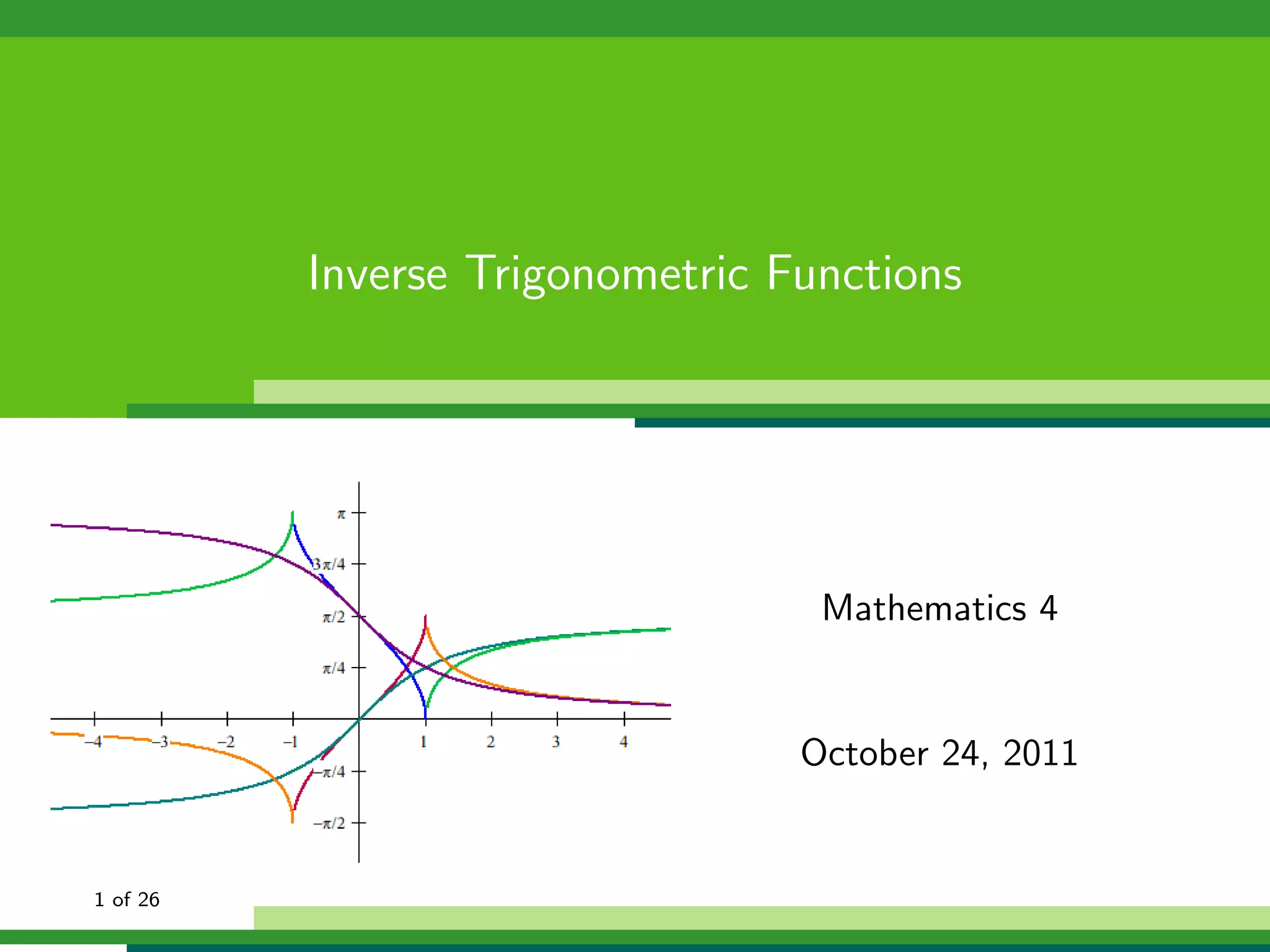
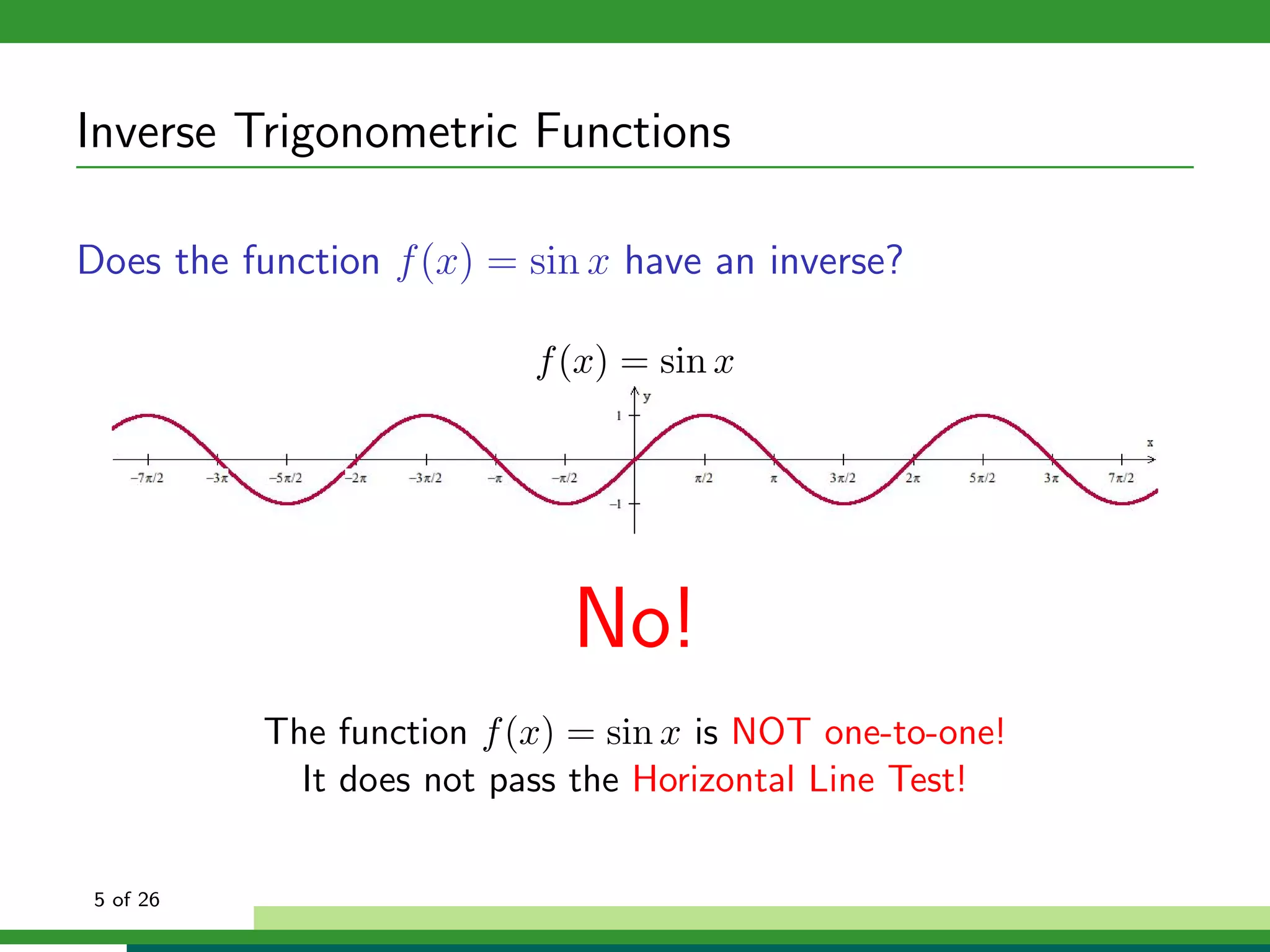
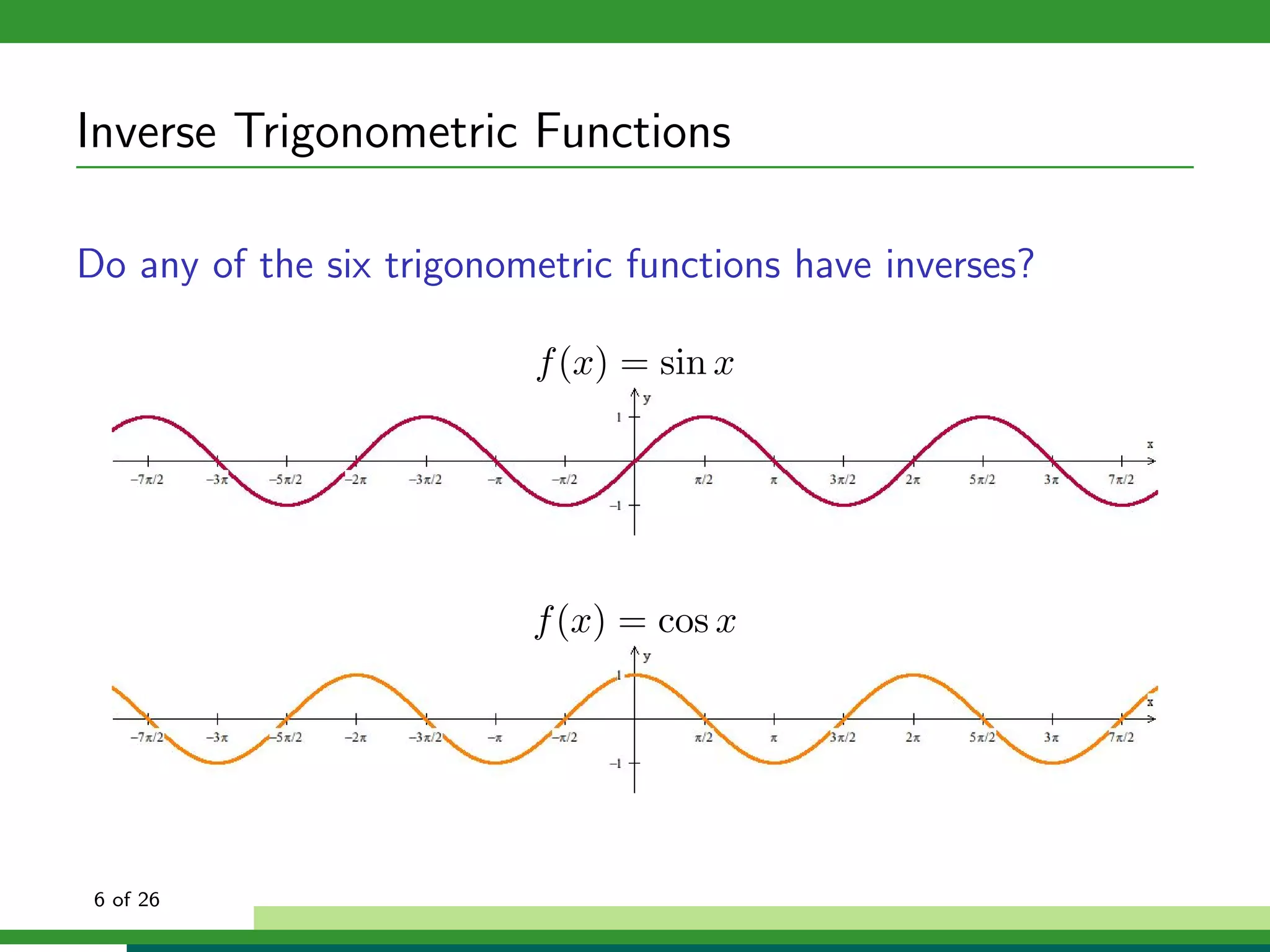
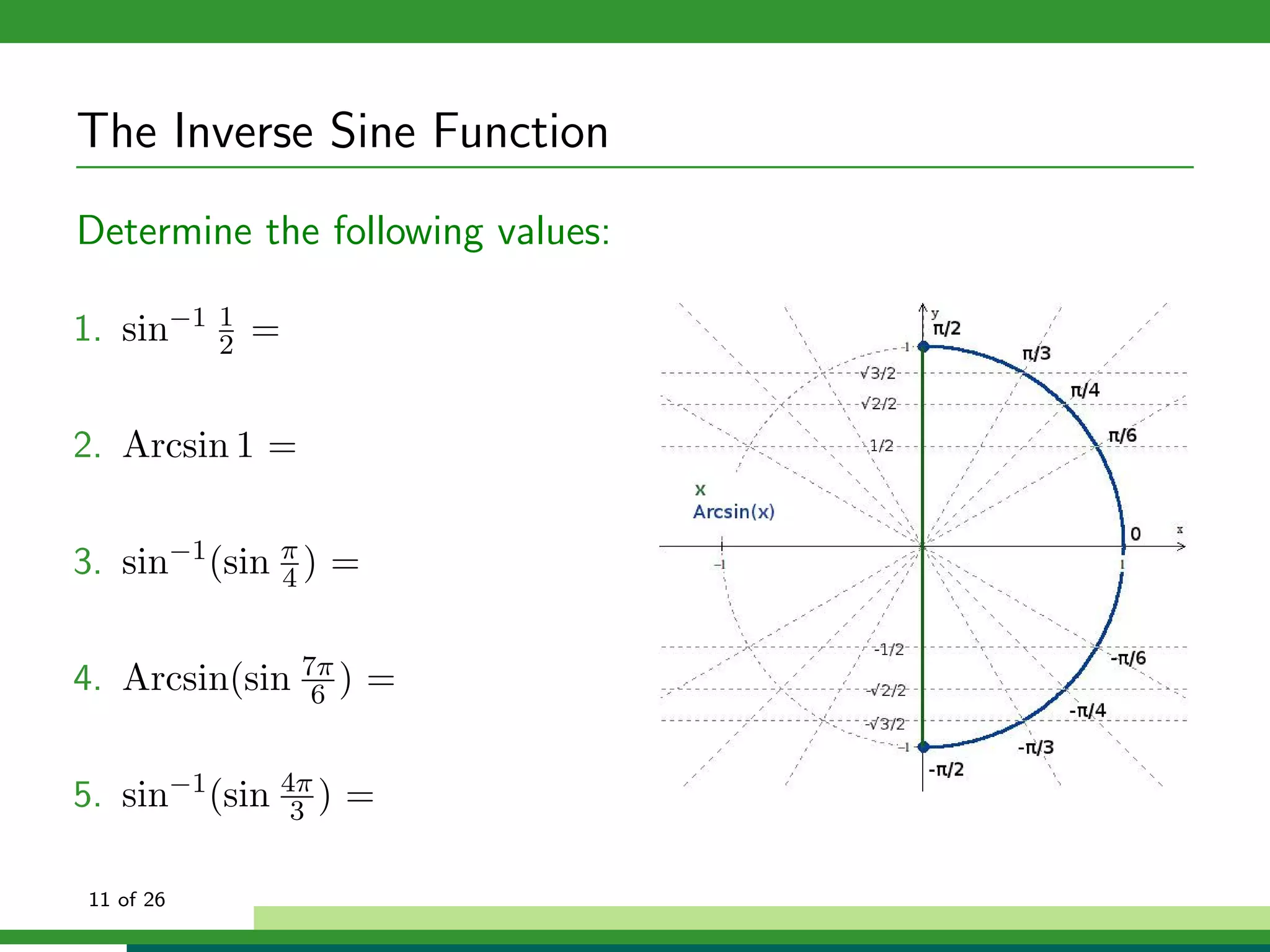
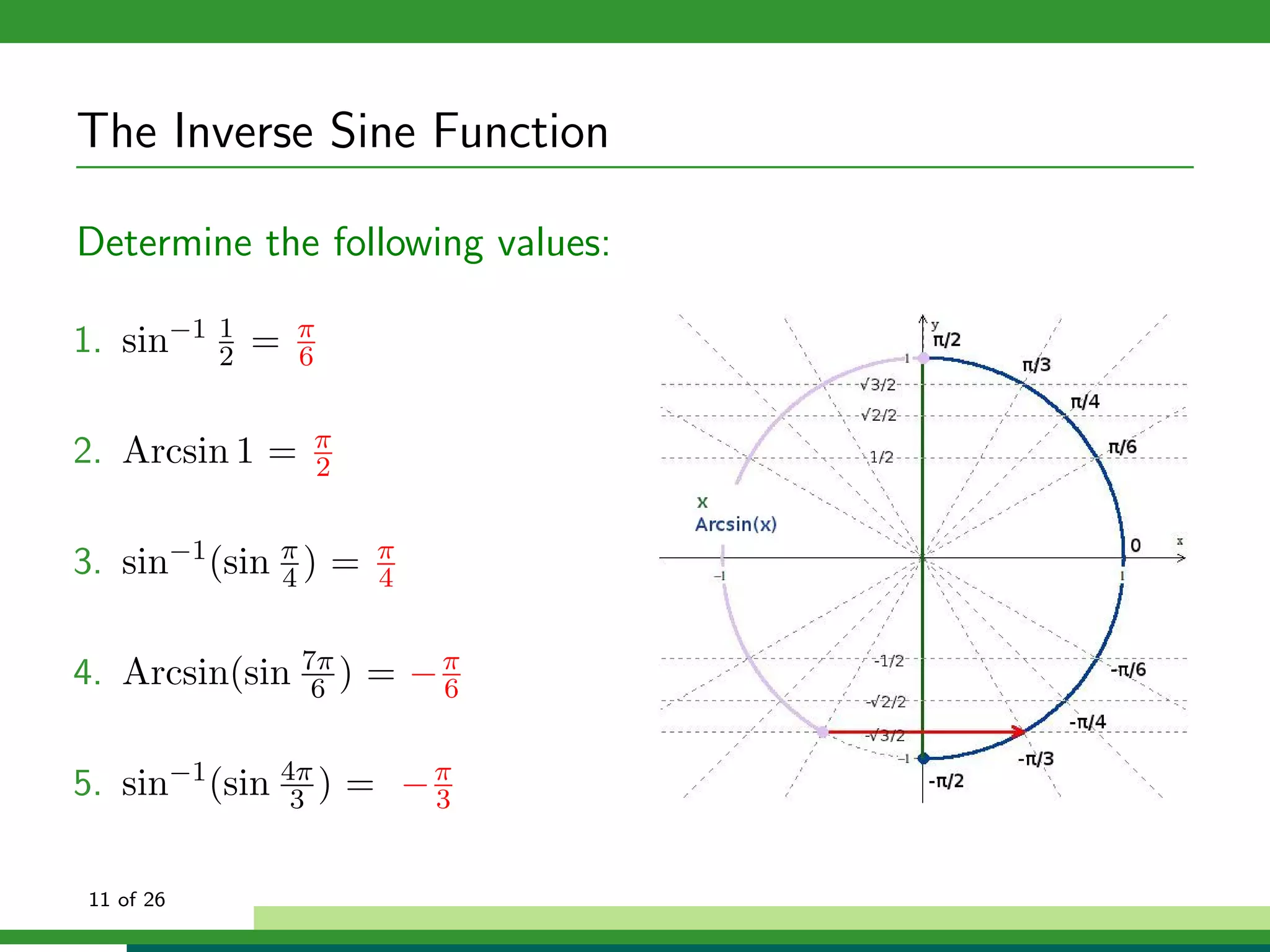
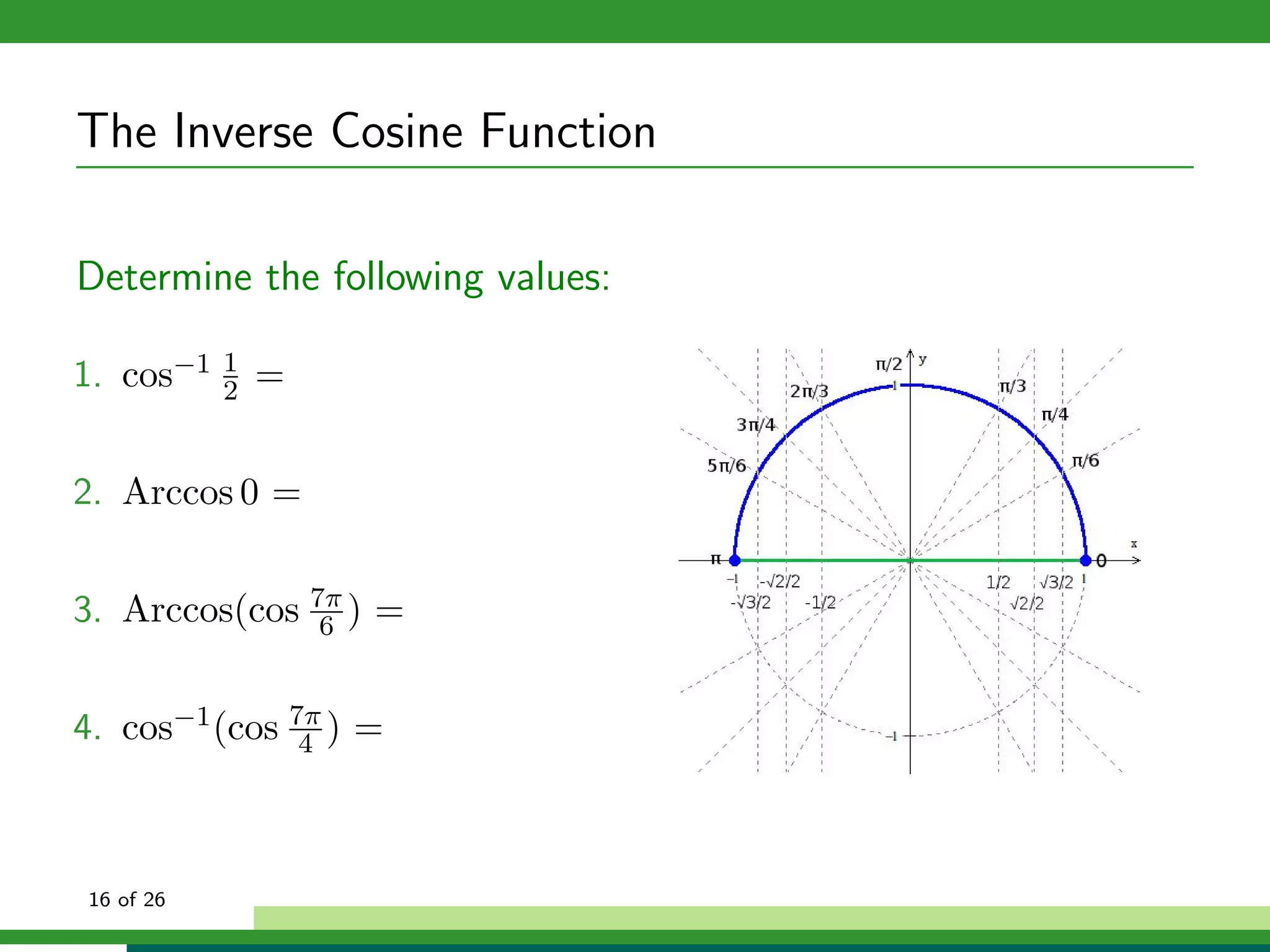
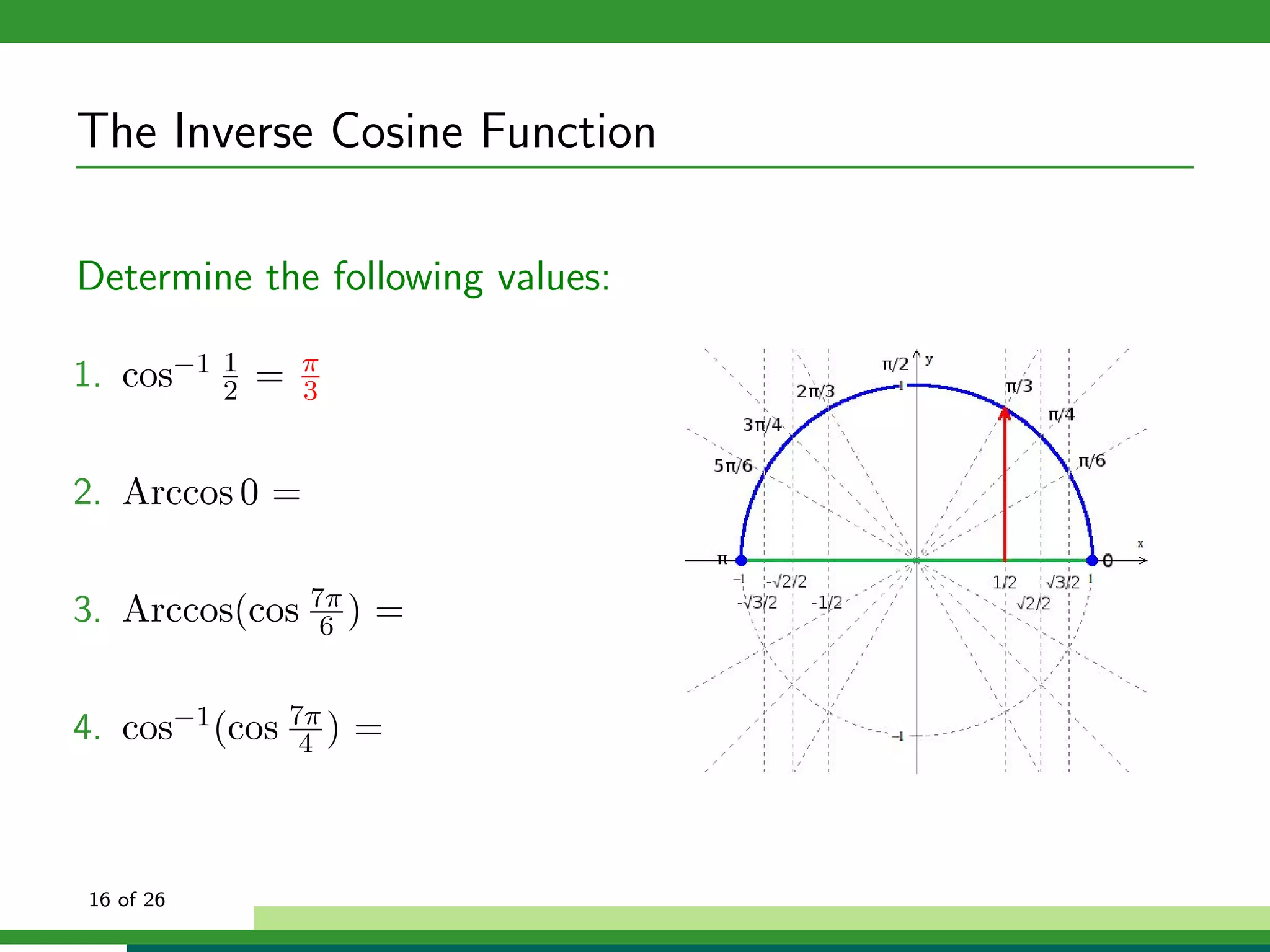
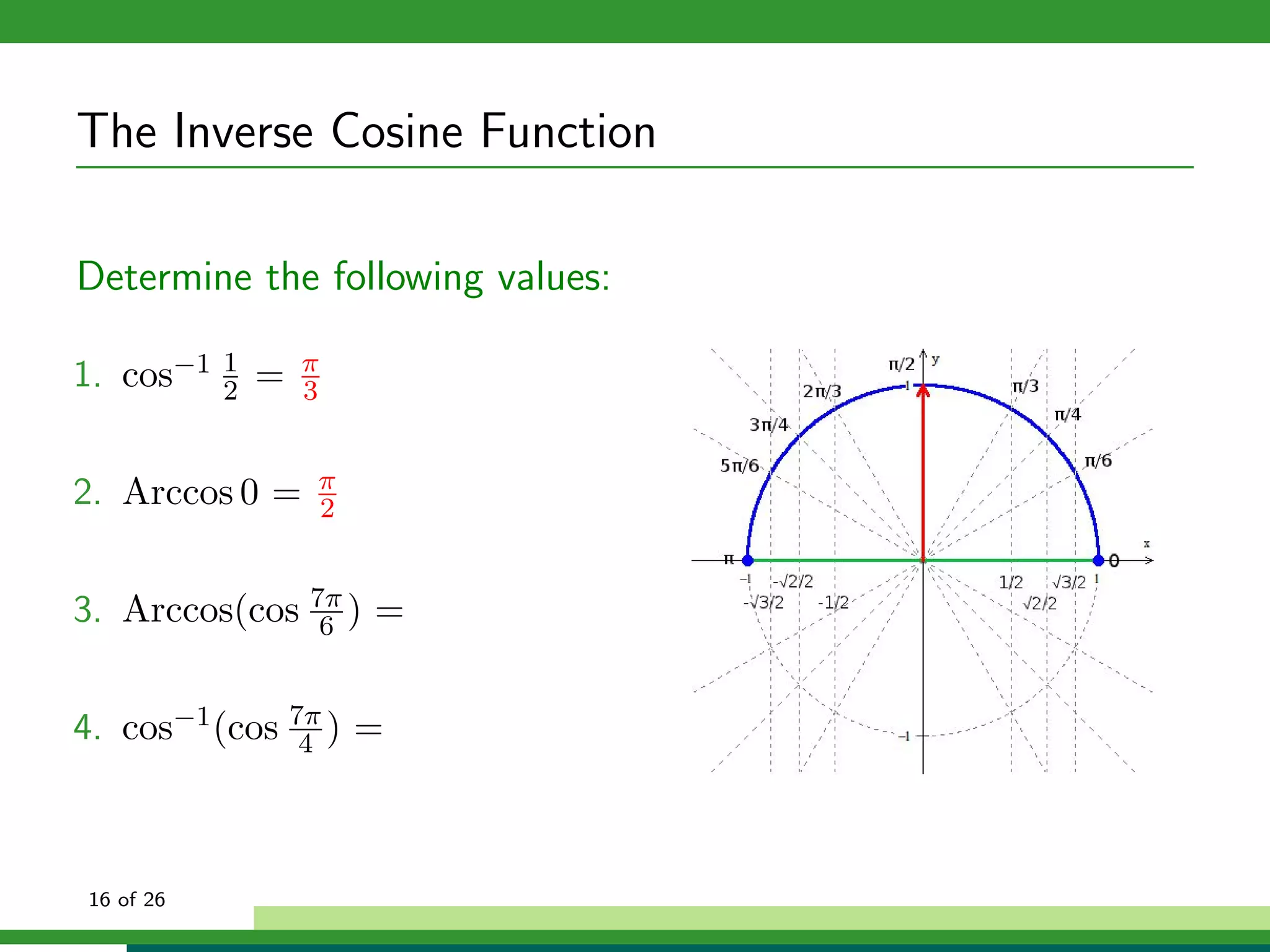
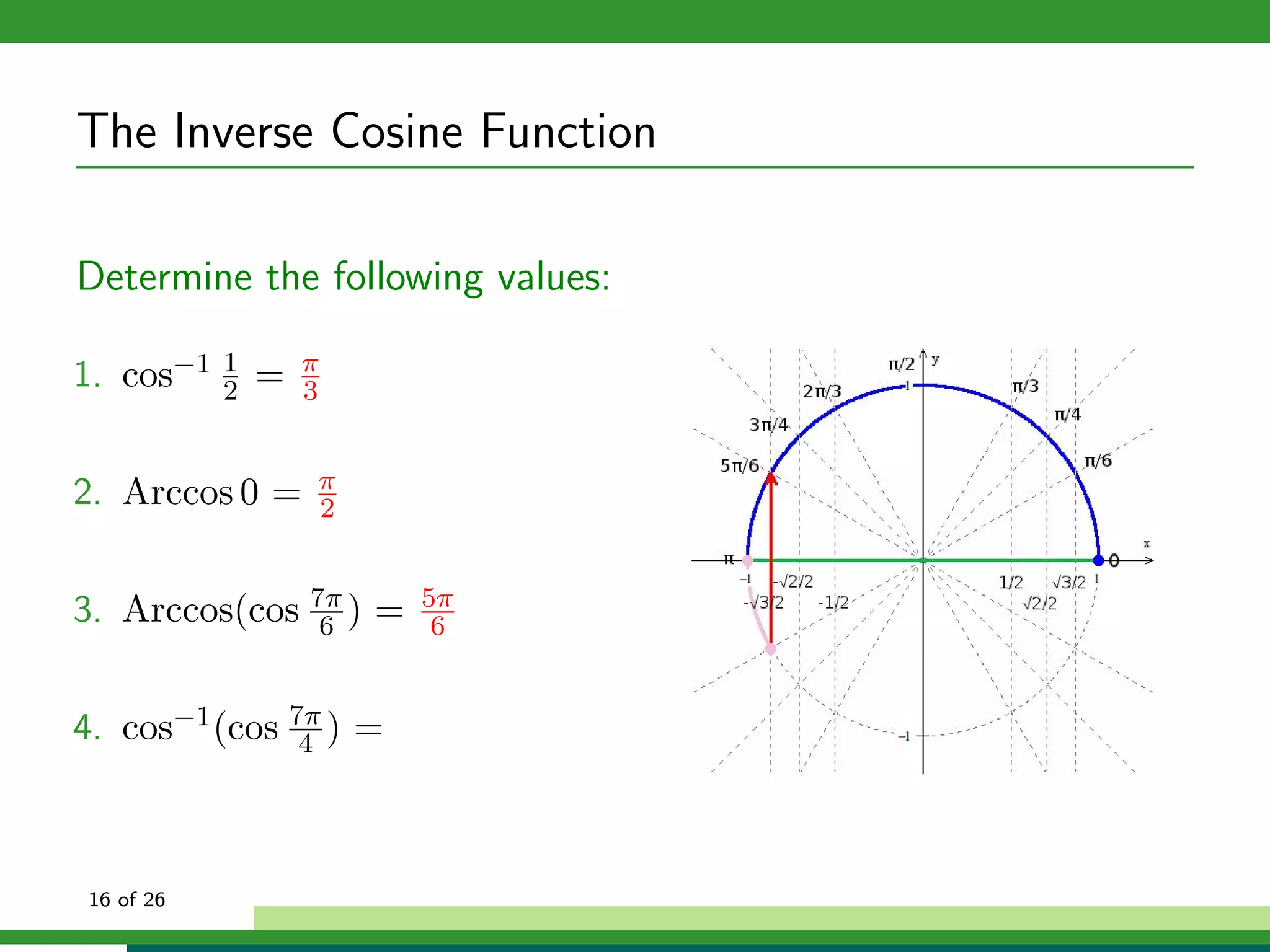
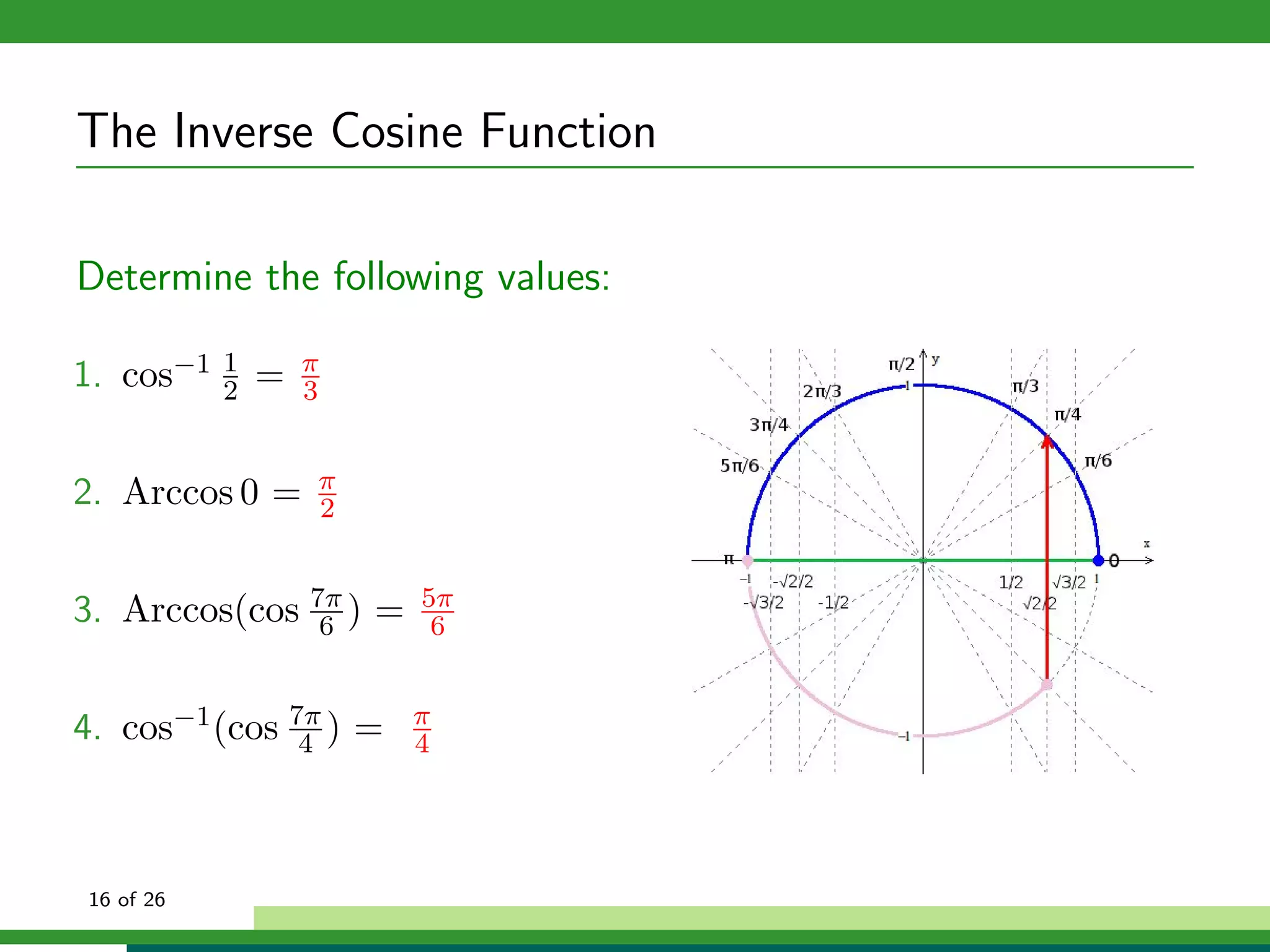
