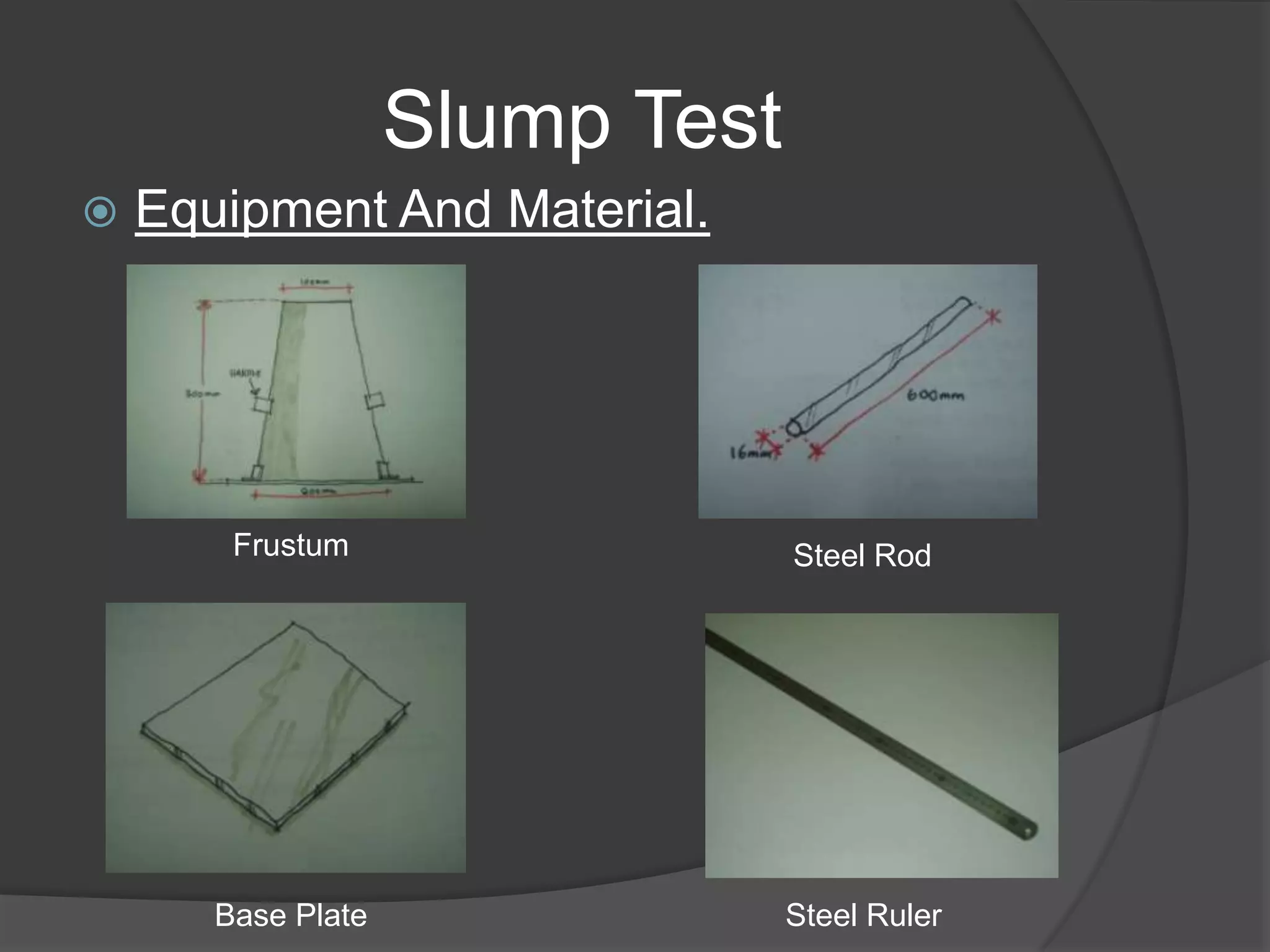
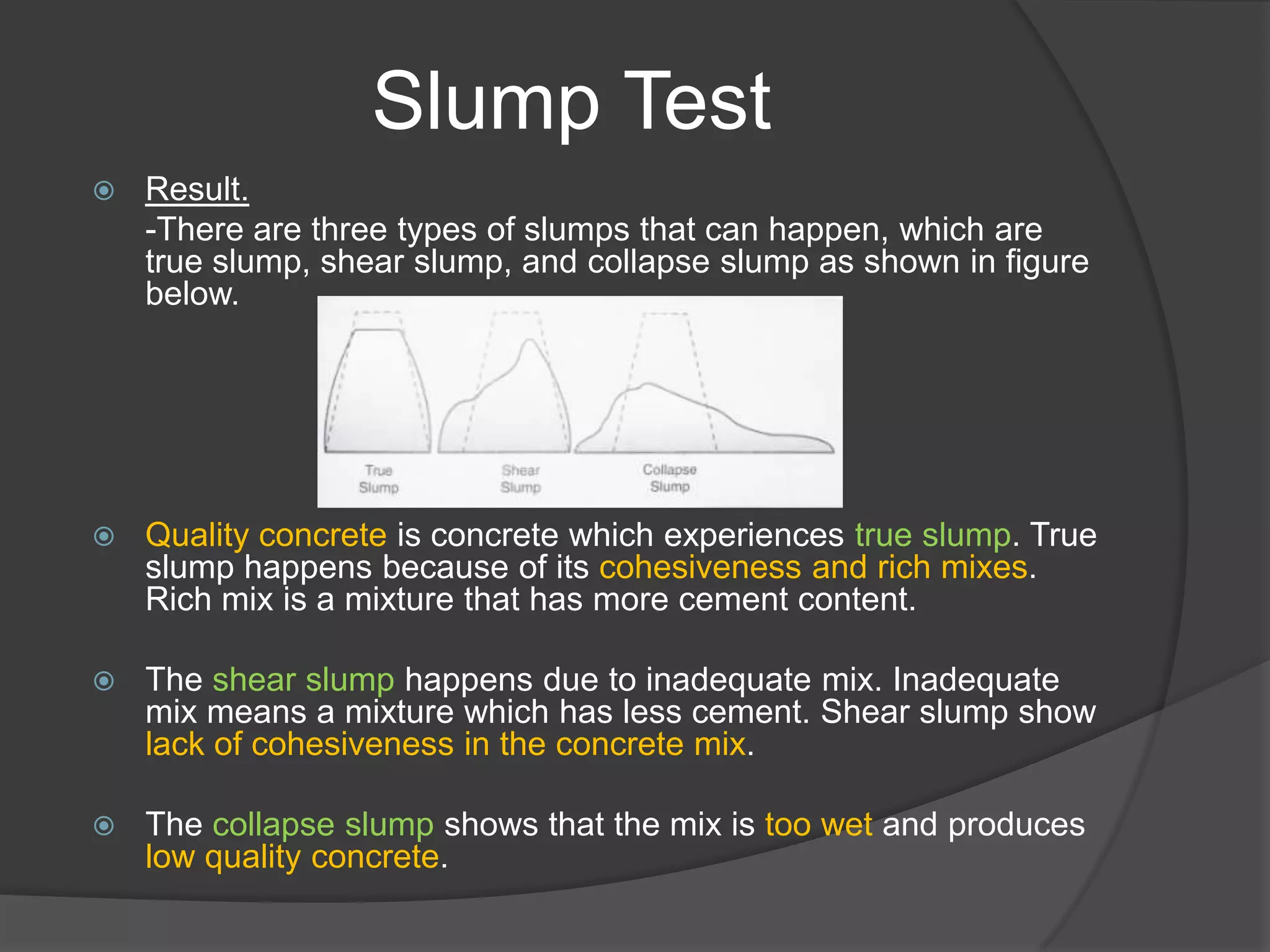
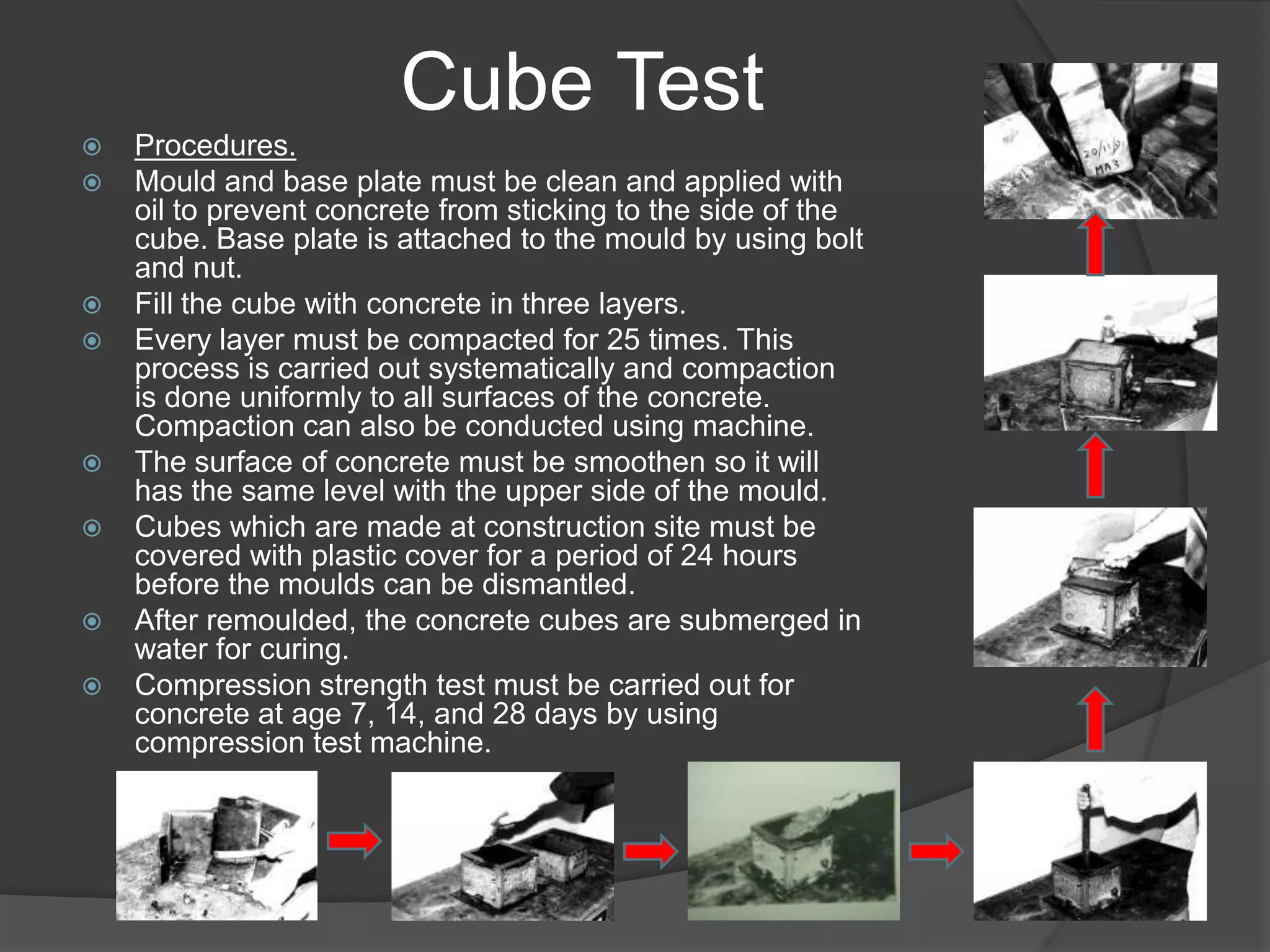
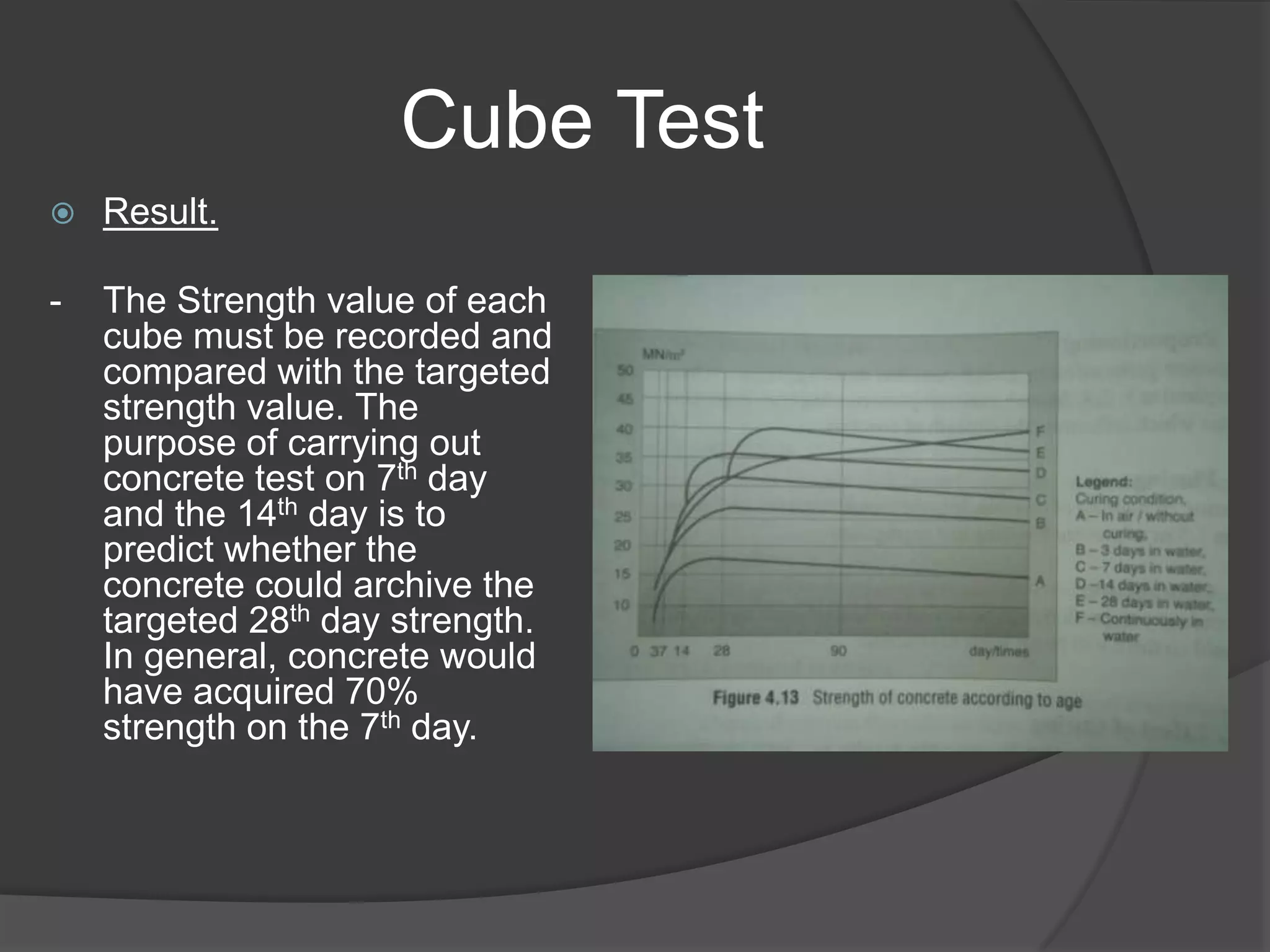
This document discusses the process of preparing and testing wet concrete. It describes concrete as a mixture of cement, sand, coarse aggregates, and water. It explains that the ratios of these materials and the water-cement ratio determine the concrete's properties. The document then covers conducting slump and cube tests to measure workability and compressive strength. It provides details on procedures, equipment, and interpreting results for each test. The goal is to produce quality concrete that meets the targeted strength values.