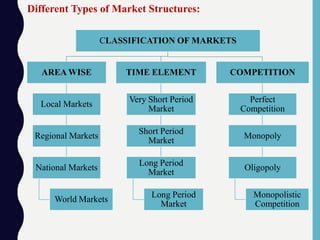
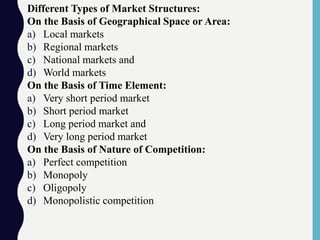
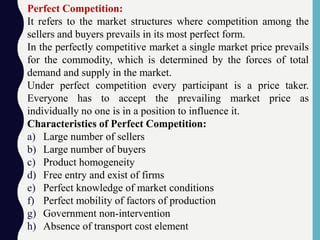
This document provides an overview of different market structures, including perfect competition, monopoly, and monopolistic competition. It defines a market as an arrangement where buyers and sellers can directly or indirectly buy and sell goods. Markets are classified based on geographical area, time period, and level of competition. Perfect competition has many small sellers and buyers, homogeneous products, free entry and exit, and price-taking firms. A monopoly has a single seller controlling the entire market supply of a unique product without substitutes. Monopolistic competition involves differentiated products, many firms and free entry. The document outlines characteristics and pricing dynamics for each market structure.