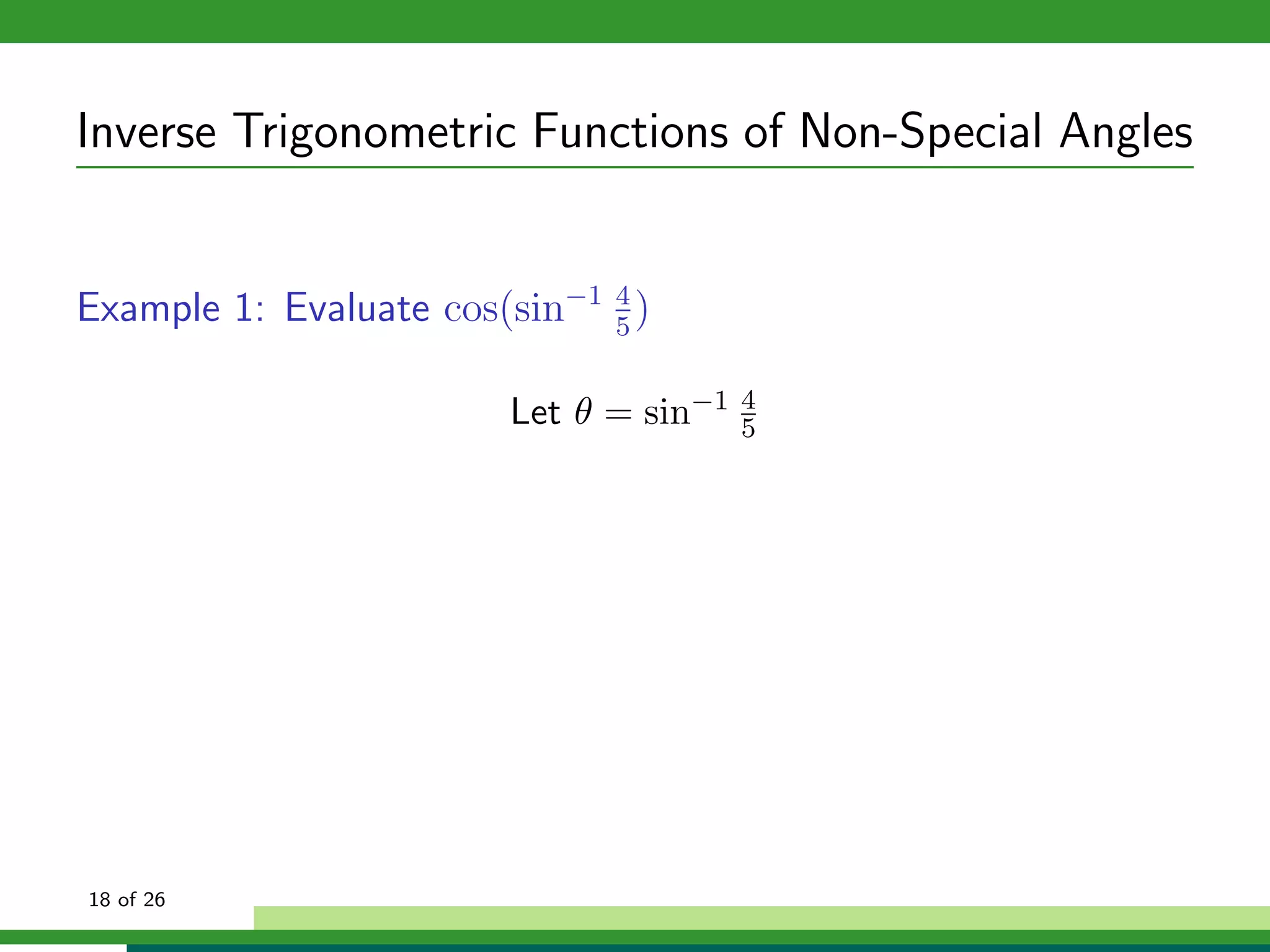
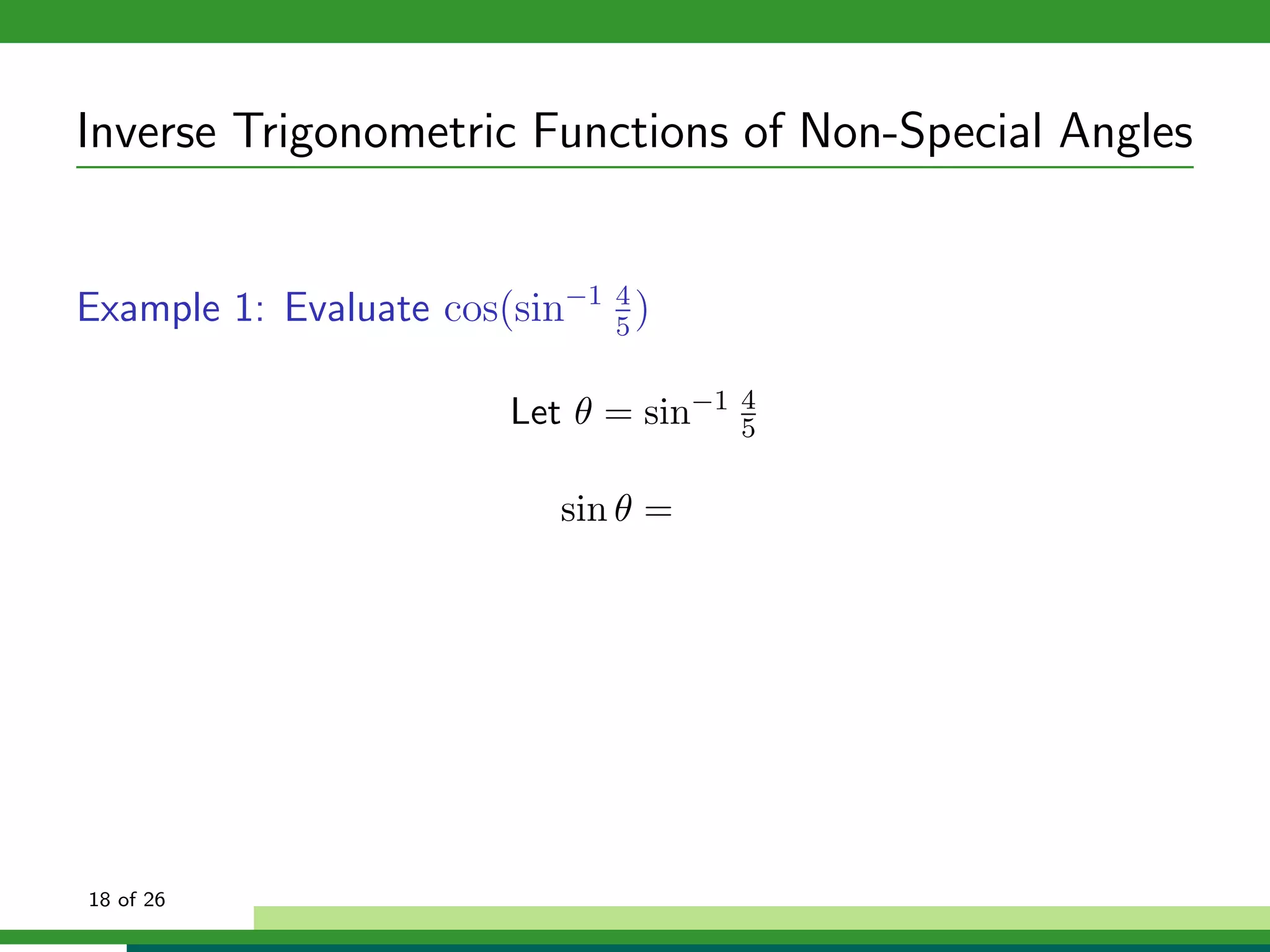
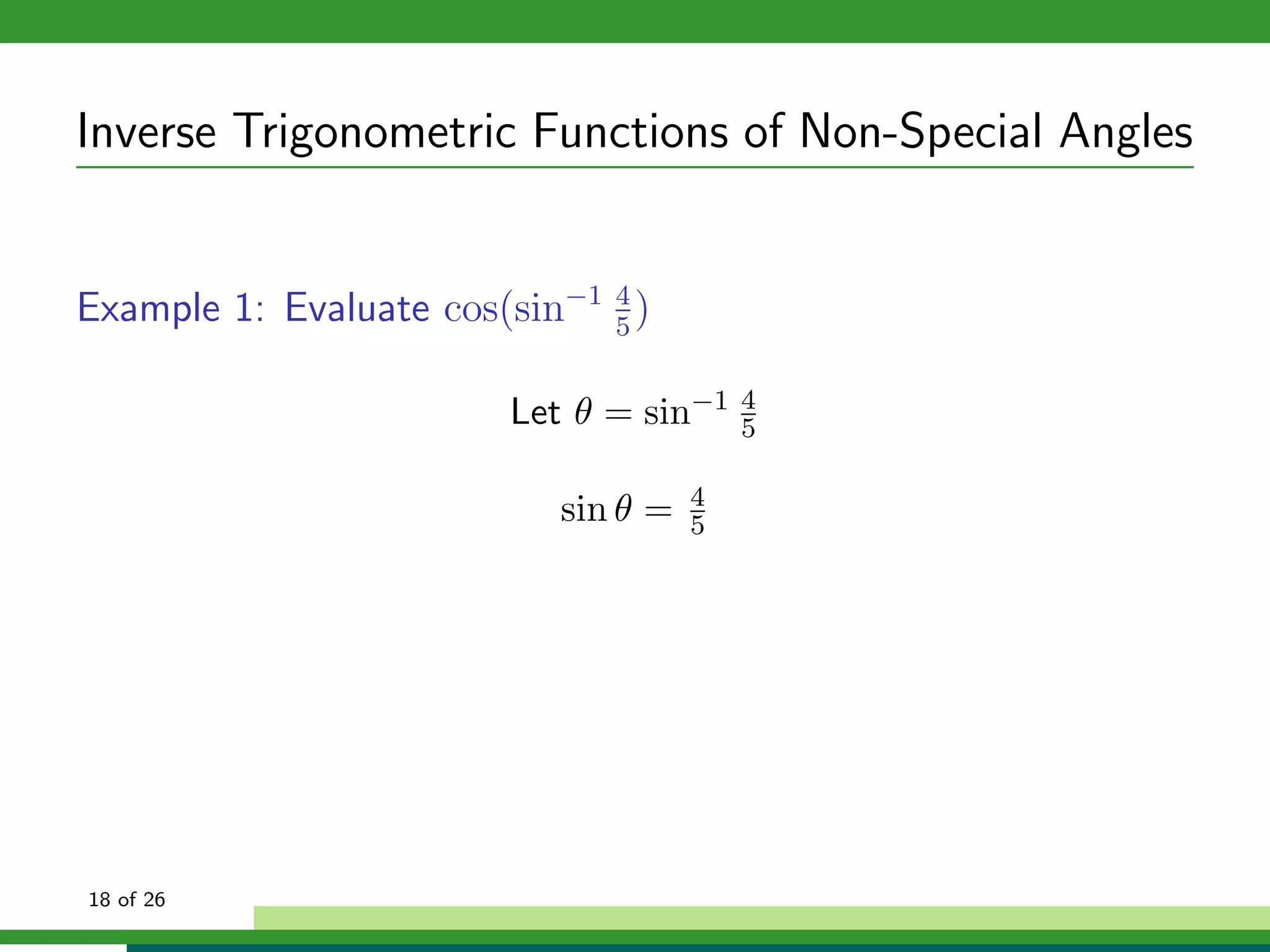
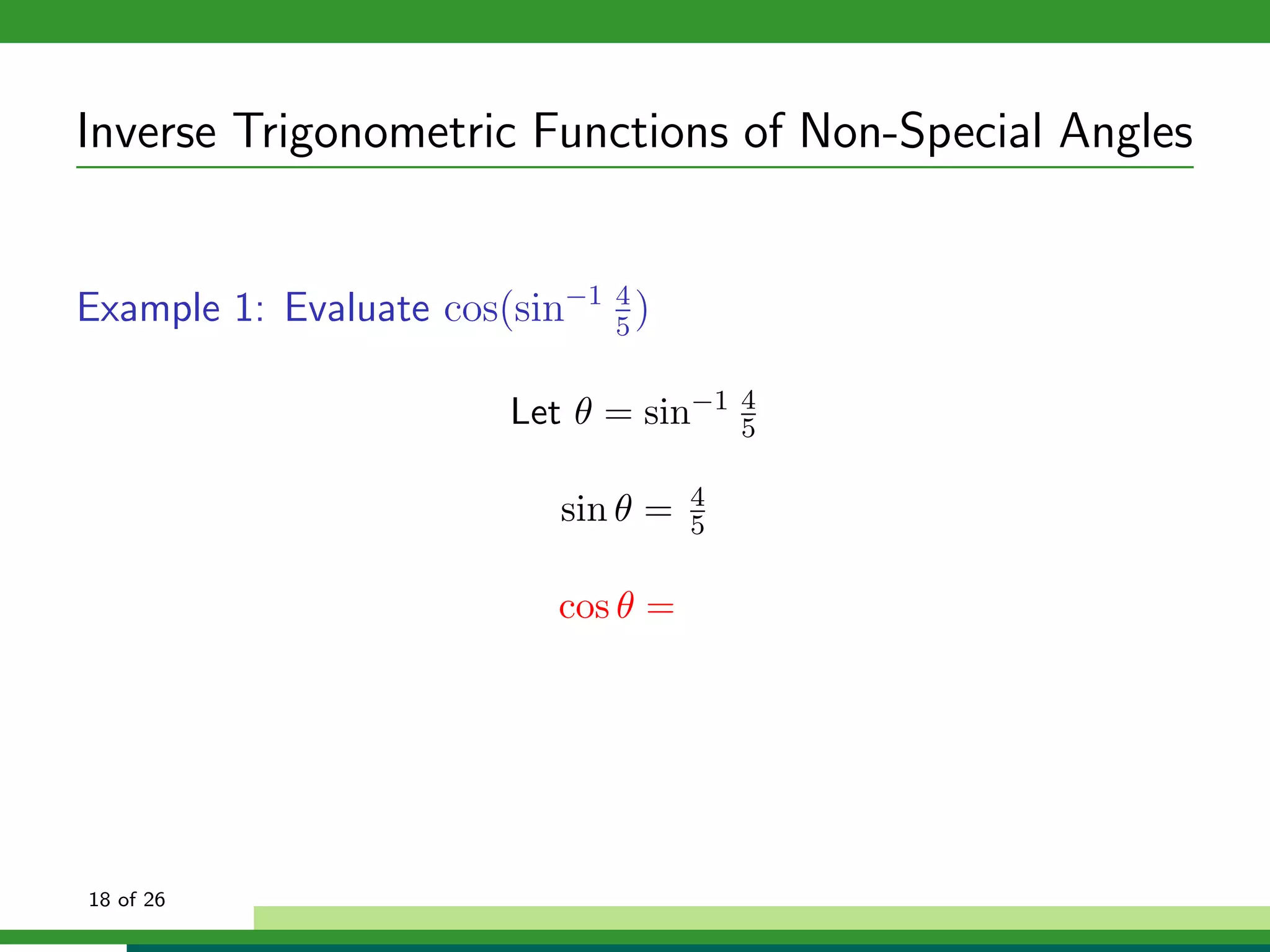
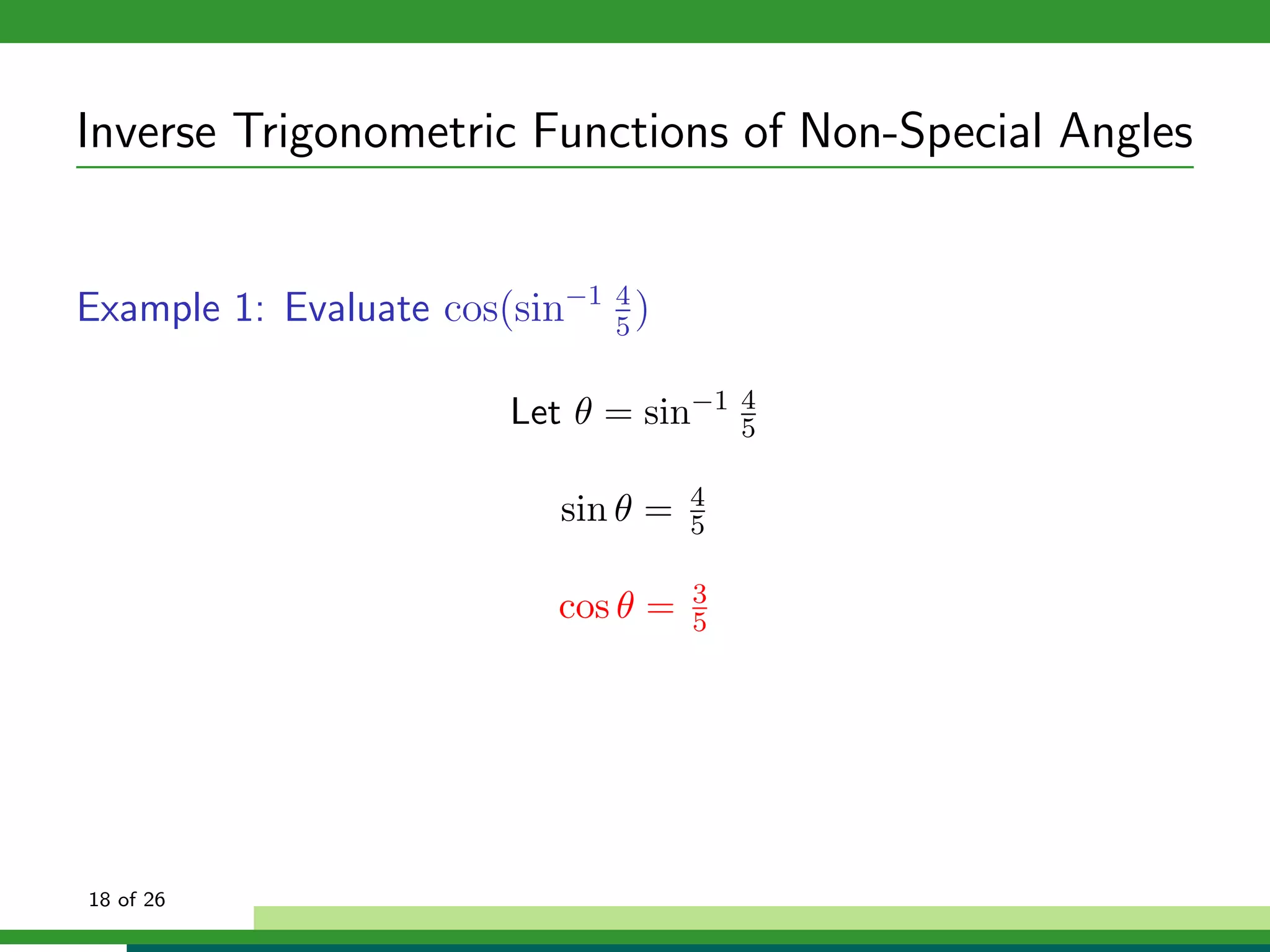
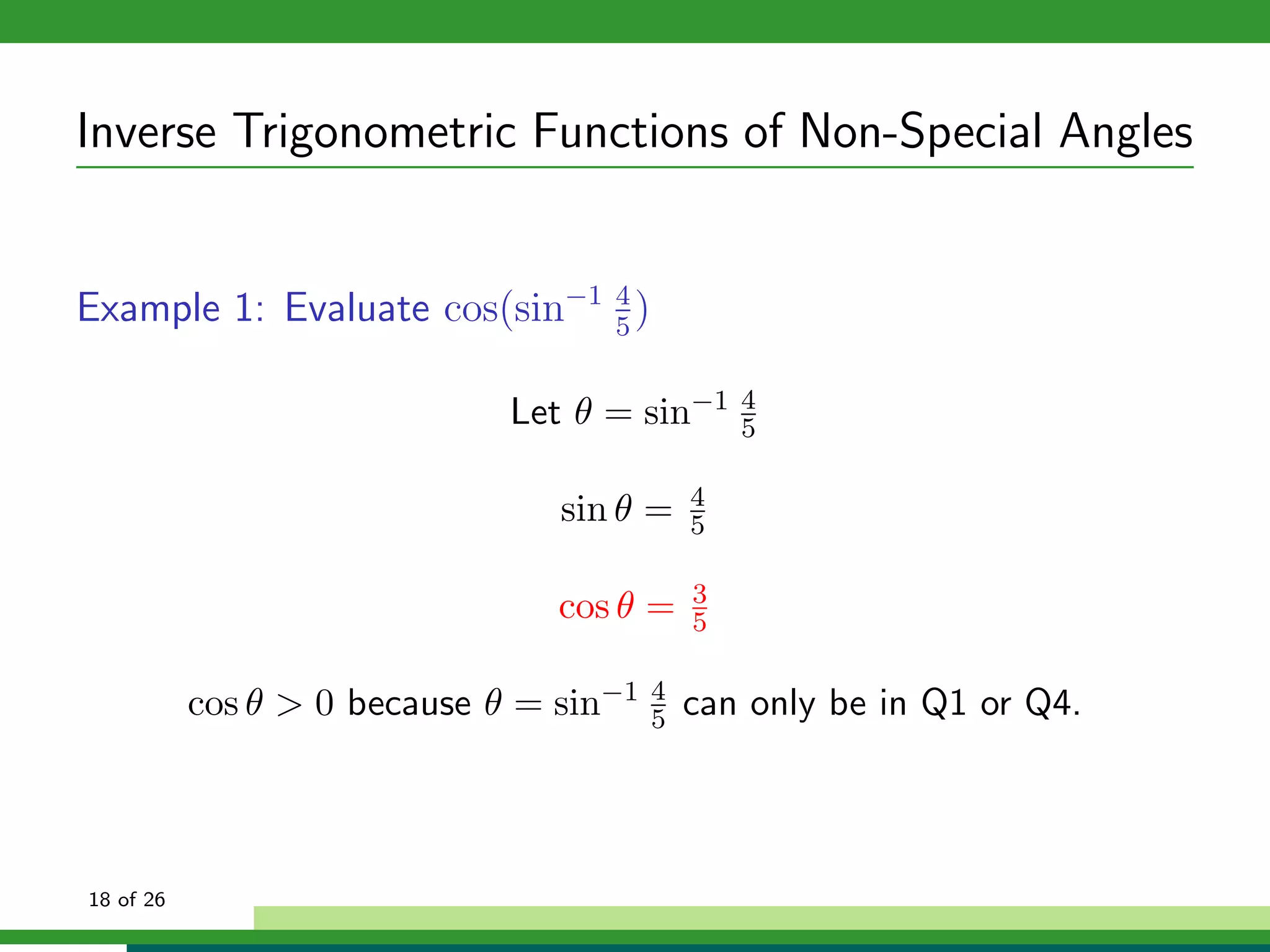
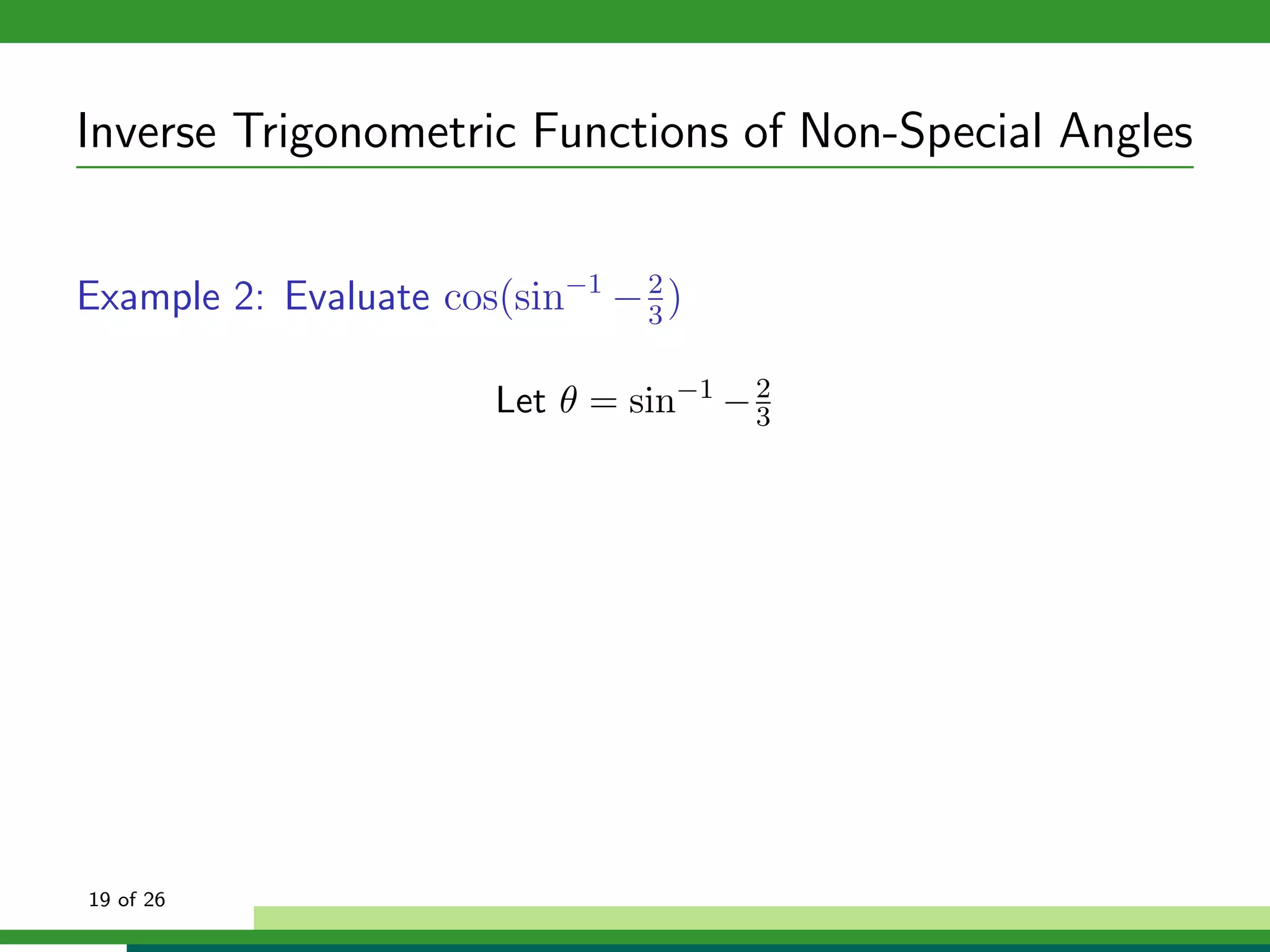
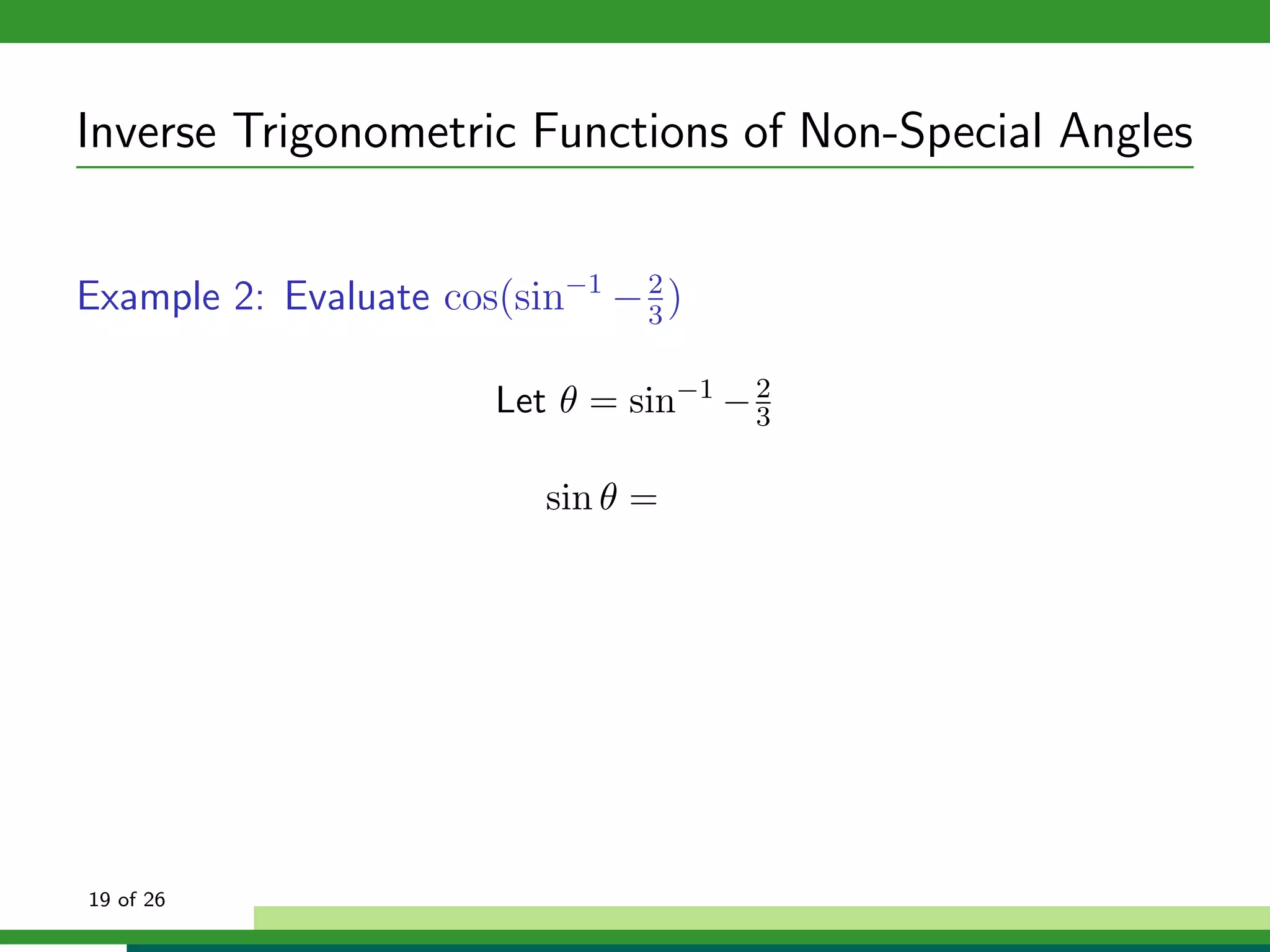
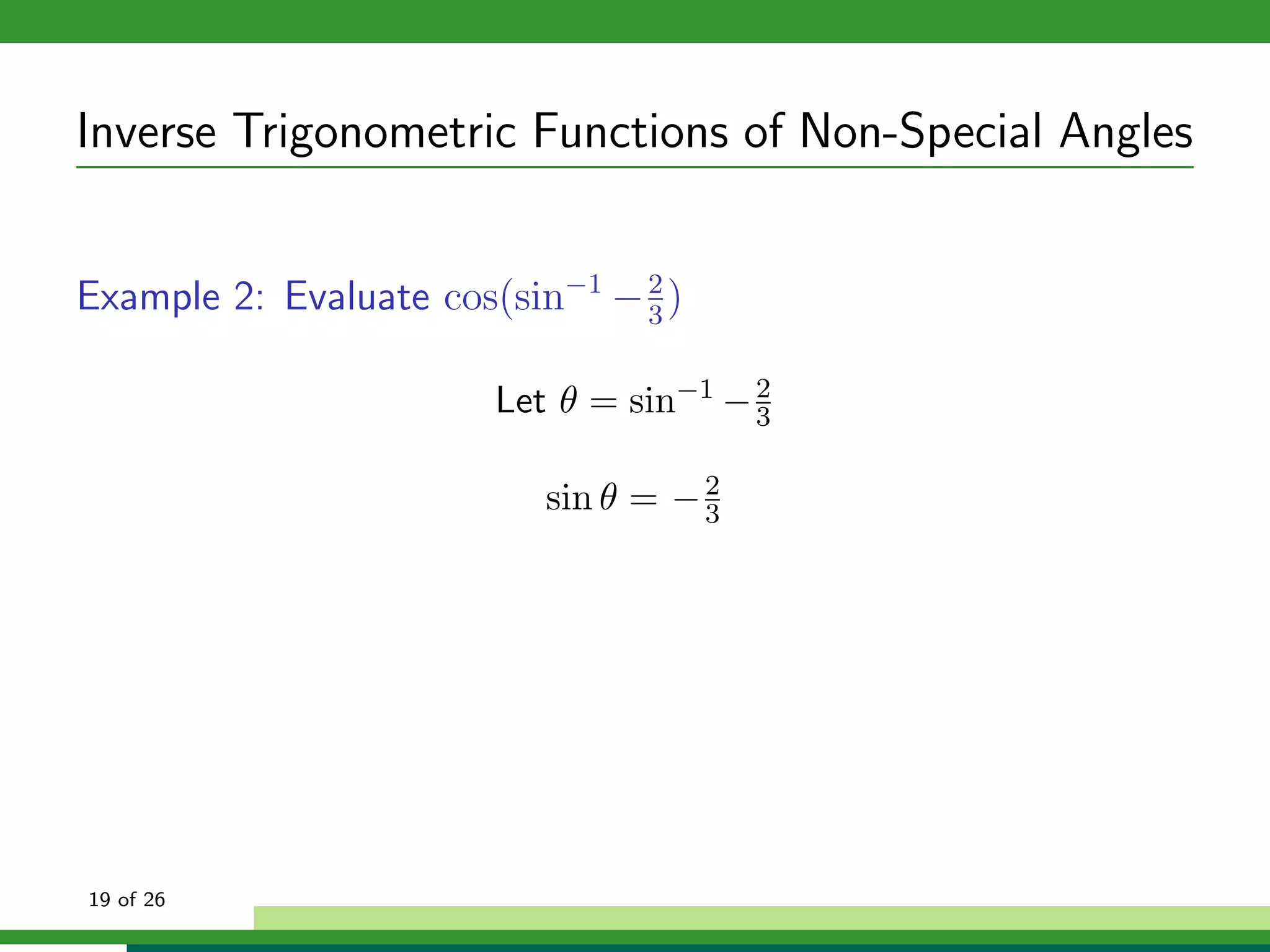
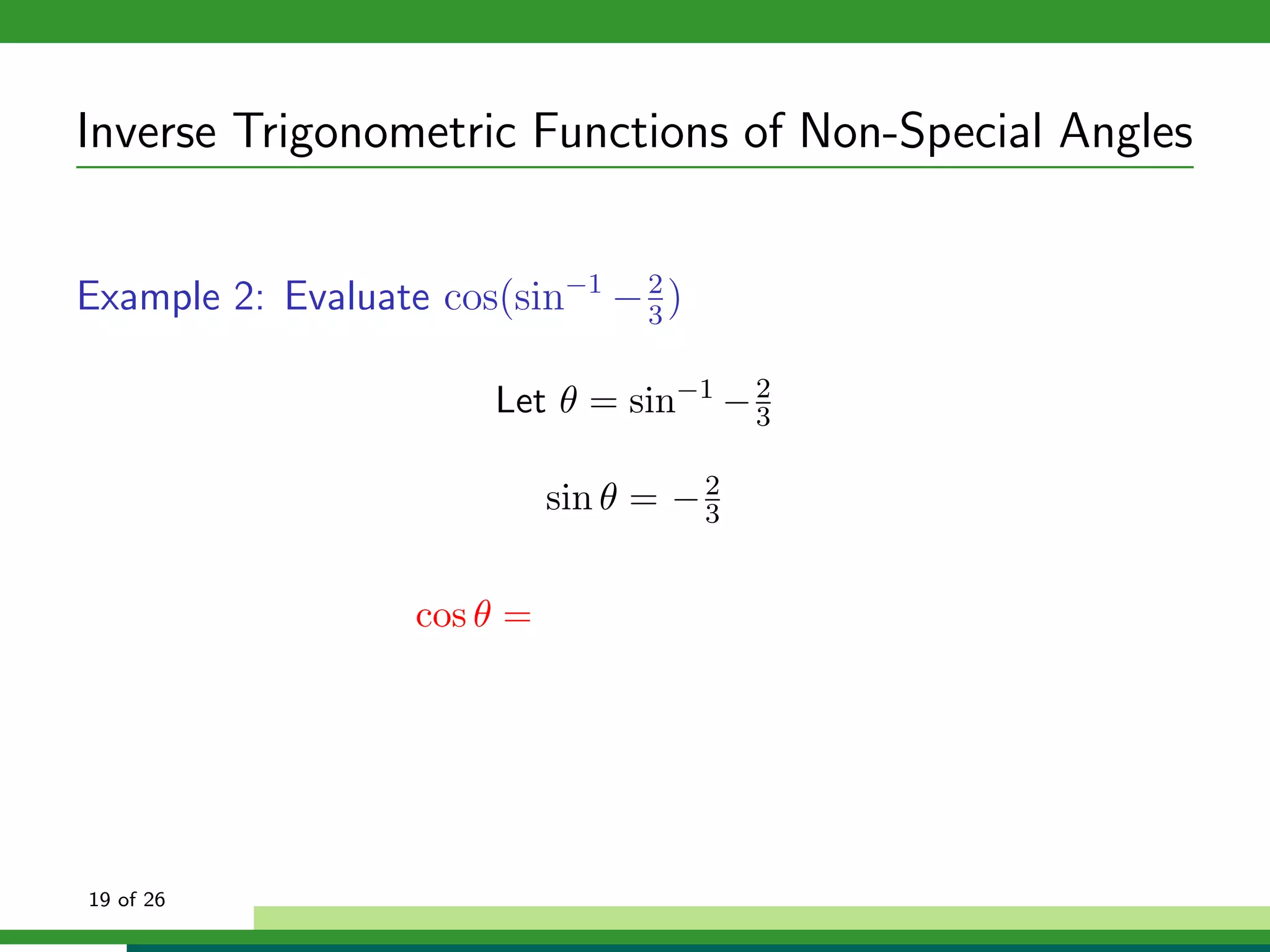
