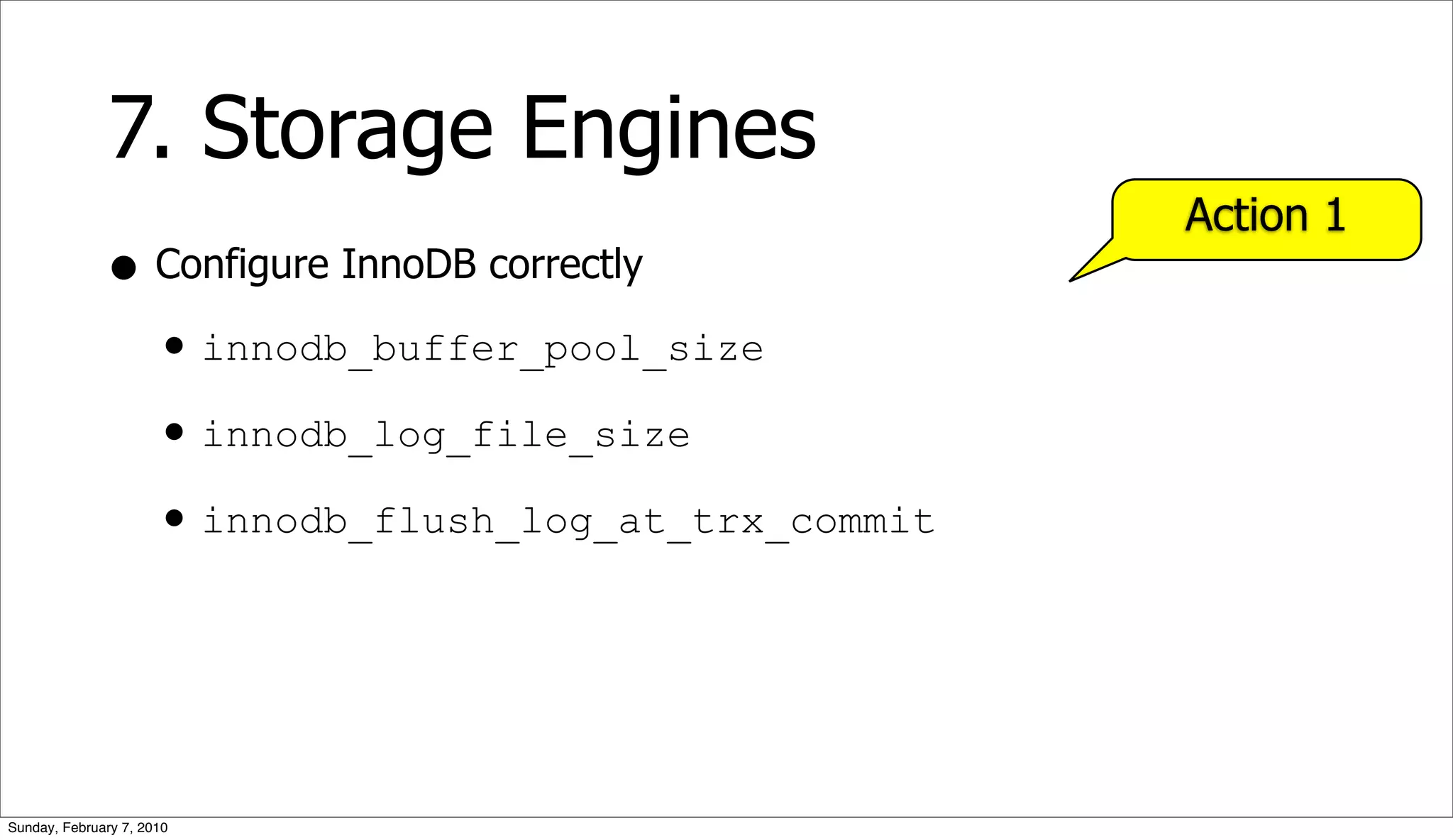
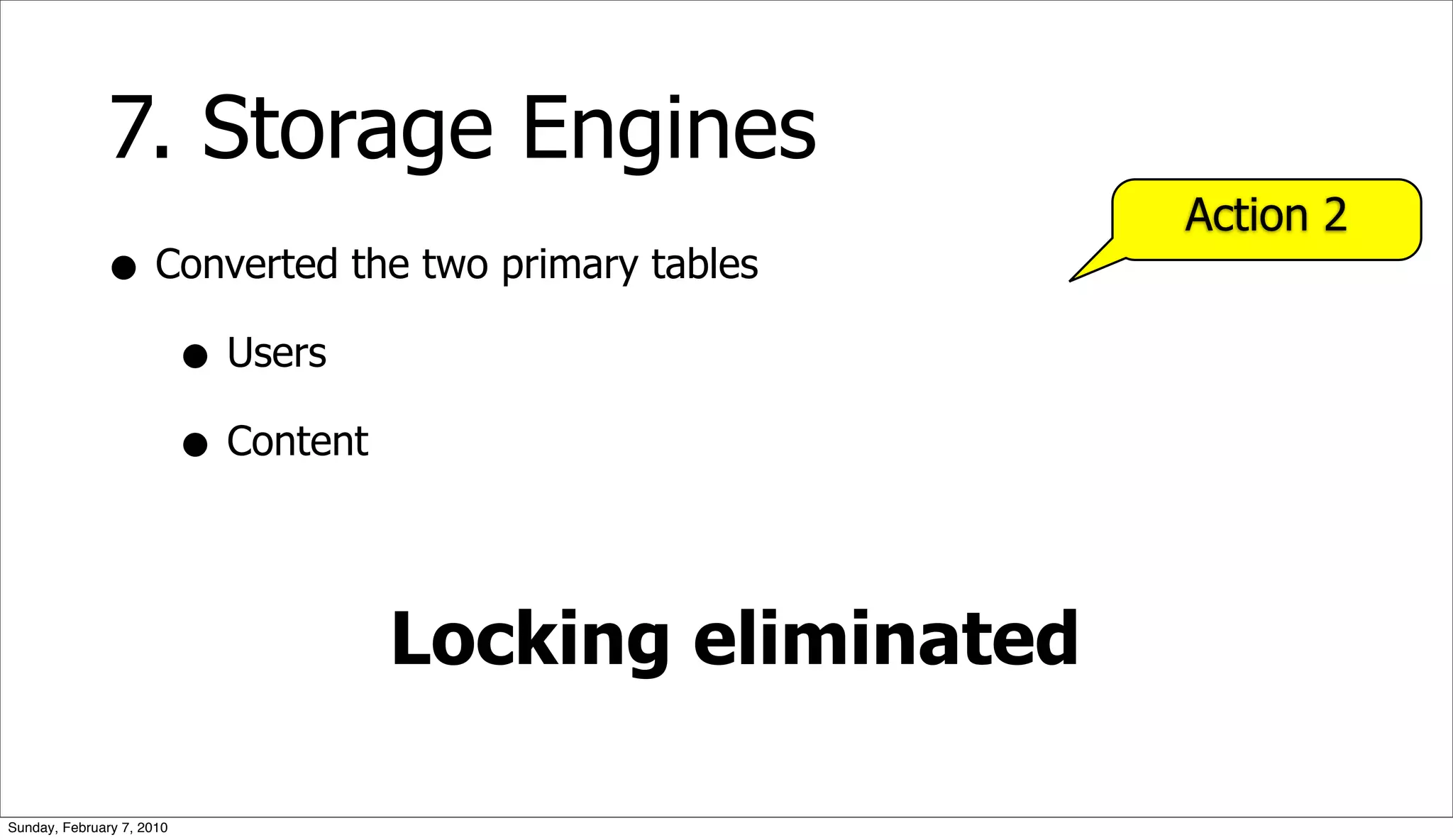
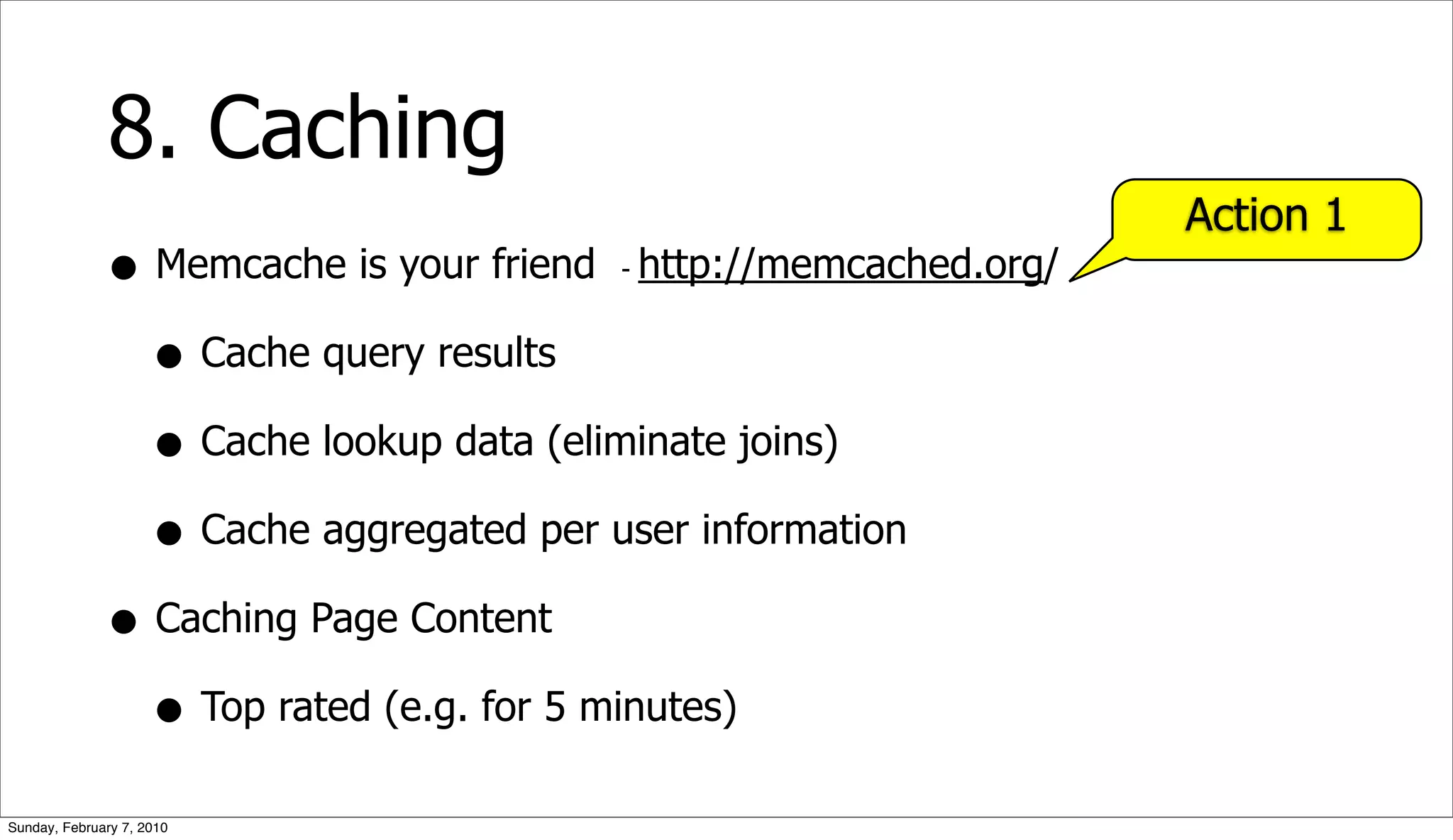
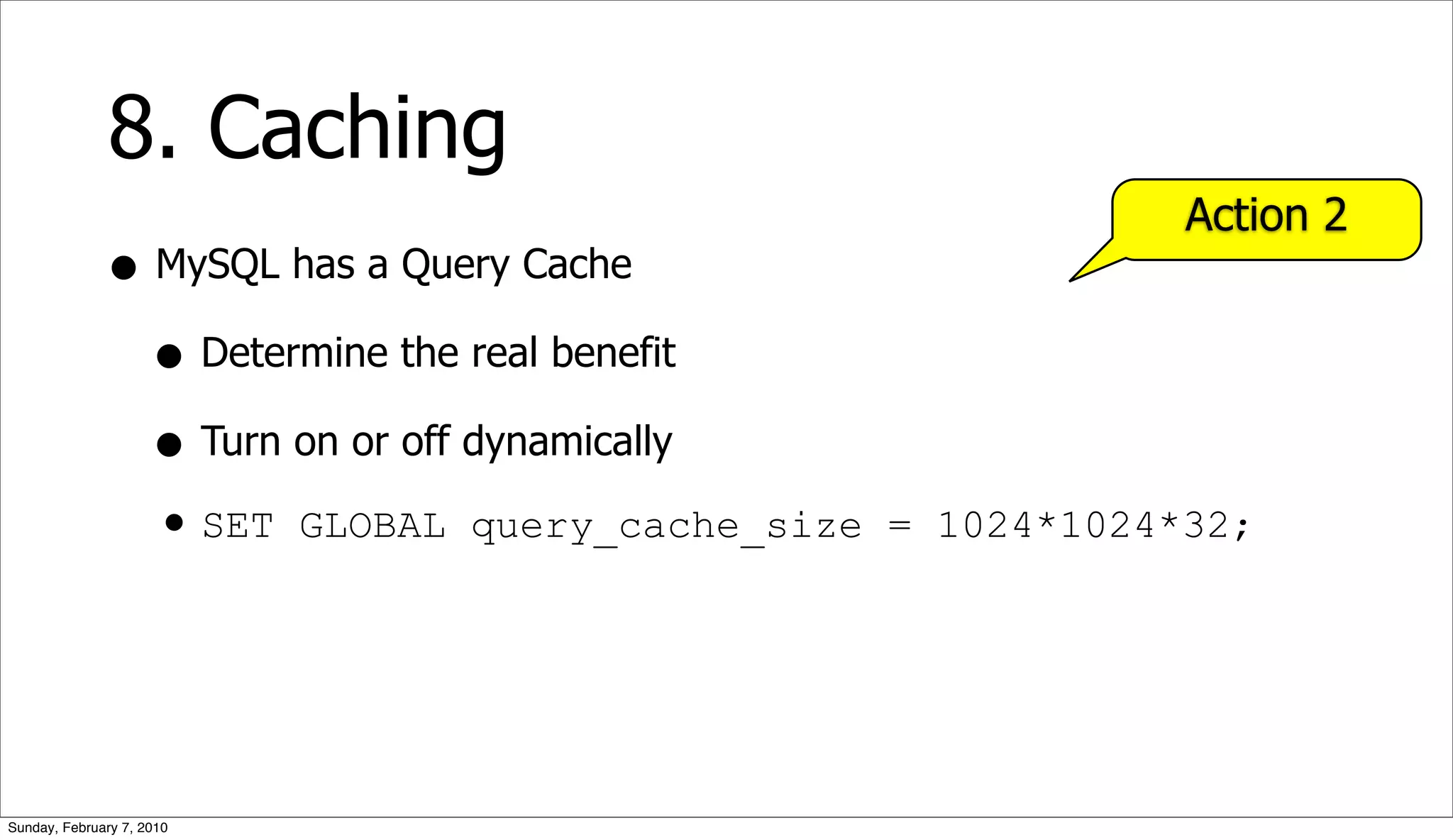
