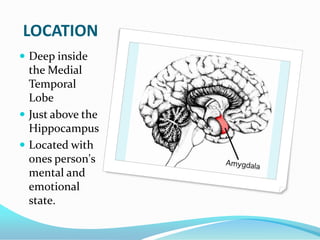
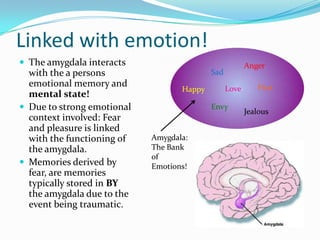
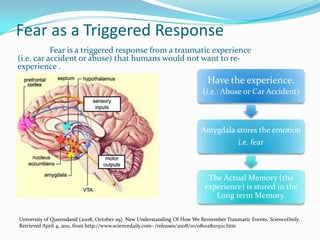
The amygdala is located within the medial temporal lobe and is involved in processing memories and emotional reactions. It forms part of the limbic system and is linked to emotions like fear, pleasure, anger, and love. The amygdala interacts with emotional memory and mental state. One study found a girl without a functioning amygdala did not experience fear from threats like spiders, snakes, or horror movies. The amygdala is important for forming memories of emotionally arousing or traumatic events. When damaged, it can result in anxiety or depression, and other brain regions like the bed nuclei may compensate for amygdala functions. A larger amygdala volume correlates with larger, more complex social networks in humans.