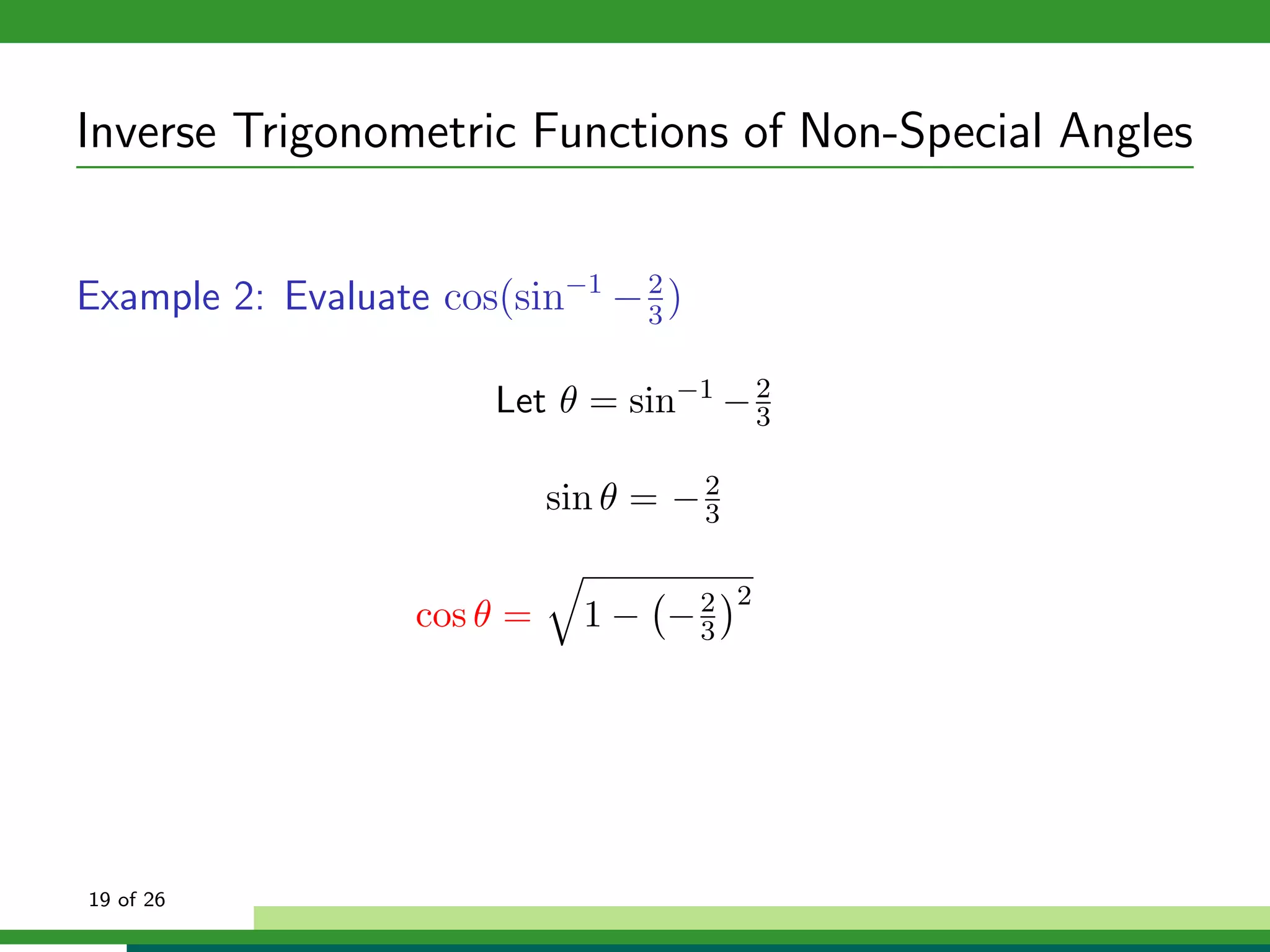
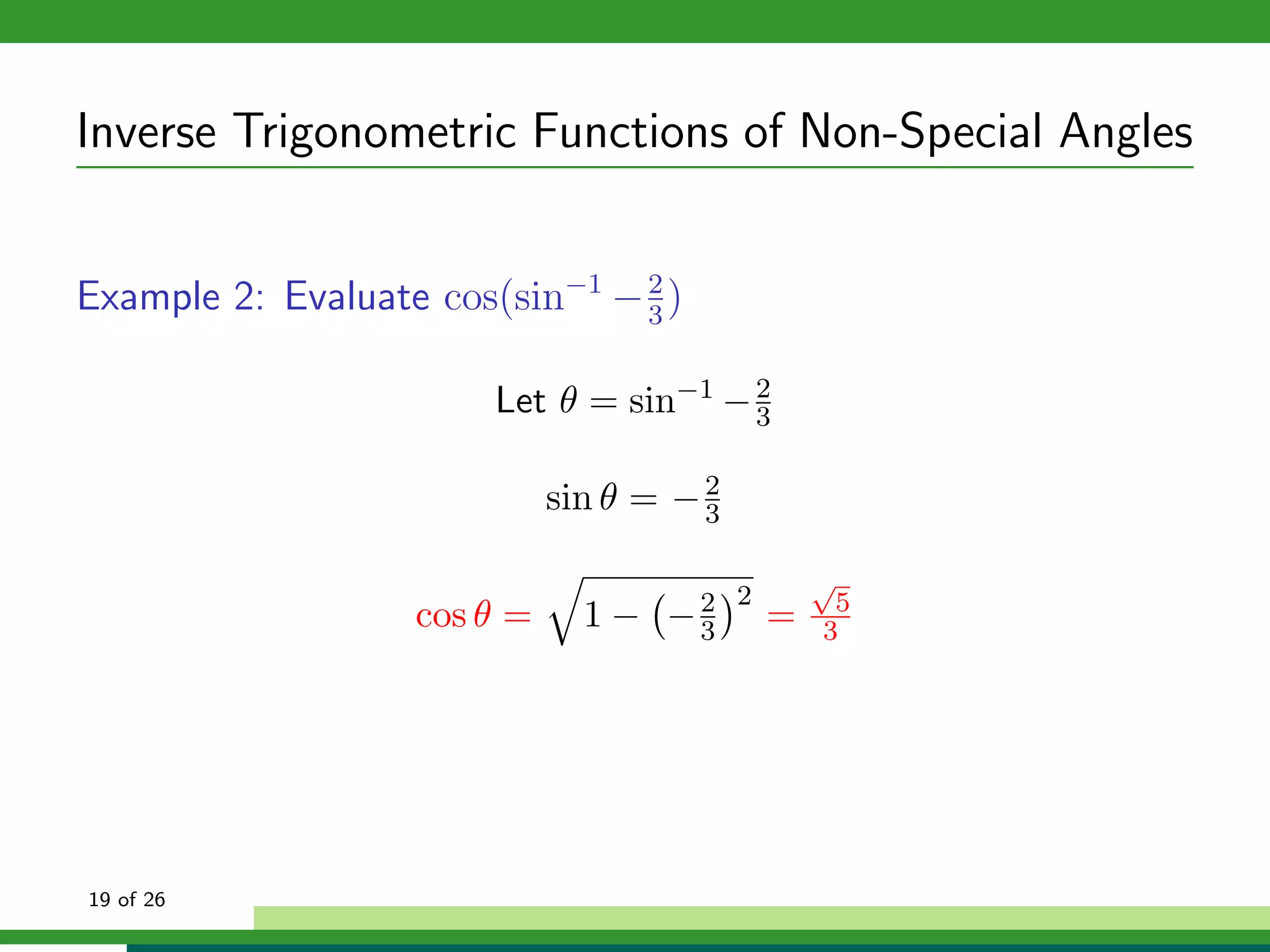
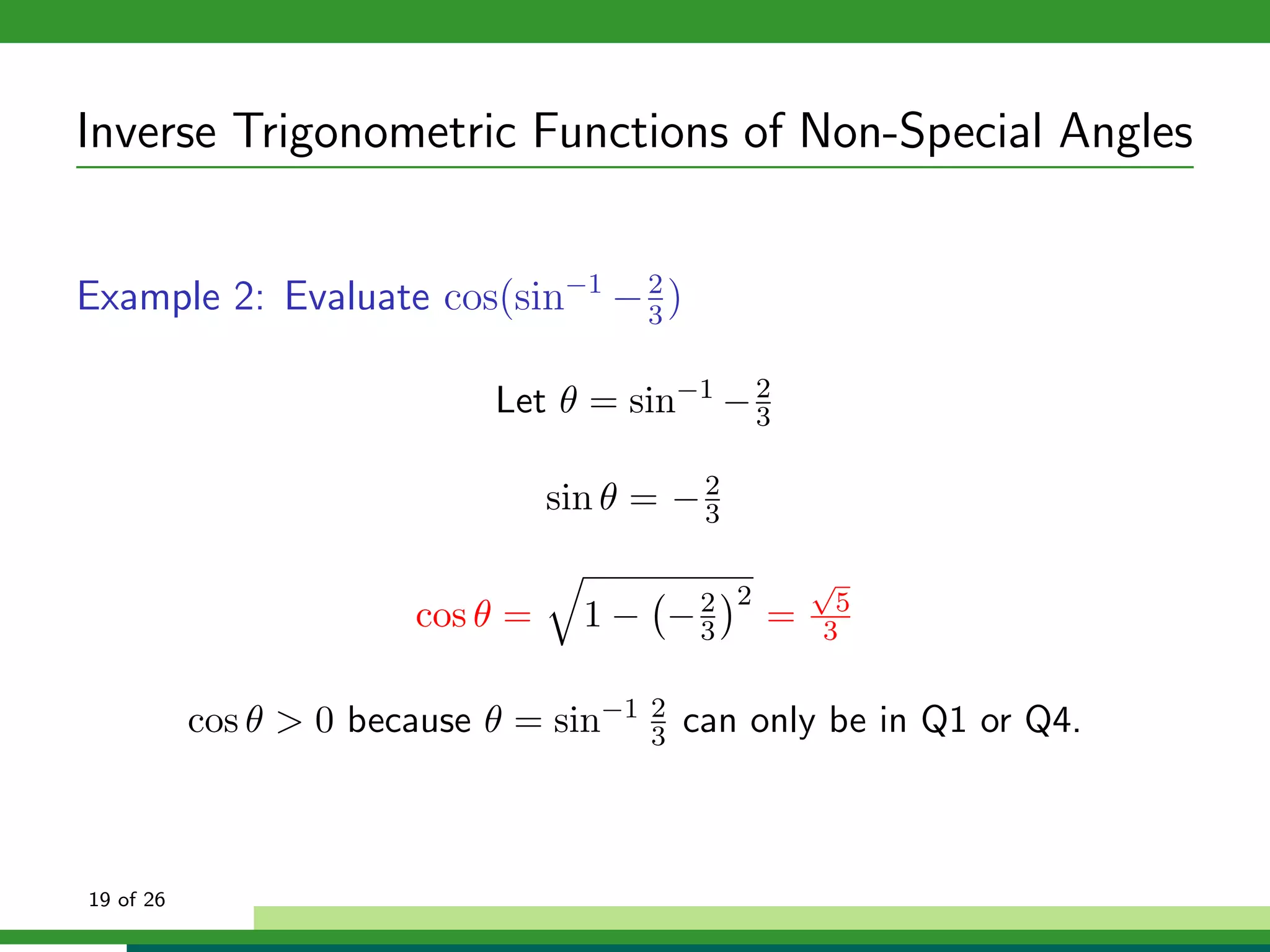
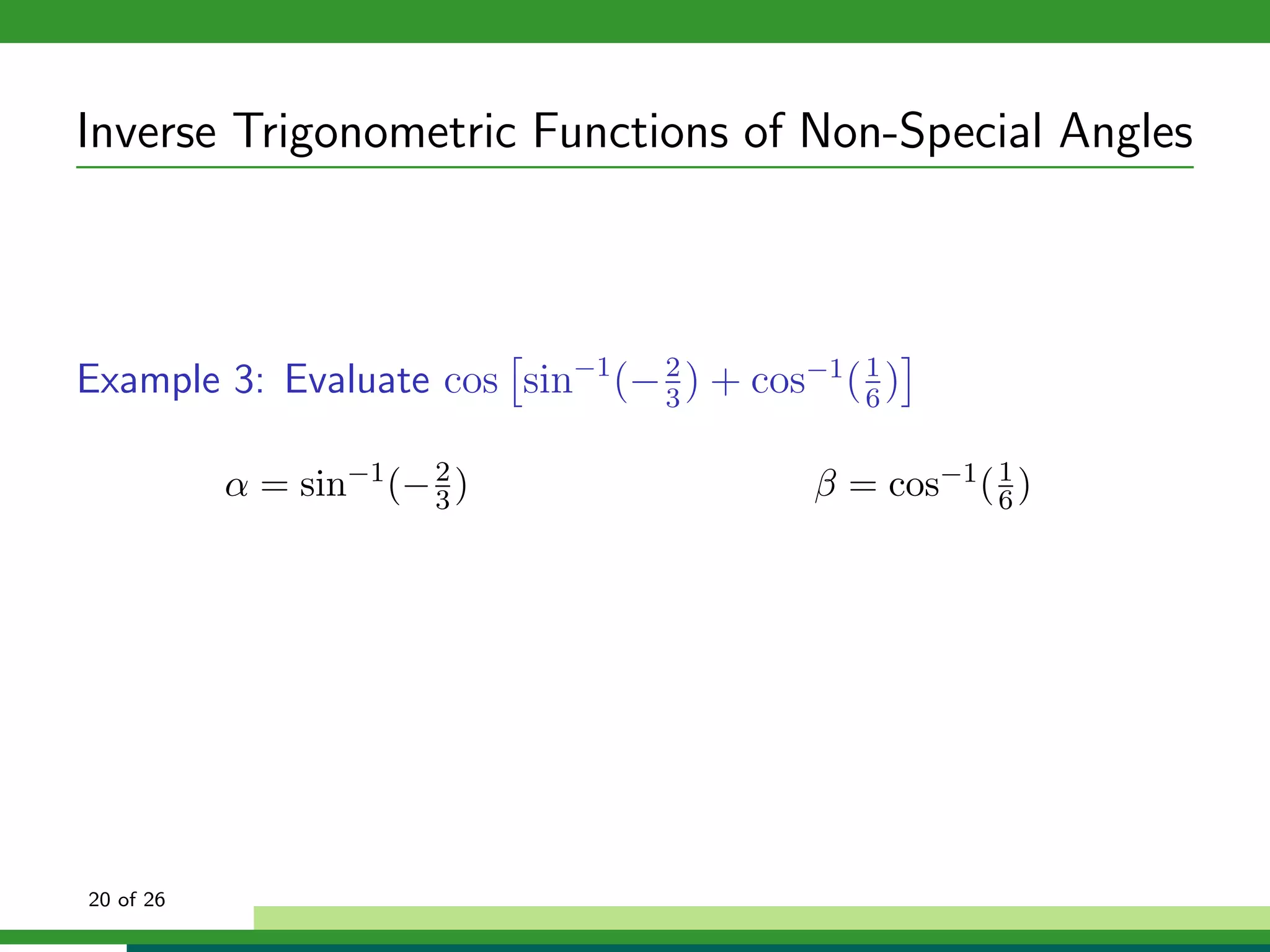
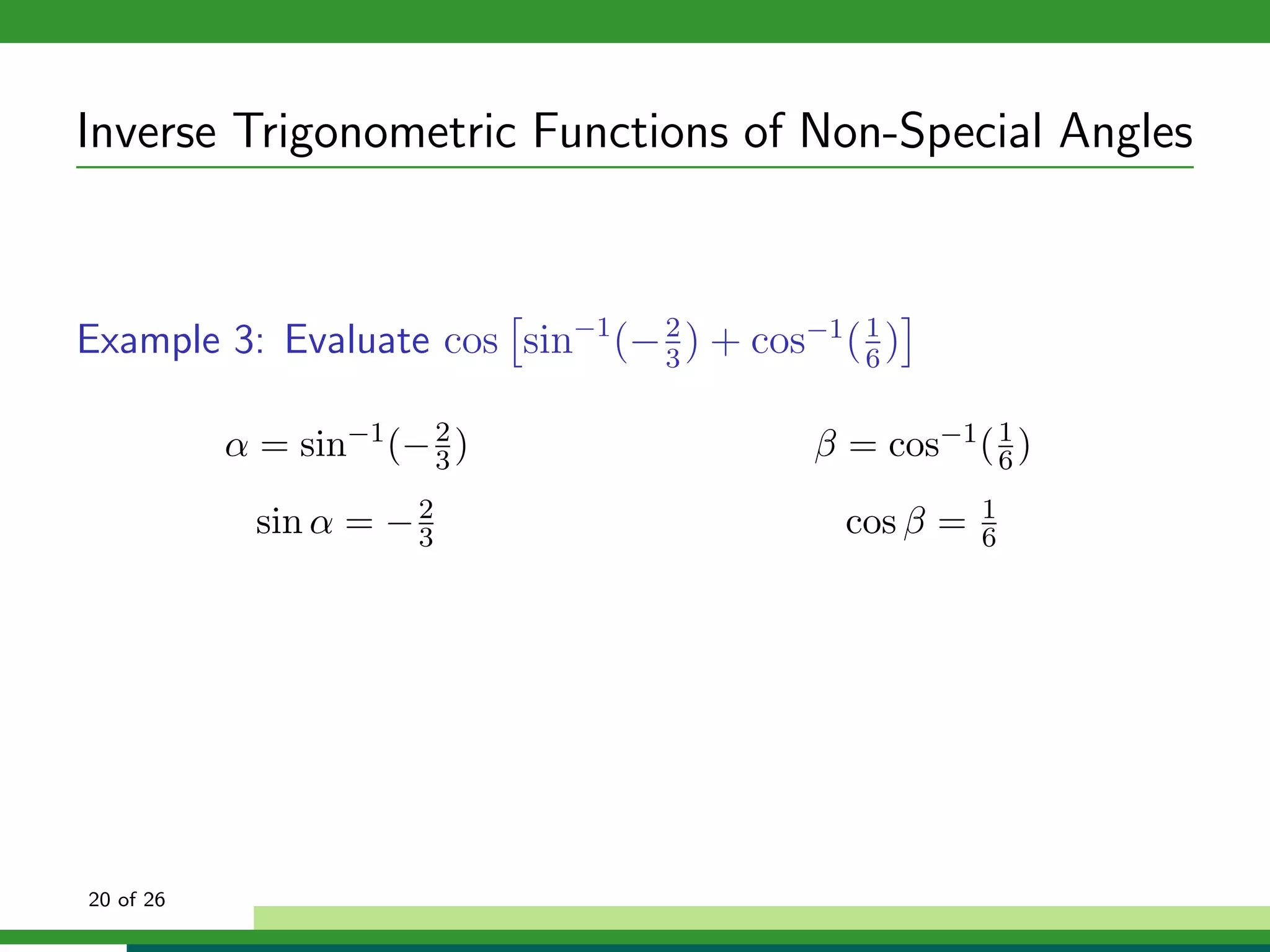
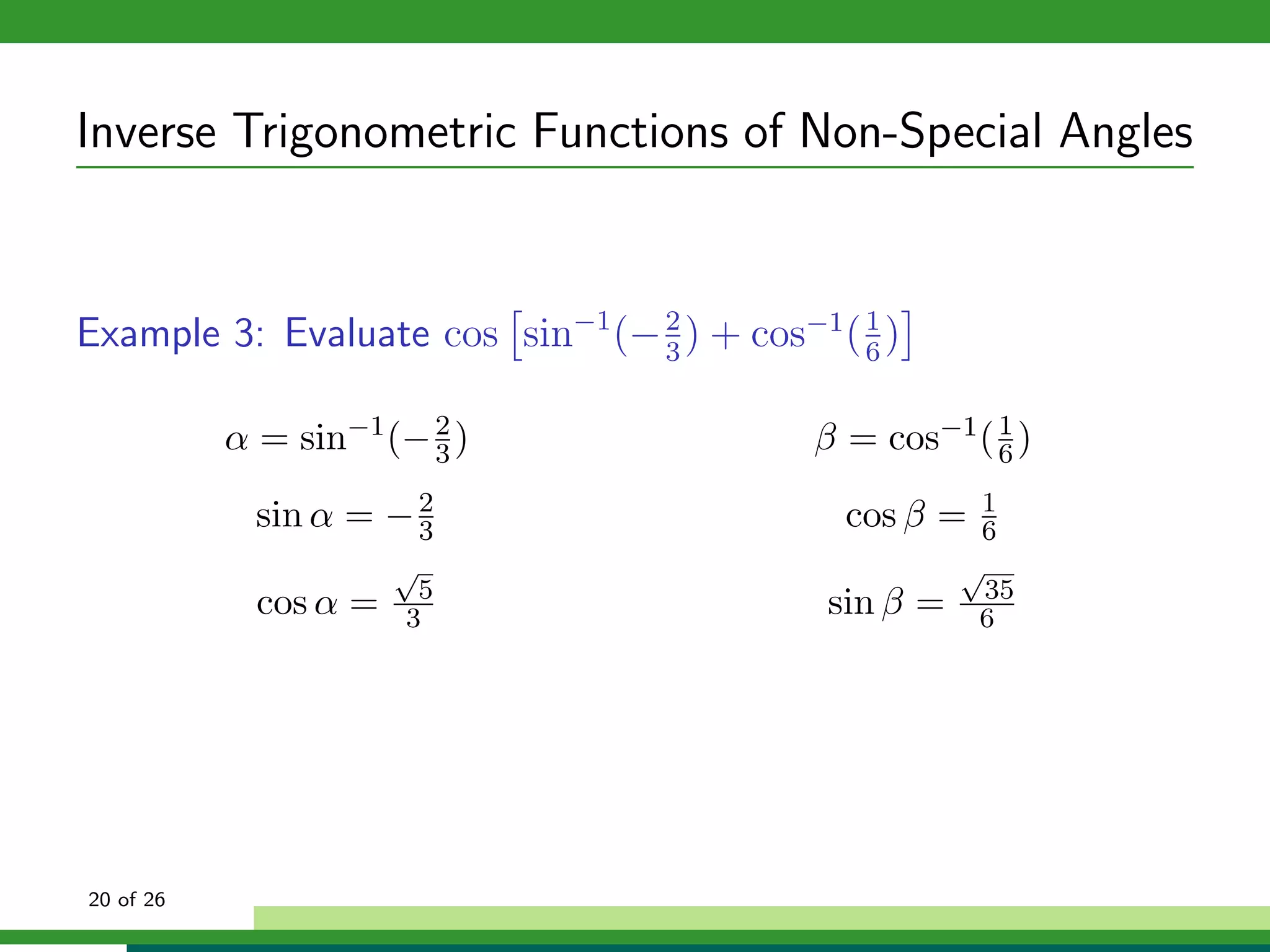
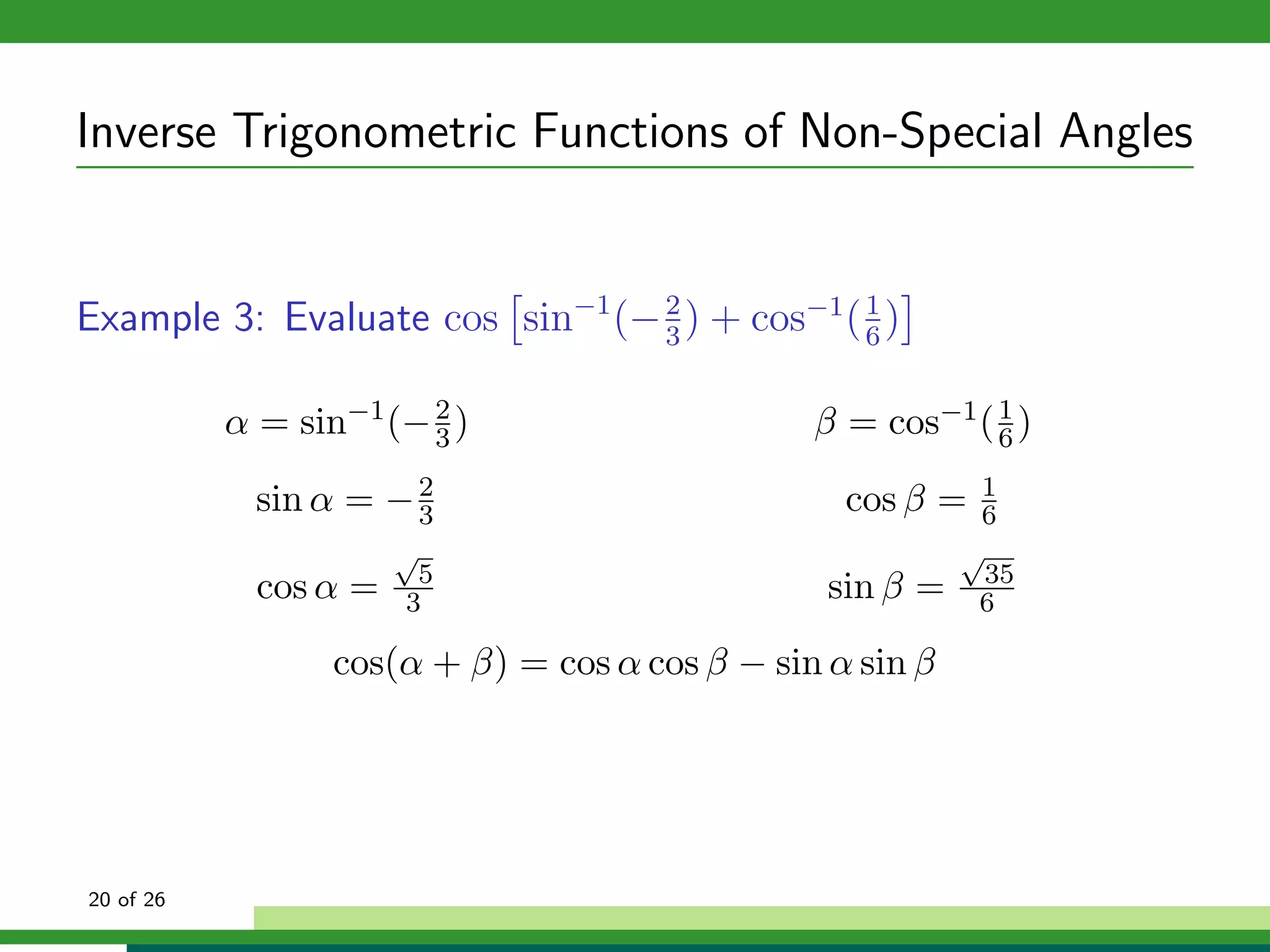
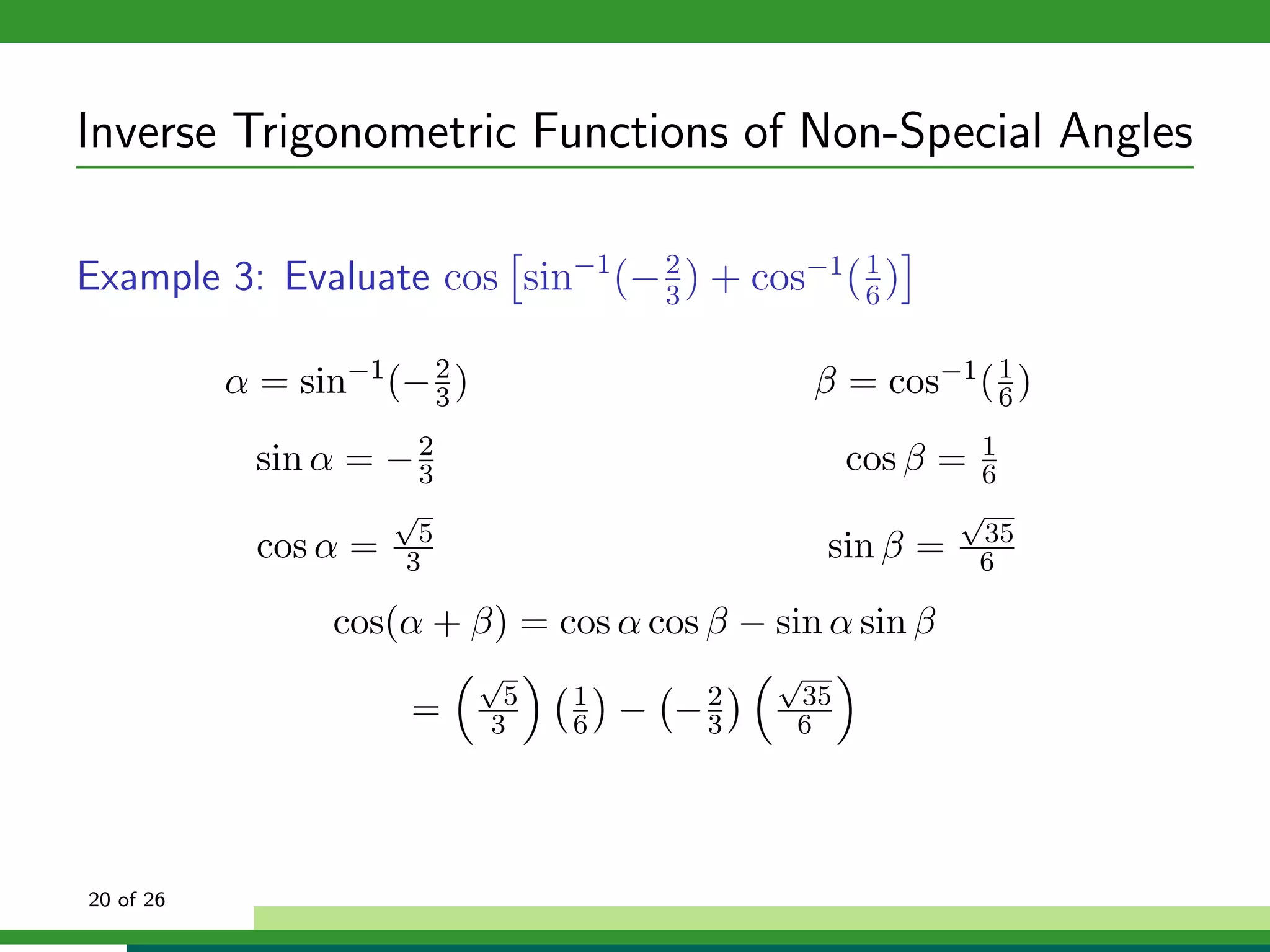
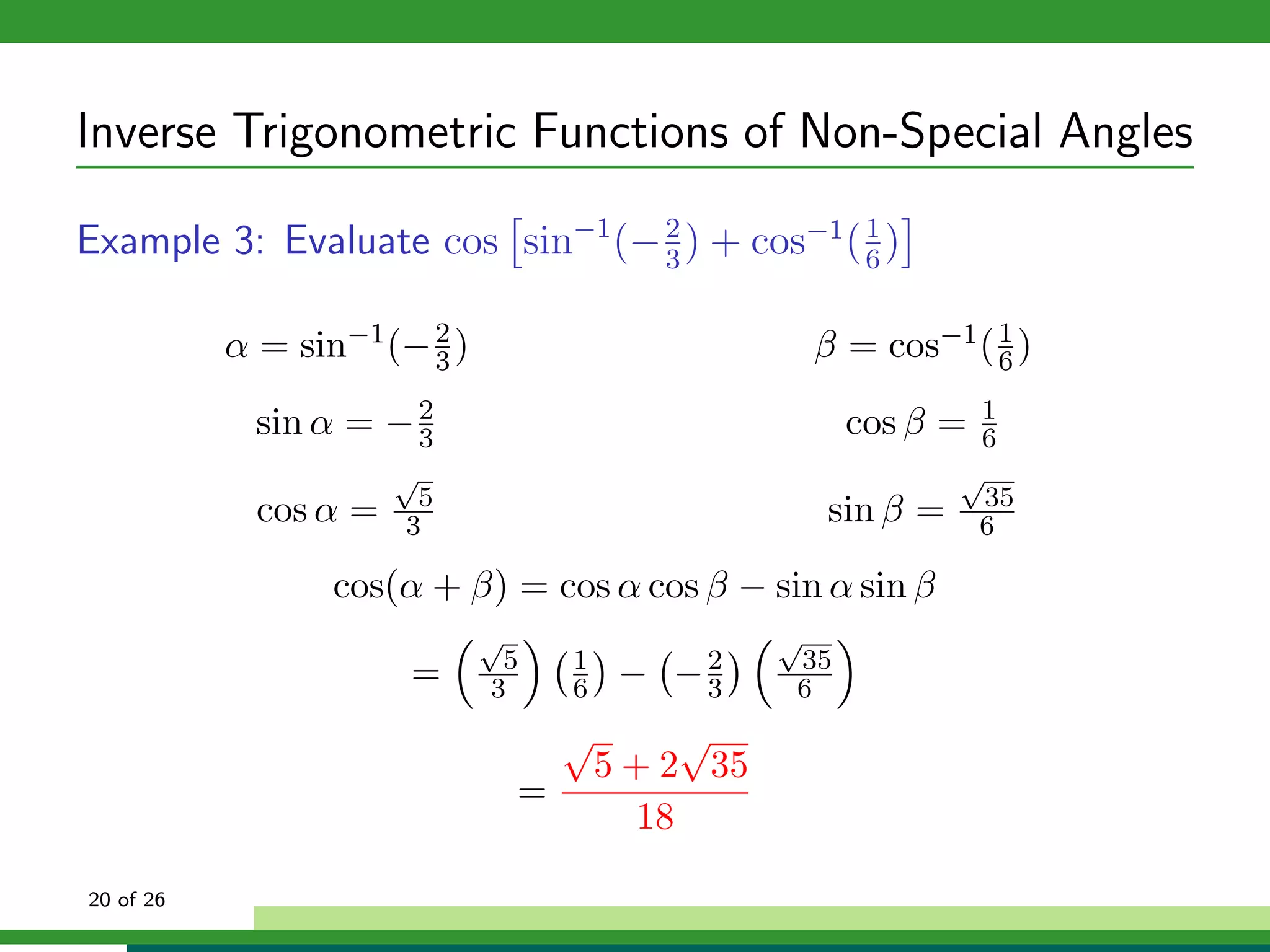
The document discusses inverse trigonometric functions. It defines the inverse sine function as sin^-1x = arcsin(x), with domain [-1,1] and range [-π/2, π/2]. It provides examples of evaluating inverse trig functions like sin^-1(1/2) = π/6. The inverse cosine function is similarly defined as cos^-1x = arccos(x), with domain [-1,1] and range [0,π]. The document concludes with a short quiz evaluating inverse trig expressions.

