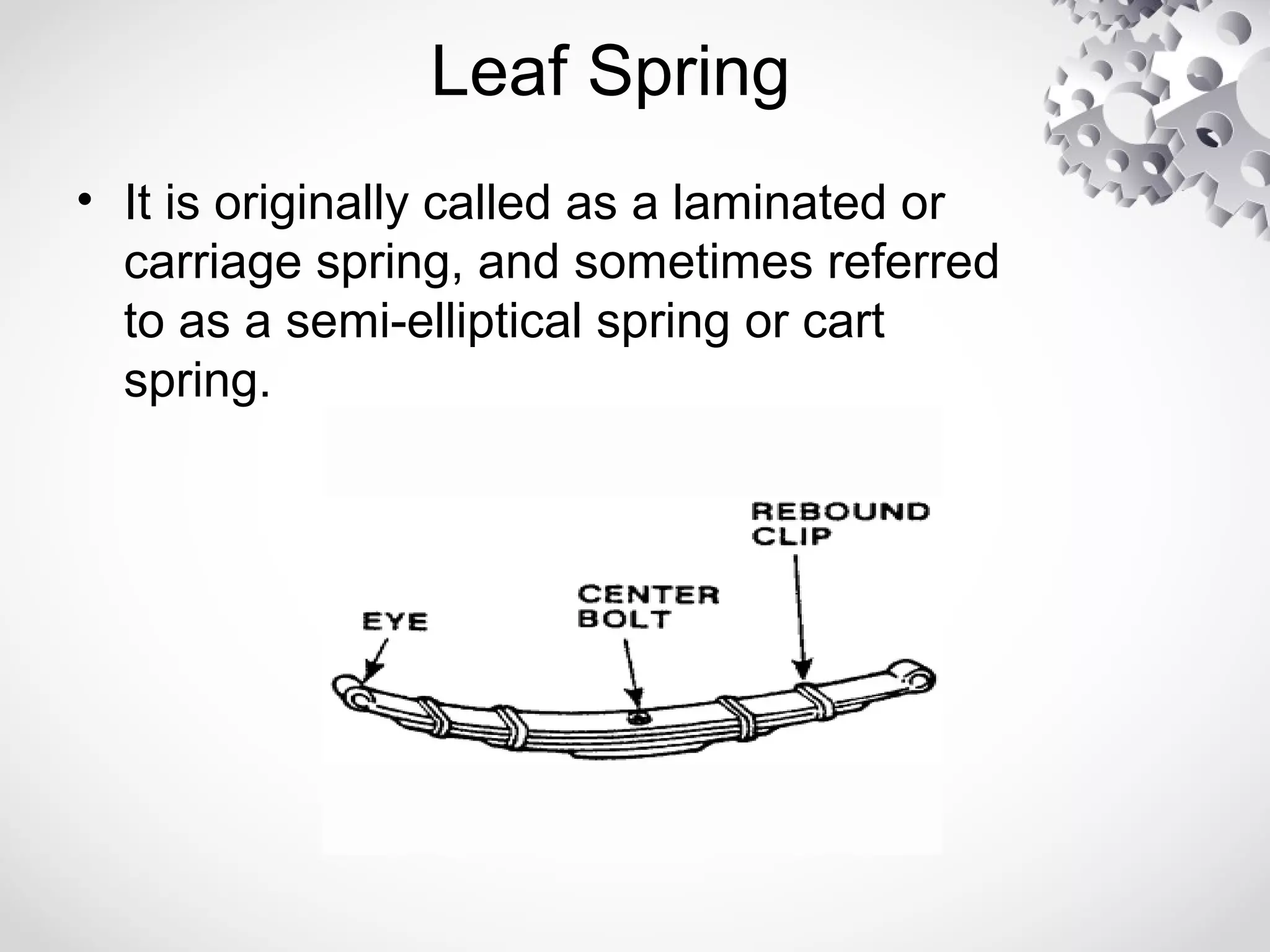
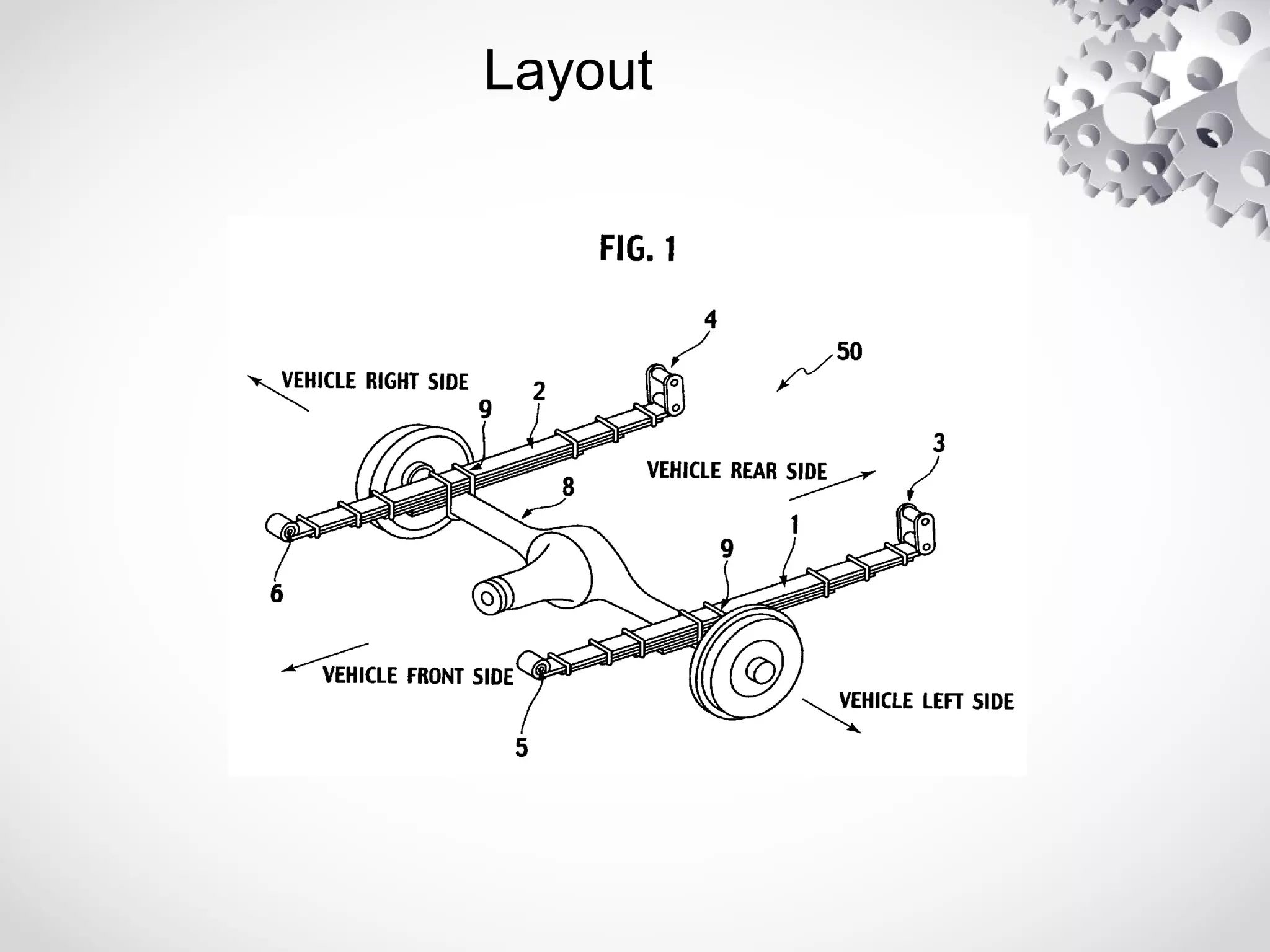
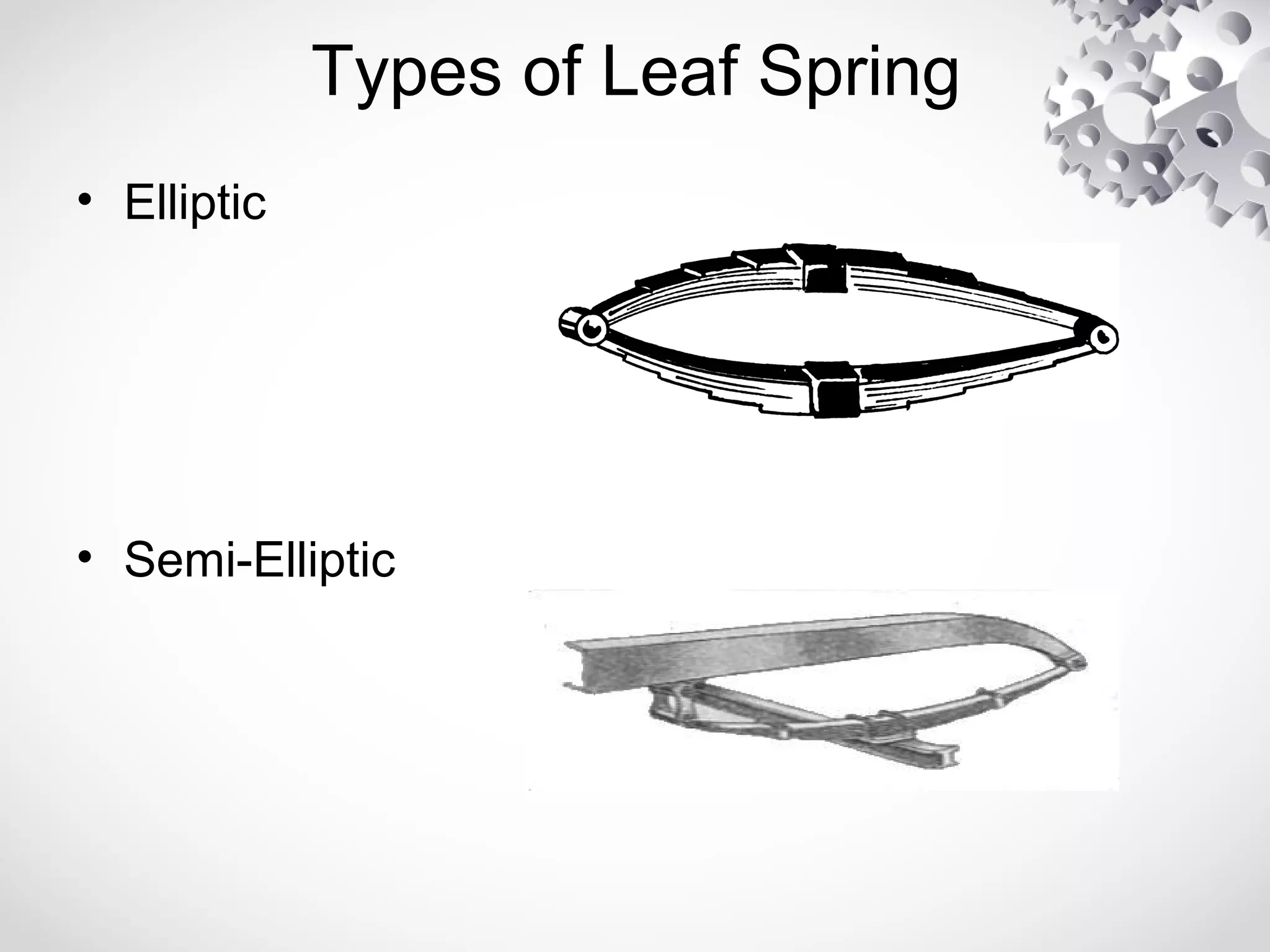
