeric structure. It is insoluble in organic solvents. xix. Write down about chlorine dioxides. Chlorine dioxide is a pale yellow gas. On warming, it explodes into Cl2 and O2. It is soluble in water. it is stable in dark. It is used as antiseptic and for the purification of water. it is prepared by the following reaction. 2ClO3ˉ + 2Clˉ + 4H⁺ 2ClO2 + Cl2 + 2H2O xx. Give the preparation of bromine monoxides. It can be prepared by reaction of bromine vapours with mercuric oxide. HgO + 2Br2 ℃ ⎯⎯ HgBr2 + Br2O It is also prepared by the treating suspension of HgO in CCl4 with bromine. HgO + 2Br2 HgBr2 + Br2O
- 38. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 38 Q 4. Give the short answers of the any SIX questions. 12 vii. What is meant by the bond dissociation energy of halogens? Bond dissociation energy of halogens decreases with increase in size of halogen atoms. Dissociation occurs in the following order. HF < HCl < HBr < HI Thus HI is dissociated more and HF is dissociated least. viii. What factors affecting the oxidizing power of halogens? Following factors affect oxidizing power. Energy of dissociation. Electron affinities of atms Hydration energy of ions. Heats of vaporization. ix. Give the trends in oxidizing power of halogens. If a halogen has low energy of dissociation, high electron affinity and high hydration energy of its ions, then it will be a better oxidizing agent. Thus oxidizing power of F2 is high due to low dissociation energy and high hydration energy of Fˉ ion. Thus general trend of oxidizing power is F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 x. Give the properties of HF. Properties of HF are HF is a colorless volatile liquid. HF attacks glass. It is handled in teflon (poly tetra flouro ethylene) containers. In dry state, it can be stored in copper stainless-steel containers under vacuume. It is strongly fuming liquid. It is used as non-aqueous solvent. HF is a strongly hydrogen bonded liquid. xi. Give the preparation and properties of oxides of fluorine. Trioxygen diflouride (O3F2) is prepared by passing electric discharge through a mixture of oxygen and fluorine. 2F2 + 3O2 2O3F2 Properties of oxides of flourine are At 363˚C , it is dark red viscous liquid but turns to reddish brown solid at 350˚C. It decomposes on heating to give oxygen gas and other oxides of flourine . 2O3F2 2O2F2 + O2 xii. Give the physical properties of bleaching powder and uses of bleaching powder. It is yellowish white powder. It has strong smell of chlorine. It is used for the preparation of chlorine and oxygen. It is used in the manufacturing of chloroform. It is used as disinfectant and in the sterilization of water. it is used for making unshrinkable wool. SECTION-ll
- 39. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 39 Give the answers of the following THREE questions.Each question is of FOUR marks. 24 Q 5.A) Give the similarities and dissimilarities of fluorine to their groups. See the topic of peculiar behaviour of fluorine. B) Give the oxidizing properties of halogens. See the topic of oxidizing properties. Q 6.A) Discuss in detail of compounds of halogens See the topic of compounds of halogens. B) Give the reaction of chlorine with cold and hot NaOH. See the topic of reactions of chlorine with cold and hot NaOH. Q 7.A) How bleaching powder is manufactured on industrial scale? See the topic of manufacturing of bleaching powder. B) Discuss in detail about compounds of xenon. See the topic of compounds of xenon. C) Discuss in detail about compounds of xenon.