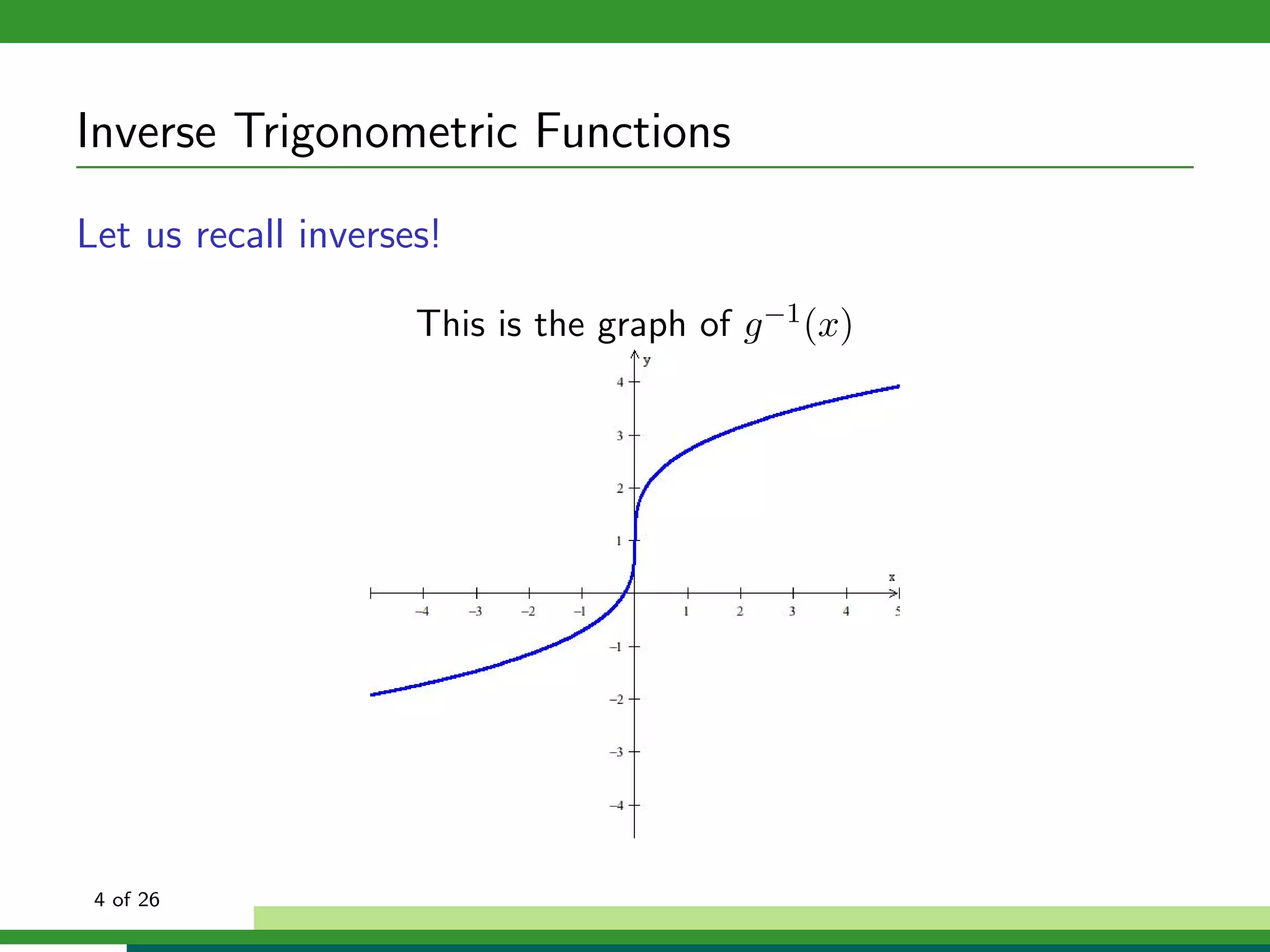
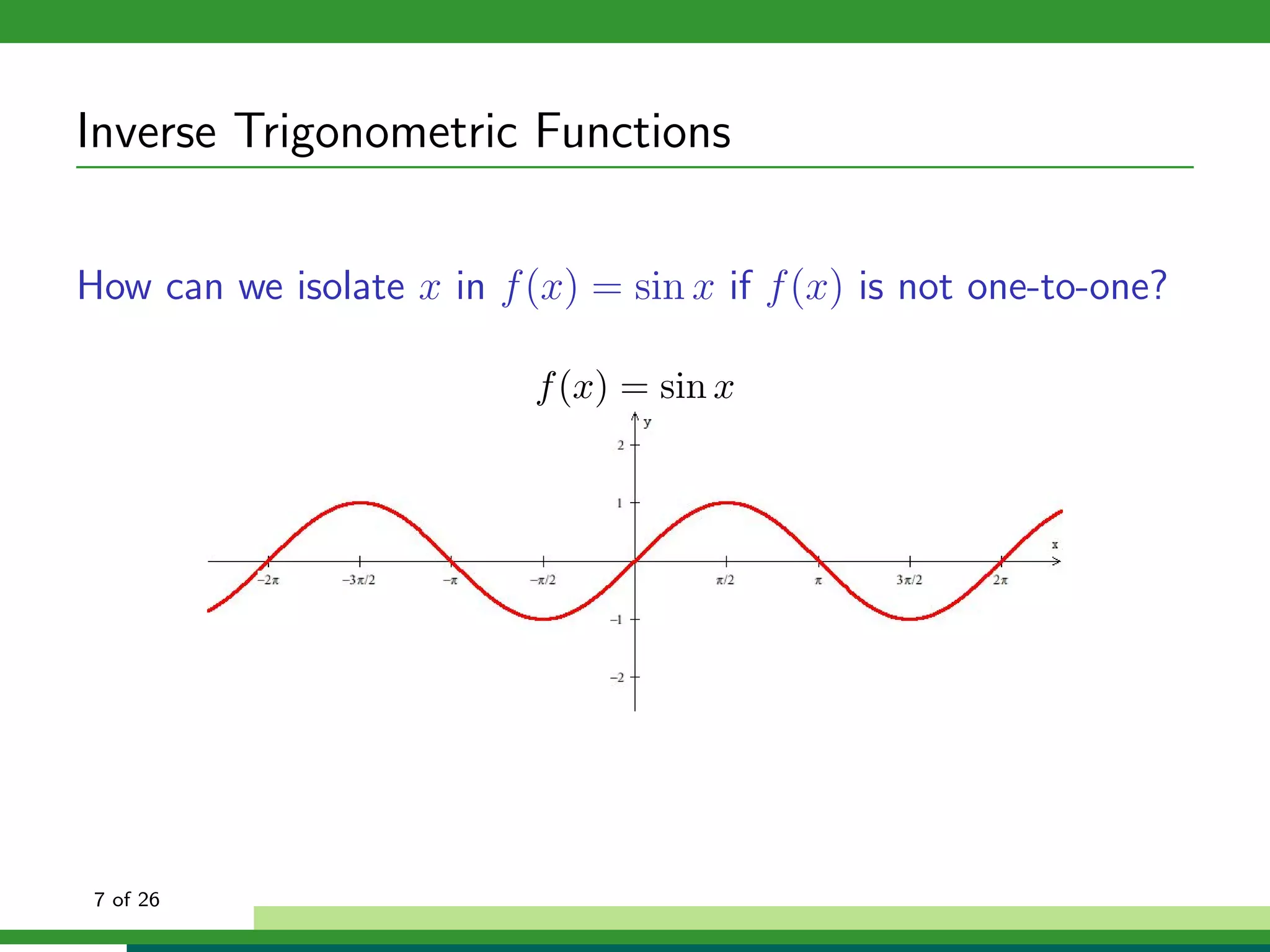
![Inverse Trigonometric Functions
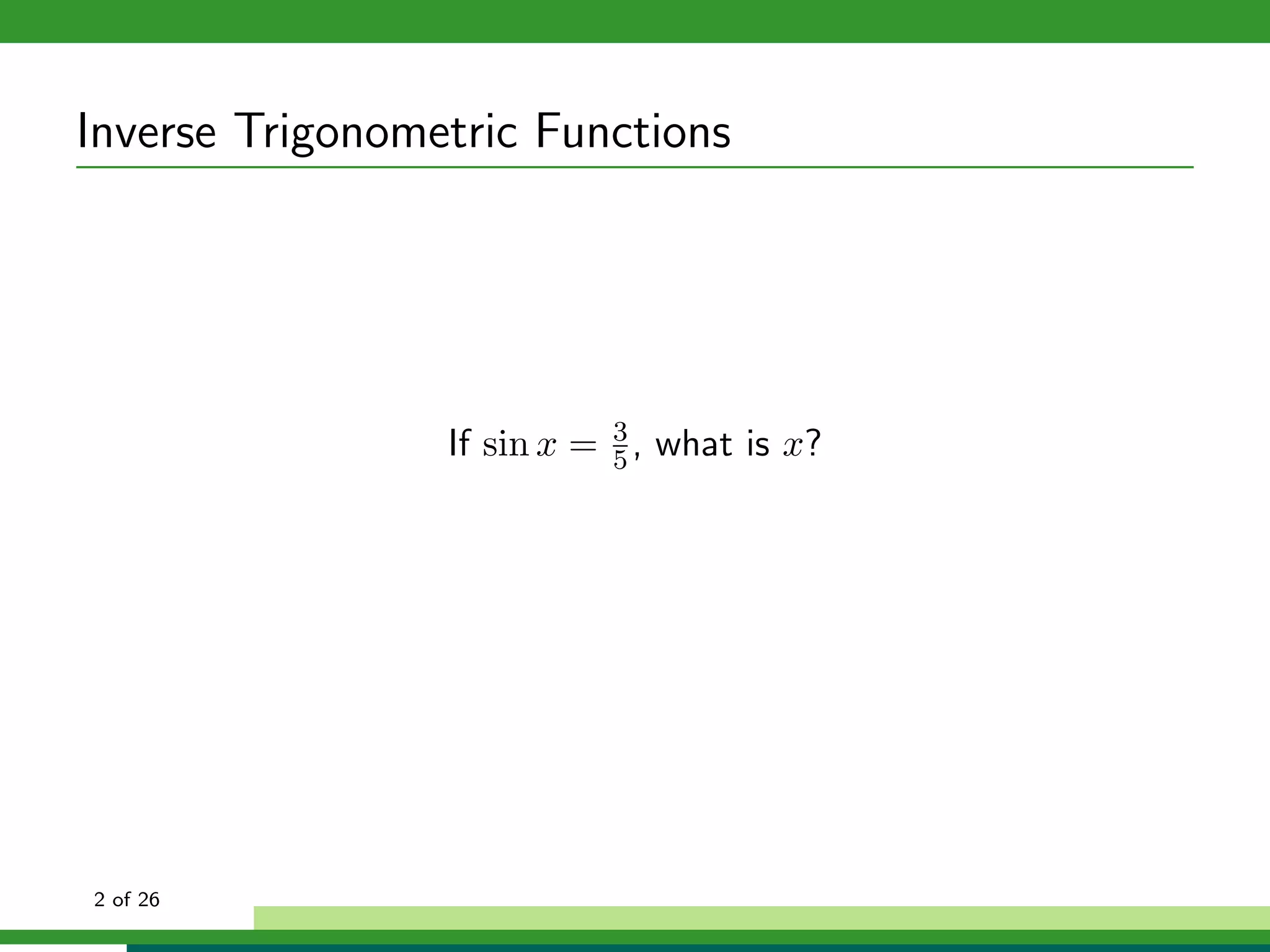
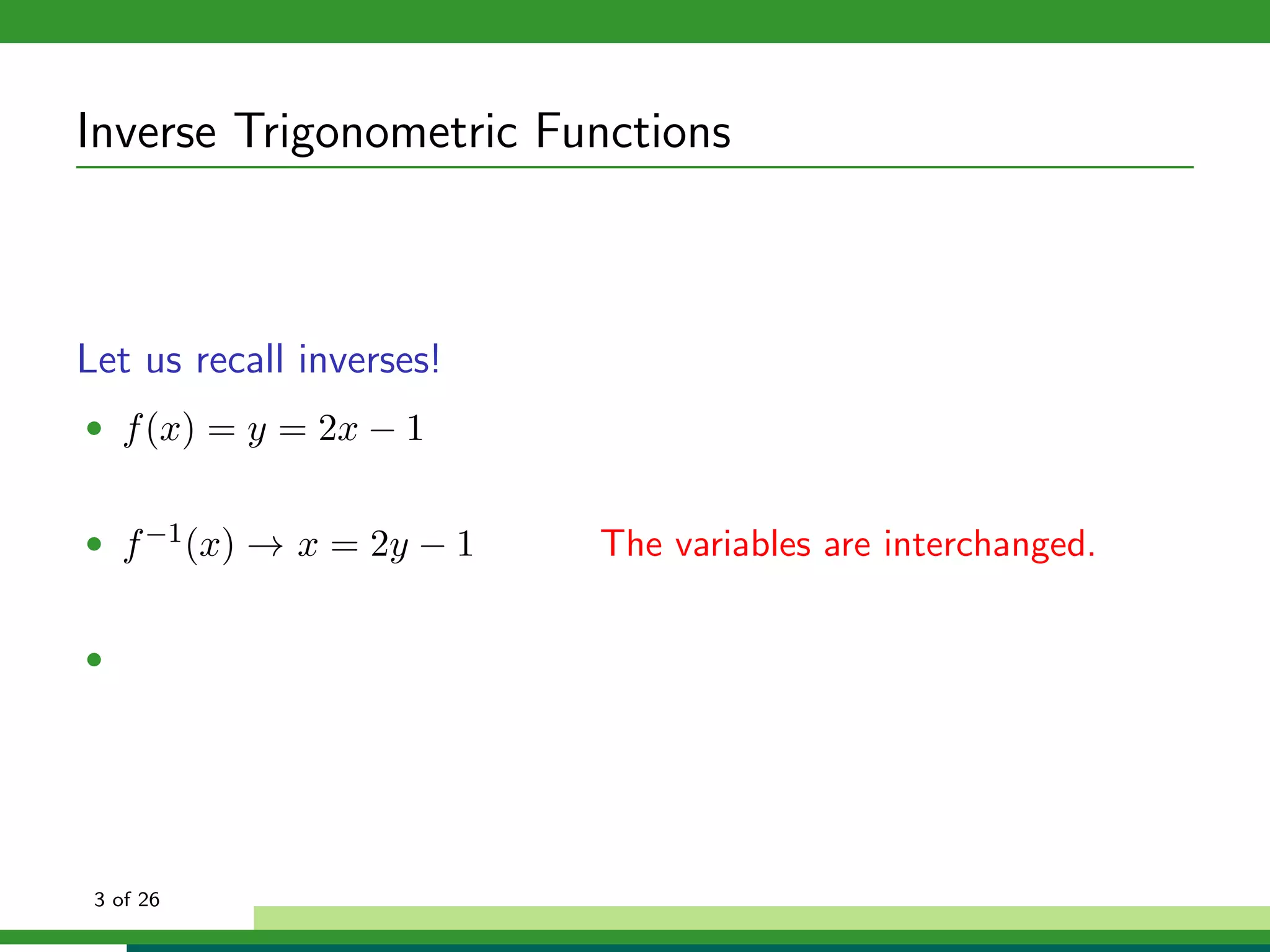
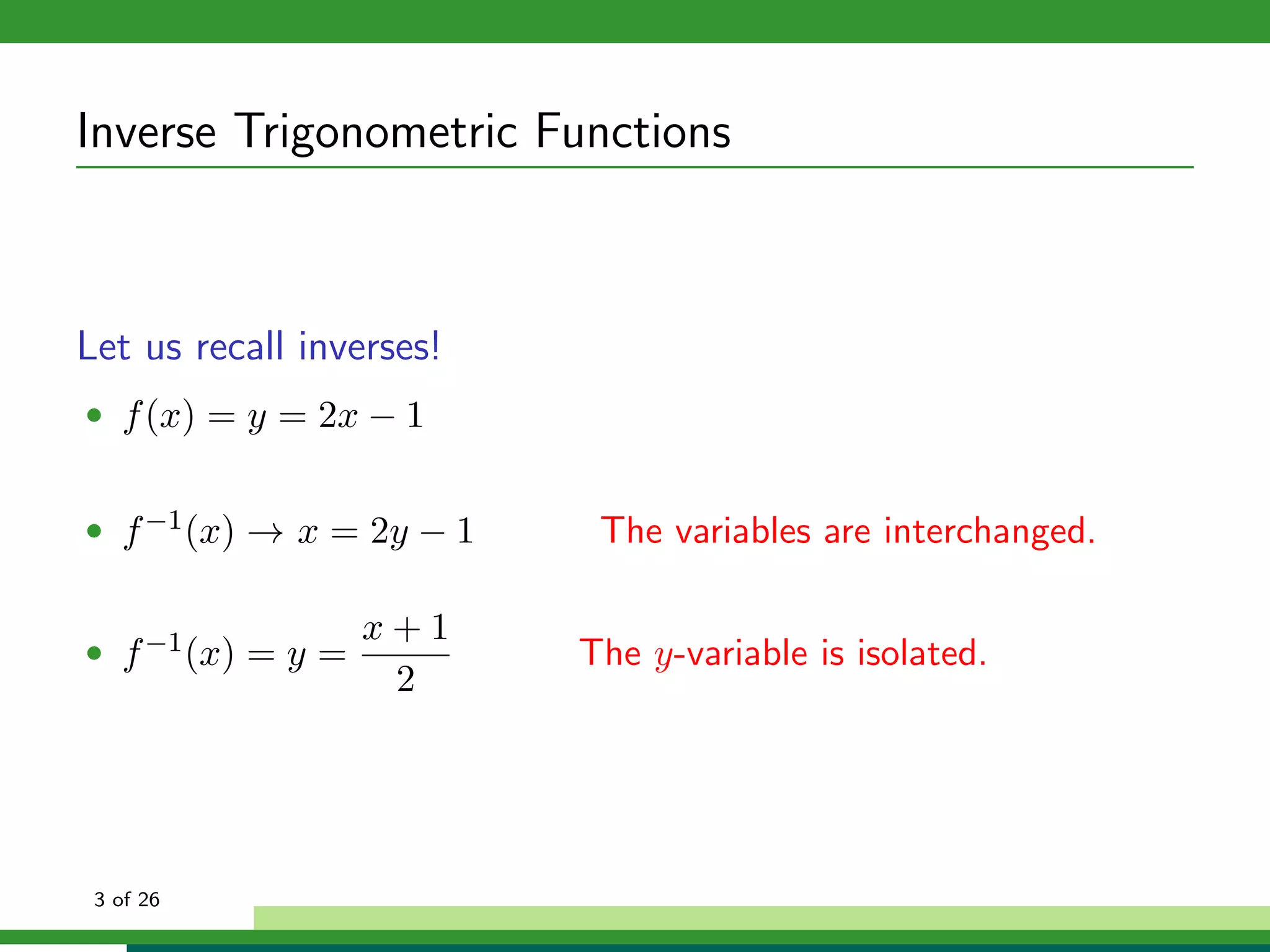
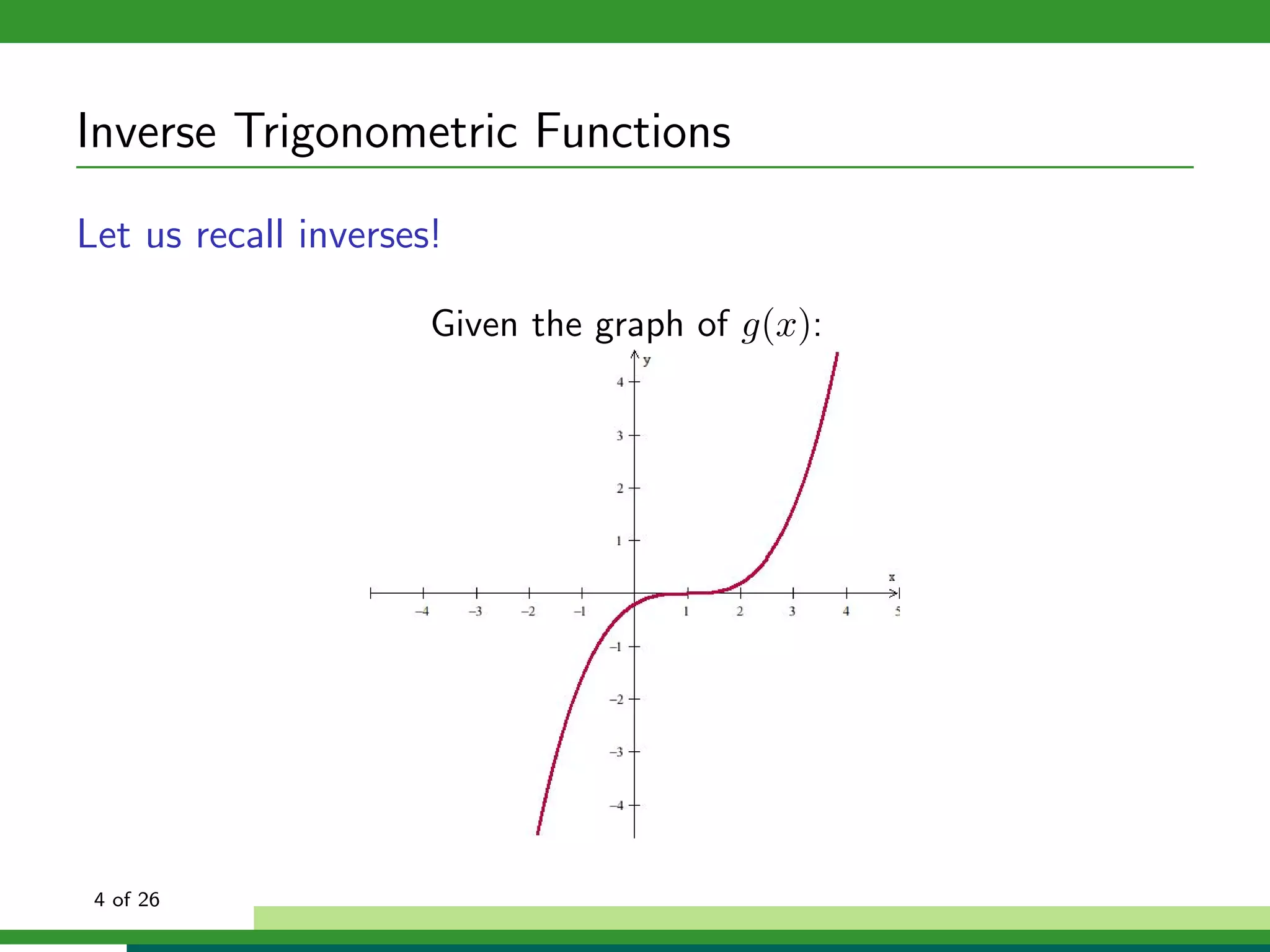
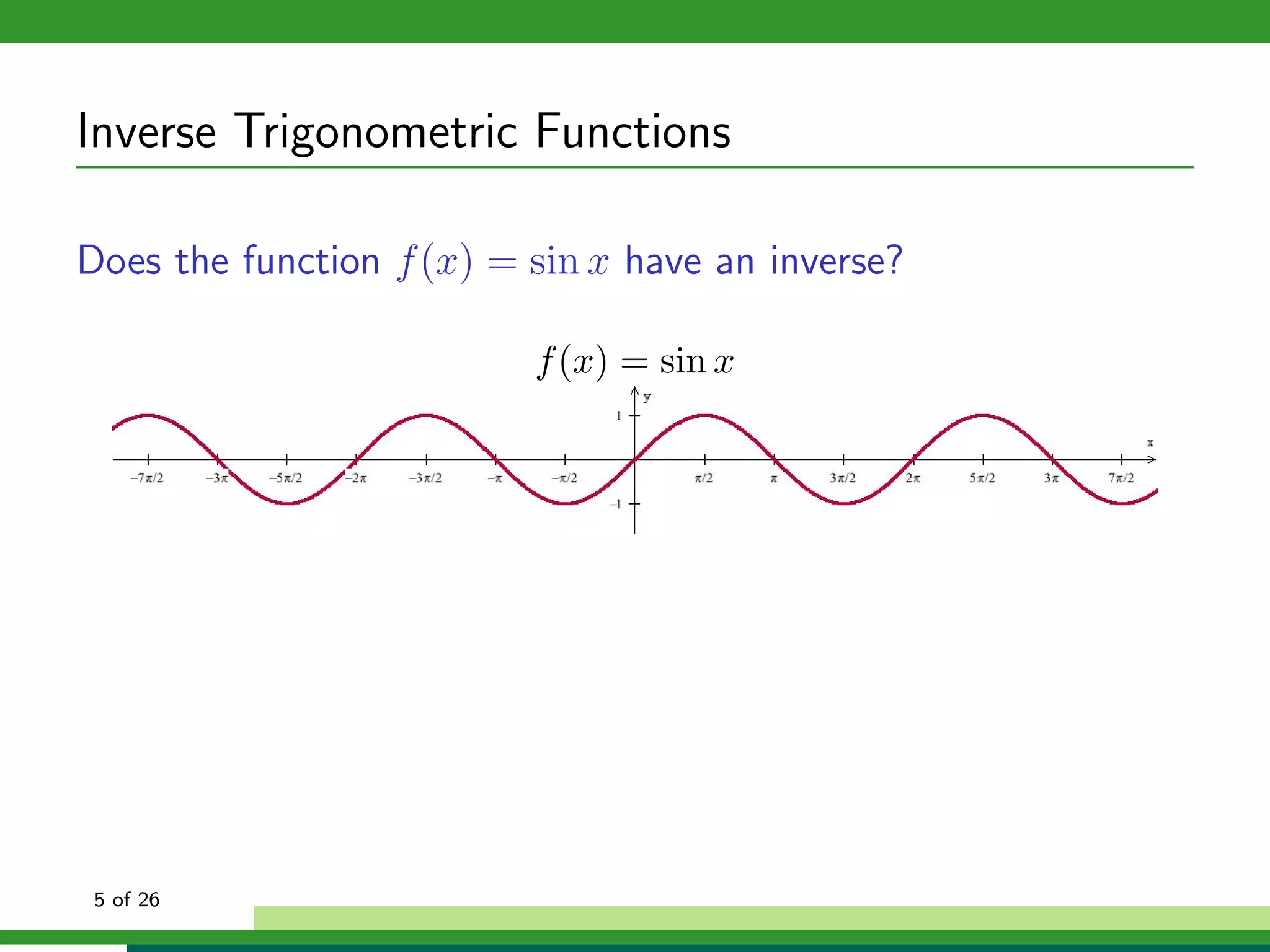
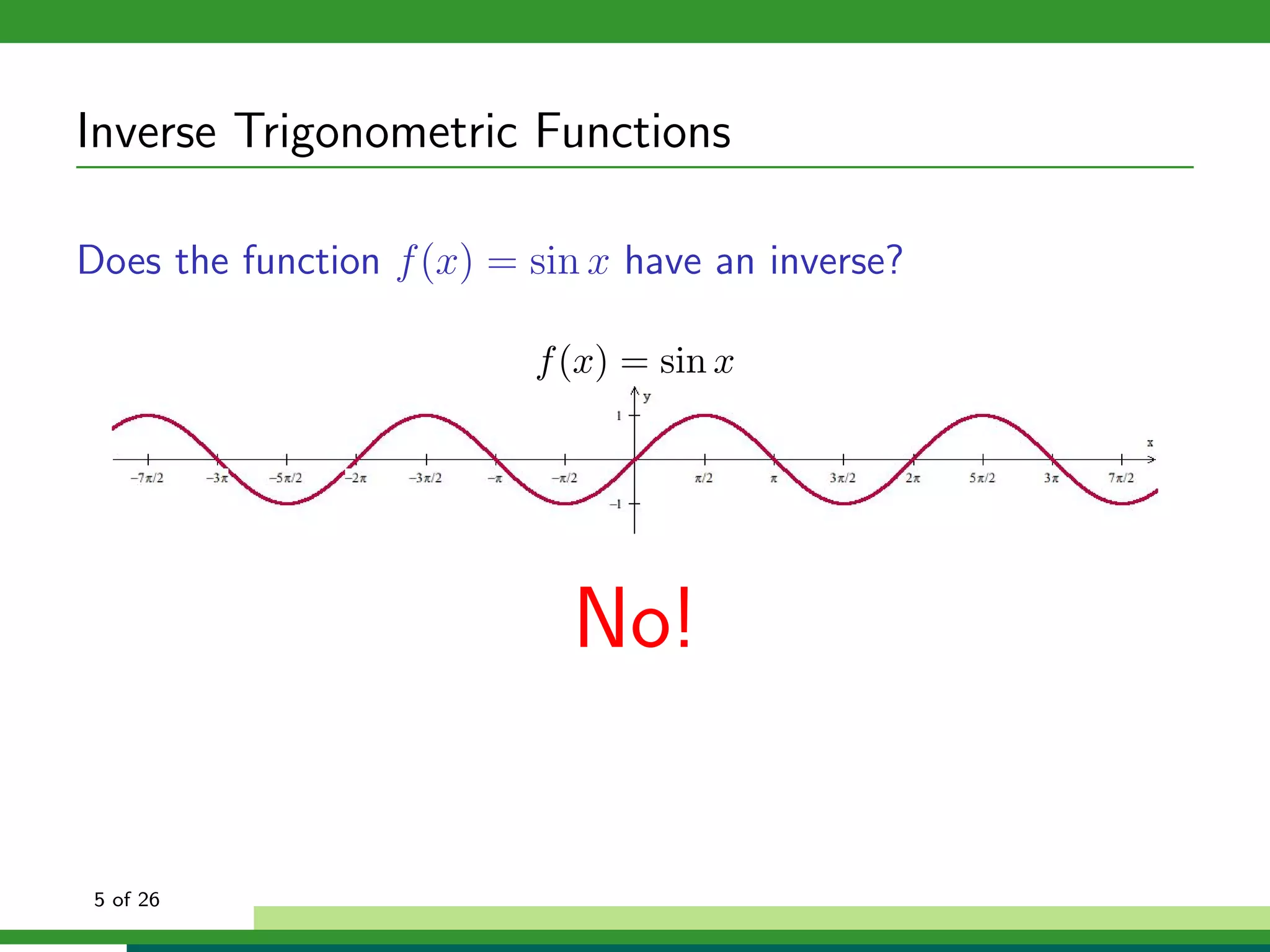
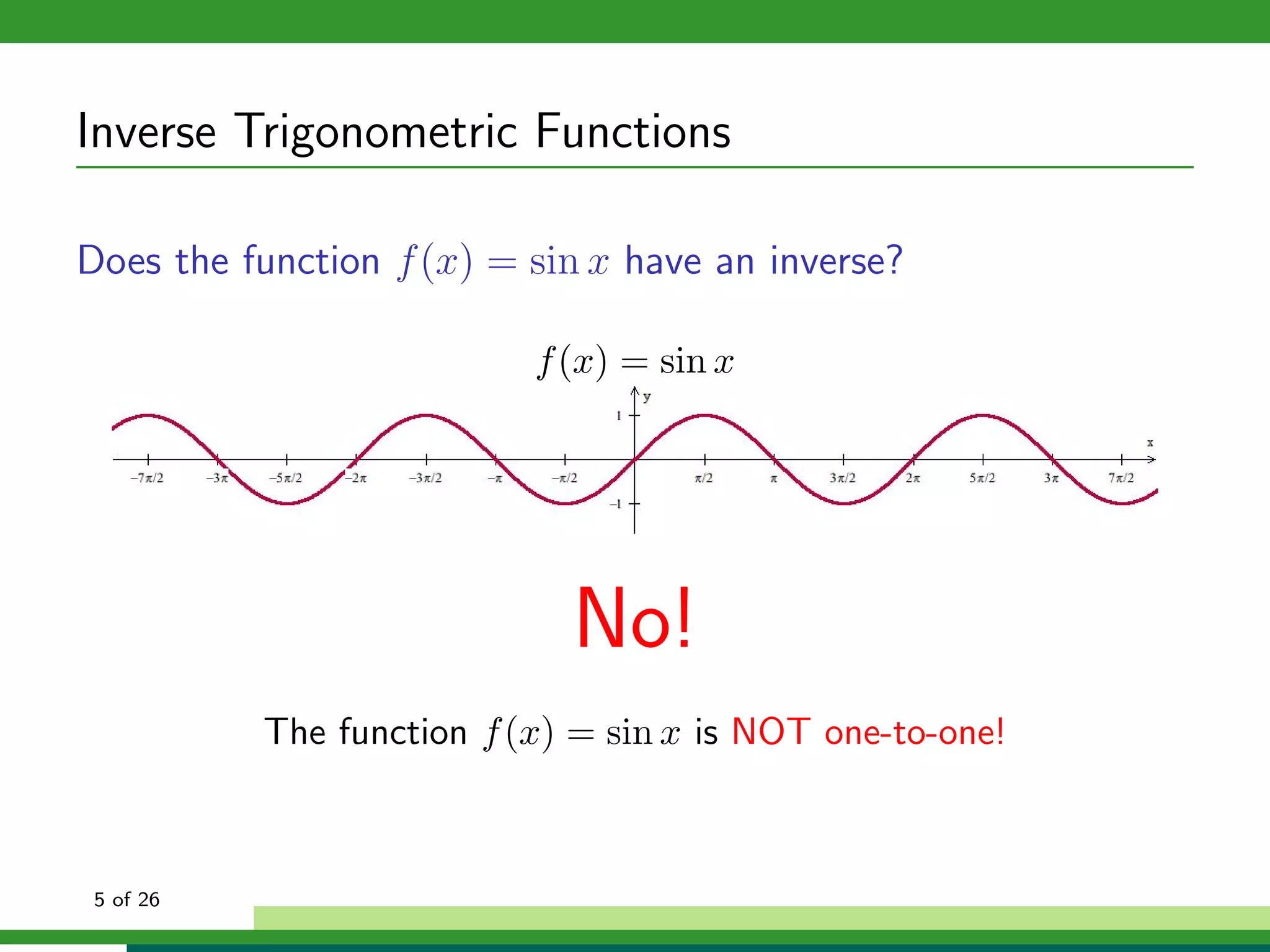
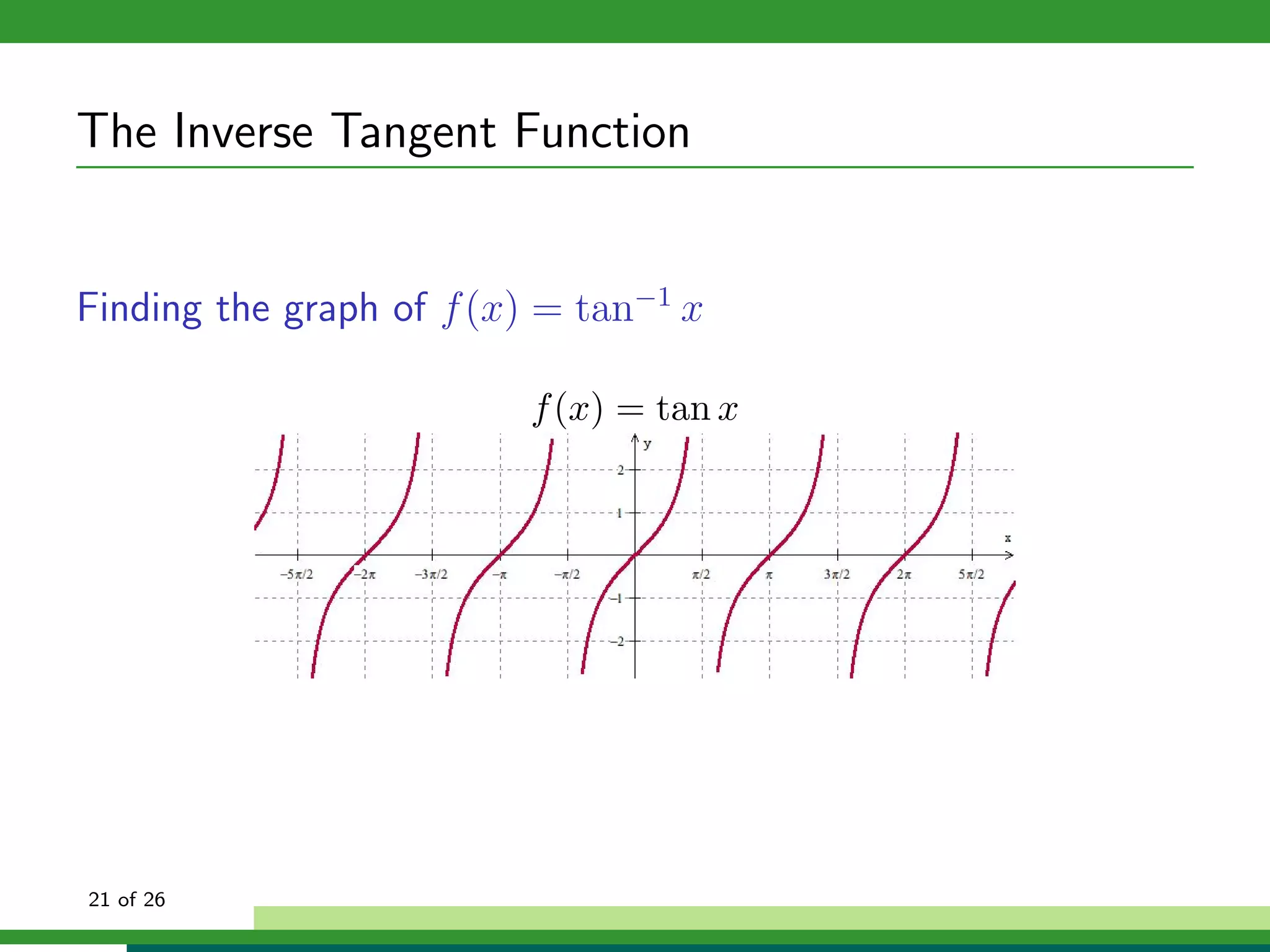
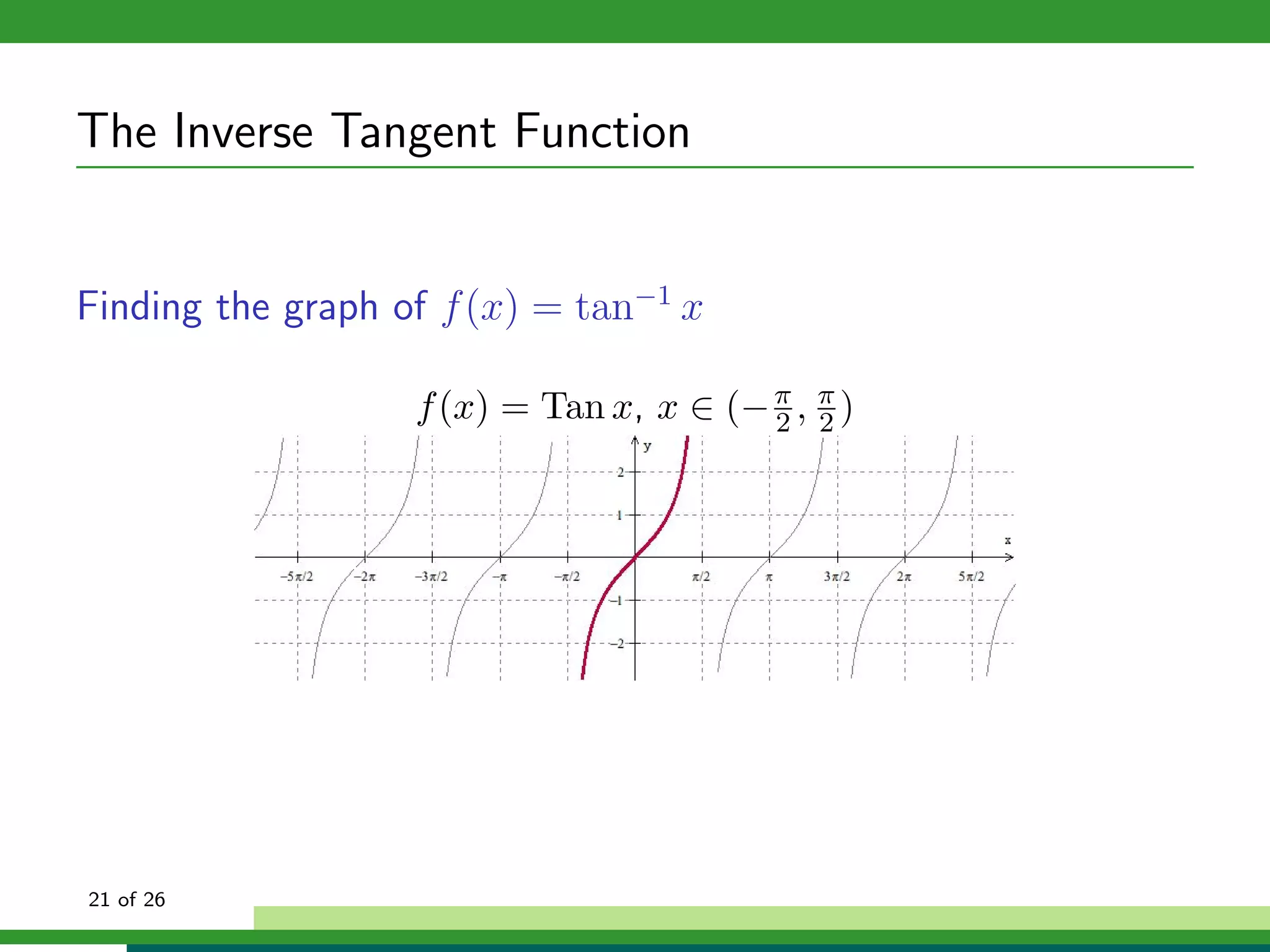
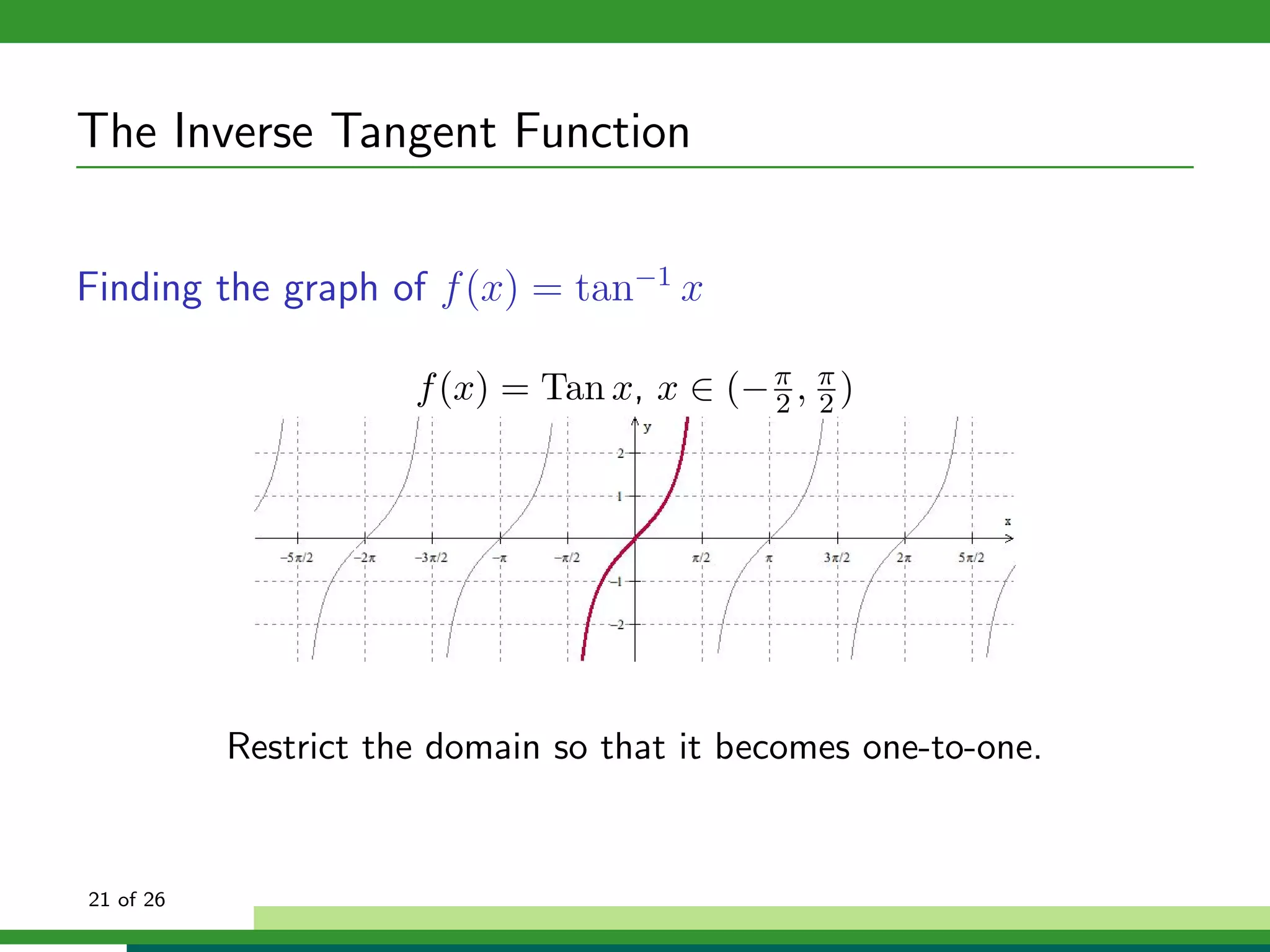
How can we isolate x in f (x) = sin x if f (x) is not one-to-one?
f (x) = Sin x, x ∈ [− π , π ]
2 2
7 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversetrigonometricfunctions-111028194453-phpapp01/75/Inverse-trigonometric-functions-19-2048.jpg)
![Inverse Trigonometric Functions
How can we isolate x in f (x) = sin x if f (x) is not one-to-one?
f (x) = Sin x, x ∈ [− π , π ]
2 2
Restrict the domain so that it becomes one-to-one.
7 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversetrigonometricfunctions-111028194453-phpapp01/75/Inverse-trigonometric-functions-20-2048.jpg)
![Inverse Trigonometric Functions
The inverse of f (x) = Sin x, x ∈ [− π , π ]
2 2
f (x) = Sin x, x ∈ [− π , π ]
2 2
