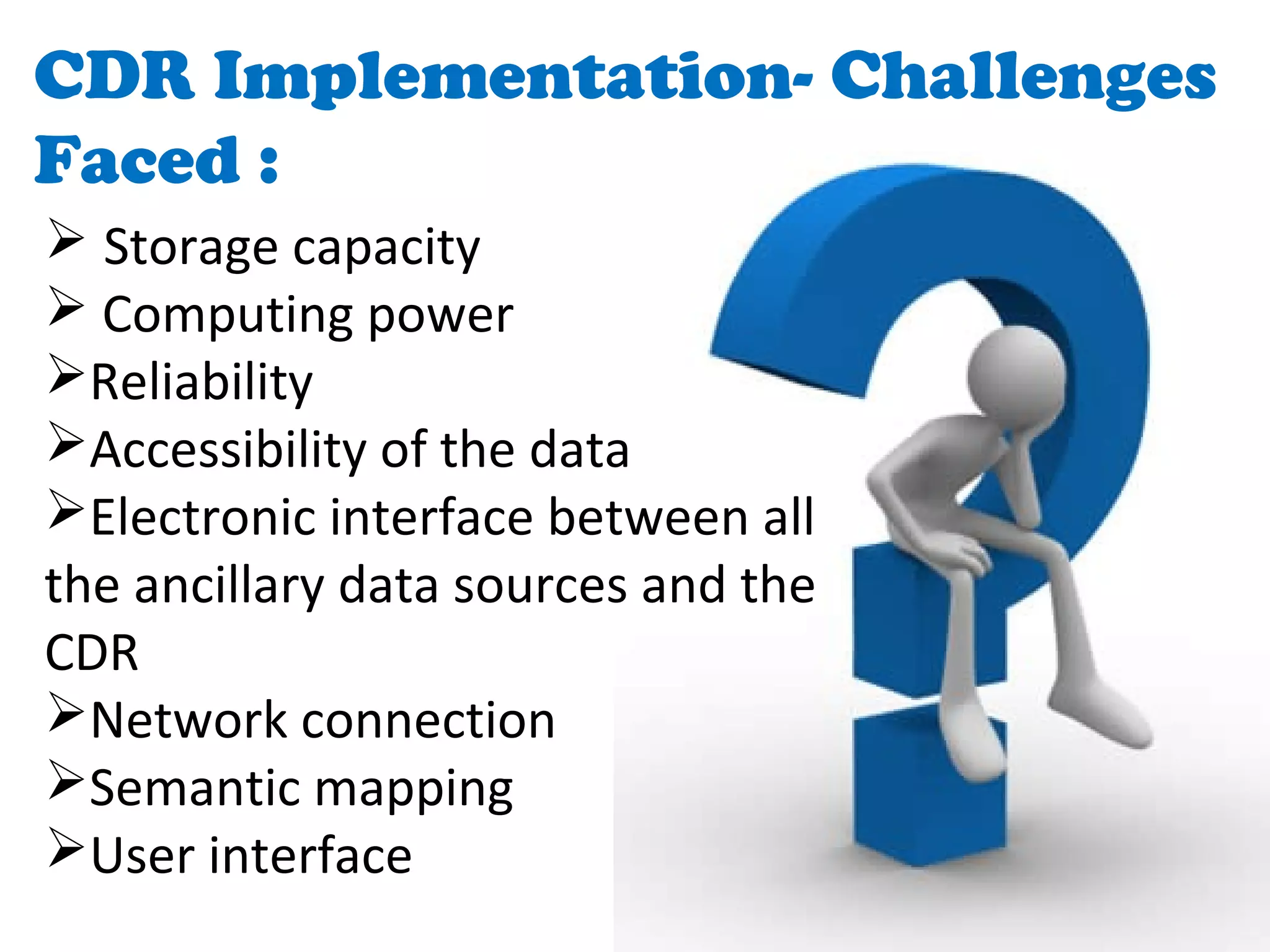
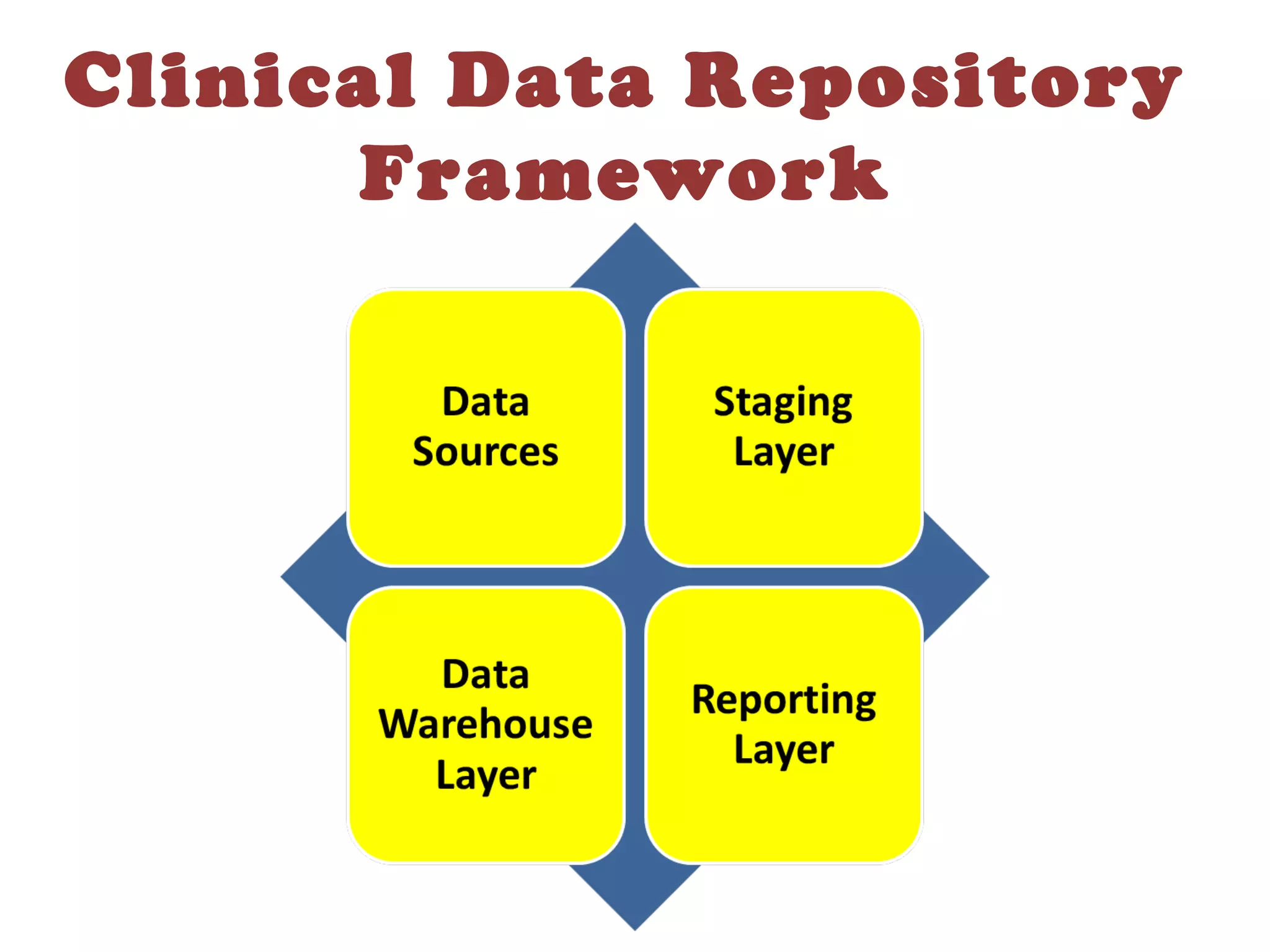
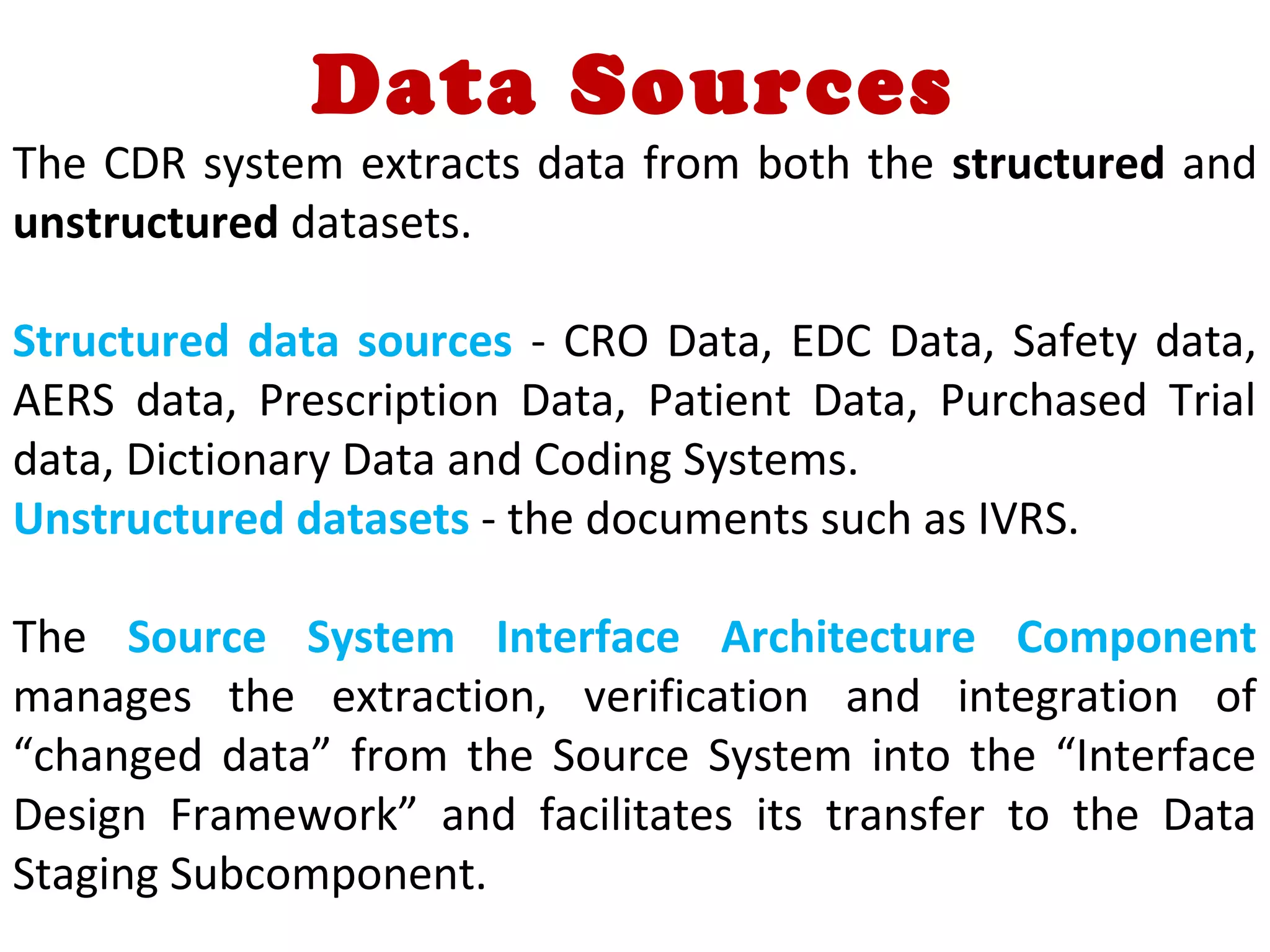
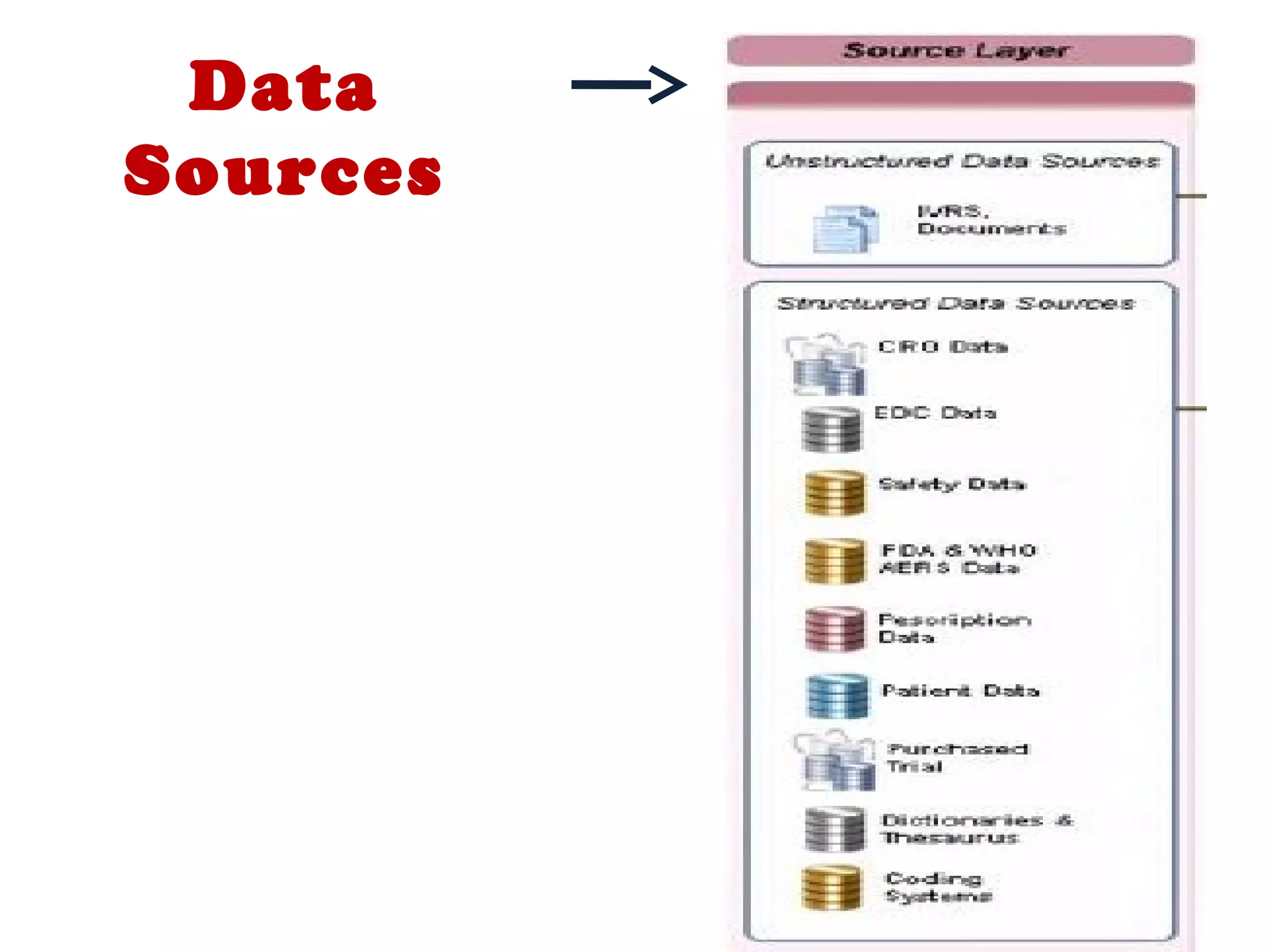