- 40. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 40 Name: Class: 12 Portion inorganic Paper: Chemistry Objective Part Marks: 17 Time: 20 Minutes. Test: 16 Chapter no: 6 Q 1. Each question has FOUR possible answers. Choose the correct answer and encircle it. 17 Sr#. Statement. A B C D 1. NH3 is the _______ ligand. Unidentate Didentate Tridentate Polydentate 2. In K4[Fe(CN)6],coordination number of Fe is: 4 8 7 6 3. Chinese used iron as early as: 2500B.C. 1500B.C. 600B.C. 1000B.C. 4. Wrought iron contains carbon to about: 0.12-0.25% 0.21-0.52% 0.25-2.5% 2.5-4.5% 5. Steel is manufactured by: Contact process Bessemer process Pulp process Screening process 6. The melting point of potassium dichromate is : 385◦C 346◦C 350◦C 396◦C 7. The total number of transtion elements is: 10 14 40 58 8. Which of the following is a typical transition metal? Sc Y Ra Co 9. Which of the following is a non-typical transition metal? Cr Mn Zn Fe 10. The first transition series ends on the element Scandium Cadmium Zinc Mercury 11. The oxidation state of Mn in KmnO4 is: +4 +2 +7 -7 12. The process of zinc coating on iron is called: Zn platting Galvanizing Tin platting All 13. All chromates are mostly: White Red Yellow Green 14. Acidified KmnO4 acts as Reducing agent Oxidizing agent Dehydrating agent Drying agent 15. Which of the following does not show variable valency? Cr Zn Mn Fe 16. The shape of [Co(NH3)6]3⁺ is: Tetrahederal Octahederal Square planar Pyramidal 17. Chromyl chloride test is performed to confirm Br⁻ ion Cl⁻ ion Both None
- 41. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 41 Name: Class: 12 Portion Inorganic Paper: Chemistry Subjective Part Marks: 68 Time: 2:40 Test: 16 Chapter no: 6 SECTON –I Q 2. Give the short answers of the any EIGHT questions. 16 i. Differentiate b/w typical and non-typical elements. ii. Give the some properties of transition elements. iii. What do you know about the Oxidation states of transition elements? iv. Differentiate b/w paramagnetic and diamagnetic substances. v. What is meant by interstitial elements? vi. What is meant by wrought iron? vii. What is meant by corrosion? Explain. viii. Give the preventive measure of corrosion. ix. What is meant by zinc coating? x. How prepared the potassium chromate? Q 3. Give the short answers of the any EIGHT questions. 16 i. Discuss the oxidizing property of potassium dichromate. ii. What is meant chromyl chloride test? iii. Give the some uses of potassium dicchoromate. iv. Give the laboratory method of preparation of potassium permagnate. v. What is stadeler’s process? vi. Give the physical properties of potassium peramaganate. vii. Give some uses of potassium peramaganate. viii. Why does damaged tin plated iron get rusted quickly? Explain. Q 4. Give the short answers of the any SIX questions. 12 i. Under what conditions does aluminium crode? Explain. ii. How does the process of galvanizing protect iron from rustling? iii. How chromate ions are converted into dichromate ions? iv. What do you know about ligands and substitution alloy? v. How does the electronic configuration of valance shell affecting the following properties of the transition elements: i) Paramagnetism ii) Melting points. SECTION-ll Give the answers of the following three questions. Each question is of FOUR marks. 24 Q 5.A) Give details on nomenclature of complex compounds. B) How steel is manufactured by open hearth and besemmer process? Q 6.A) How electrochemical theory explain corrosion? B) Discuss the following properties of transition elements: i) Paramaganetism ii) Oxidation states Q 7.A) How wrought iron is manufactured from cast iron? B) What is meant by complexes of compounds and their components? Explain.
- 42. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 42 Name: Class: 12 Portion Inorganic Paper: Chemistry Subjective Part Marks: 68 Time: 2:40 Test: 16 Chapter no: 6 SECTON –I Q 2. Give the short answers of the any EIGHT questions. 16 xi. Differentiate b/w typical and non-typical elements. Typical elements Non-typical elements i) Elements which show typical i) Elements which do not show properties of transition elements are called typical properties of transition elements typical transition elements. are called non-typical transition elements. ii) For example ii) For example Coinage metals include Cu, Ag and Au. These are Group llB include Zn, Cd and Hg. Typical transition elements because Cu2+ has 3d9 These elements do not have partially filled configuration, Ag2+ has 4d9 configuration and Au3+ d-orbital in atomic state. Moreover, these has 5d8 configuration. These elements are called elements do not show typical properties of typical transition elements. because these have transition elements except complex typical properties. formation. xii. Give the some properties of transition elements. Properties of transition elements are They are all