8 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversetrigonometricfunctions-111028194453-phpapp01/75/Inverse-trigonometric-functions-21-2048.jpg)
![Inverse Trigonometric Functions
The inverse of f (x) = Sin x, x ∈ [− π , π ]
2 2
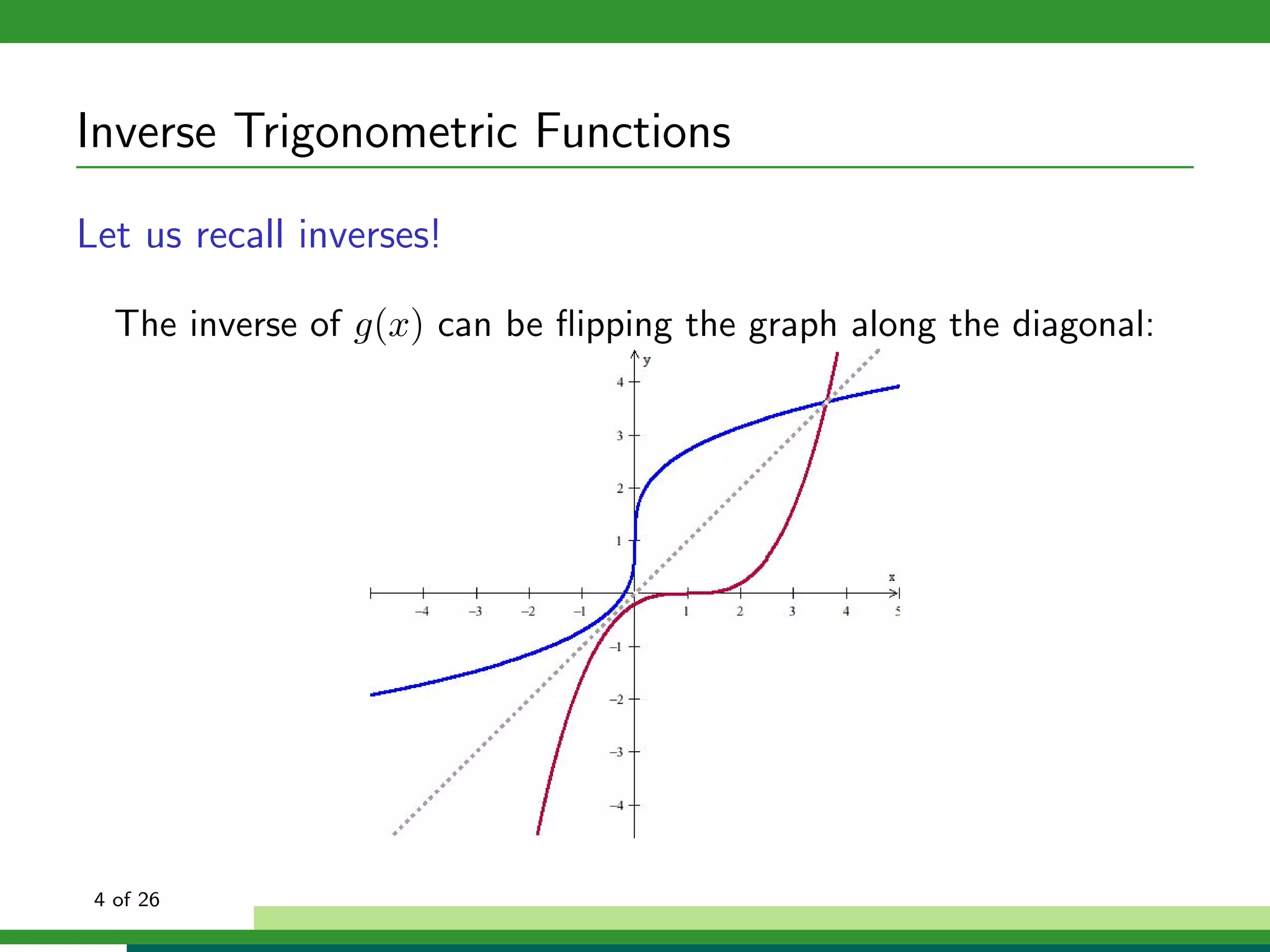
Find the graph of the inverse by flipping along the diagonal
8 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversetrigonometricfunctions-111028194453-phpapp01/75/Inverse-trigonometric-functions-22-2048.jpg)
![Inverse Trigonometric Functions
The inverse of f (x) = Sin x, x ∈ [− π , π ]
2 2
f (x) = sin−1 x = Arcsin x = inverse sine of x
8 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversetrigonometricfunctions-111028194453-phpapp01/75/Inverse-trigonometric-functions-23-2048.jpg)
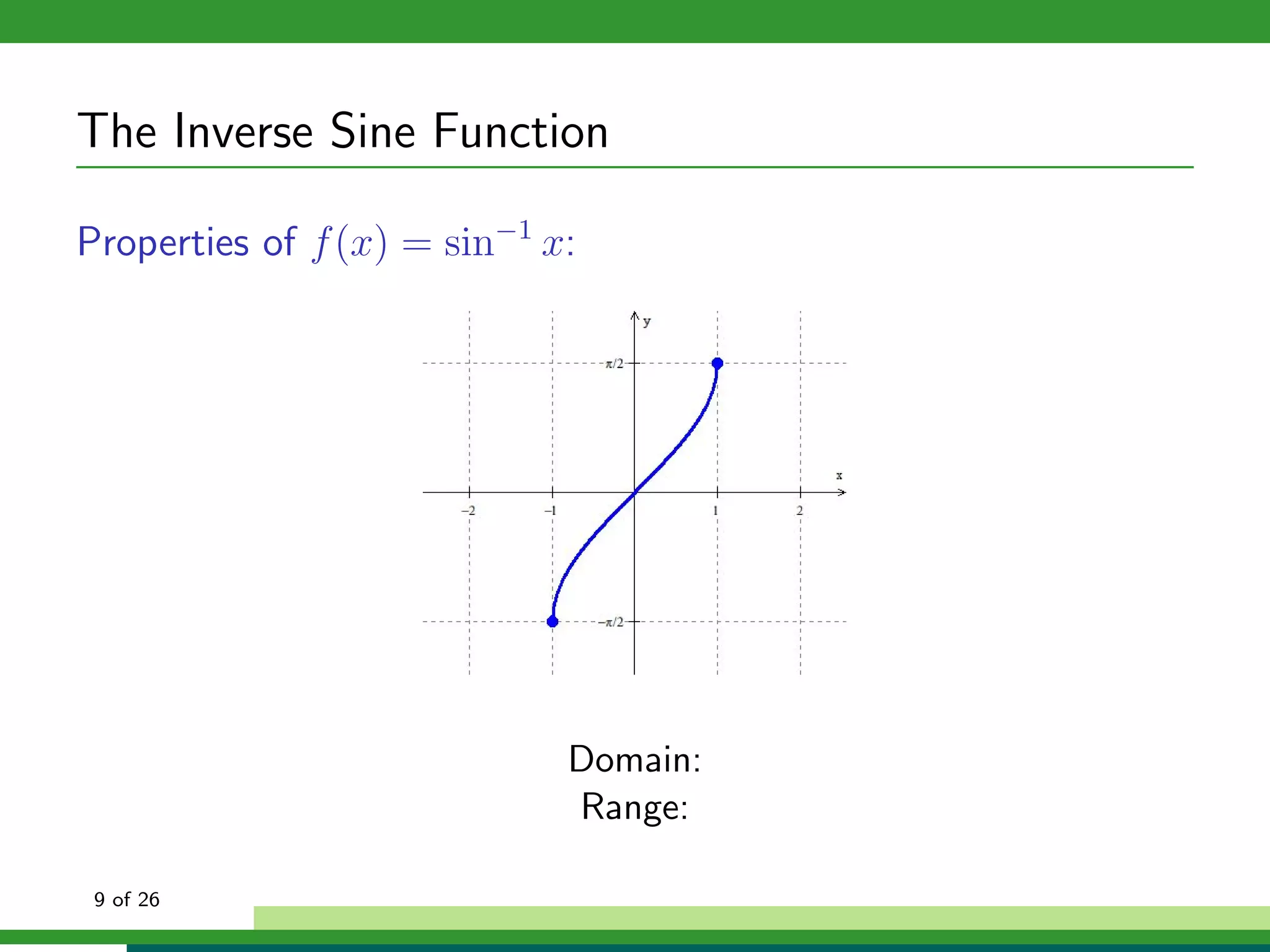
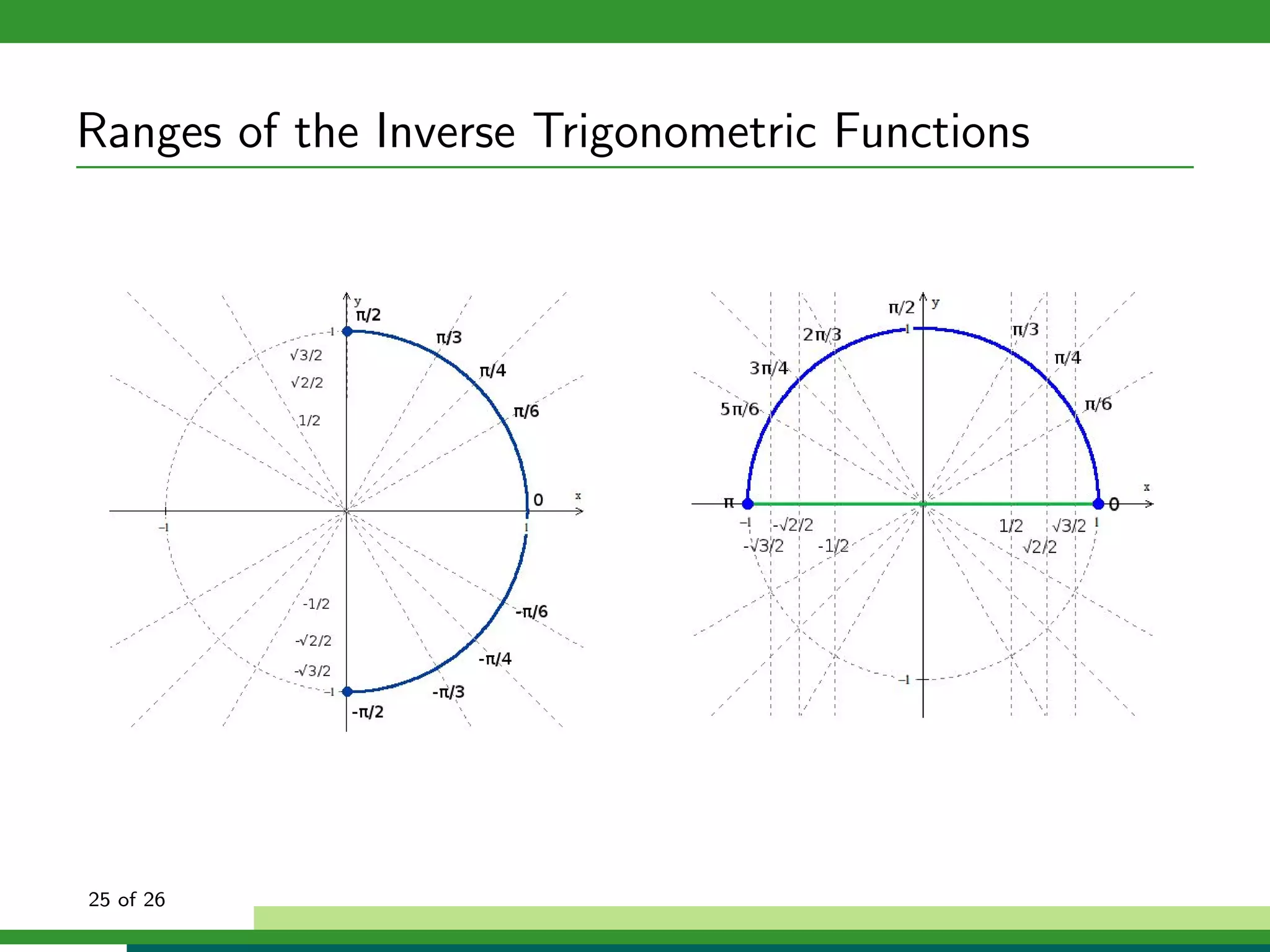
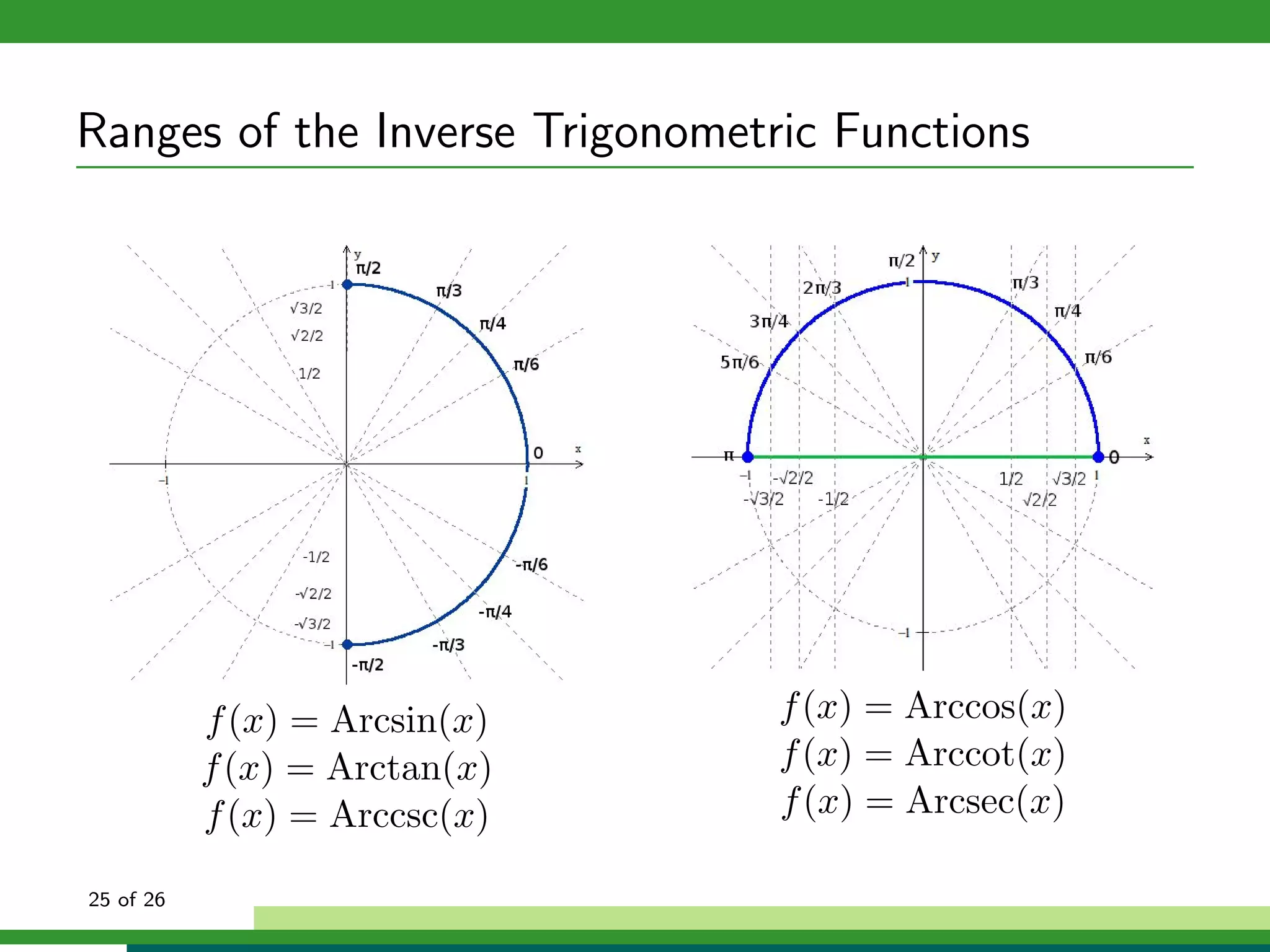
![The Inverse Sine Function
Properties of f (x) = sin−1 x:
Domain: x ∈ [−1, 1]
Range:
9 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversetrigonometricfunctions-111028194453-phpapp01/75/Inverse-trigonometric-functions-25-2048.jpg)
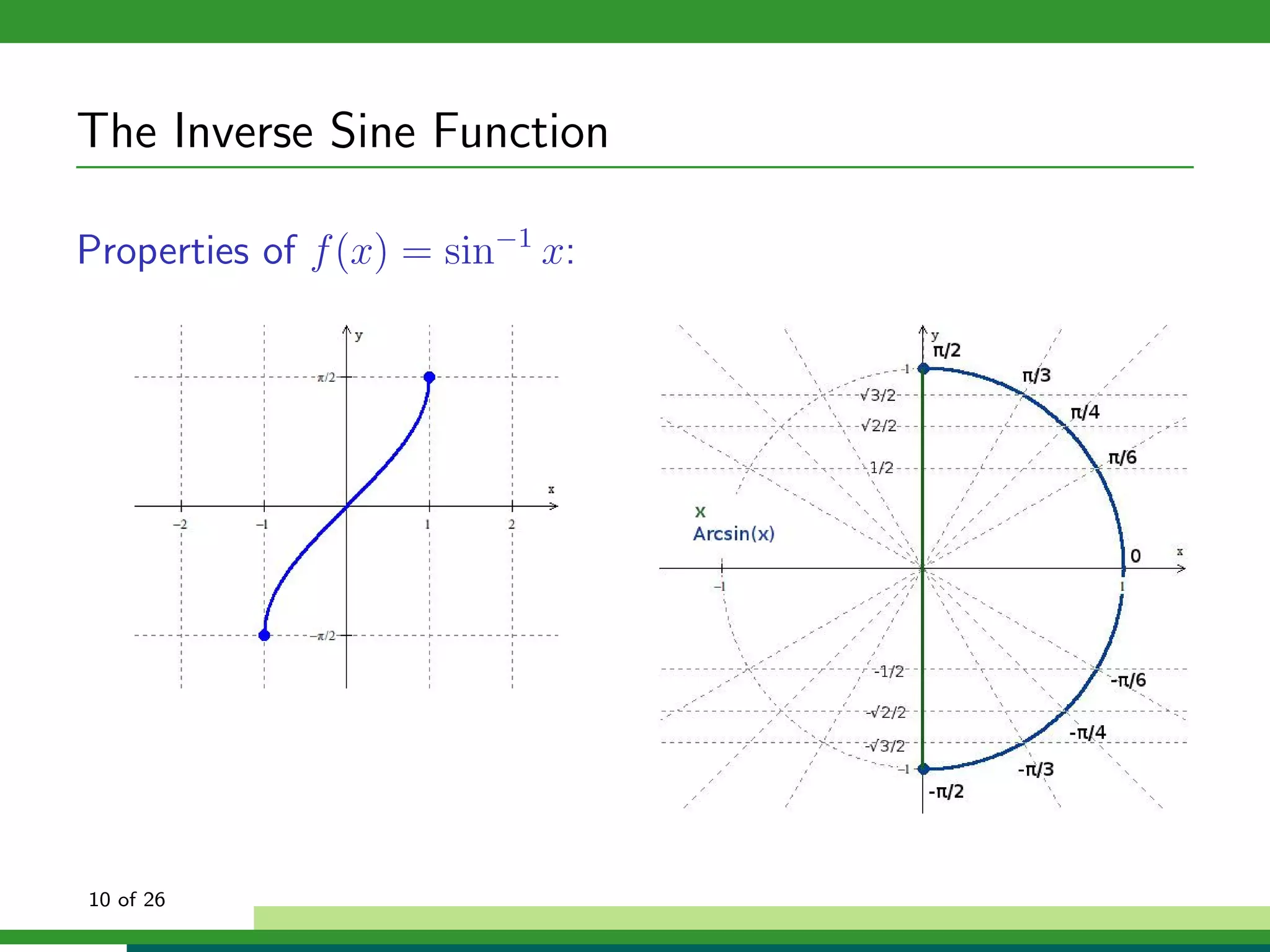
![The Inverse Sine Function
Properties of f (x) = sin−1 x:
Domain: x ∈ [−1, 1]
Range: y ∈ [− π , π ]
2 2
