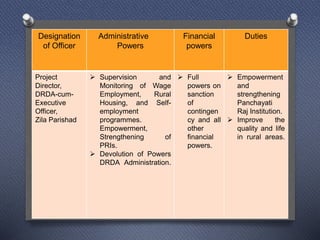
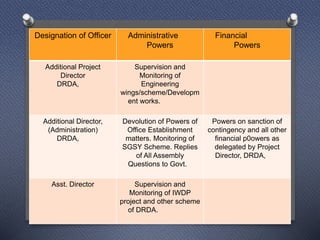
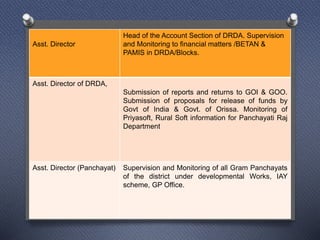
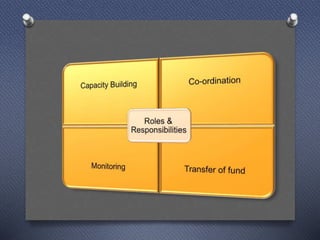
DRDAs were established to effectively implement anti-poverty programs in rural areas at the district level. Their primary objectives are managing anti-poverty programs and coordinating different agencies. DRDAs have wings for self-employment, women, wage employment, accounts, and monitoring. They oversee program implementation and ensure funds are properly utilized but do not directly implement projects.









![Continue..
Indian States(29)
23 states
Have DRDAs
6 states [KARNATAKA,
RJ, MP, CH, WB,
KERALA]
Functioning through
PRI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drda1-160302191539/85/DRDA-Basic-strategy-12-320.jpg)