metals. Some are very important in industry e.g. Ti, Fe, Cr, Ni, Cu, Mo, Zr, Nb, Ta etc. They are hard with high melting and boiling points. They are good conductors of haet and electricity. Generally, they show variable valancy. They form alloys with one another and with other elements. xiii. What do you know about the Oxidation states of transition elements? Transition elements show variable oxidation state. It is because d-electrons of inner d-orbital are also involved in bonding in addition to outer s-electrons. Due to the presence of large number of unpaired electrons these can show variable valancy. For higher oxidation states, d-orbital involve in bonding. +2 oxidation state is produced due to the involvement of s-electrons in bonding. xiv. Differentiate b/w paramagnetic and diamagnetic substances. Paramagnetic substances Diamagnetic substances i) Substances which are weakly attracted i) Substances which are weakly repelled by strong magnetic field, are called paramagnetic by strong magnetic field, are called substances. diamagnetic substances. ii) The paramagnetic behavior is caused by ii) When electrons are paired, their Unpaired electrons. It is because moving electrons magnetic moments cancel the effect of
- 43. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 43 have magnetic moments. each other thus the substances becomes diamagnetic. xv. What is meant by interstitial compounds? Transition elements have close packed structure in which interstices are present. Small non-metallic atoms like H, B, C and N can enter into these interstices and absorbed on the surface of metal atoms to form interstitial compounds. These compounds are non-stechiometric in nature and do not obey the laws of chemical combination. Sometimes they are also called interstial alloys. xvi. What is meant by wrought iron? It is the purest form of commercial iron. It has the lowest percentage of carbon. It has upto 0.3% impurities like S, P, Si, Mn etc. S = 0.2 to 0.15%, Mn = upto 0.25%, P = 0.04 to 0.2% xvii. What is meant by corrosion? Explain. The process of chemical decay of metals due to the action of surrounding medium is called corrosion. When metals come into contact of atmospheric gases, the surface of metals is coated with oxides, sulphides, carbonates etc. sometimes these compounds form a compact layer on the surface. Thus metal is protected from further attack. However, if water is present in layer of oxides, sulphides and carbonates are dissolvrd in water. thus corrosion penetrate into metal. xviii. Give the preventive measure of corrosion. Following measure or methods are used to prevent the metals from corrosion. Coating of metals: It is the simple method. In this metal surface is coated with oil, paints or enamels. Alloying: Corrosion can be prevented by alloying of metal with other metals.e.g. corrosion of Fe is prevented by alloying it with Ni, Cr etc. Metallic coating: A protective layer of another metal on the surface of metal can also prevent corrosion. xix. What is meant by zinc coating? It is done by dipping clear iron sheets in a ZnCl2 bath and heating. Iron sheets are removed and rolled into Zn bath and air cooled. If protective coating of Zn is destroyed then a galvanic cell is set up. In this cell Zn acts as anode and iron acts as cathode. Electrons flow from Zn to iron. Thus Zn decays while Fe remains intact. This is called sacrifical corrosion. Fe2+ + Zn Zn2+ + Fe This type of galvanizing is used in water pipes. xx. How prepared the potassium chromate?
- 44. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 44 Chromates of alkali metals are soluble in water. These are obtained by oxidizing trivalent chromium compounds in the presence of an alkali. 2KCrO2 + 3Br2 + 8KOH 2K2CrO4 + 6KBr + 4H2O Fusing Cr2O3 with an alkali in the presence of an oxidant, e.g potassium chlorate, can also produce chromates. Cr2O3 + 4KOH + KClO3 2K2CrO4 + KCl + 2H2O Q 3. Give the short answers of the any EIGHT questions. 16 ix. Discuss the oxidizing property of potassium dichromate. Dichromates are powerful oxidizing agents. Oxidation is carried out in an acid solution. In this process, hexavalent chromium ion is reduced to trivalent chromium ion. Reaction with Ferrous sulphate: K2Cr2O7 + 7H2SO4 + 6FeSO4 K2SO4 + Cr2 (SO4)3 + 3Fe2(SO4)3 + 7H2O x. What is meant chromyl chloride test? When solid potassium dicchromate is heated with solid metal chloride in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid chromyl chloride is produced. This test is used for the detection of metal chloride. K2Cr2O7 + 6H2SO4 + 4NaCl 2KHSO4 + NaHSO4 + 2CrO2Cl2 + 3H2O xi. Give the some uses of potassium dicchoromate. Potassium dicchromate is used in dyeing. It is used in leather industries for chrome tanning. It is used as an oxidizing agent. xii. Give the laboratory method of preparation of potassium permagnate. It is prepared by acidifying the solution of potassium manganate, KmnO4 by H2SO4. 