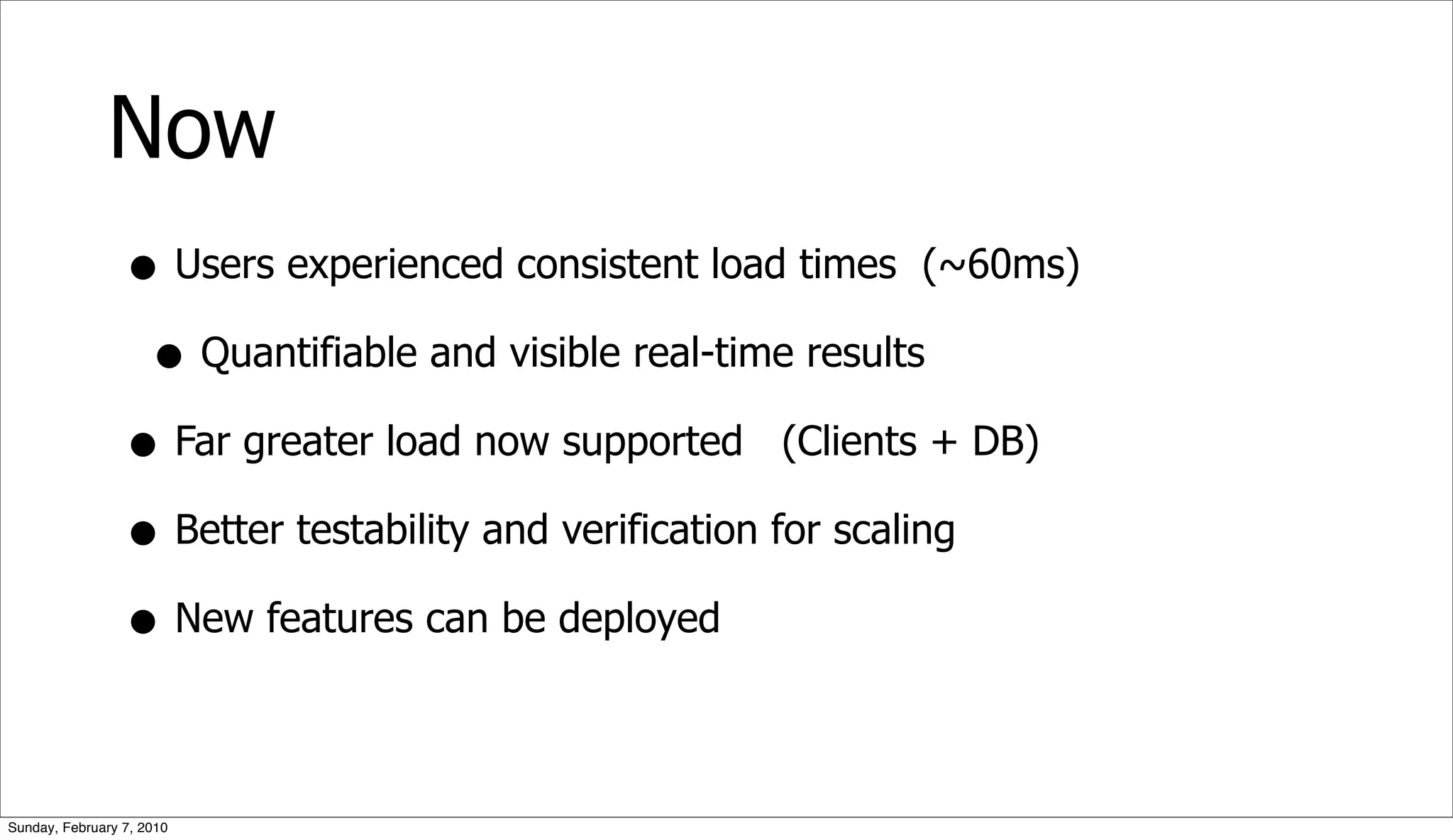
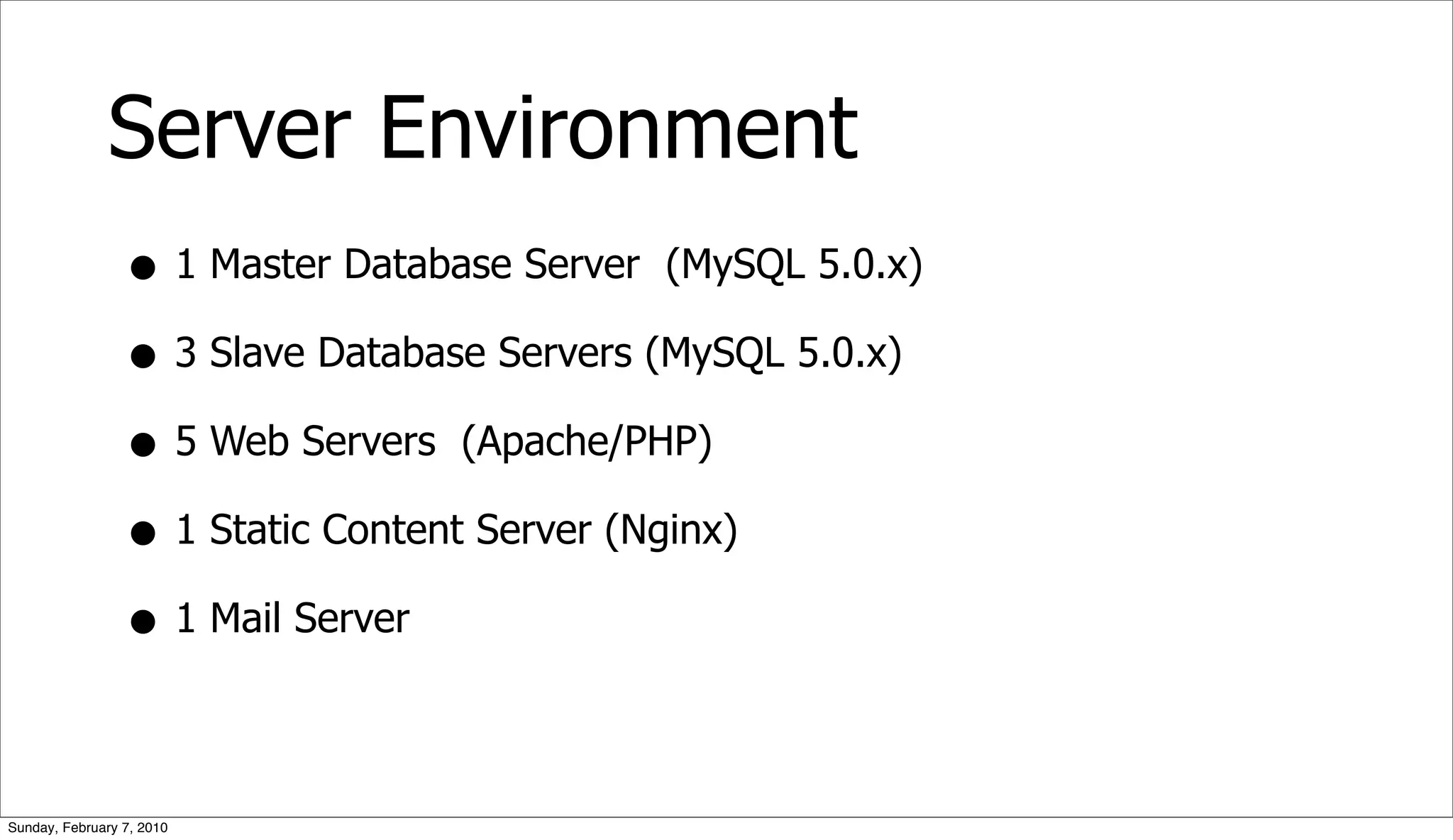
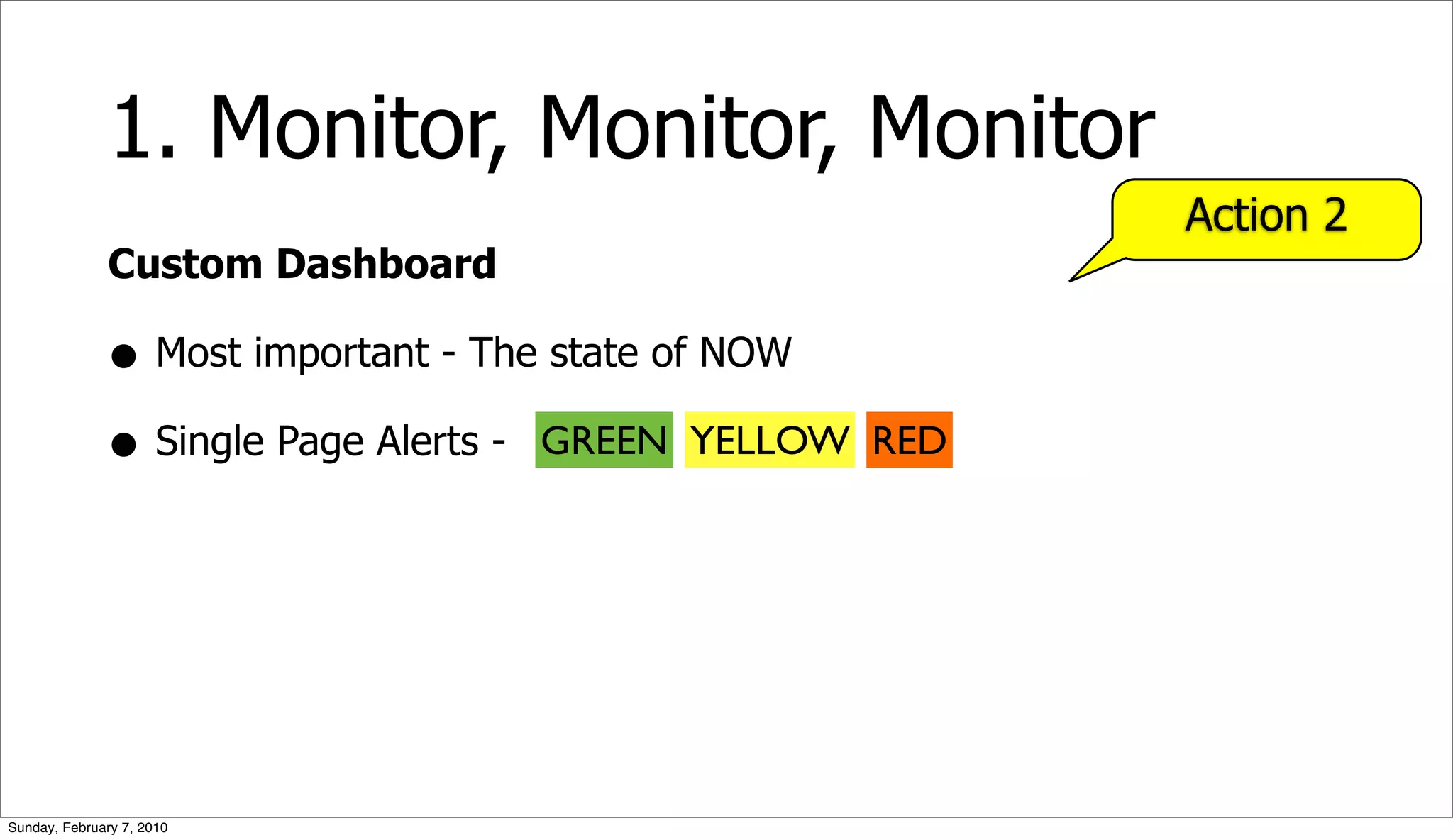
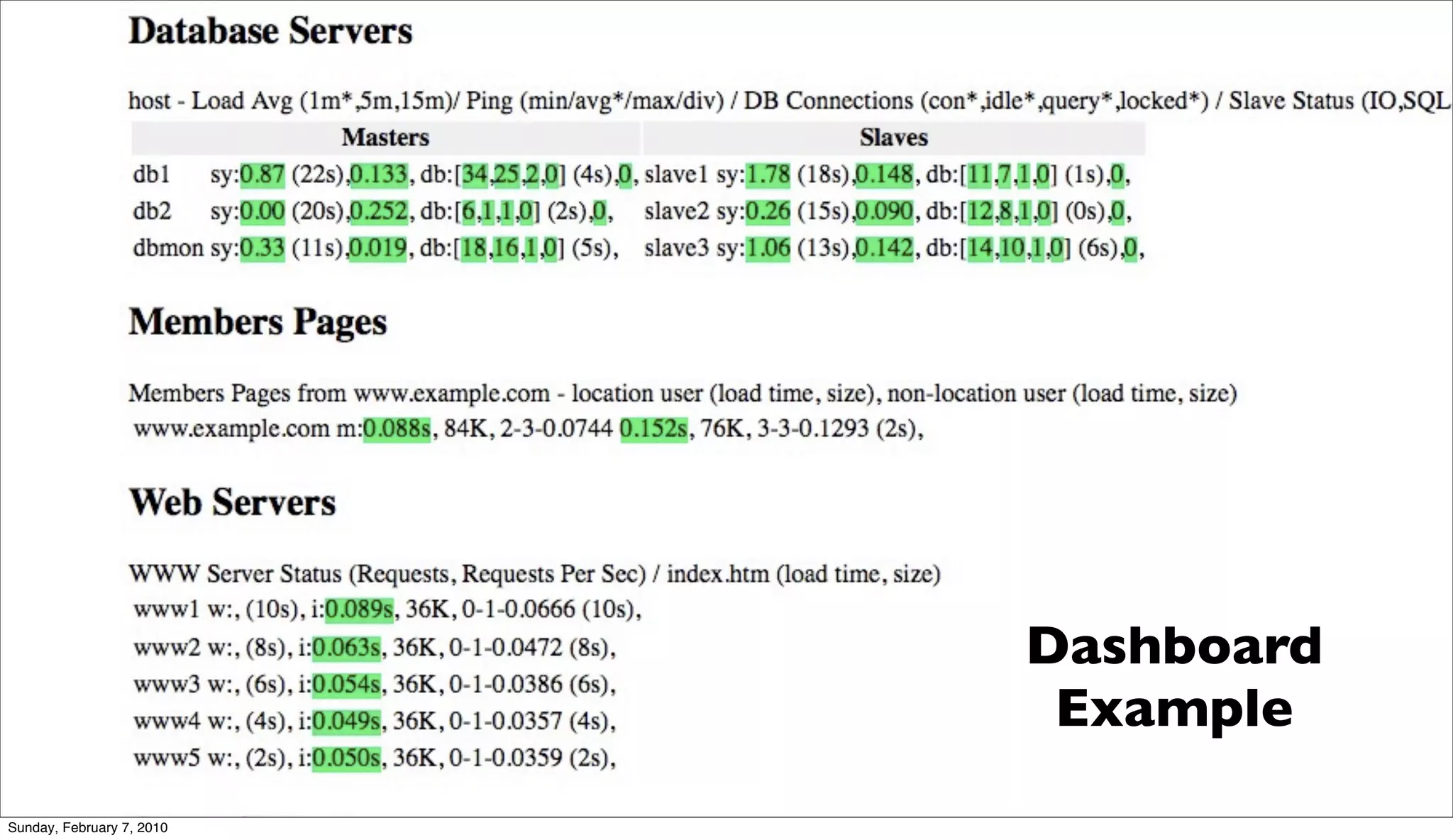
