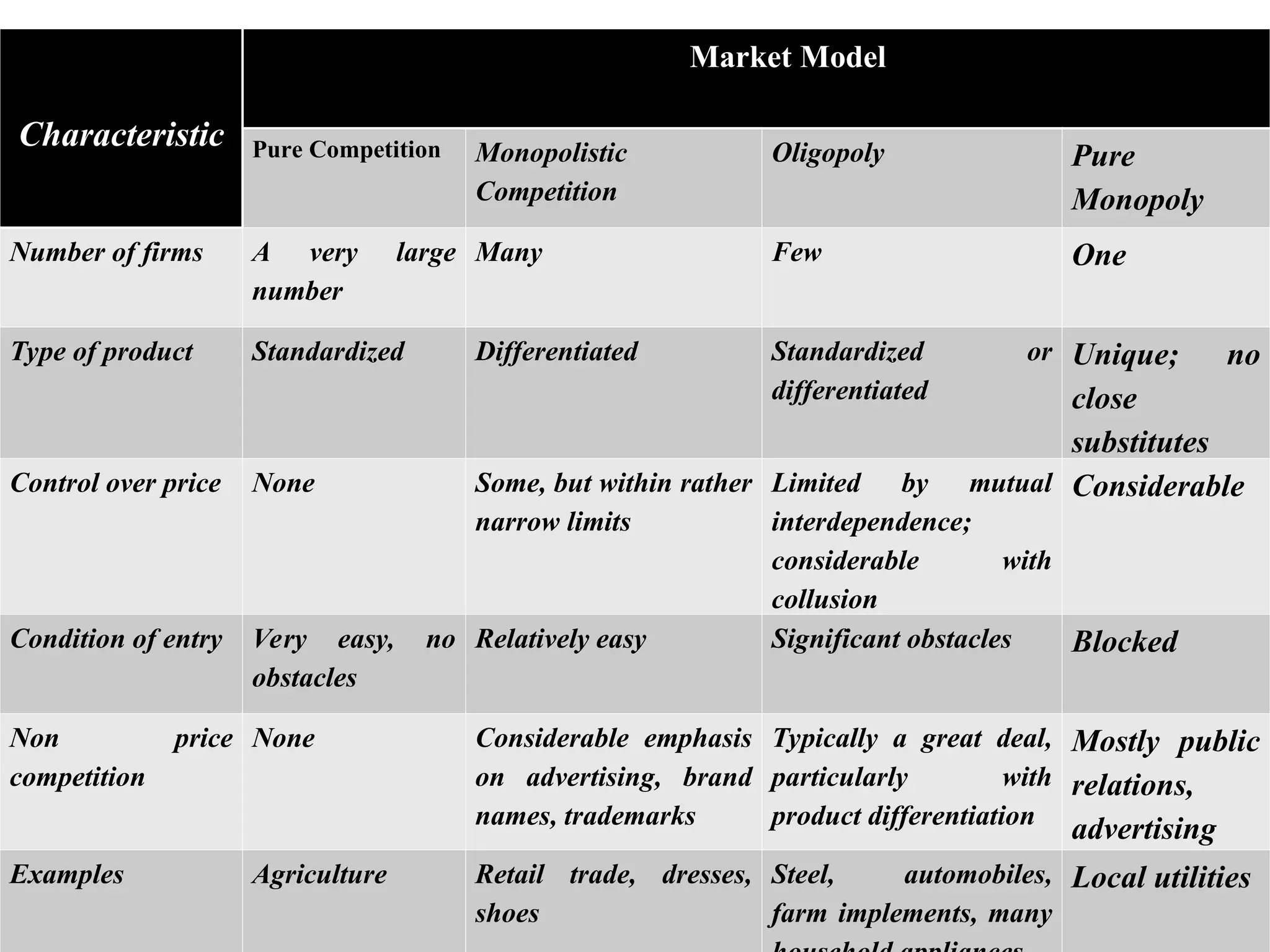
Chapter five discusses market structures, categorizing them into four types: pure competition, pure monopoly, monopolistic competition, and oligopoly, each varying in the number of firms, product standardization, and entry barriers. Pure competition features numerous firms with standardized products and easy market entry, while a pure monopoly consists of a single firm with a unique product and high entry barriers. Monopolistic competition and oligopoly involve differentiated products and a limited number of firms, with varying levels of price control and competitive strategies.