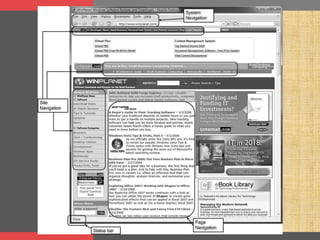
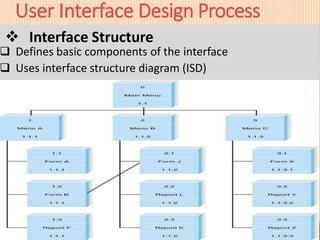
This document discusses user interface design principles and processes. It outlines key terms like user interfaces and system interfaces. The fundamental parts of a user interface are navigation, input, and output mechanisms. Design principles covered include layout, content awareness, aesthetics, user experience, consistency, and minimizing user effort. The user interface design process involves four steps: use scenario development to describe common system uses, interface structure design, standards design, and evaluation. Evaluation approaches include heuristic, walk-through, interactive, and formal usability testing.