3K2MnO4 + 2H2SO4 2K2SO4 + 2KMnO4 + MnO2 + 2H2O xiii. What is stadeler’s process? In this method, Cl2 is passed through green solution of K2MnO4 until it becomes purple due to the formation of KMn4. Hence Cl2 oxidizes K2MnO4 into KMnO4. 2K2MnO4 + Cl2 2KCl + 2KMnO4 xiv. Give the physical properties of potassium peramaganate. It forms dark purple lustrous crystals which gives deep pink color in solution. Its solubility in water at 20˚C is only about 7%. It dissolves more at higher temperature (25% at 63˚C). xv. Give some uses of potassium peramaganate. Potassium permaganate is used as an oxidizing agent. It is used as a disinfectant and a germicide. It is used in the manufacturing of many organic compounds. xvi. Why does damaged tin plated iron get rusted quickly? Explain. In tin plated iron a protective layer of tin is deposited on iron. If protective coating of tin is damaged, then iron comes in contact with moisture of air. A galvanic cell is established in which tin acts as
- 45. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 45 cathode and iron acts as anode. The electrons flow from iron towards tin, where they discharge H+ ions of moisture and leaving behind OH- ions in solution. Q 4. Give the short answers of the any SIX questions. 12 vi. Under what conditions does aluminium crode? Explain. Aluminium corrodes only, when it is contact with those metals, which have greater reduction potential than aluminium in the presence of moisture. In the presence of moisture if aluminium is in contact with copper, silver or gold then Al is corroded. Thus, two conditions are necessary for aluminium corrosion. 1. Moisture. 2. Contact with metals having greater reduction potential than aluminium such as copper, gold and silver etc. vii. How does the process of galvanizing protect iron from rustling? The corrosion of iron can be prevented by galvanizing with zinc. It is done by dipping clear iron sheets in a ZnCl2 bath and heating. Iron sheets are removed and rolled into Zn bath and air cooled. If protective coating of Zn is destroyed then a galvanic cell is set up. In this cell Zn acts as anode and iron acts as cathode. Electrons flow from Zn to iron. Thus Zn decays while Fe remains intact. This is called sacrifical corrosion. Fe2+ + Zn Zn2+ + Fe This type of galvanizing is used in water pipes. viii. How chromate ions are converted into dichromate ions? K2CrO4 and K2Cr2O4 show similar properties because in aqueous solution Cr2O7 2- and CrO4 2- ions exist in equilibrium. 2CrO4 2- + 2H+ Cr2O7 2- + H2O ix. What do you know about ligands and chelates? The atom or ion or neutral molecules which surrond the central metal atom or ion by denoting electron pairs are called ligands. For example: In K4[Fe(CN)6] and K3[Fe(CN)6] , CN- is the ligand. There are two types of ligands. These are unidentate and polydentate ligands. When all the donor atoms of a polydentate ligand are coordinated with the same metal ion, a complex compound is formed which contains one or more rings in its structure. It is called a chelate. x. How does the electronic configuration of valance shell affecting the following properties of the transition elements: i) Paramagnetism. Substances which are weakly attracted by strong magnetic field, are called paramagnetic substances. Substances which are weakly repelled by strong magnetic field, are called diamagnetic substances. The paramagnetic behavior is caused by unpaired electrons. It is because moving electrons Have magnetic moments. when electrons are paired, their magnetic moments cancel the effect of each other thus the substances becomes diamaganetic. ii) Melting points.
- 46. 2020 CHEMISTRY PART-2: SOLUTION MANUAL BY MALIK XUFYAN CELL # 03137355727 S u p e r W i n g s G r o u p o f C o l l e g e s K a l l a r R a w a l p i n d i Page 46 Transition elements have very high melting points due to strong binding forces.melting points increases upto middle and then decreases to a minimum at the end of series. It is due to increase in binding forces upto middle and then decrease upto end. SECTION-ll Give the answers of the following three questions. Each question is of FOUR marks. 24 Q 5.A) Give details on nomenclature of complex compounds. See the topic of nomenclature of complex compounds. B) How steel is manufactured by open hearth and besemmer process? See the topic of manufacturing of steel. Q 6.A) How electrochemical theory explain corrosion? See the topic of corrosion. B) Discuss the following properties of transition elements: i) Binding energies ii) Covalent and atomic radii See the topic of properties of transition elements. Q 7.A) How wrought iron is manufactured from cast iron? See the topic of wrought iron . B) What is meant by complexes of compounds and their components? Explain. See the topic of complex compounds.