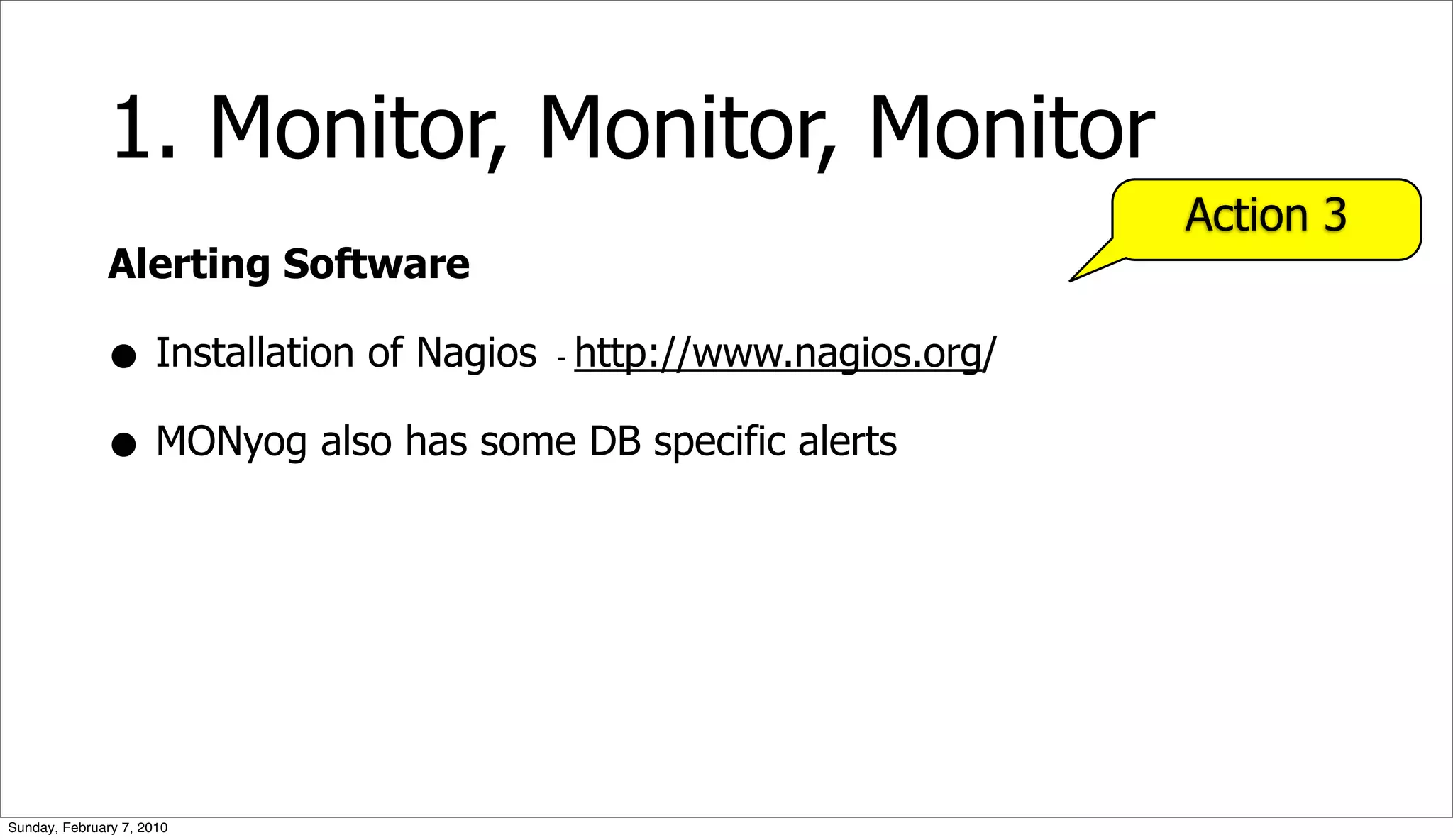
The document presents a case study on optimizing the performance of a web 2.0 social media site, which highlights a ten-step process to achieve 10x performance improvements. Key steps include monitoring application metrics, identifying and analyzing problematic SQL queries, and employing strategies such as indexing, caching, and sharding to enhance performance. The result of these optimizations led to significantly improved user experience with consistent load times and enhanced scalability.