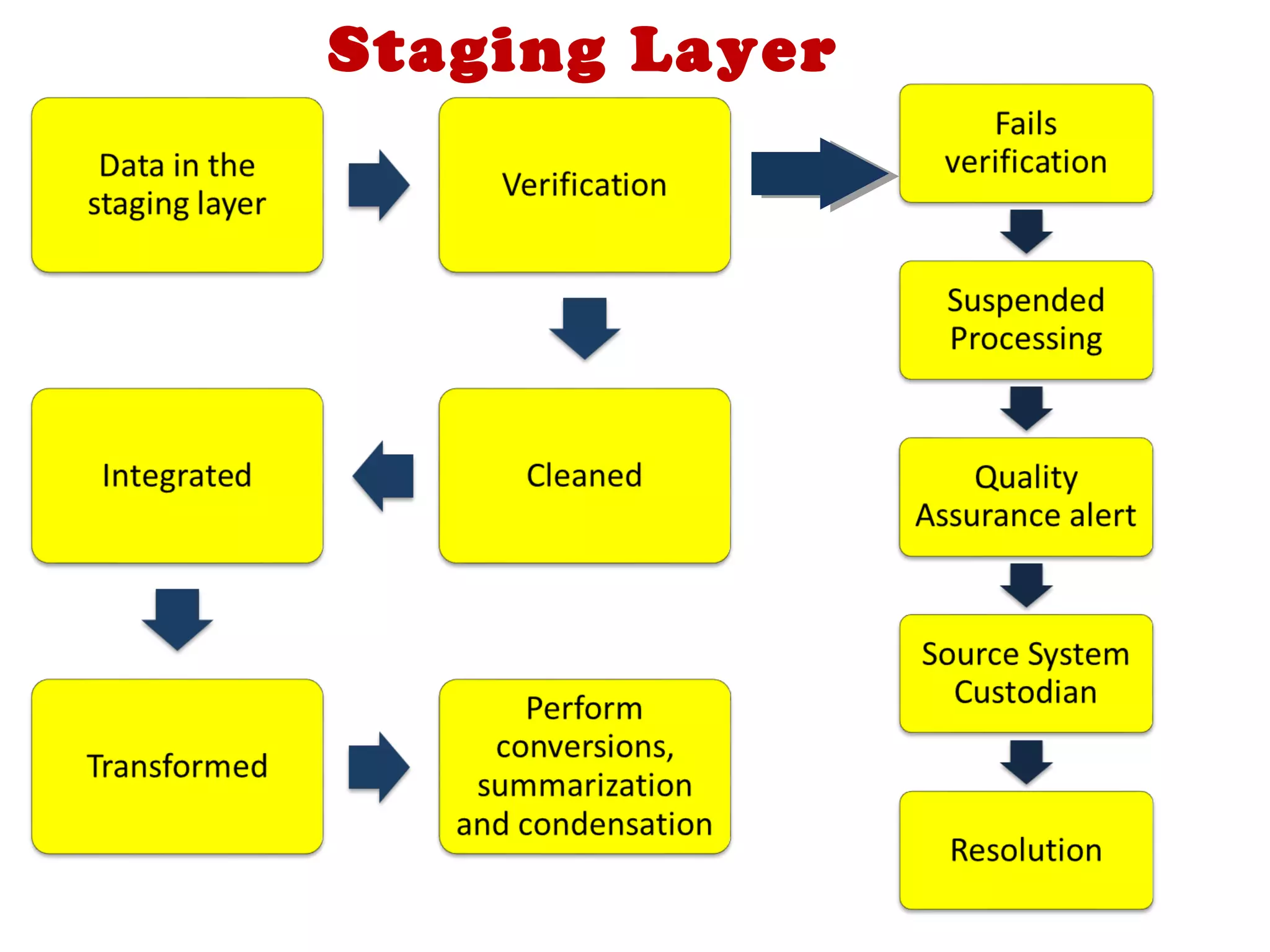
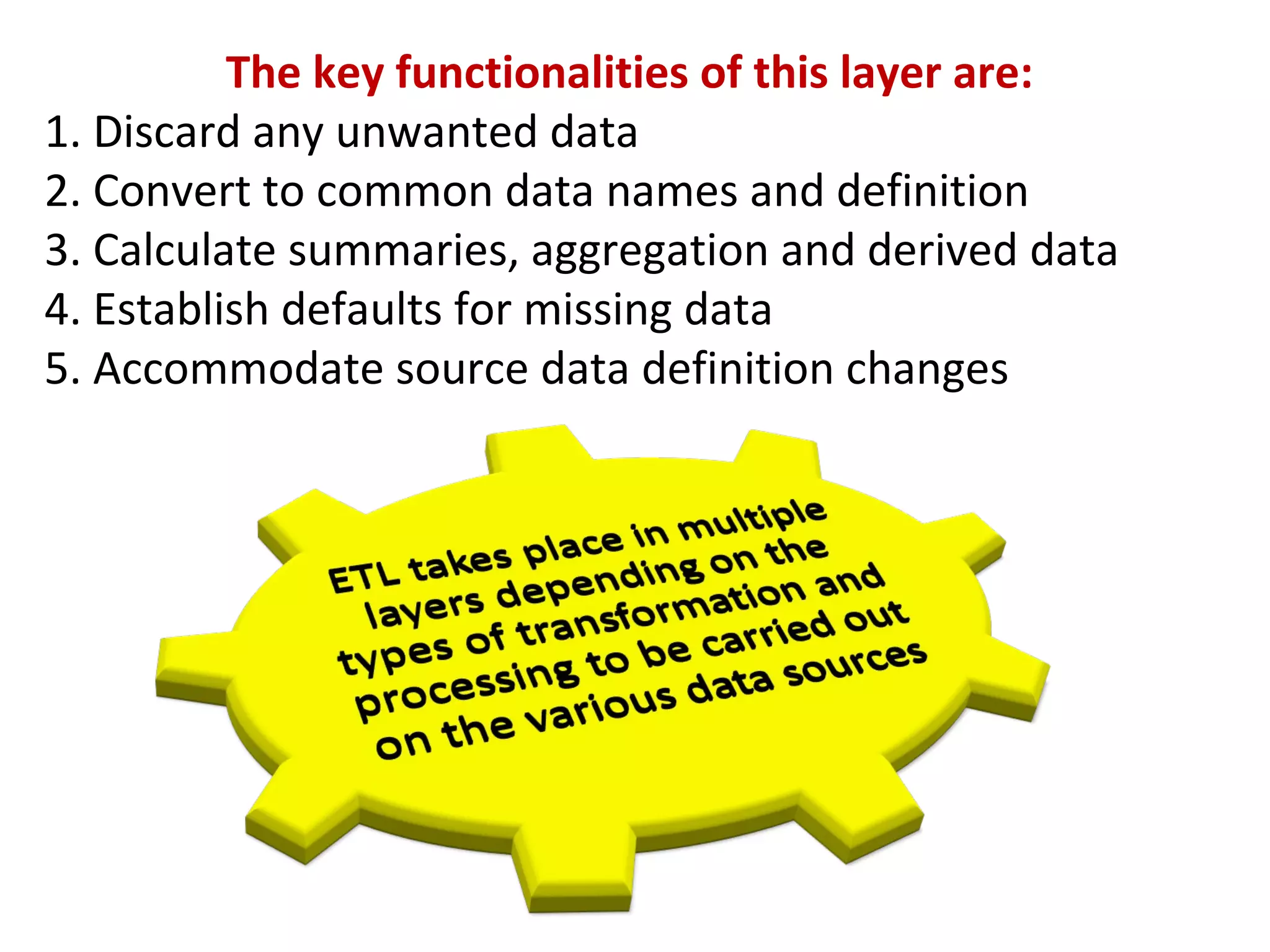
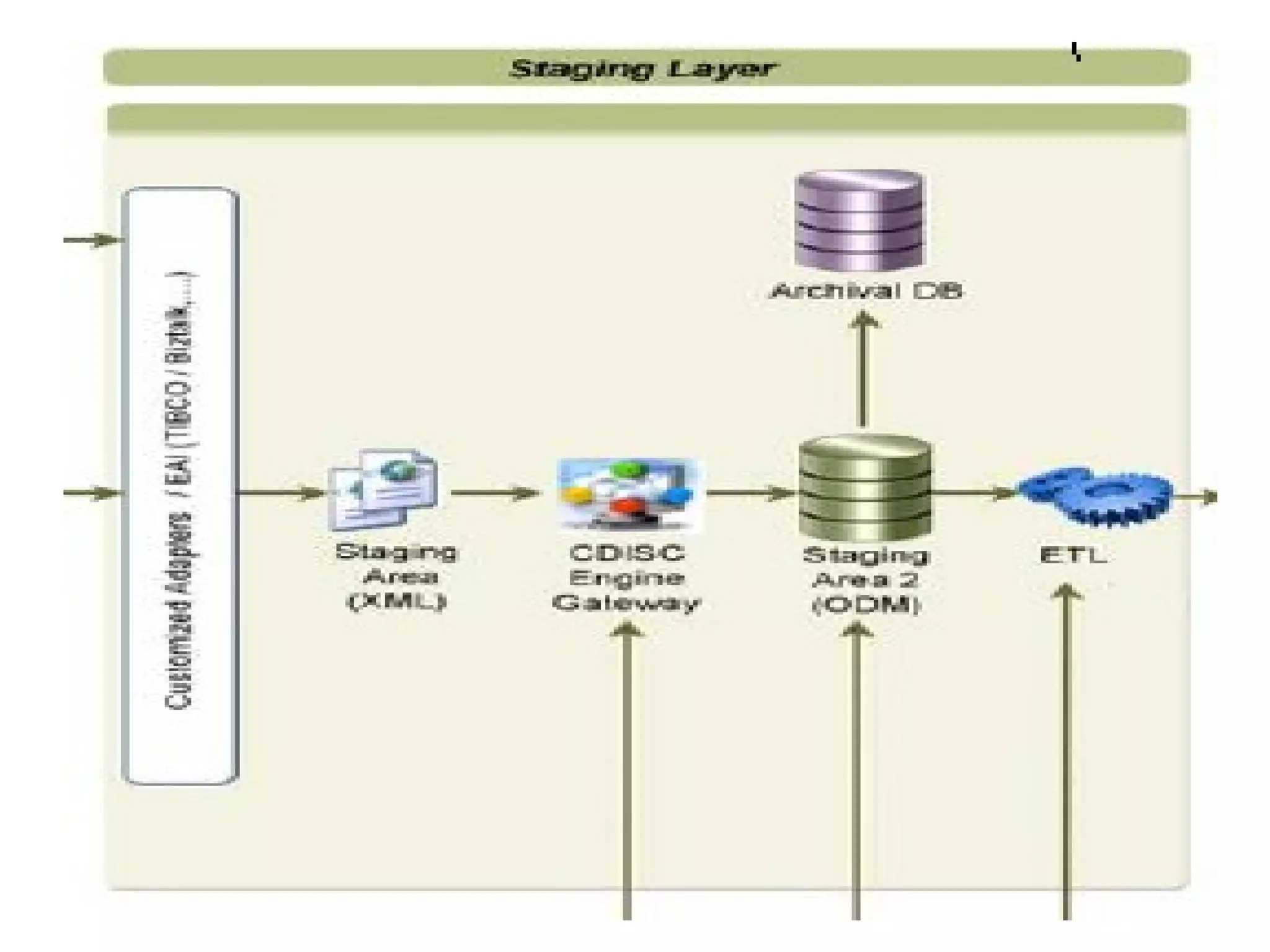
