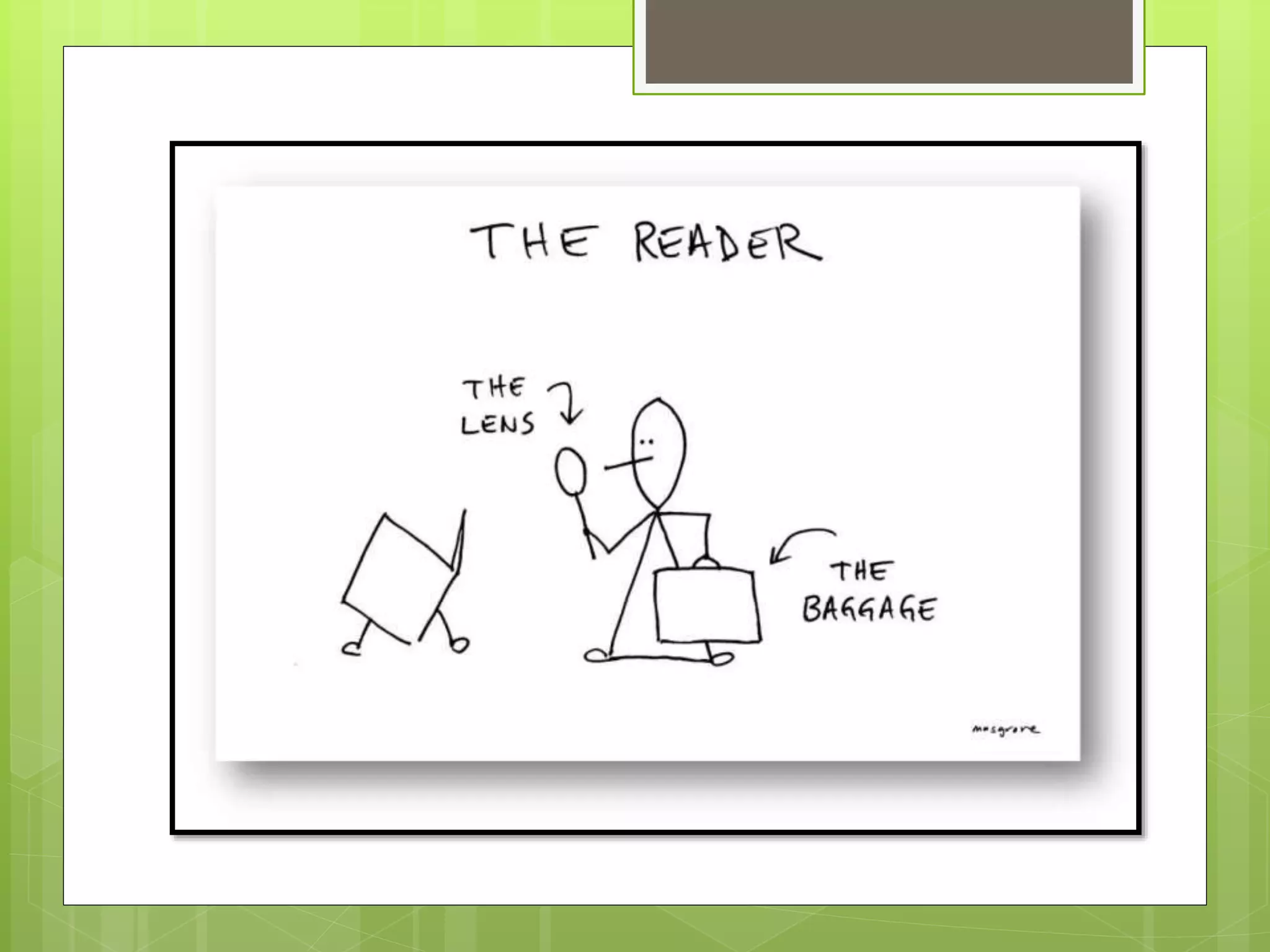
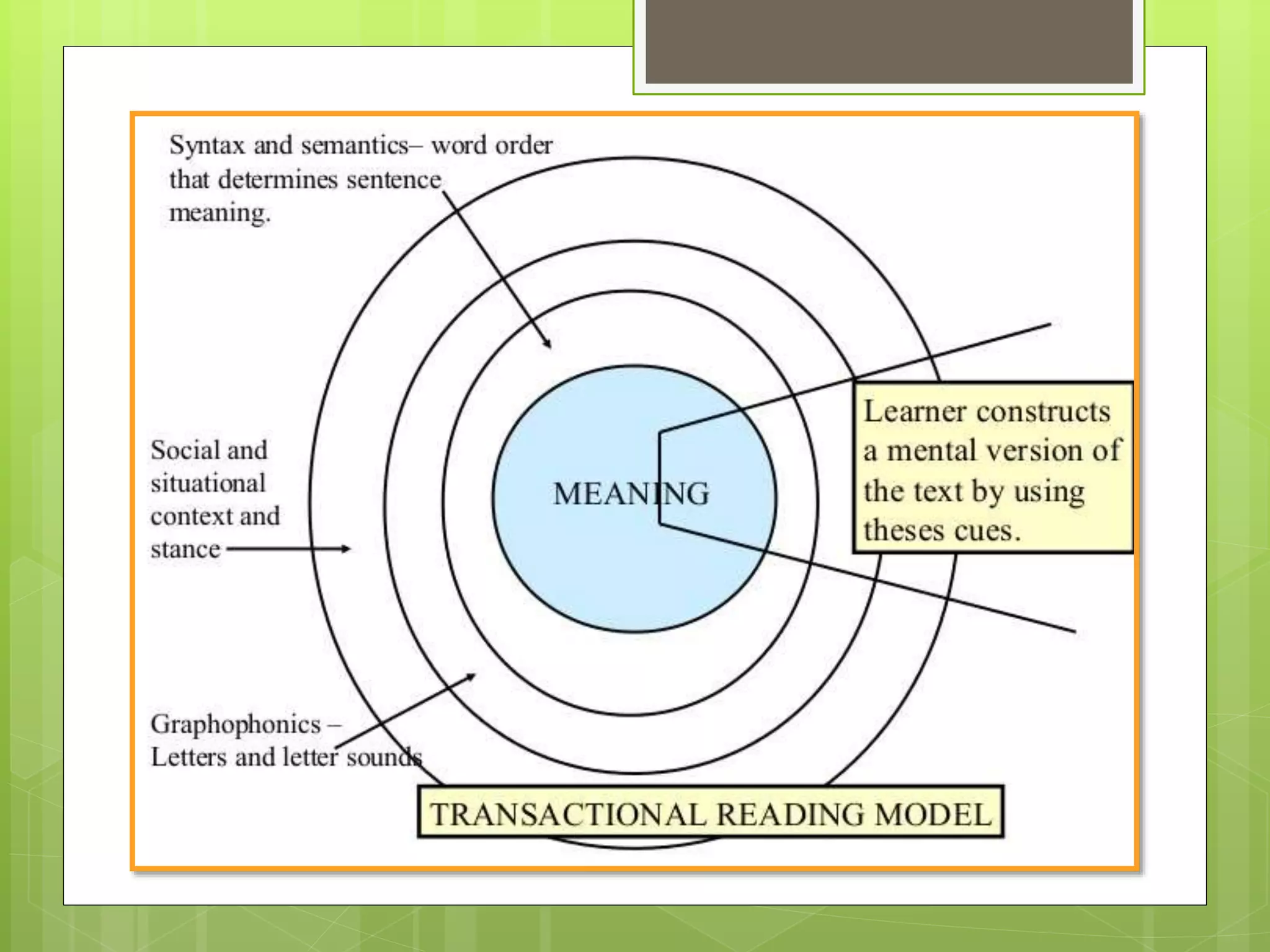
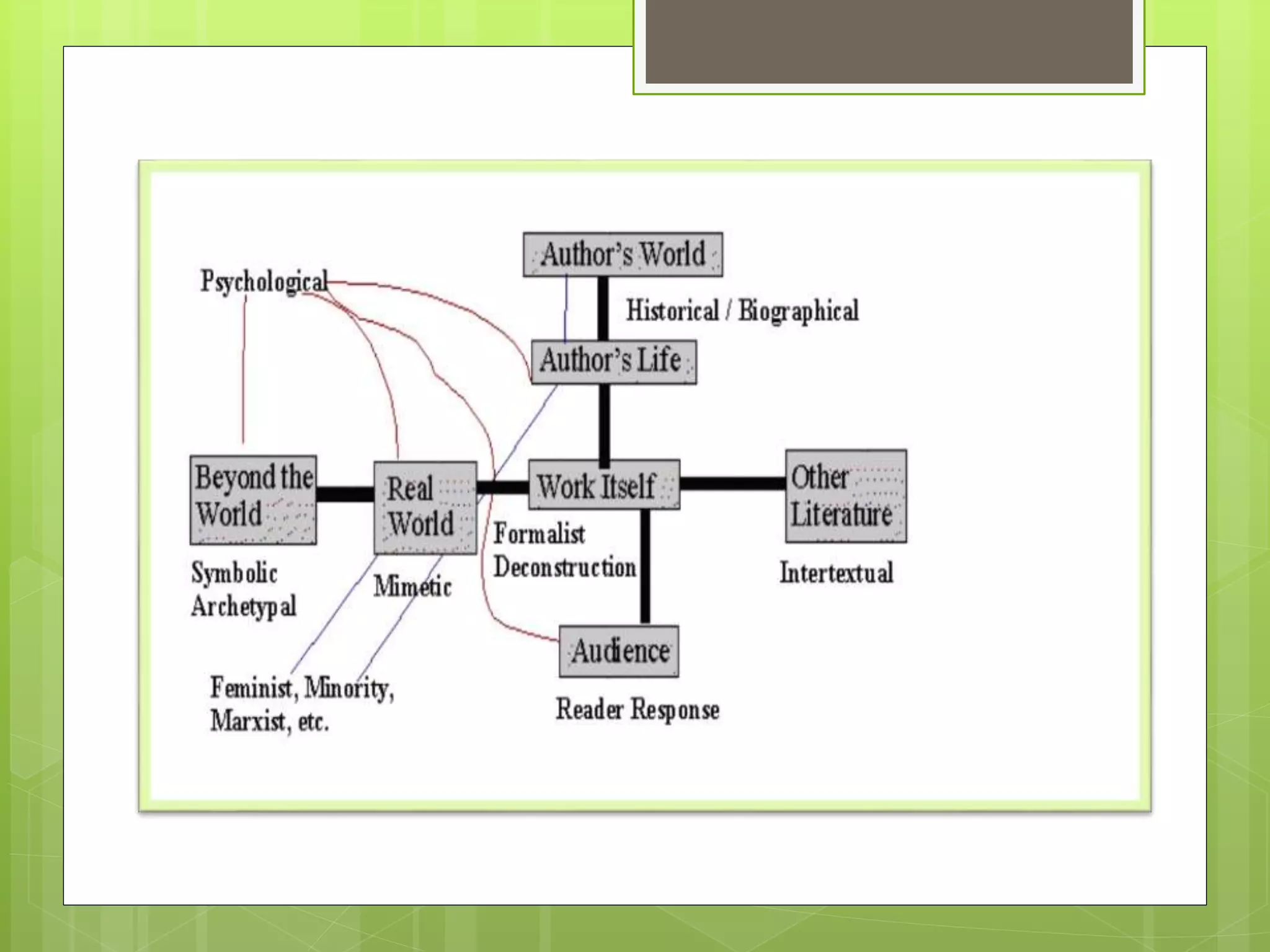
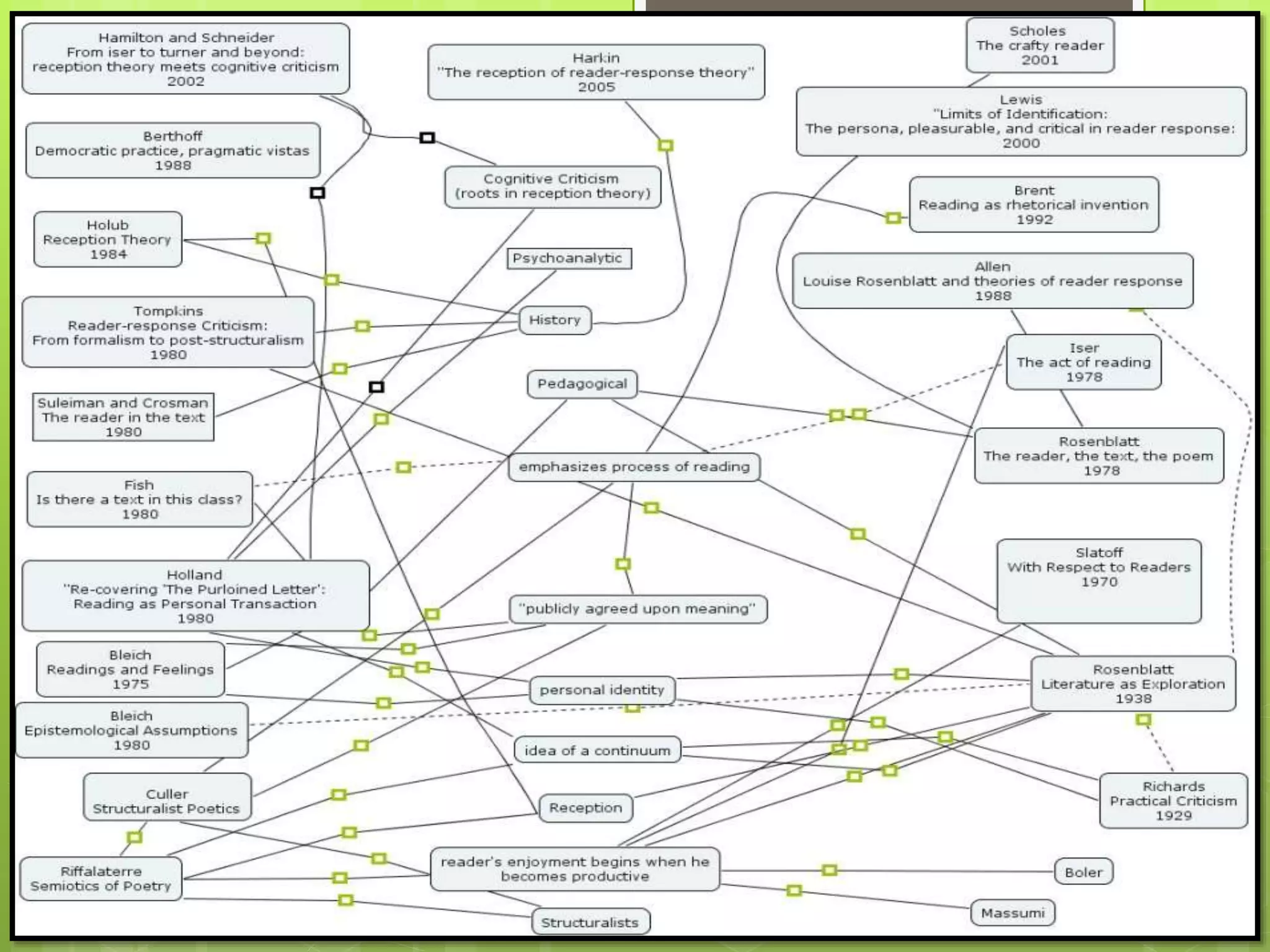