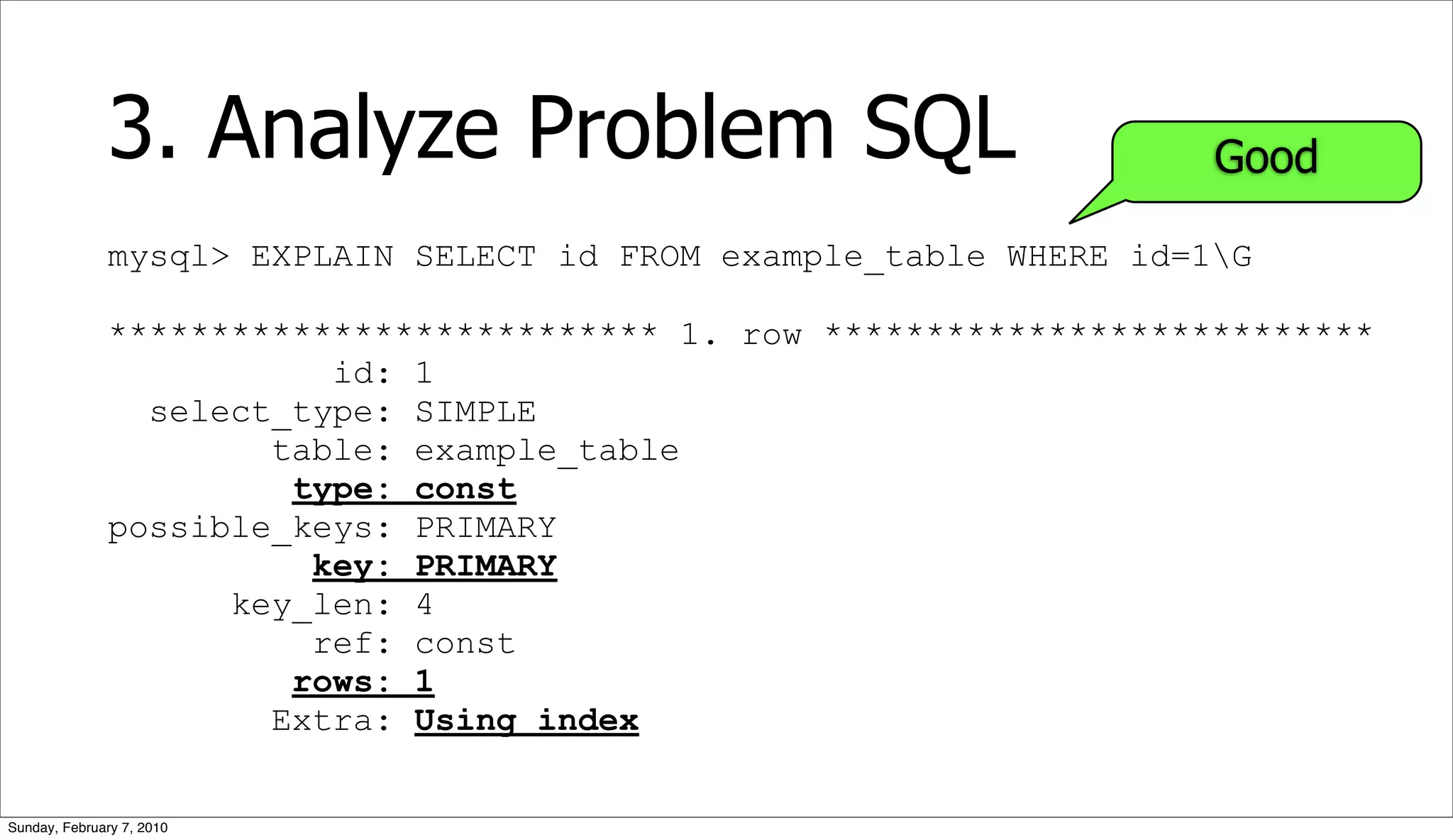
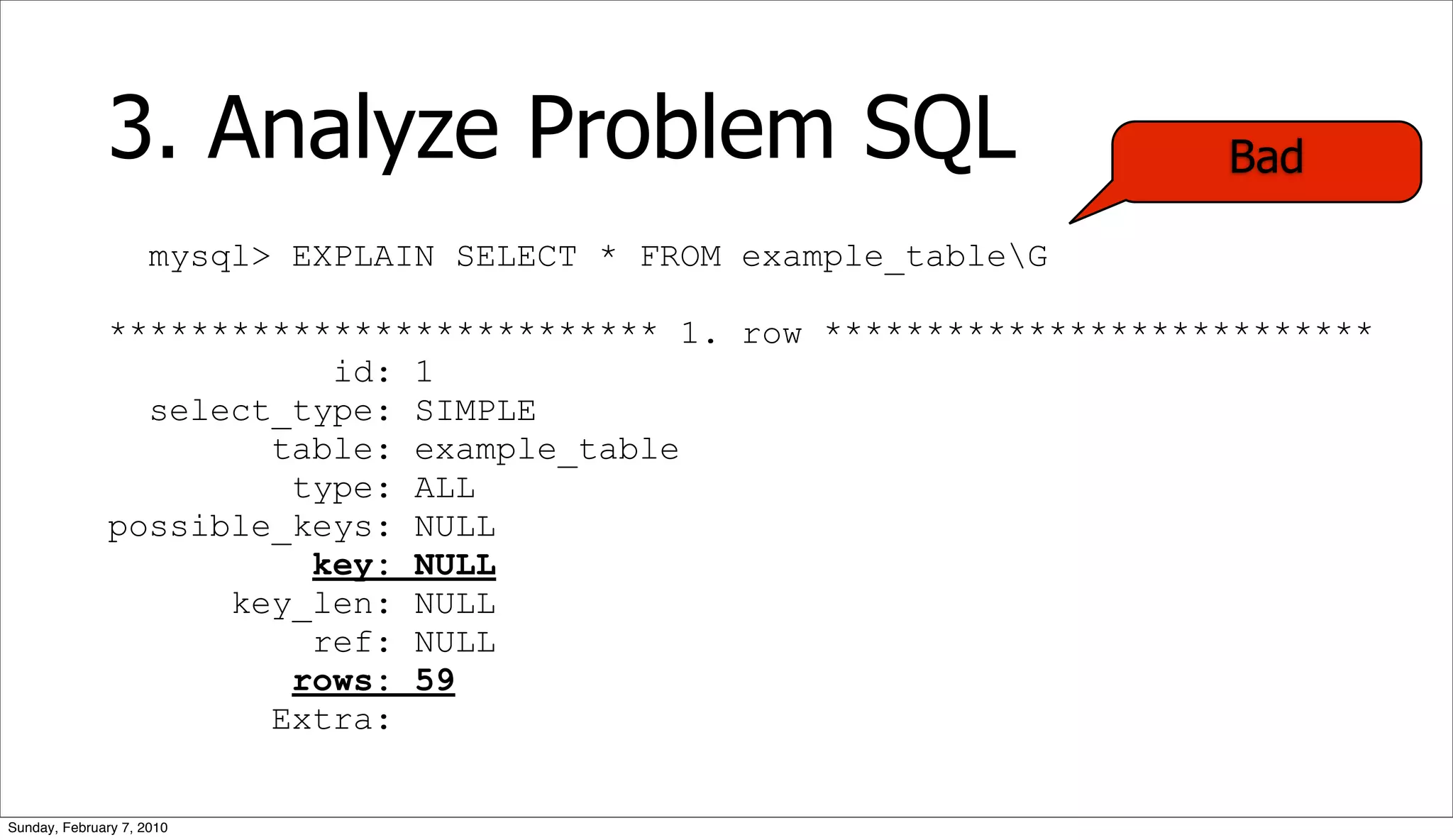
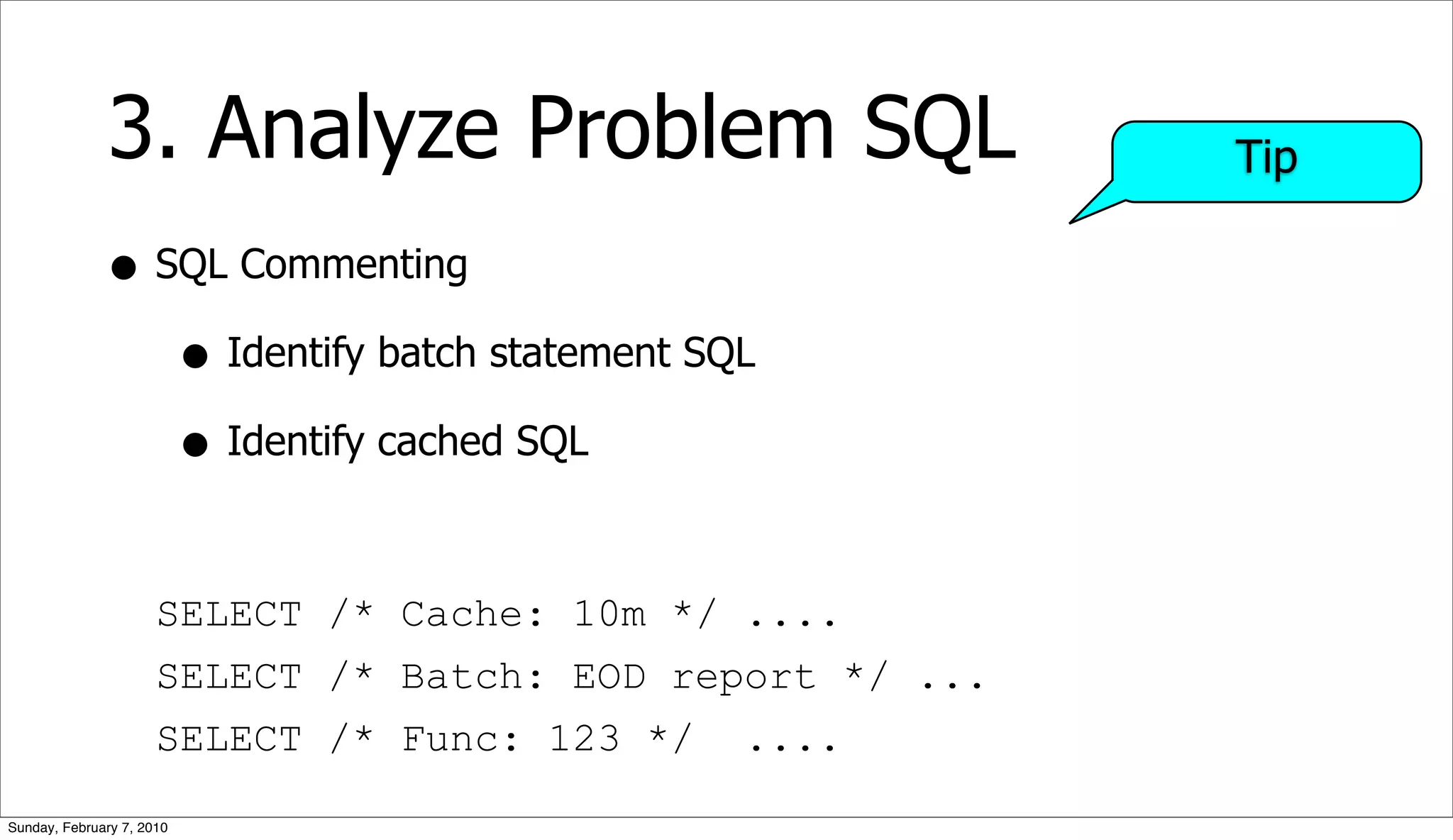
![3. Analyze Problem SQL
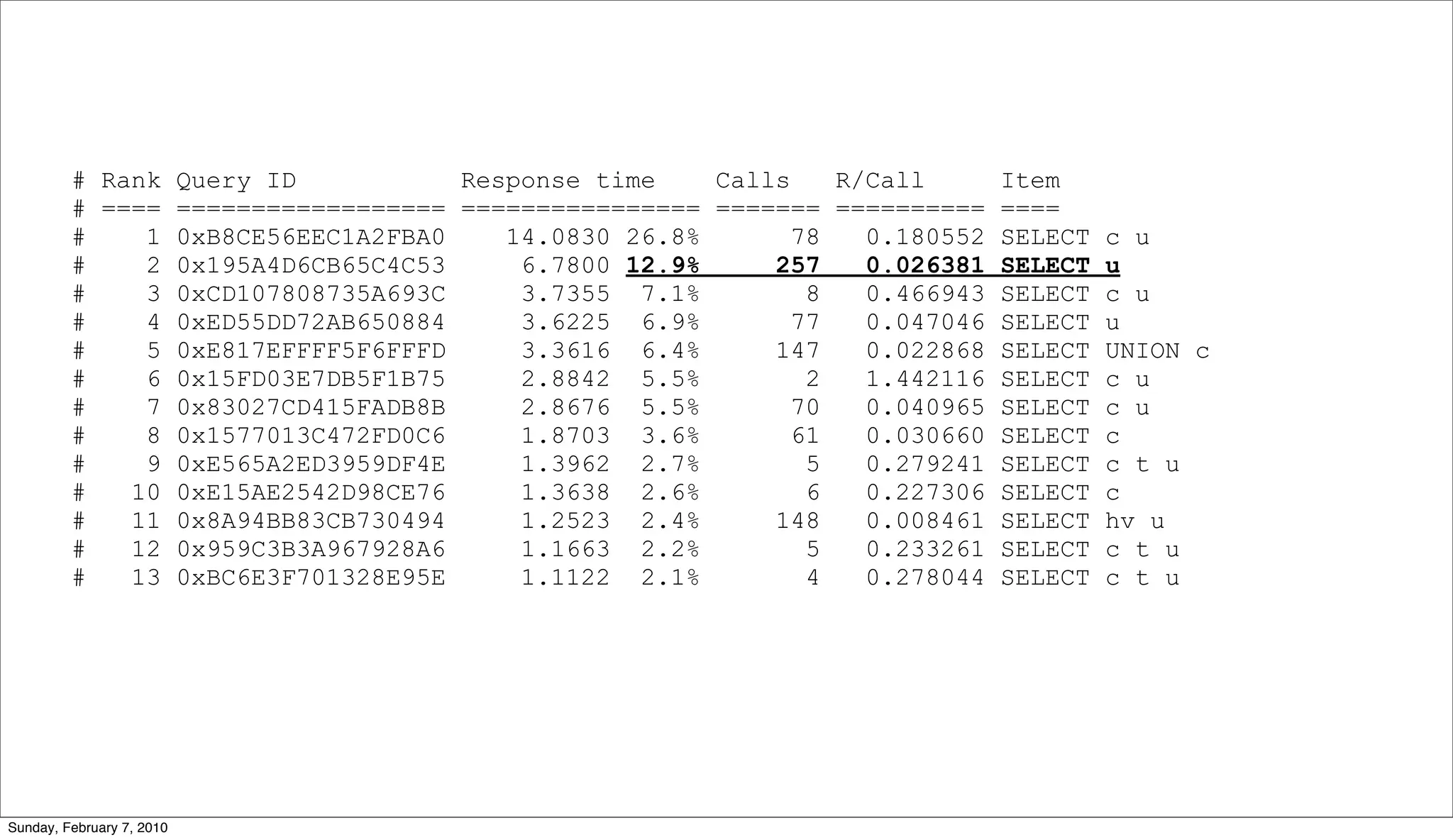