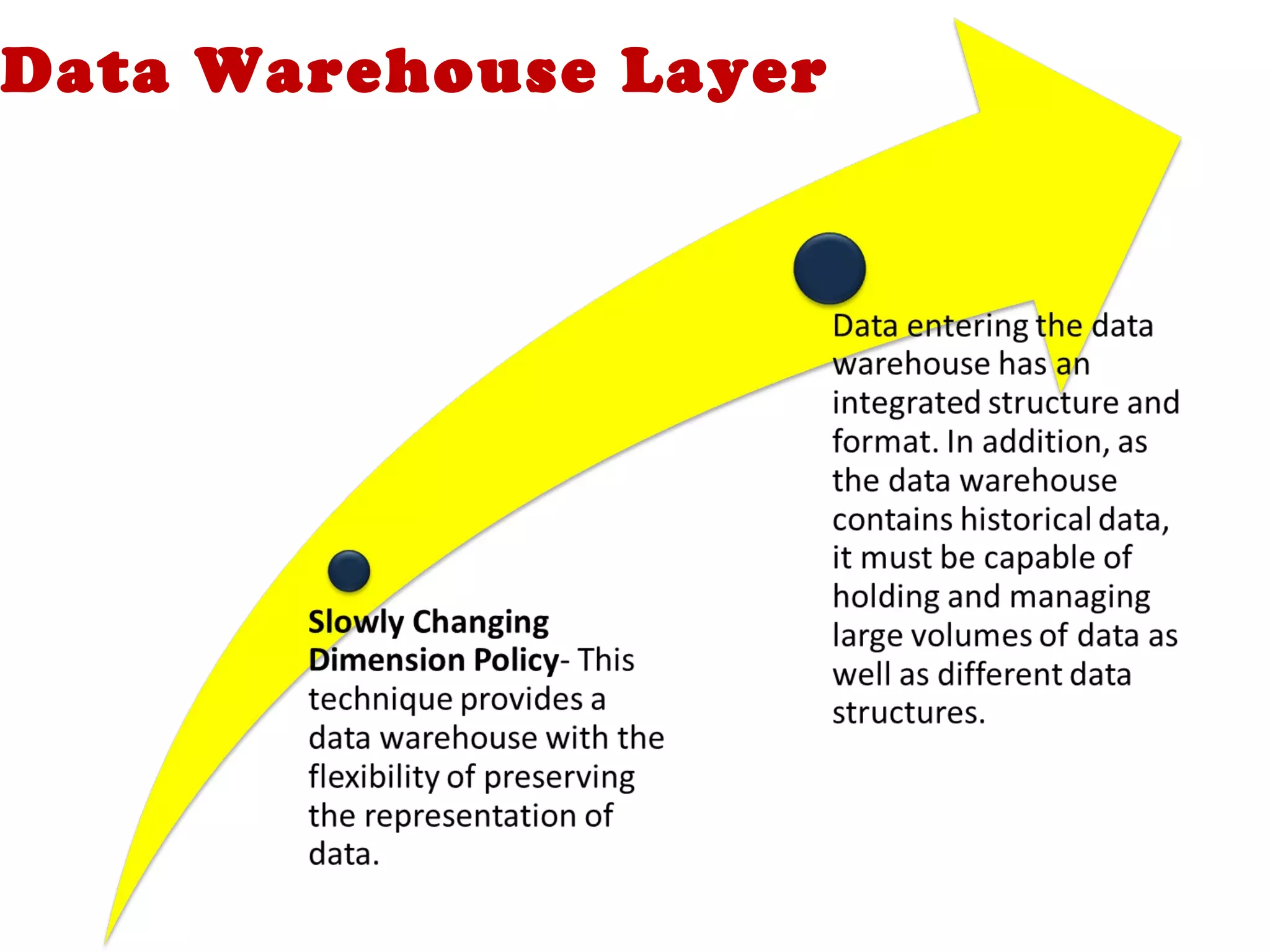
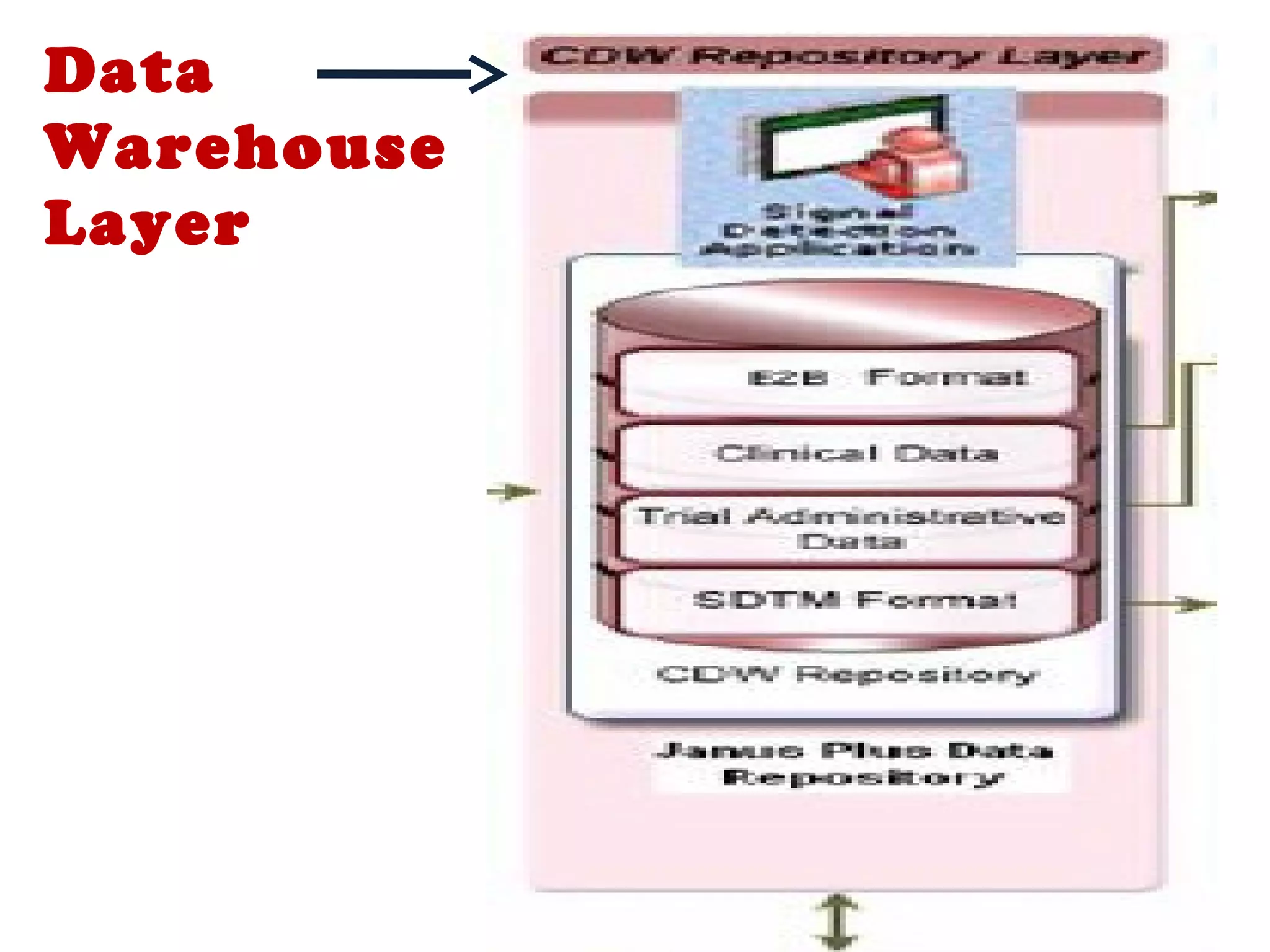
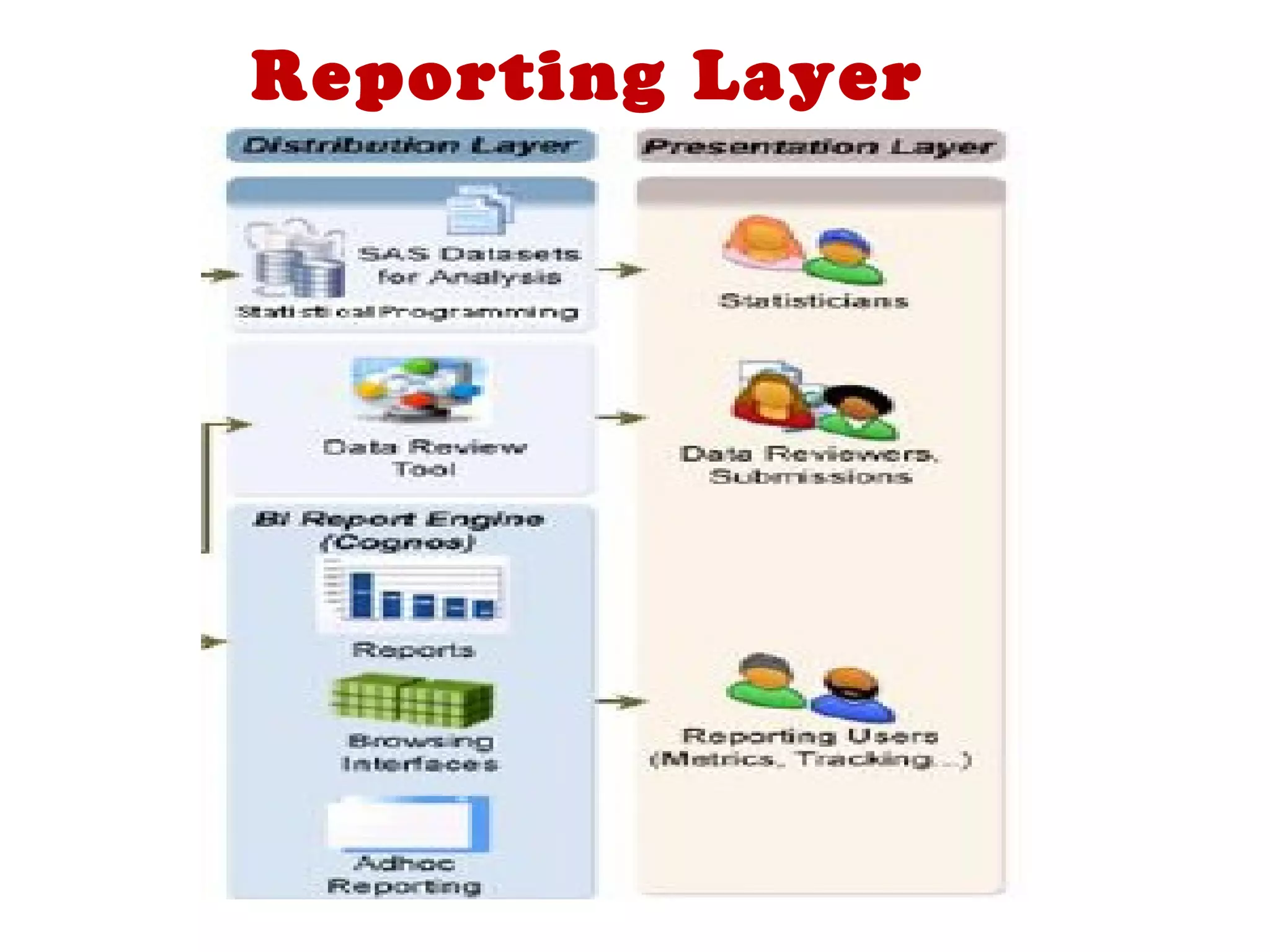
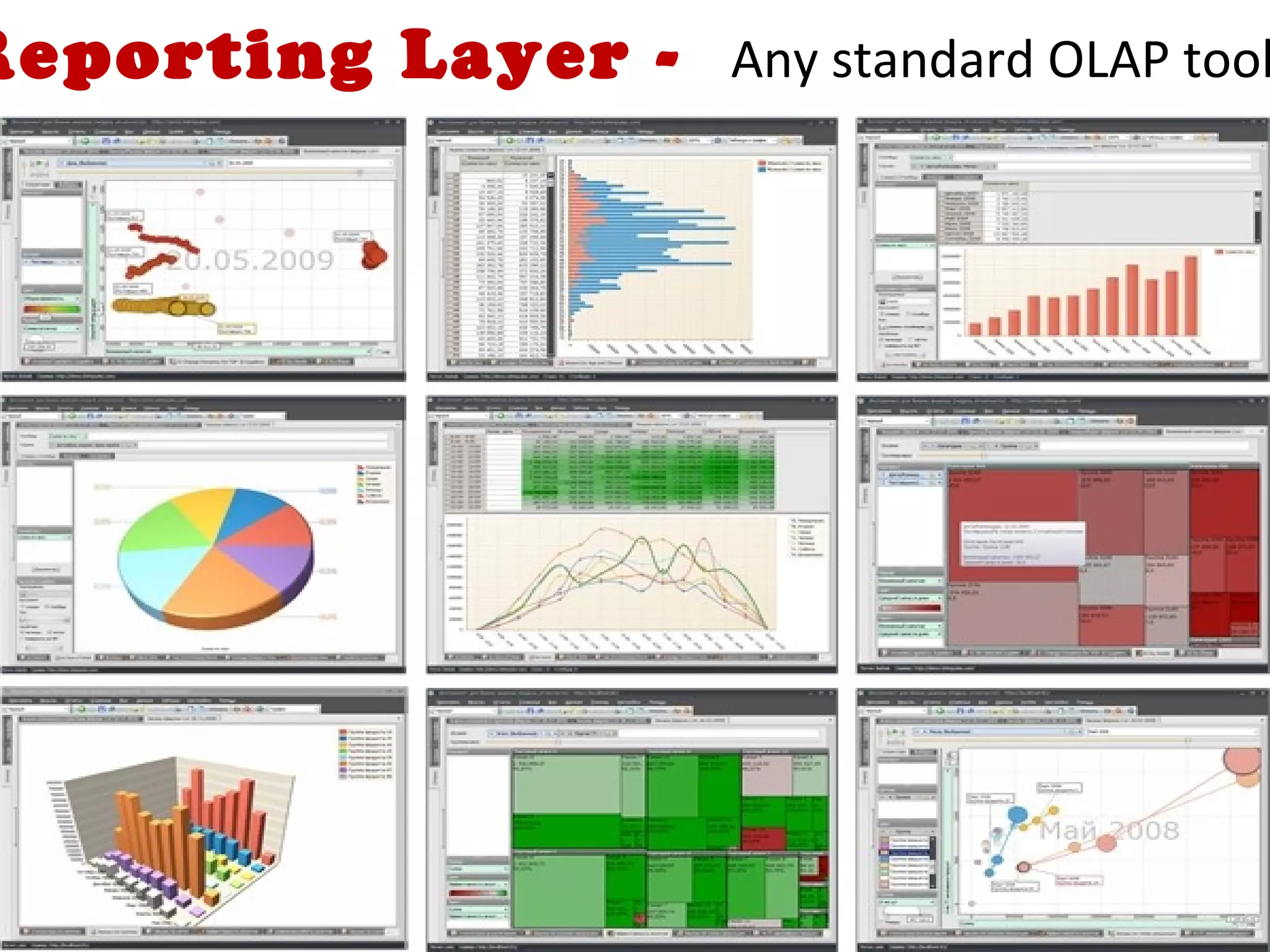