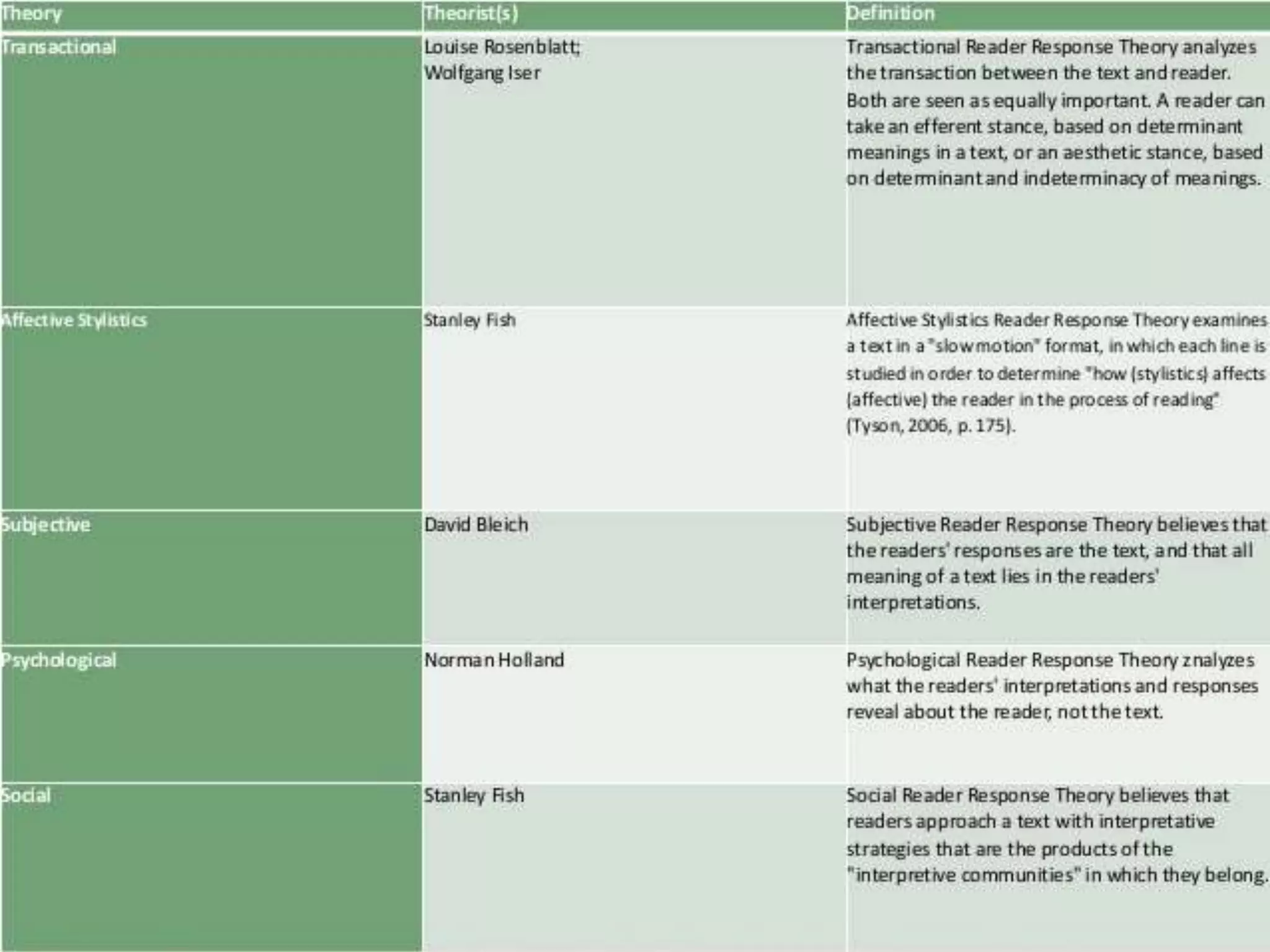
- Reader-response theory proposes that the meaning of a text is derived from the reader's interaction with it rather than being inherent in the text itself or determined by the author.
- Key aspects of reader-response theory include the implied reader, implied author, competent reader, and phenomenological approach which sees meaning as generated in the reading process through interaction between text and reader.
- There are three main types of reader-response theory: transactional, which sees a transaction between text and reader; subjective, which sees the reader's interpretations as creating the text; and psychological, which applies psychoanalytic concepts to the reading process.