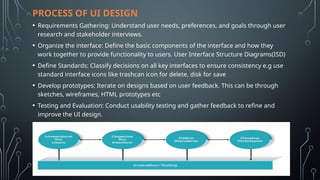
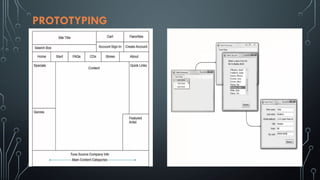
The document provides a comprehensive overview of user interface (UI) design, emphasizing its critical role in enhancing user experience and system usability. It outlines the UI design process, including requirements gathering, prototyping, and evaluation, while also highlighting principles for effective design and tools used in the industry. Best practices are shared to ensure accessibility, usability, and ongoing design improvement based on user feedback.