9 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversetrigonometricfunctions-111028194453-phpapp01/75/Inverse-trigonometric-functions-26-2048.jpg)
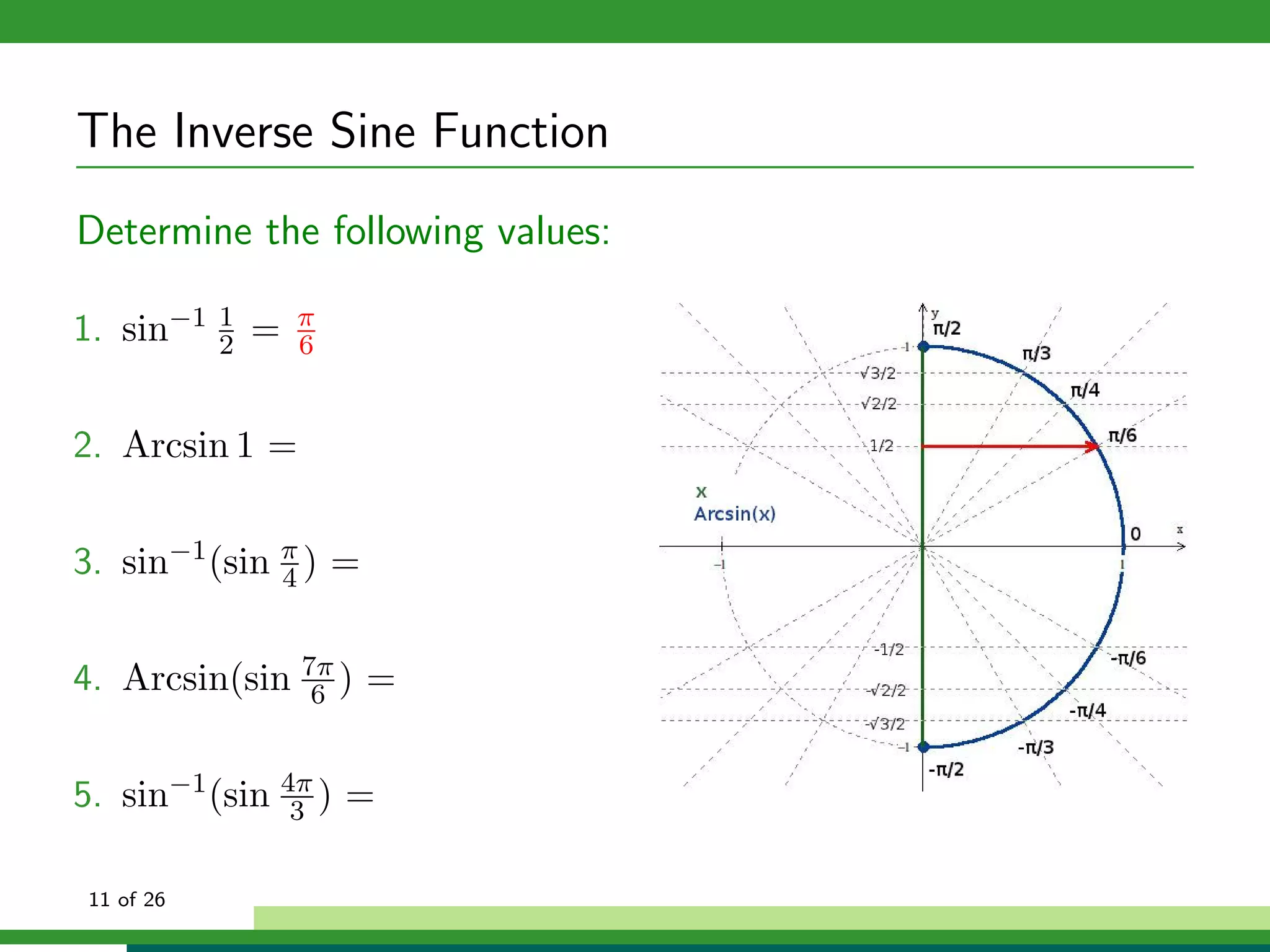
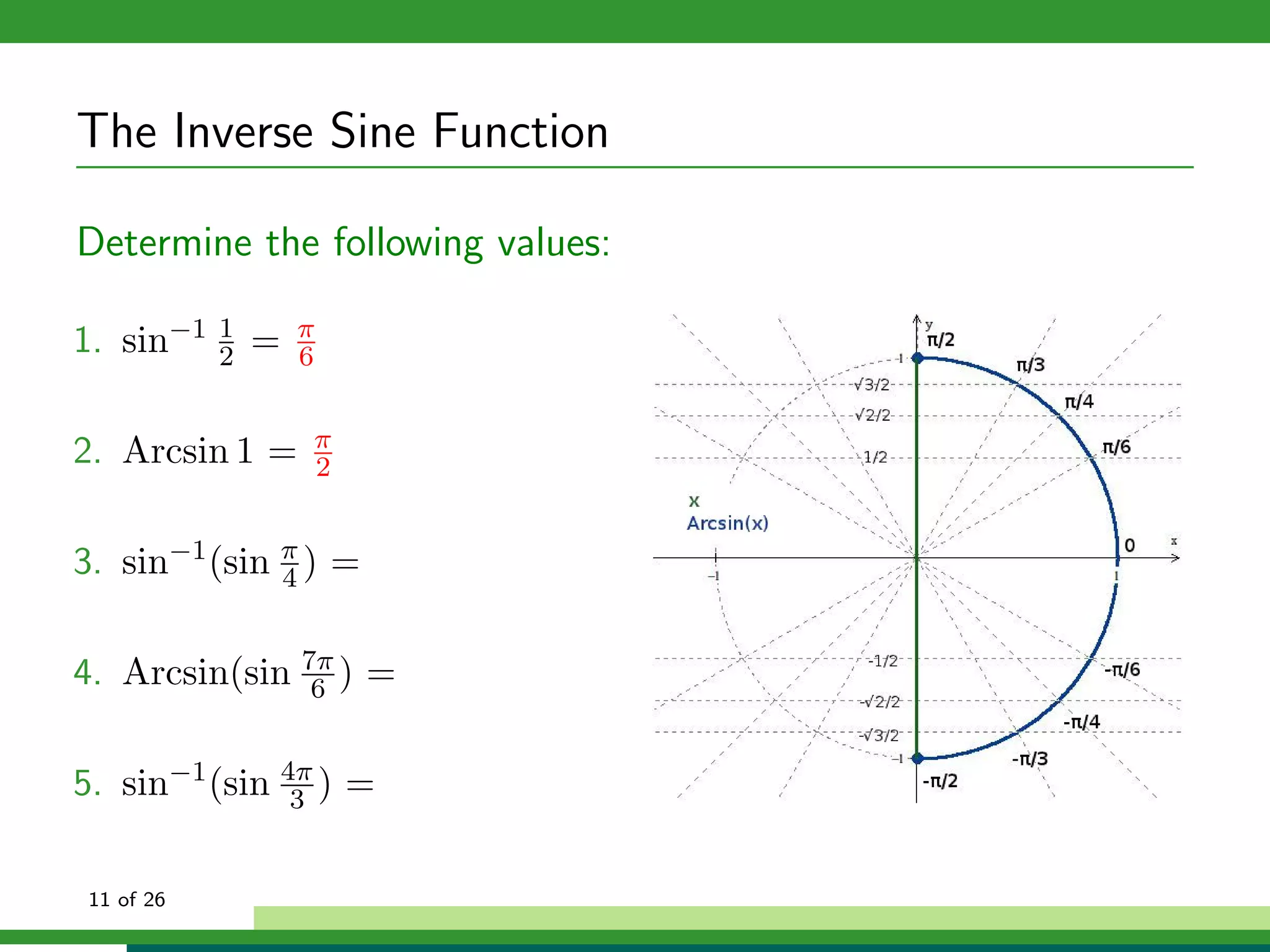
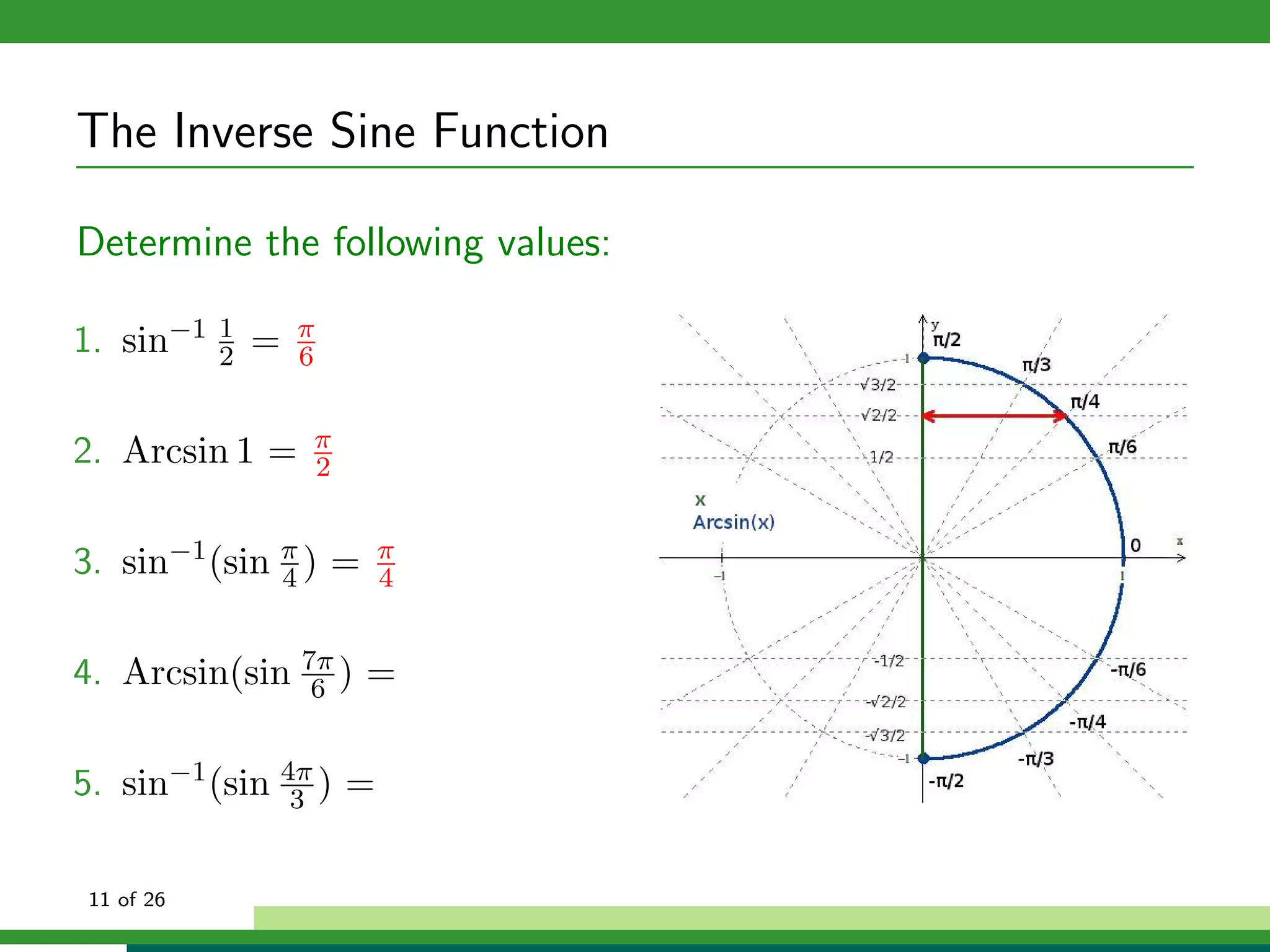
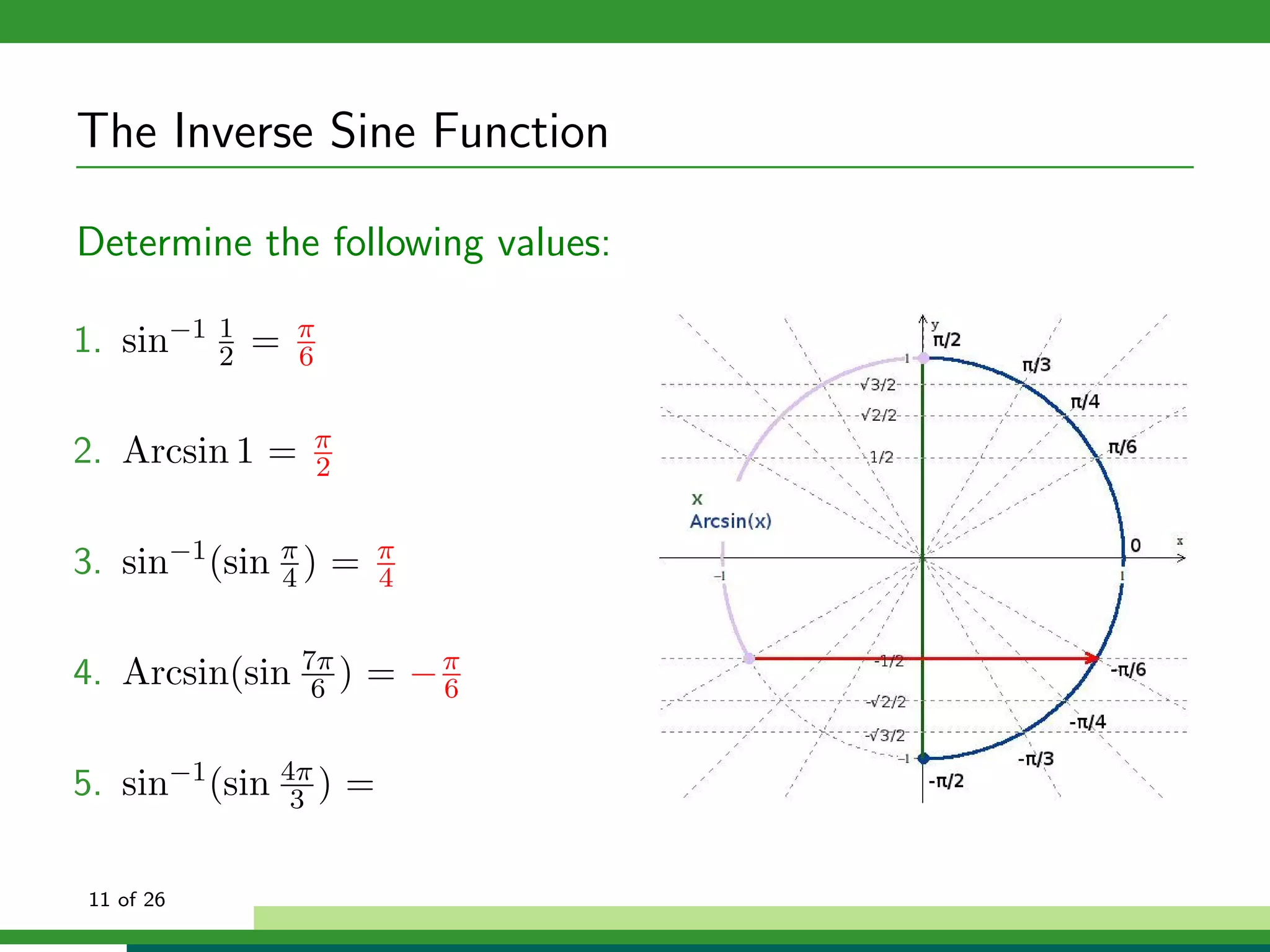
![The Inverse Cosine Function
Graphing the inverse cosine function
f (x) = Cos x, x ∈ [0, π]
12 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversetrigonometricfunctions-111028194453-phpapp01/75/Inverse-trigonometric-functions-35-2048.jpg)
![The Inverse Cosine Function
Graphing the inverse cosine function
f (x) = Cos x, x ∈ [0, π]
Restrict the domain so that it becomes one-to-one.
12 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversetrigonometricfunctions-111028194453-phpapp01/75/Inverse-trigonometric-functions-36-2048.jpg)
![The Inverse Cosine Function
The inverse of f (x) = Cos x, x ∈ [0, π]
f (x) = Cos x, x ∈ [0, π]
13 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversetrigonometricfunctions-111028194453-phpapp01/75/Inverse-trigonometric-functions-37-2048.jpg)
![The Inverse Cosine Function
The inverse of f (x) = Cos x, x ∈ [0, π]
Find the graph of the inverse by flipping along the diagonal