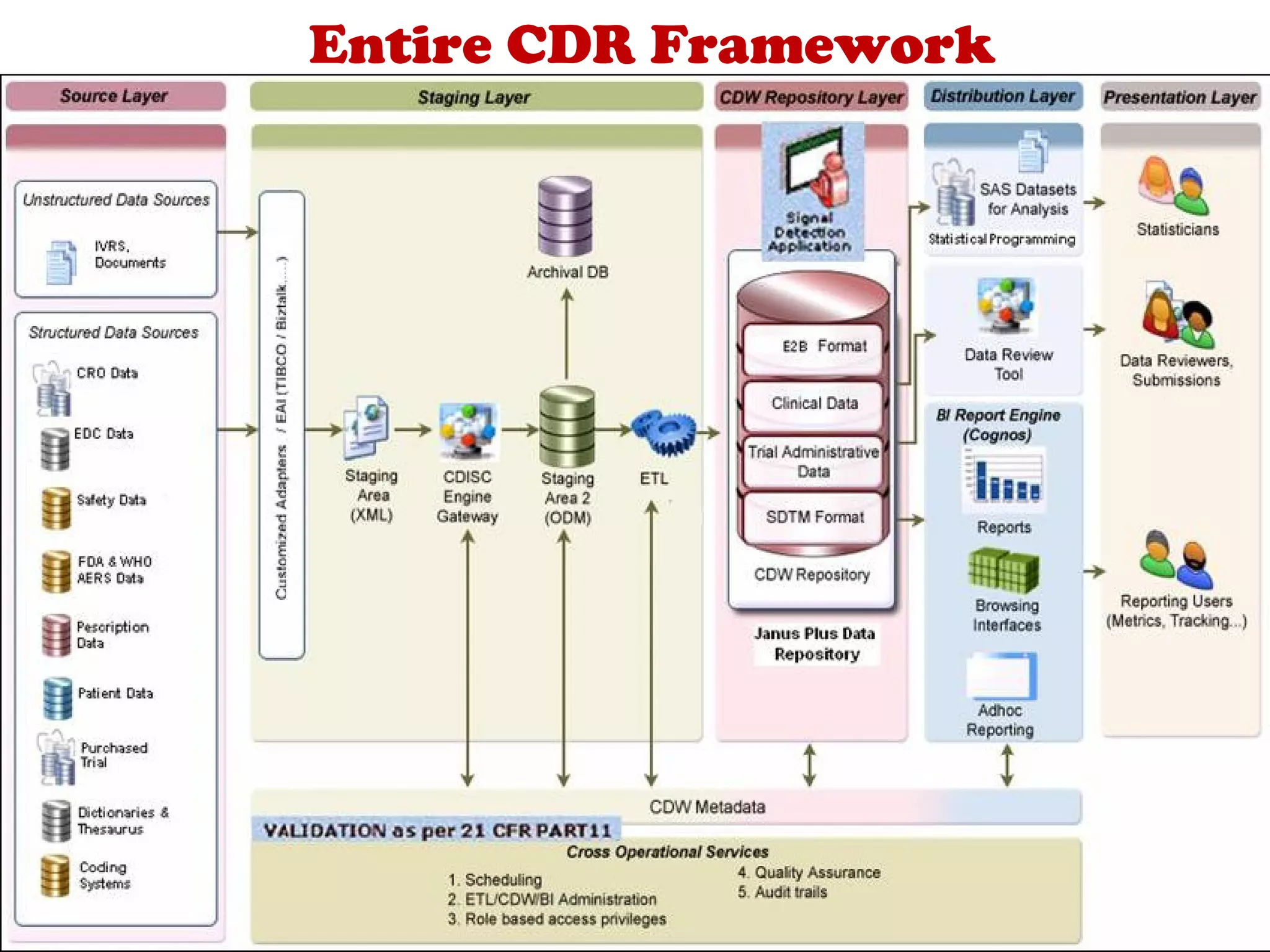
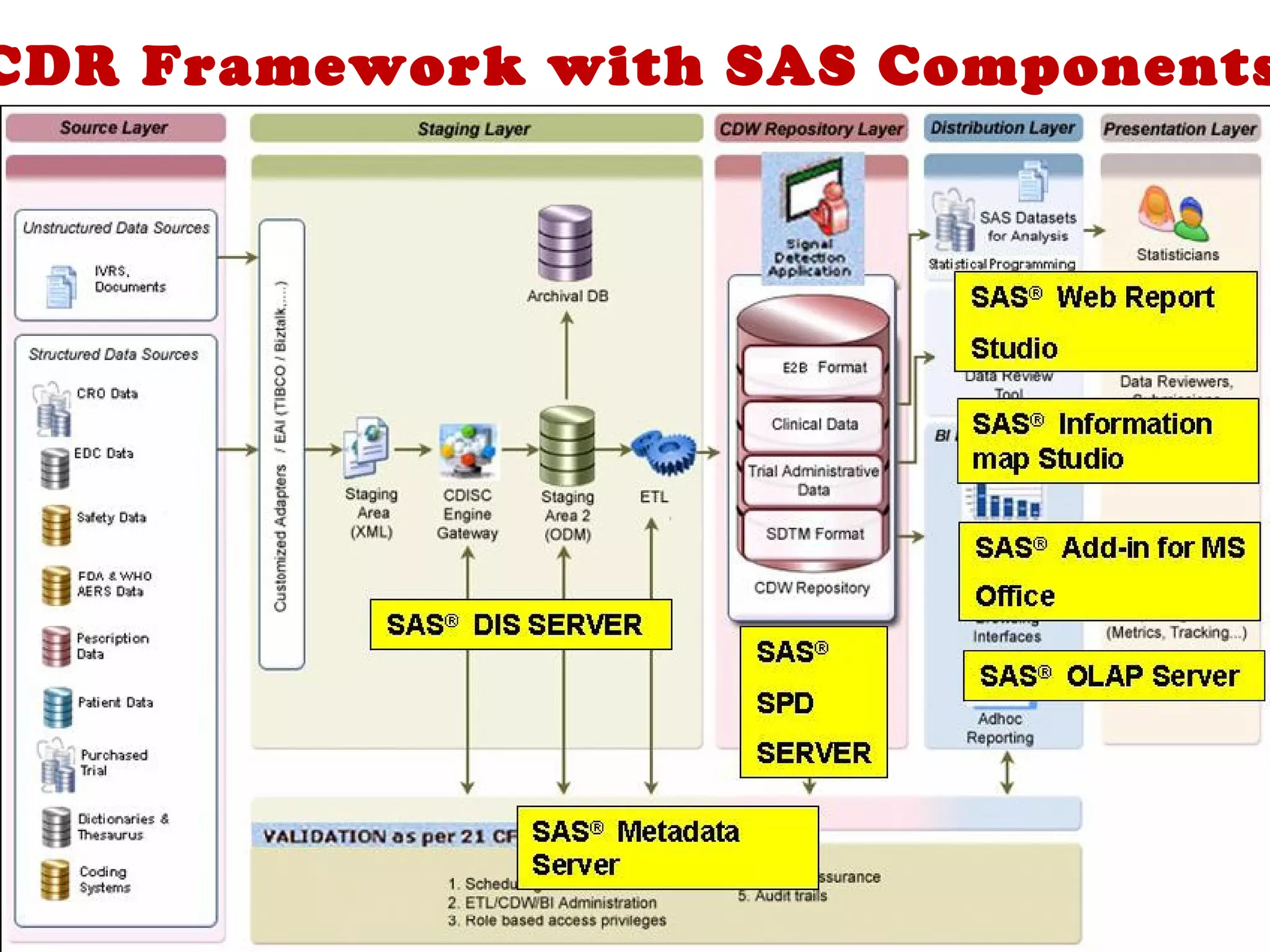
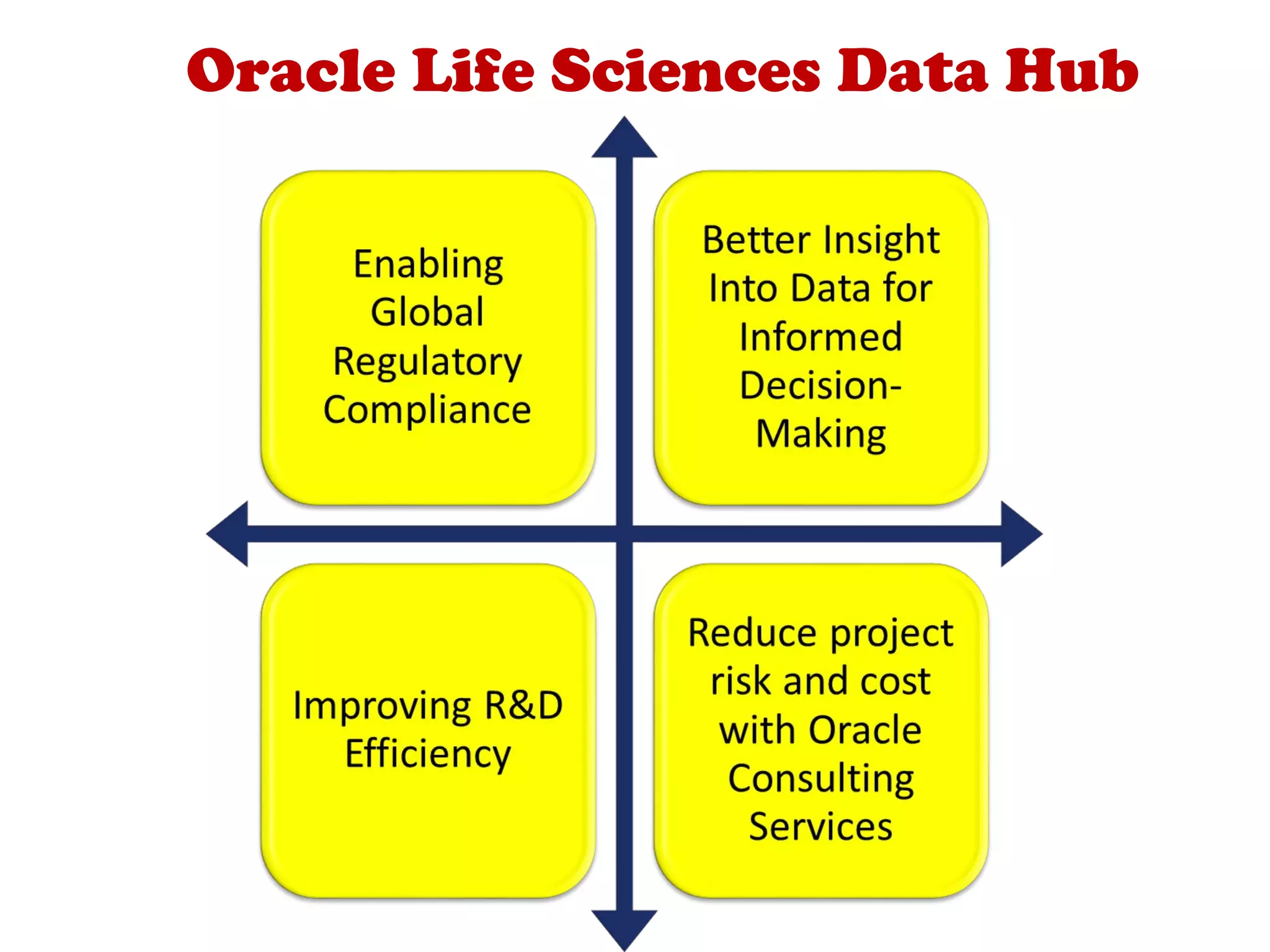
