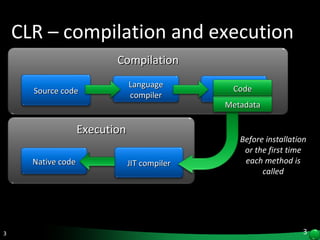
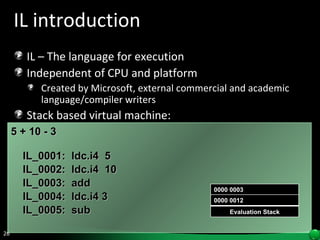
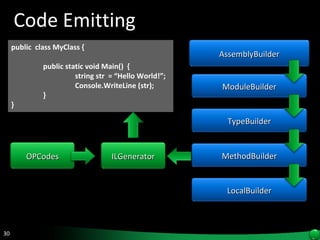
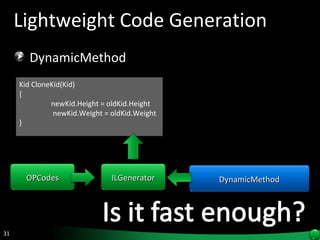
The document discusses reflection in .NET, which allows examining and modifying programs at runtime. Reflection provides objects that encapsulate metadata about types and members. It allows dynamically creating instances, invoking methods, and accessing fields and properties. The System.Reflection and System.Reflection.Emit namespaces contain classes for reading and modifying metadata.