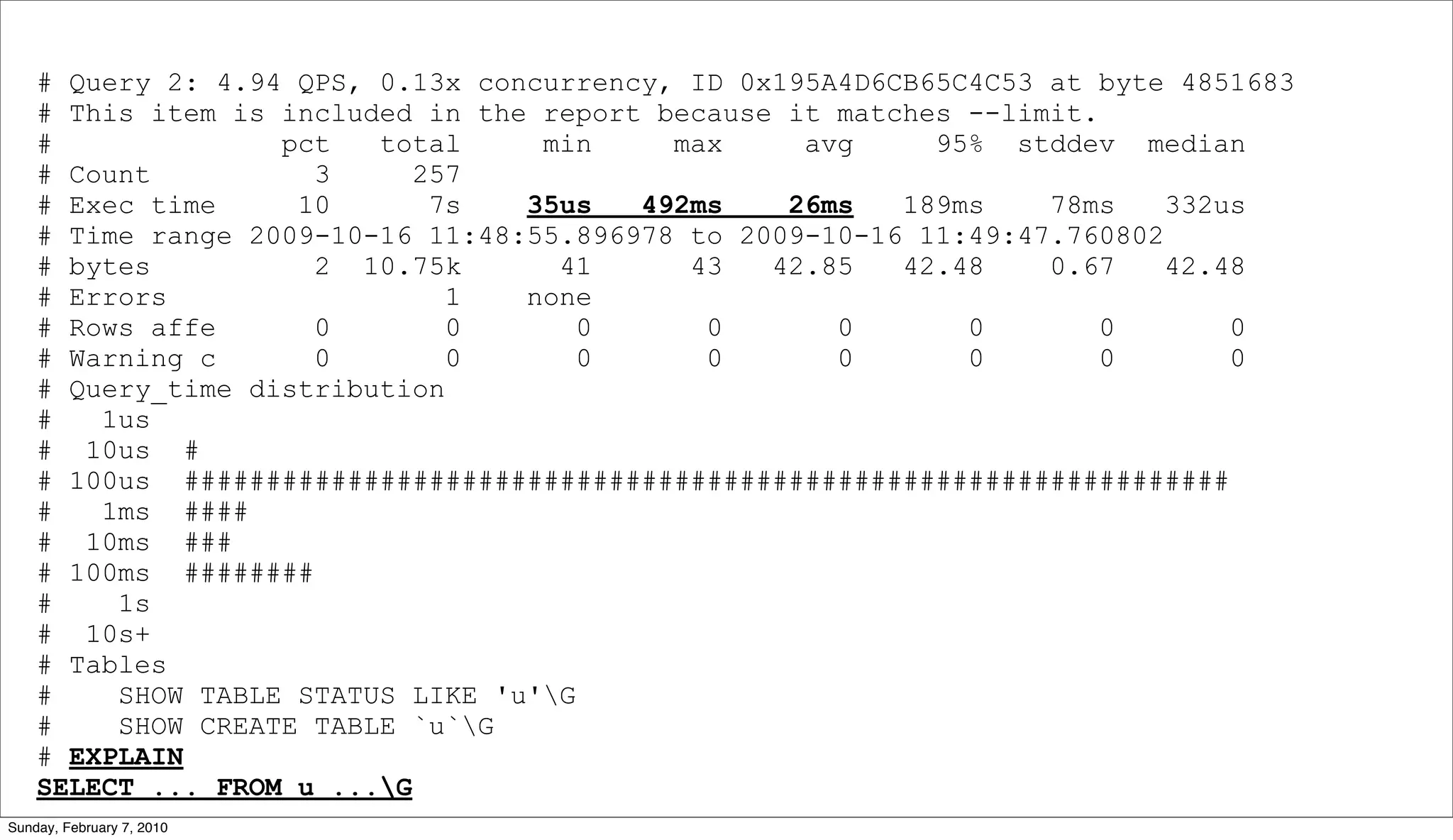
• Query Execution Plan (QEP)
• EXPLAIN [EXTENDED] SELECT ...
• Table/Index Structure
• SHOW CREATE TABLE <tablename>
• Table Statistics
• SHOW TABLE STATUS <tablename>
Sunday, February 7, 2010](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10x-improvement-100207072450-phpapp02/75/10x-Performance-Improvements-A-Case-Study-21-2048.jpg)