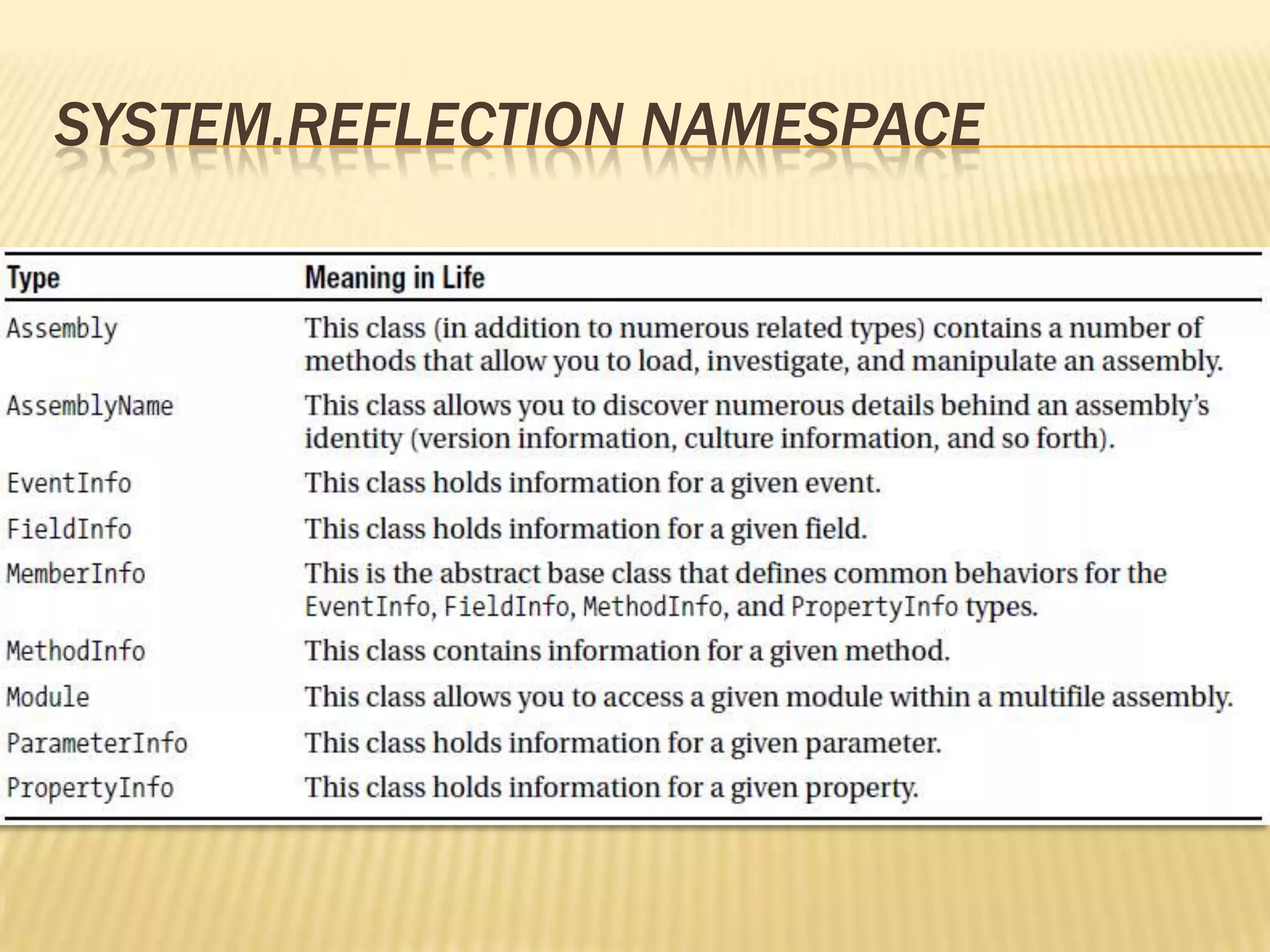
The document focuses on reflection in programming, which allows for runtime type discovery and manipulation of program elements. It details the System.Reflection namespace, including the System.Type class and its methods for examining type metadata, such as getting fields, methods, properties, and interfaces. It also discusses dynamic assembly loading and late binding techniques for increased extensibility in applications.









![REFLECTING ON METHODS
Type.GetMethods() returns an array of
System.Reflection.MethodInfo types.
// Display method names of type.
public static void ListMethods(Type t)
{
Console.WriteLine("Methods");
MethodInfo[] mi = t.GetMethods();
foreach(MethodInfo m in mi)
Console.WriteLine("->{0}", m.Name);
Console.WriteLine("");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reflectionpowerpointpresentationppt-120313231128-phpapp02/75/Reflection-power-pointpresentation-ppt-11-2048.jpg)
![REFLECTING ON FIELDS
Type.GetFields() returns an array of
System.Reflection.FieldInfo types.
// Display field names of type
public static void ListFields(Type t)
{
Console.WriteLine("Fields");
FieldInfo[] fi = t.GetFields();
foreach(FieldInfo field in fi)
Console.WriteLine("->{0}", field.Name);
Console.WriteLine("");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reflectionpowerpointpresentationppt-120313231128-phpapp02/75/Reflection-power-pointpresentation-ppt-12-2048.jpg)
![REFLECTING ON PROPERTIES
Type. GetProperties() returns an array of
System.Reflection. PropertyInfo types.
// Display property names of type.
public static void ListProps(Type t)
{
Console.WriteLine("***** Properties *****");
PropertyInfo[] pi = t.GetProperties();
foreach(PropertyInfo prop in pi)
Console.WriteLine("->{0}", prop.Name);
Console.WriteLine("");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reflectionpowerpointpresentationppt-120313231128-phpapp02/75/Reflection-power-pointpresentation-ppt-13-2048.jpg)
![REFLECTING ON IMPLEMENTED INTERFACES
ListInterfaces() prints out the names of any
interfaces supported on the incoming type.
The call to GetInterfaces() returns an array of
System.Types, as interfaces are indeed types.
public static void ListInterfaces(Type t)
{
Console.WriteLine("***** Interfaces *****");
Type[] ifaces = t.GetInterfaces();
foreach(Type i in ifaces)
Console.WriteLine("->{0}", i.Name);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reflectionpowerpointpresentationppt-120313231128-phpapp02/75/Reflection-power-pointpresentation-ppt-14-2048.jpg)


![using System;
using System.Reflection;
using System.IO;
namespace ExternalAssemblyReflector
{
class Program
{
static void DisplayTypesInAsm(Assembly asm)
{
Console.WriteLine("n Types in Assembly");
Console.WriteLine("->{0}", asm.FullName);
Type[] types = asm.GetTypes();
foreach (Type t in types)
Console.WriteLine("Type: {0}", t);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reflectionpowerpointpresentationppt-120313231128-phpapp02/75/Reflection-power-pointpresentation-ppt-17-2048.jpg)
![static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("External Assembly Viewer ");
Assembly asm = null;
Console.WriteLine("nEnter an assembly to evaluate");
asmName = Console.ReadLine();
try
{
asm = Assembly.LoadFrom(asmName);
DisplayTypesInAsm(asm);
}
catch
{
Console.WriteLine("Sorry, can't find assembly.");
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reflectionpowerpointpresentationppt-120313231128-phpapp02/75/Reflection-power-pointpresentation-ppt-18-2048.jpg)


