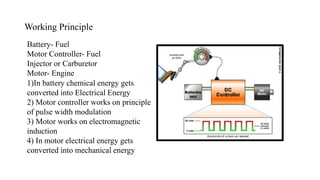
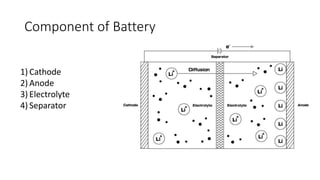
The document discusses the key components and working principles of electric vehicle batteries and motors. It provides information on:
1) The main components of lithium-ion batteries used in EVs including the cathode, anode, electrolyte, and separator. It also discusses battery parameters like storage capacity, energy density, and cycle life.
2) The types of motors used in EVs like AC induction motors and brushed vs brushless DC motors. It provides a basic overview of how motors work using electromagnetic induction to convert electrical energy from batteries into mechanical energy.
3) The function of motor controllers to precisely control the motor based on driver input and convert battery power into vehicle motion using components like sensors and power electronics.