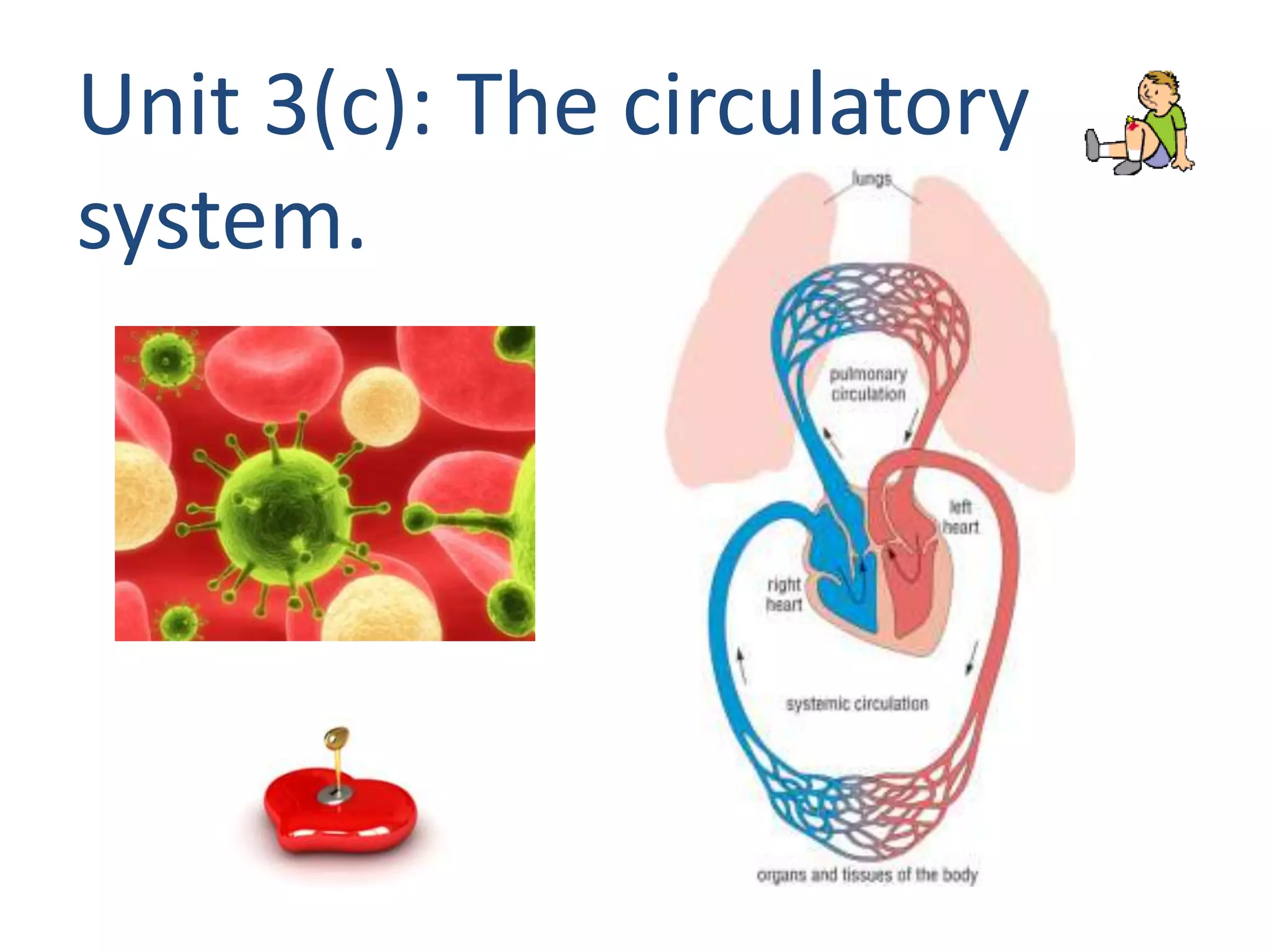
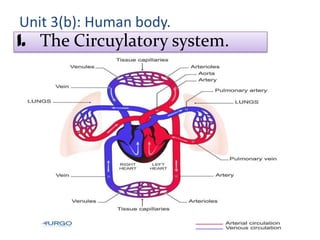
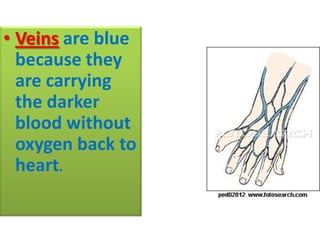
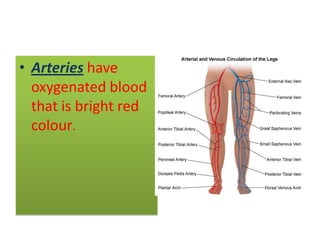
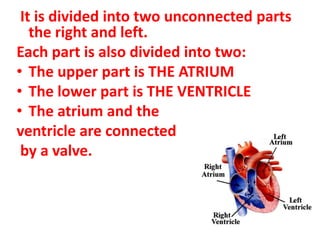
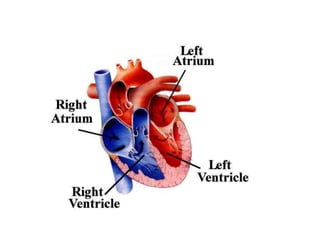
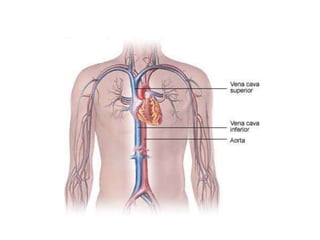
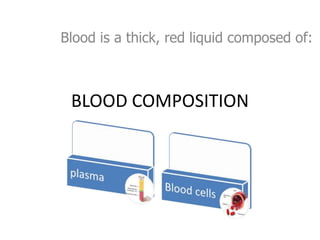
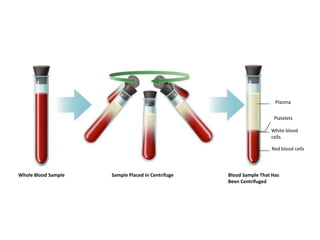
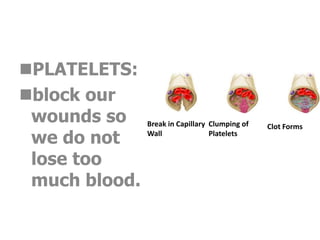
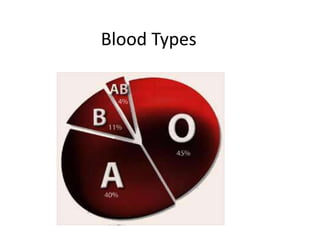
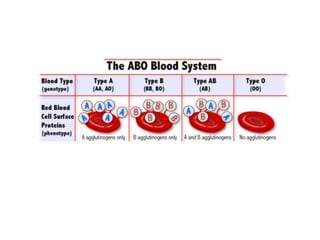
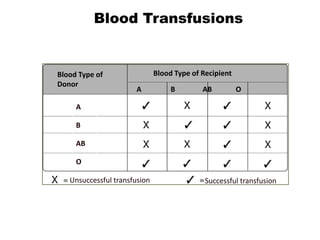
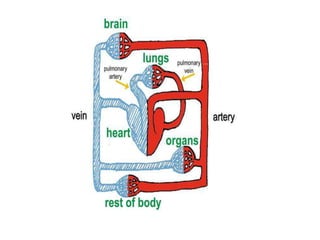
The document describes the circulatory system and its key components. It explains that the circulatory system consists of blood vessels, blood, and the heart. It details the three types of blood vessels - arteries, veins, and capillaries. The heart is divided into four chambers - two atria and two ventricles. Blood transports oxygen, nutrients, carbon dioxide and waste. Maintaining a healthy circulatory system requires regular exercise, a healthy diet, avoiding smoking and maintaining a healthy weight.