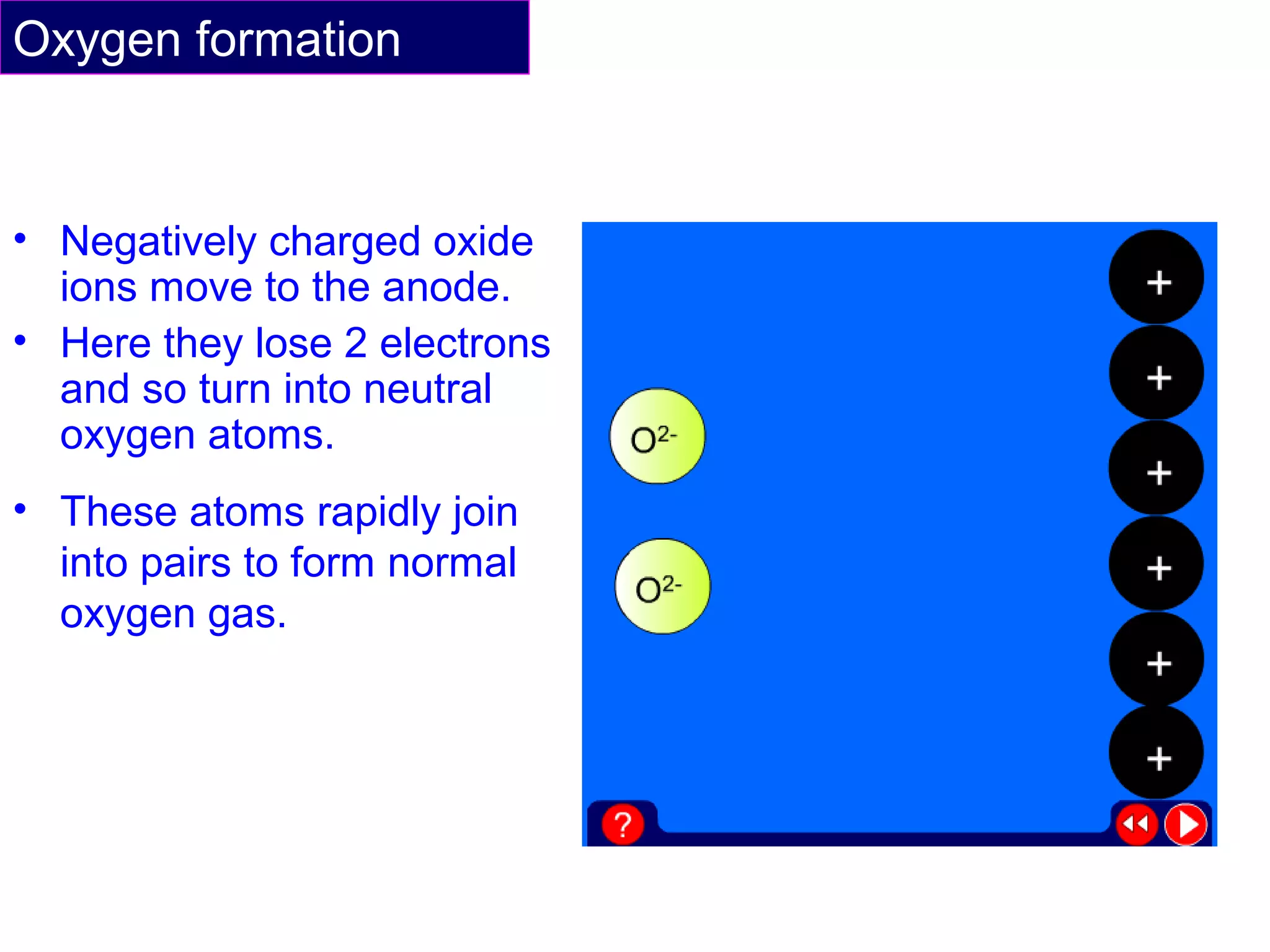
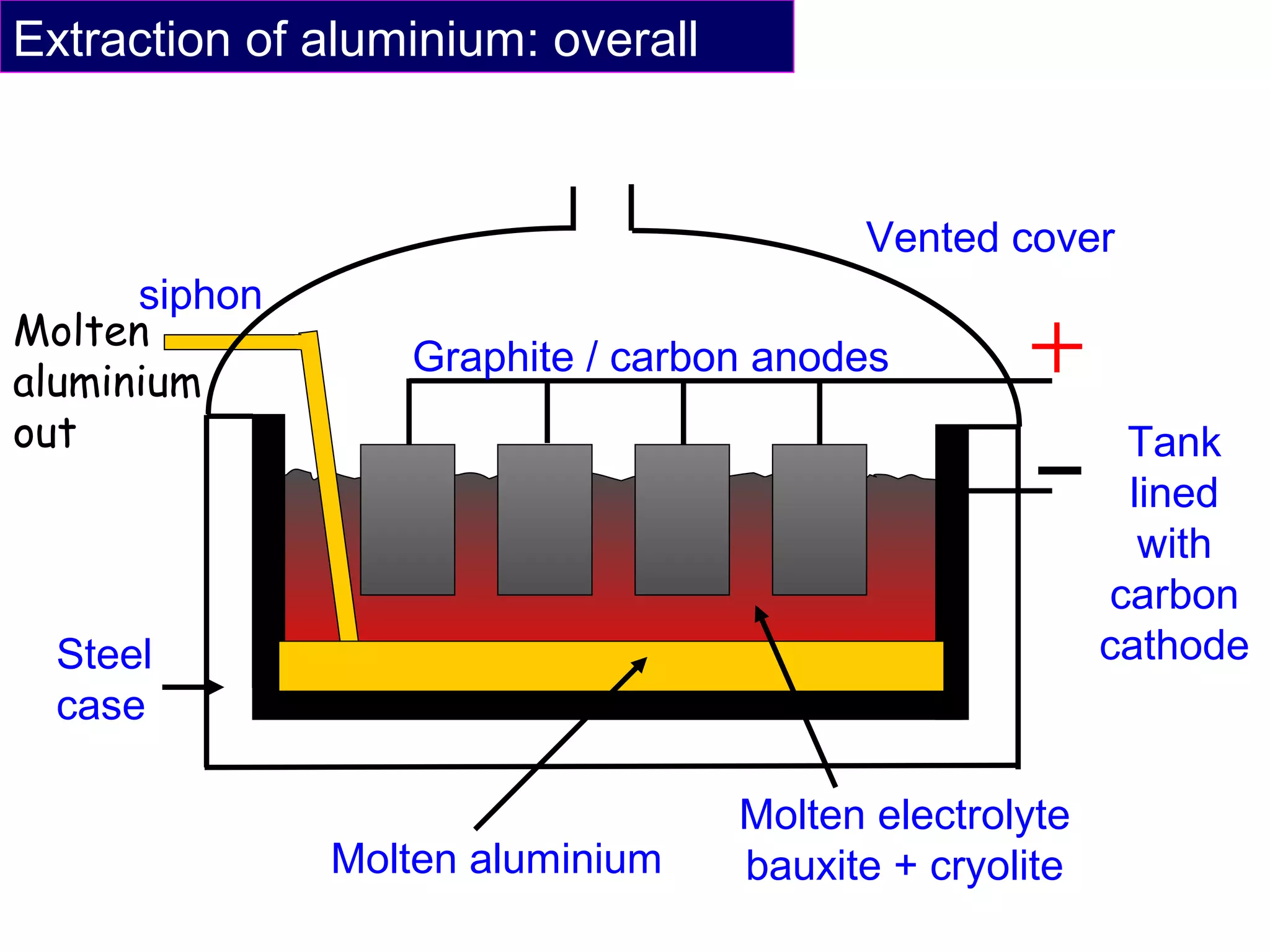
The document summarizes the process of extracting aluminium from bauxite ore. Bauxite ore is dissolved in cryolite to lower its melting point before being electrolyzed in a molten electrolyte. During electrolysis, positively charged aluminium ions move to the negatively charged carbon cathode, gaining electrons and forming aluminium atoms. Negatively charged oxide ions move to the positively charged carbon anode, losing electrons and forming oxygen gas. Some oxygen reacts with the carbon anode to form carbon dioxide, requiring frequent anode replacement. The overall process uses electrolysis to extract aluminium from bauxite ore dissolved in cryolite.