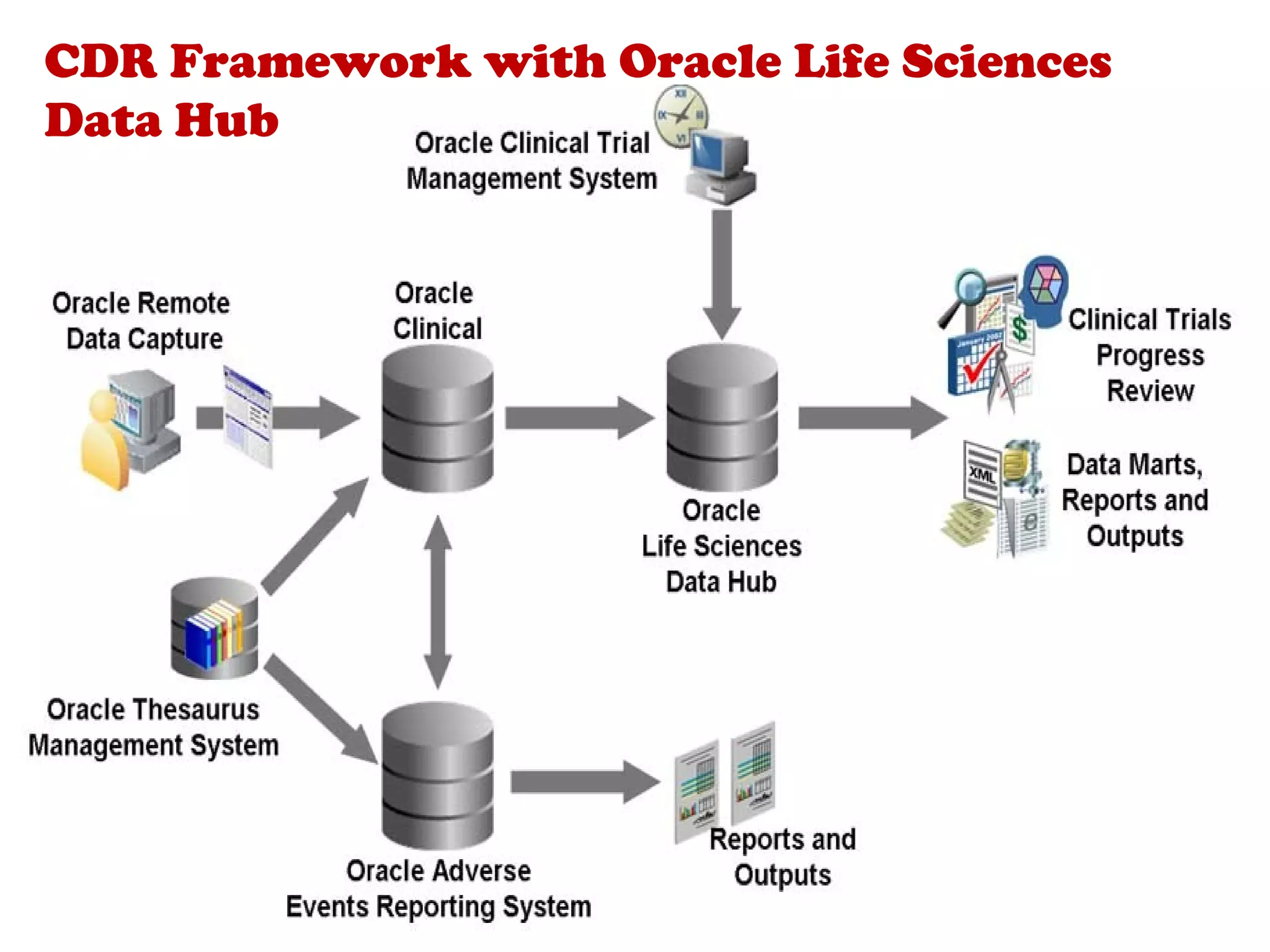
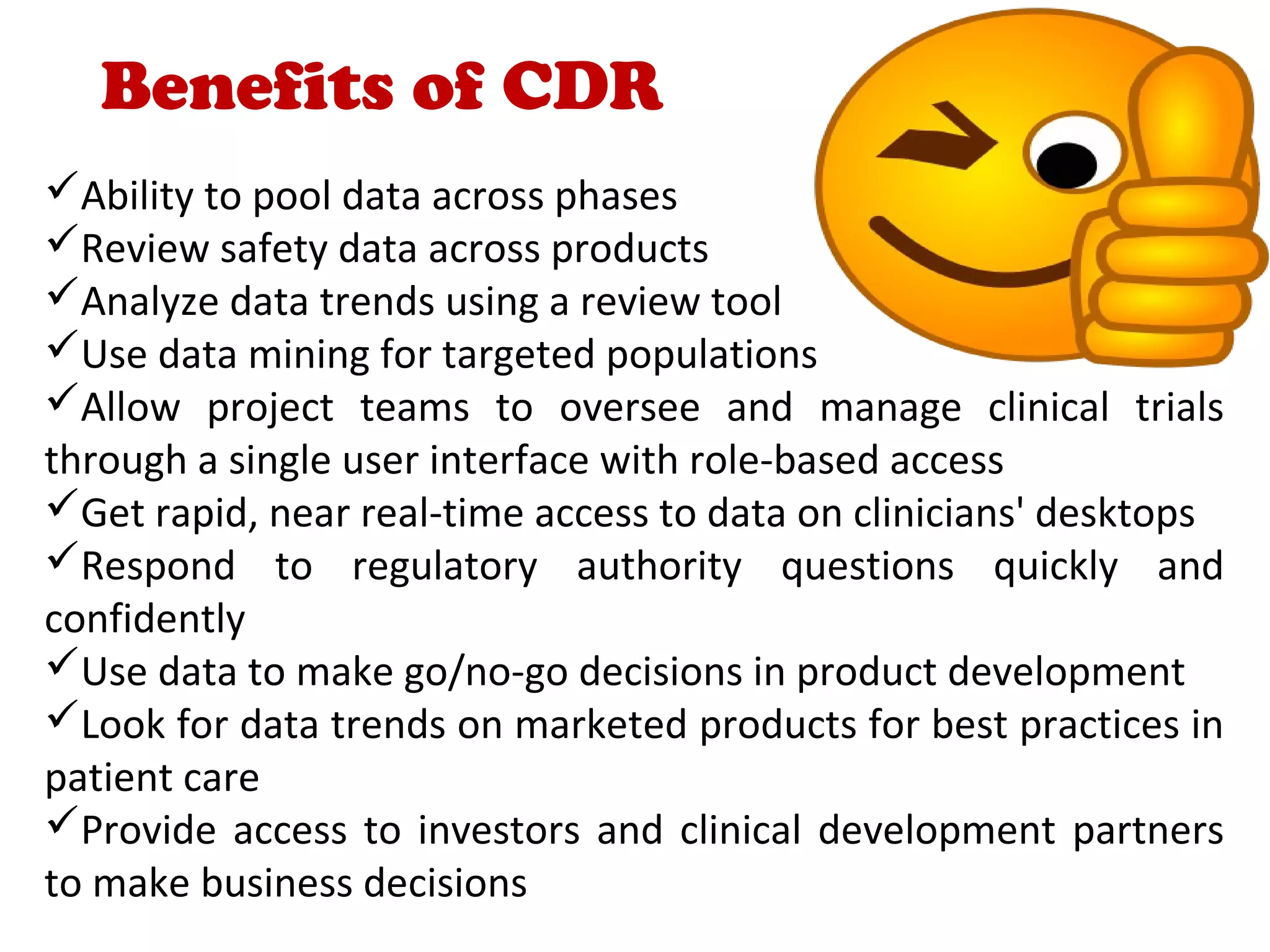
A clinical data repository (CDR) consolidates clinical data from multiple sources to provide a unified view of individual patients. It integrates non-uniform data like lab results, demographics, prescriptions, and reports. Challenges to implementing a CDR include storage capacity, computing power, reliability, and connecting diverse data sources. Effective CDRs require standard data formats, verification of integrated data, and the ability to generate analytical reports from the consolidated data warehouse.