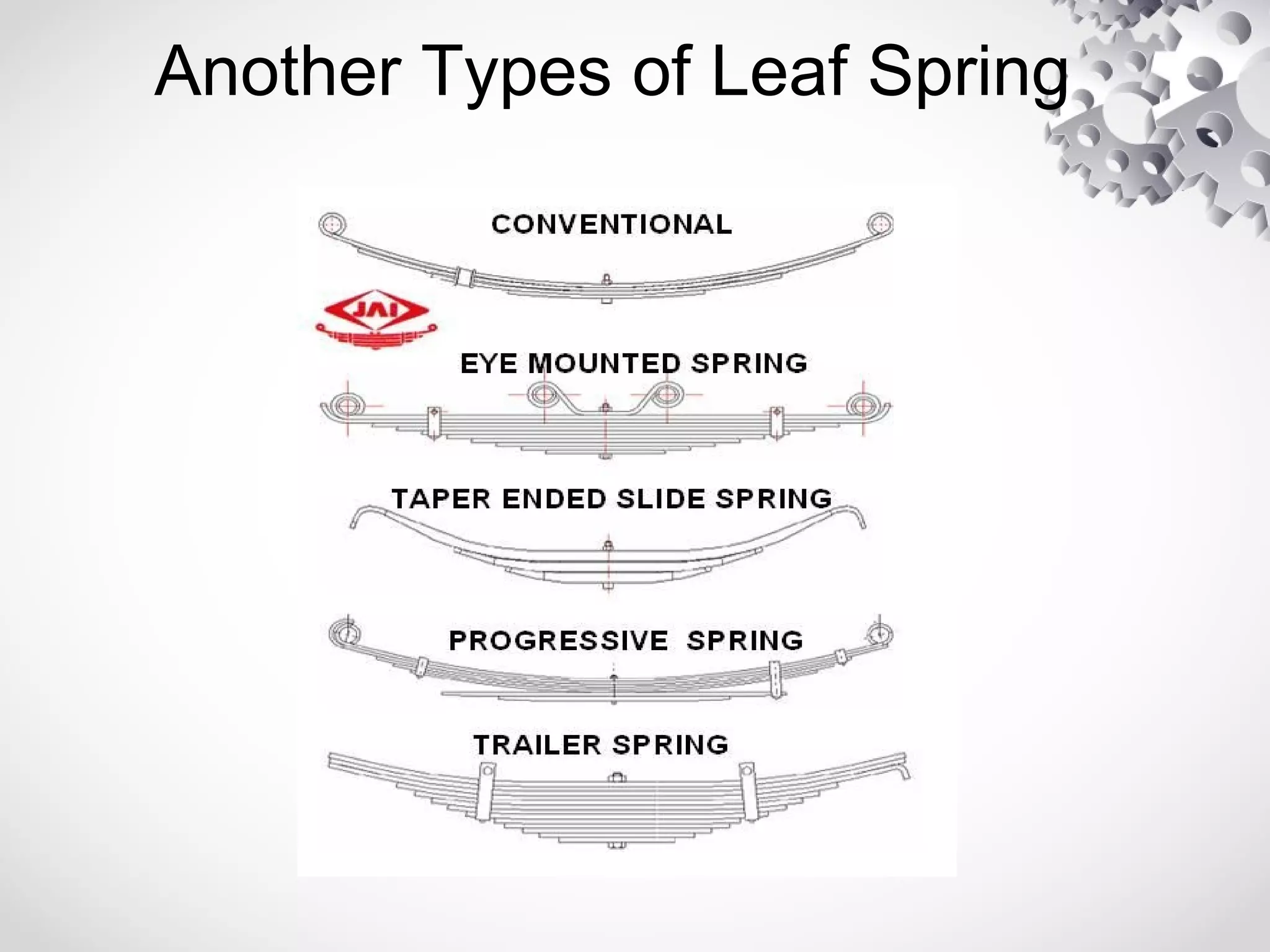
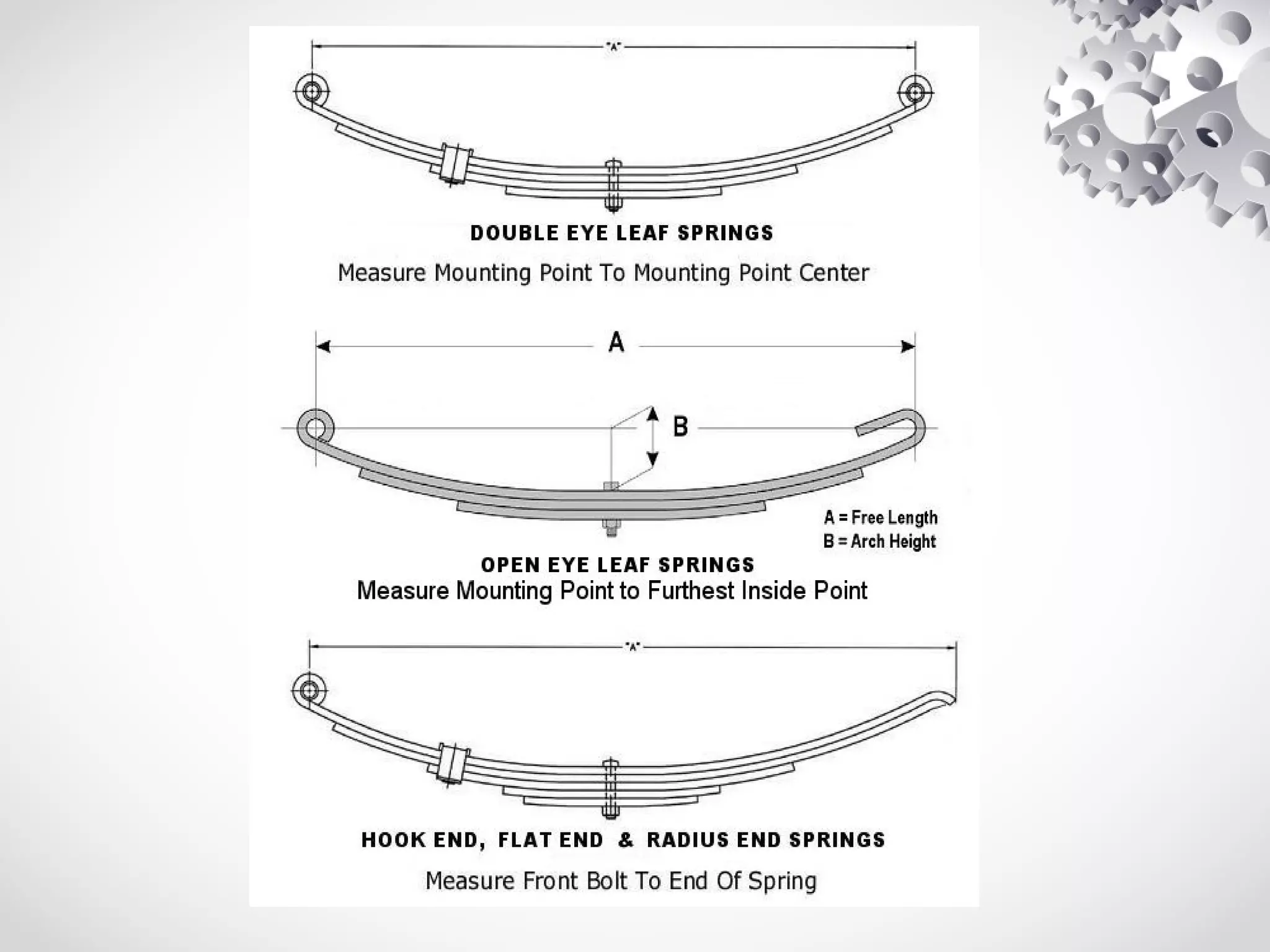
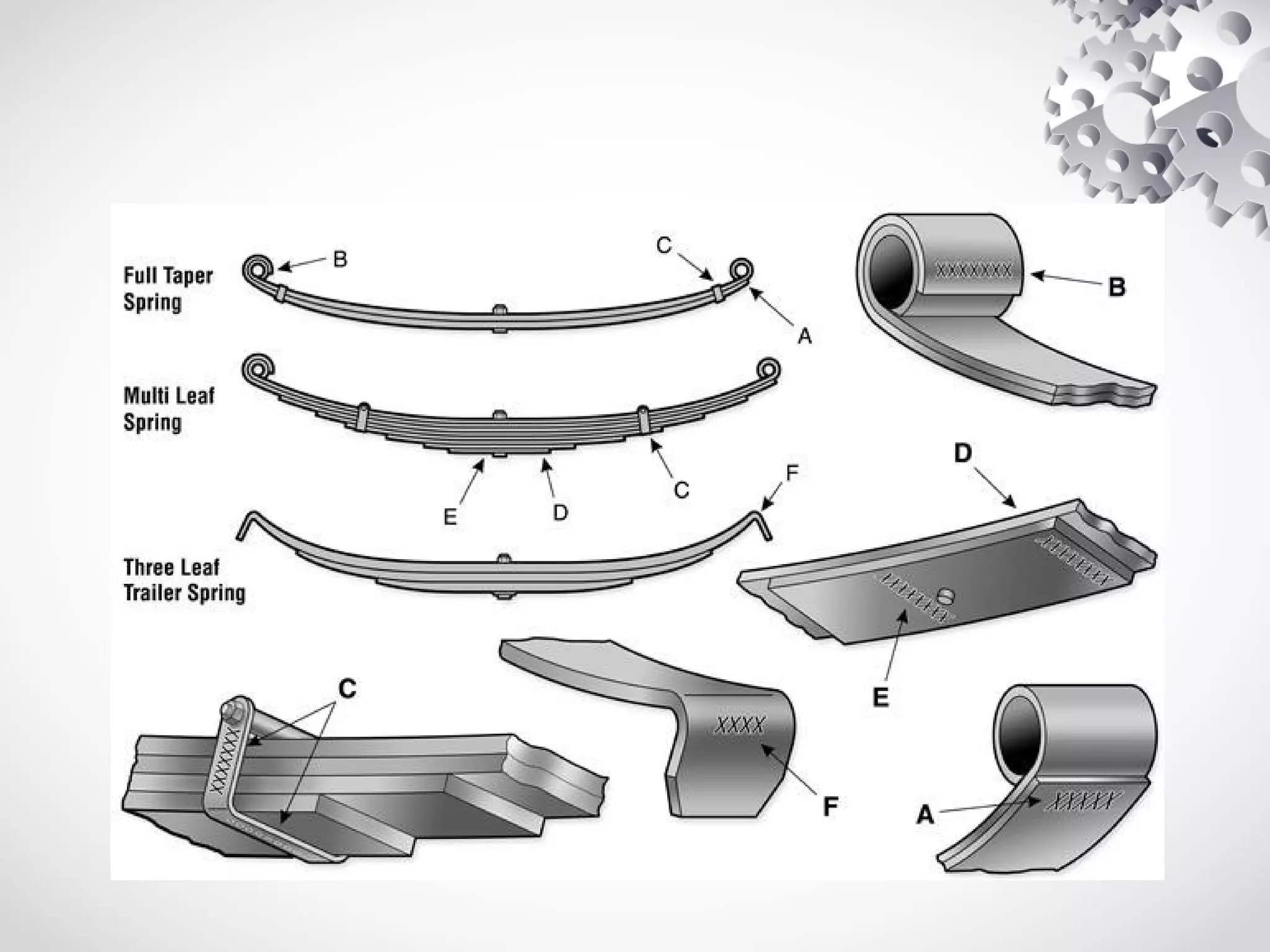
The leaf spring, invented by Obadiah Elliot in the 18th century, is a type of suspension spring commonly used in heavy-duty vehicles and has various configurations like elliptic and semi-elliptic. It consists of multiple steel plates, with the main leaf clamped to the axle, providing structural linkage and positioning for the axle, though it can affect riding comfort due to inter-leaf friction. The manufacturing process involves shearing, heating, forging, and surface preparation, using materials such as plain carbon steel with specific variations for automotive and railroad applications.