13 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversetrigonometricfunctions-111028194453-phpapp01/75/Inverse-trigonometric-functions-38-2048.jpg)
![The Inverse Cosine Function
The inverse of f (x) = Cos x, x ∈ [0, π]
f (x) = cos−1 x = Arccos x = inverse cosine of x
13 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversetrigonometricfunctions-111028194453-phpapp01/75/Inverse-trigonometric-functions-39-2048.jpg)
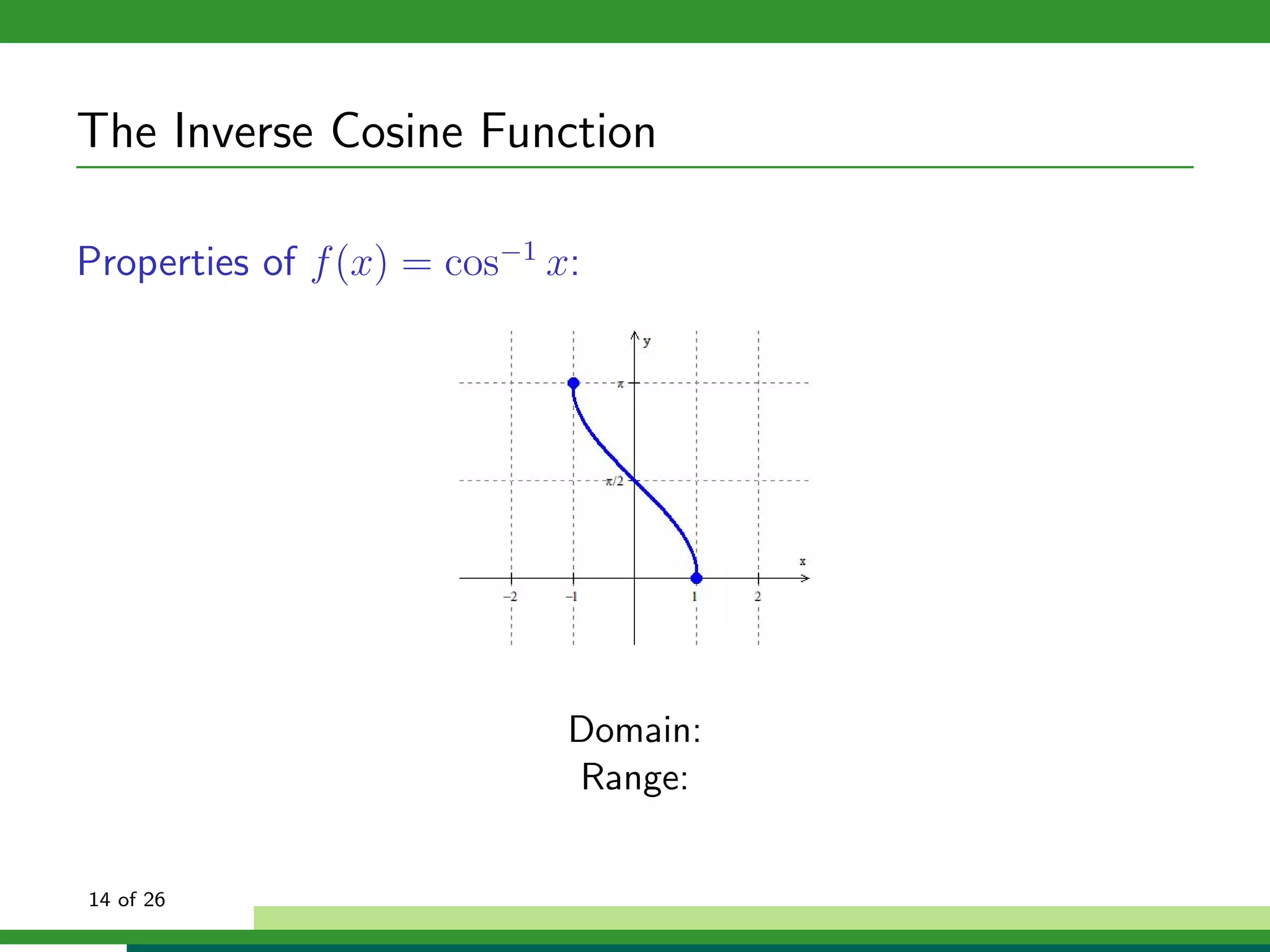
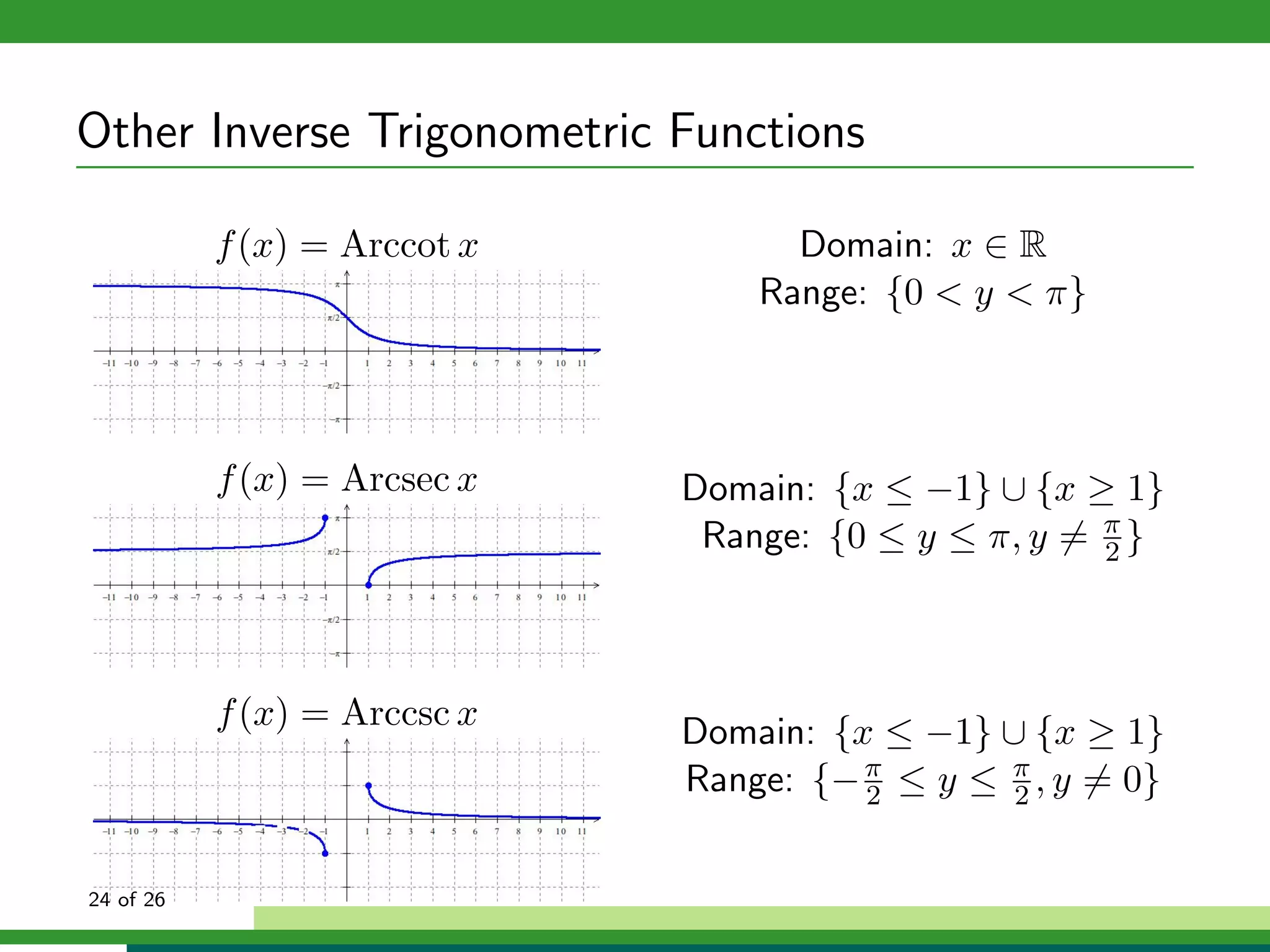
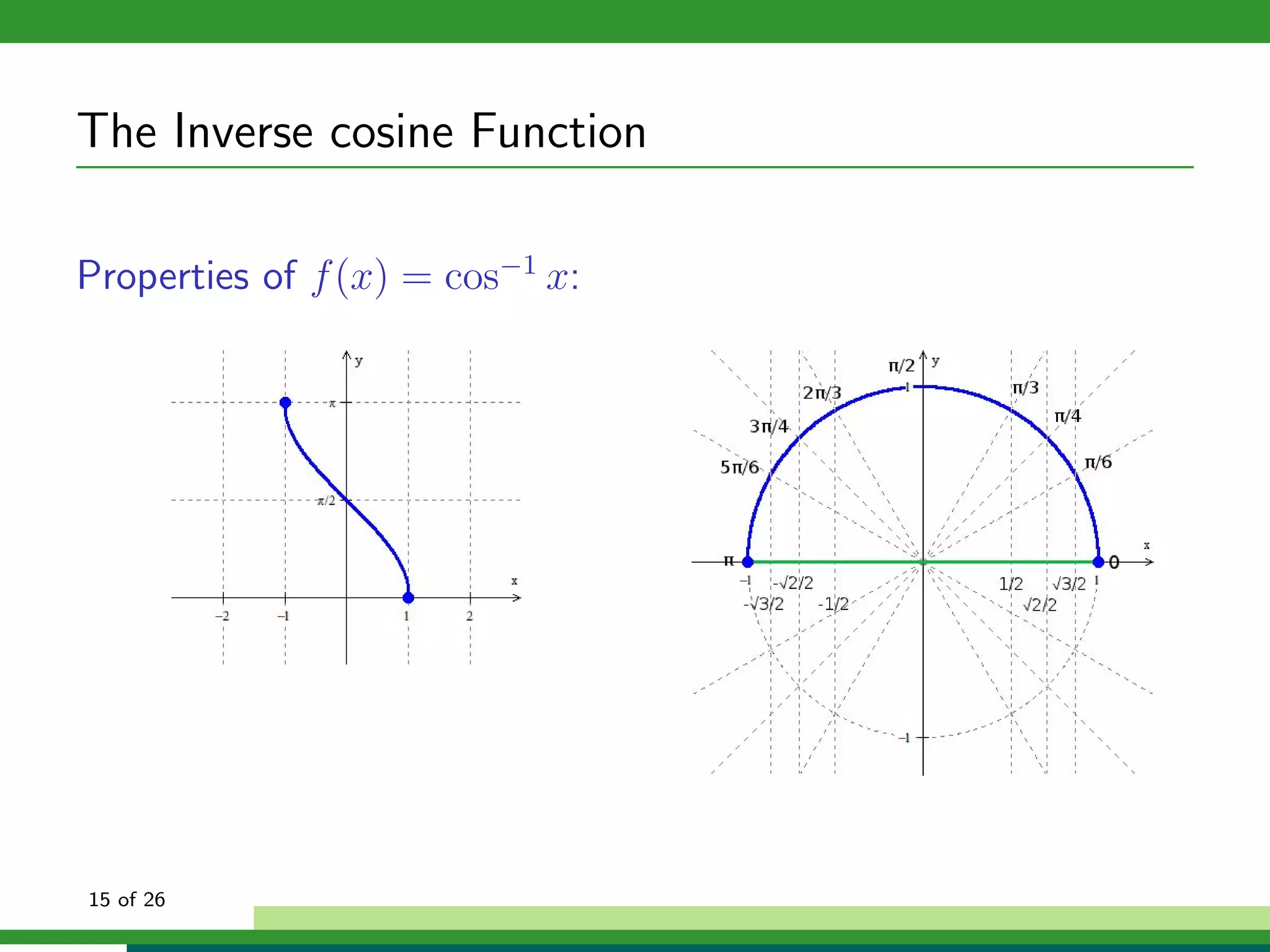
![The Inverse Cosine Function
Properties of f (x) = cos−1 x:
Domain: x ∈ [−1, 1]
Range:
14 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversetrigonometricfunctions-111028194453-phpapp01/75/Inverse-trigonometric-functions-41-2048.jpg)
![The Inverse Cosine Function
Properties of f (x) = cos−1 x:
Domain: x ∈ [−1, 1]
Range: y ∈ [0, π]
14 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversetrigonometricfunctions-111028194453-phpapp01/75/Inverse-trigonometric-functions-42-2048.jpg)


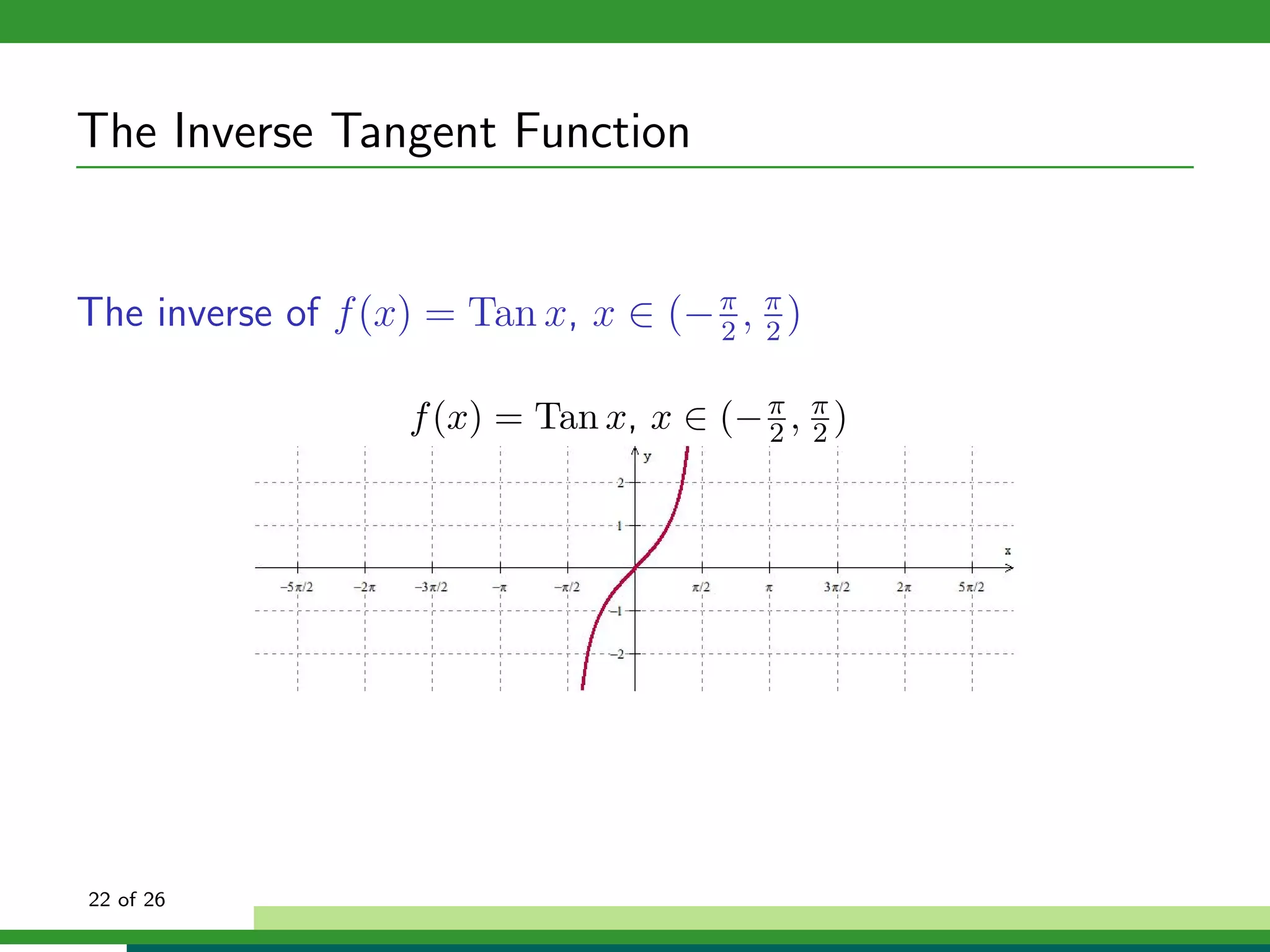
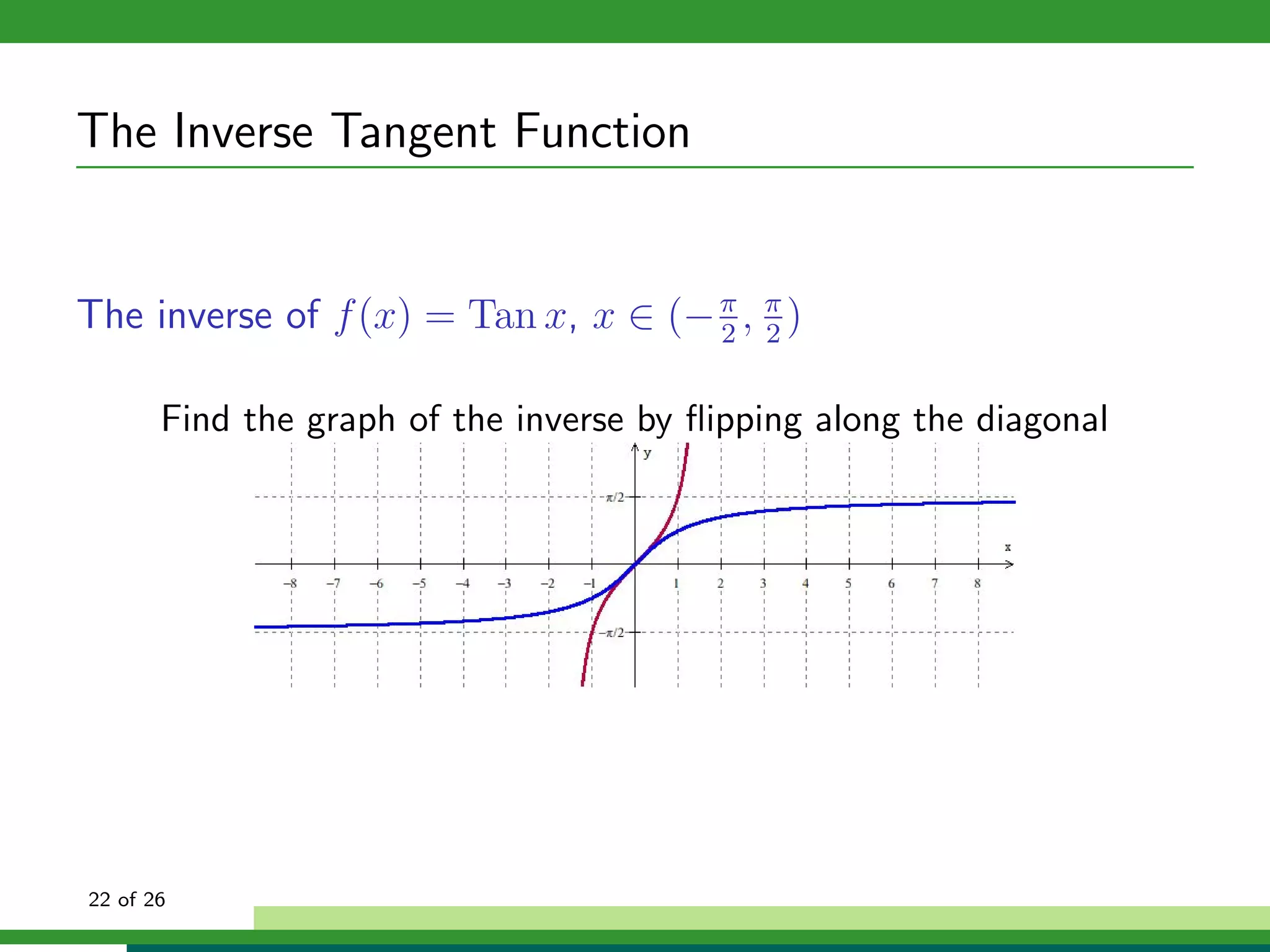
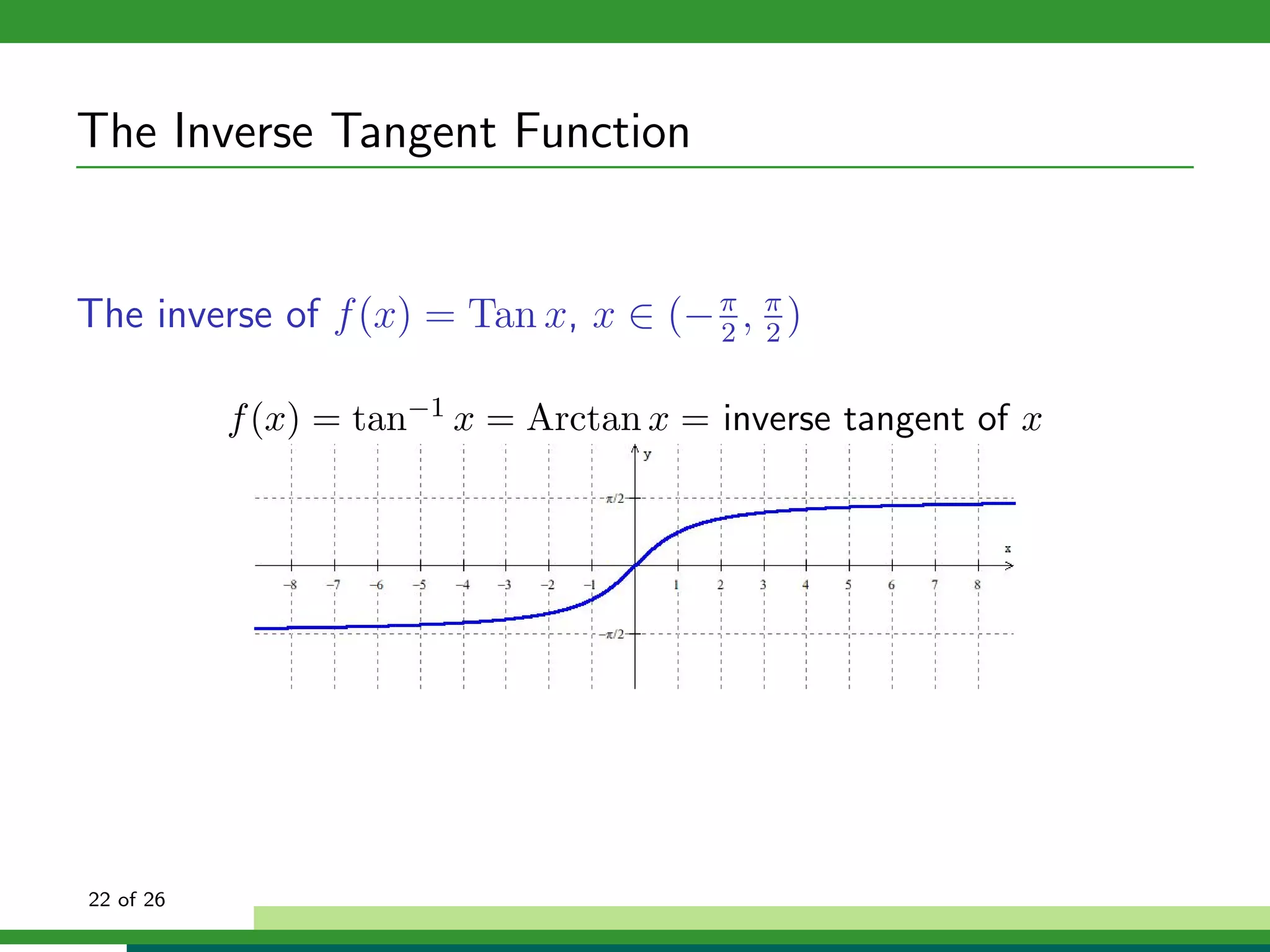
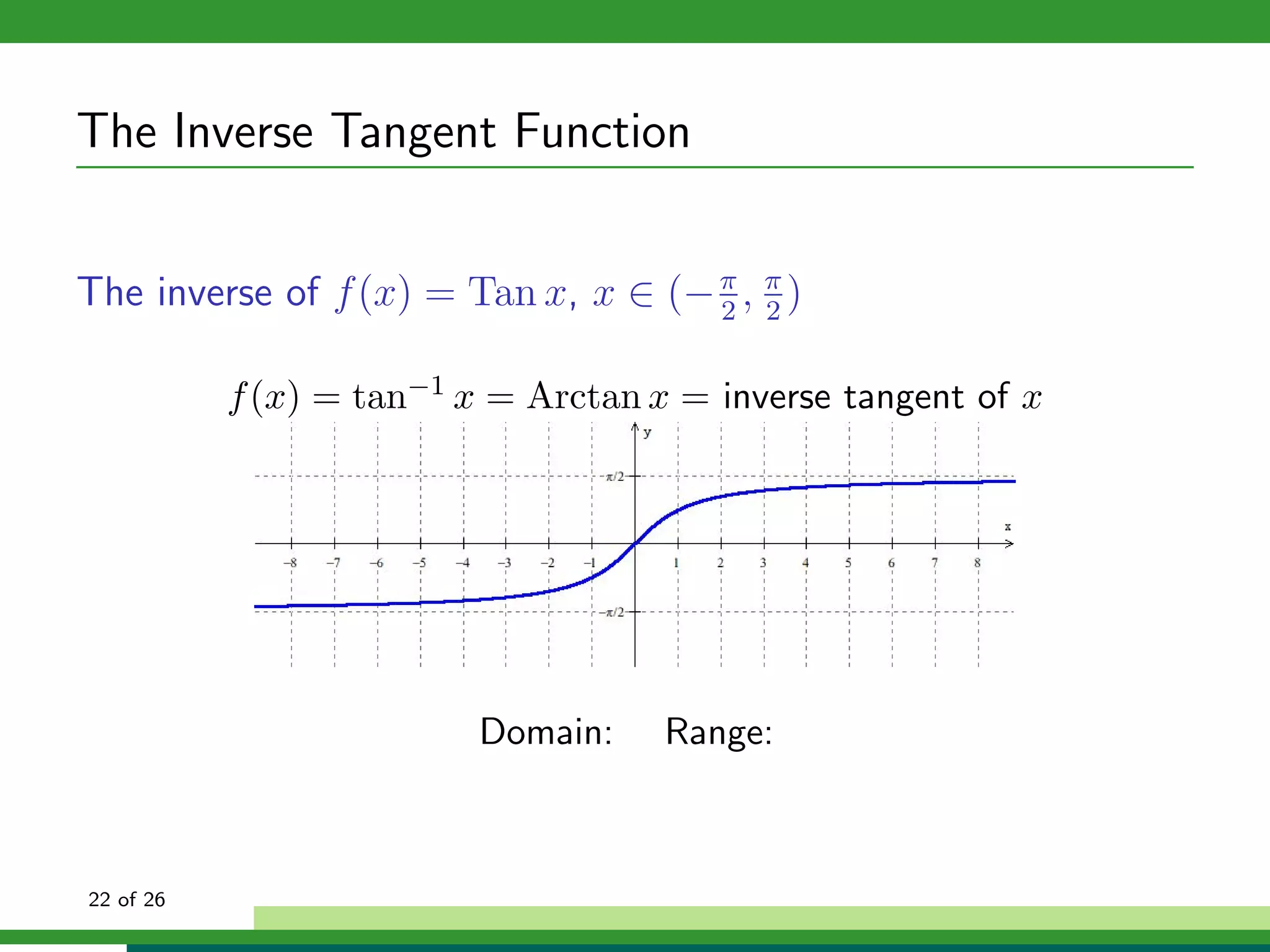
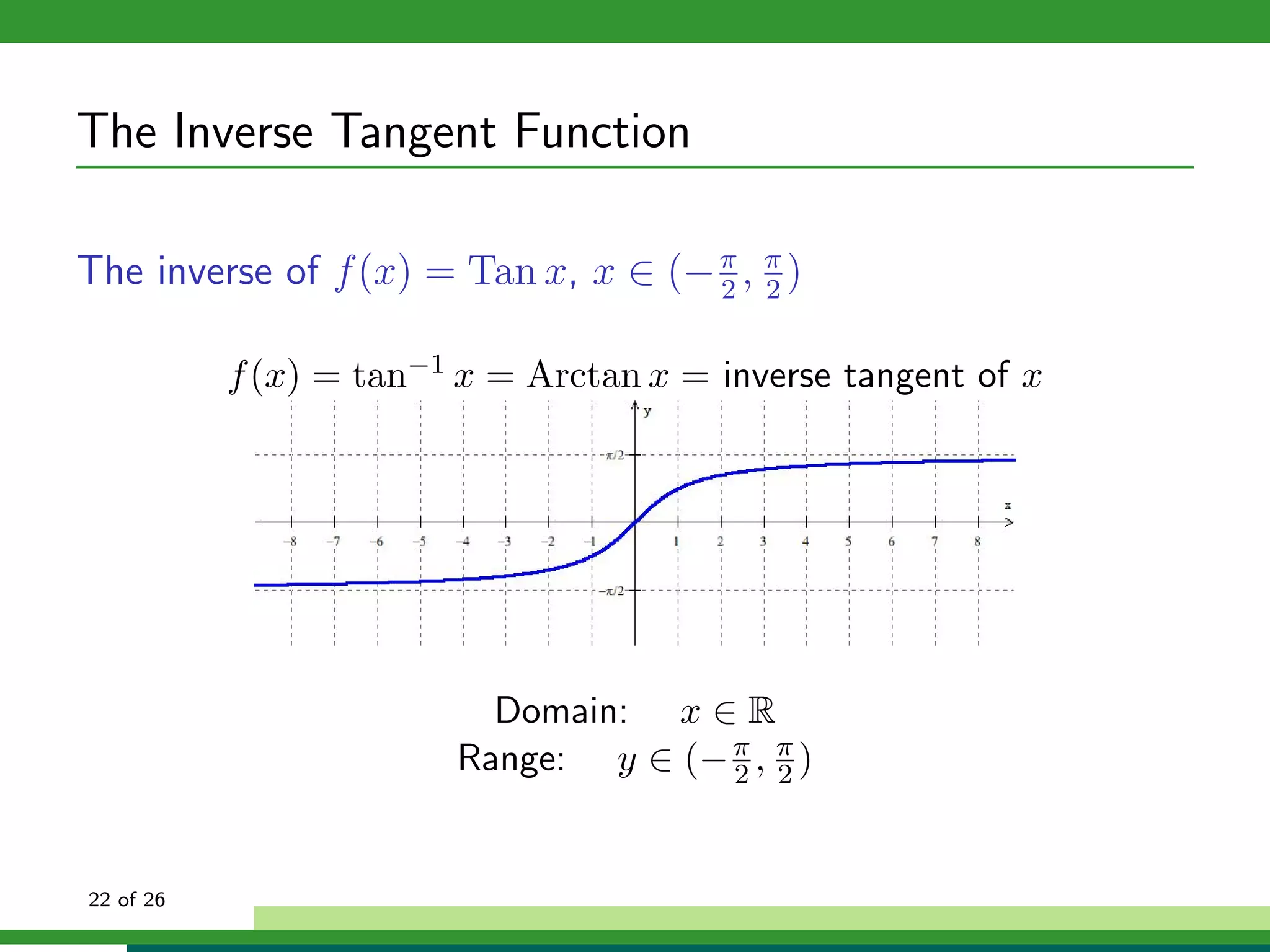
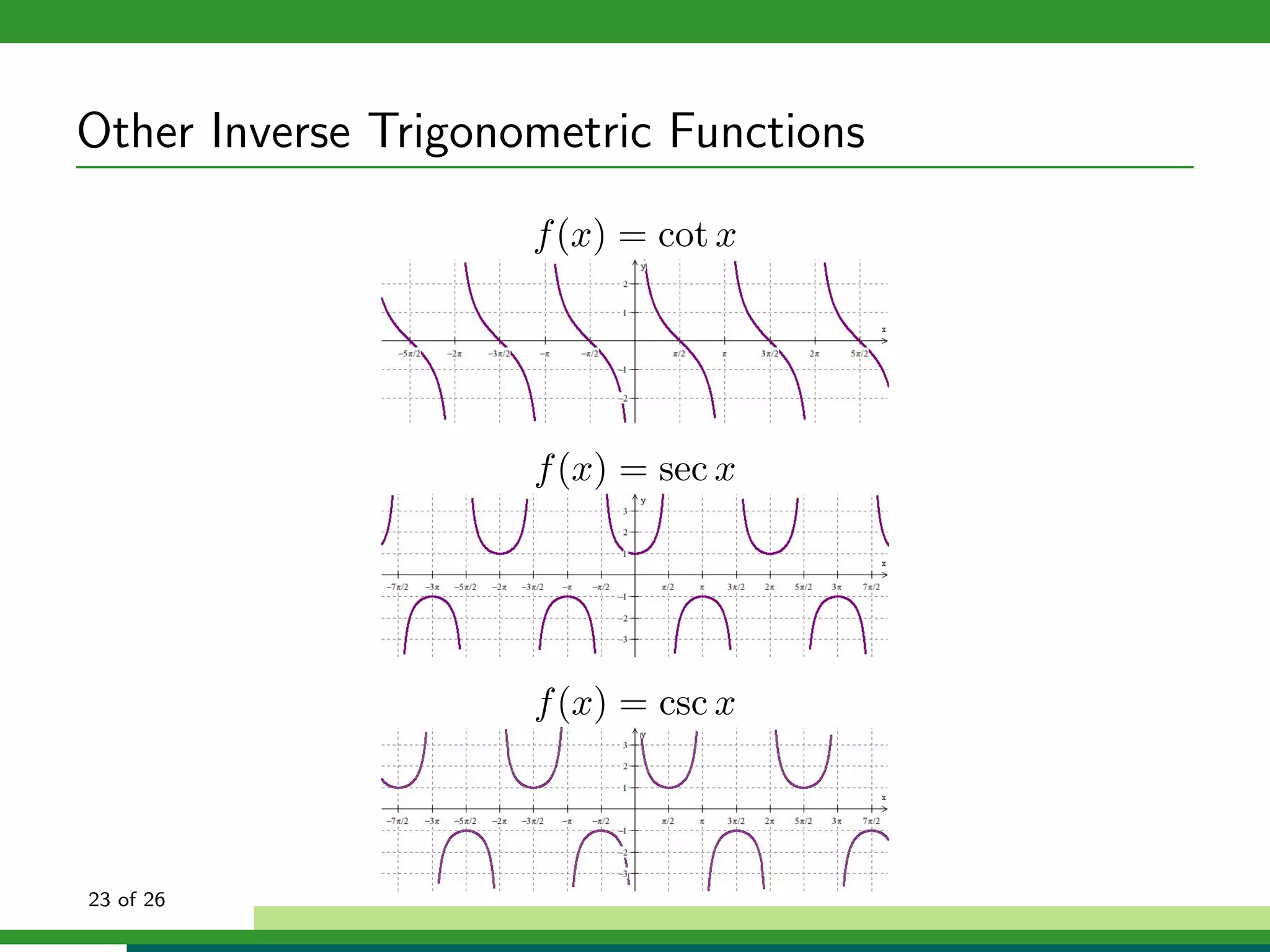
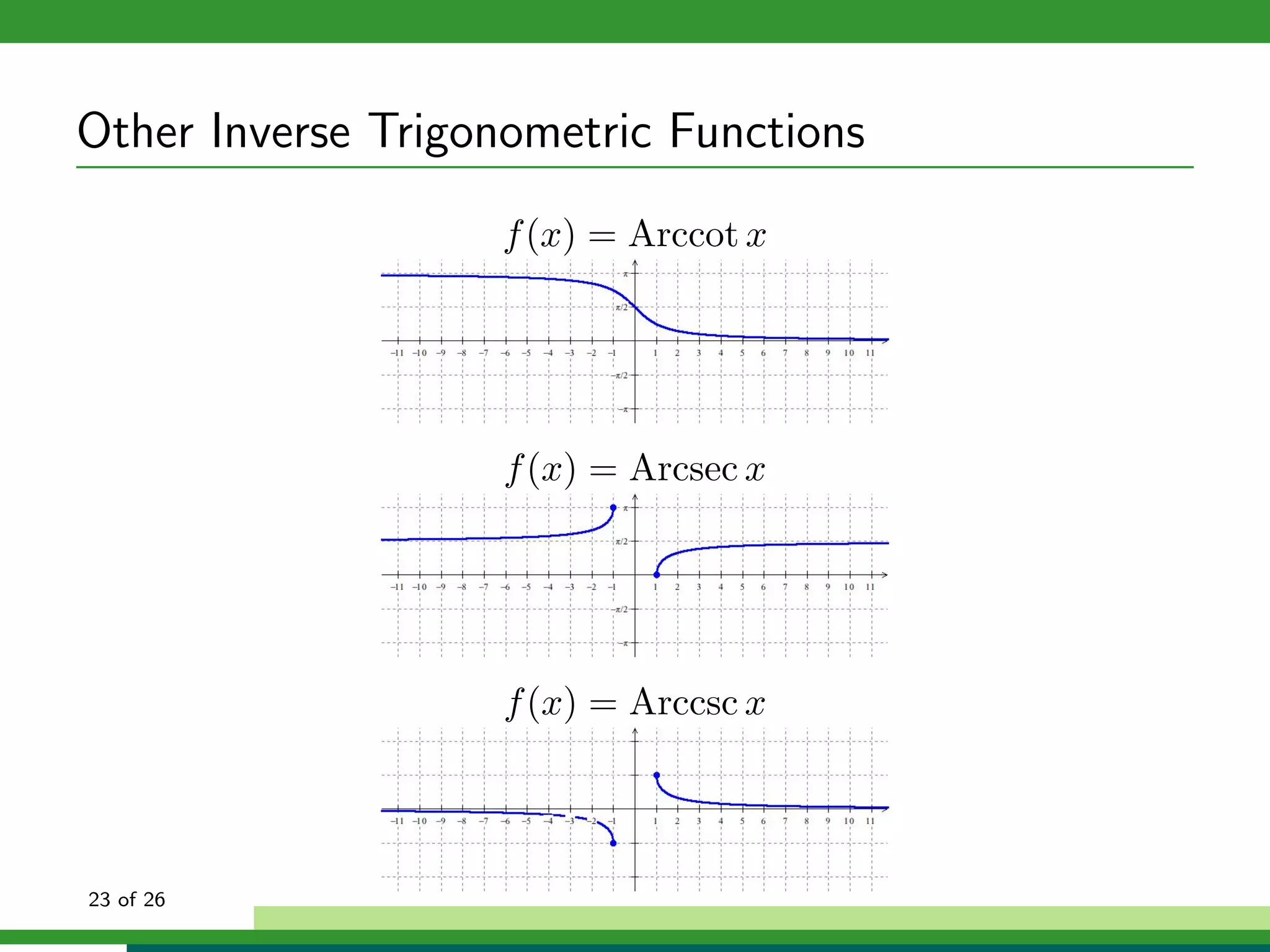
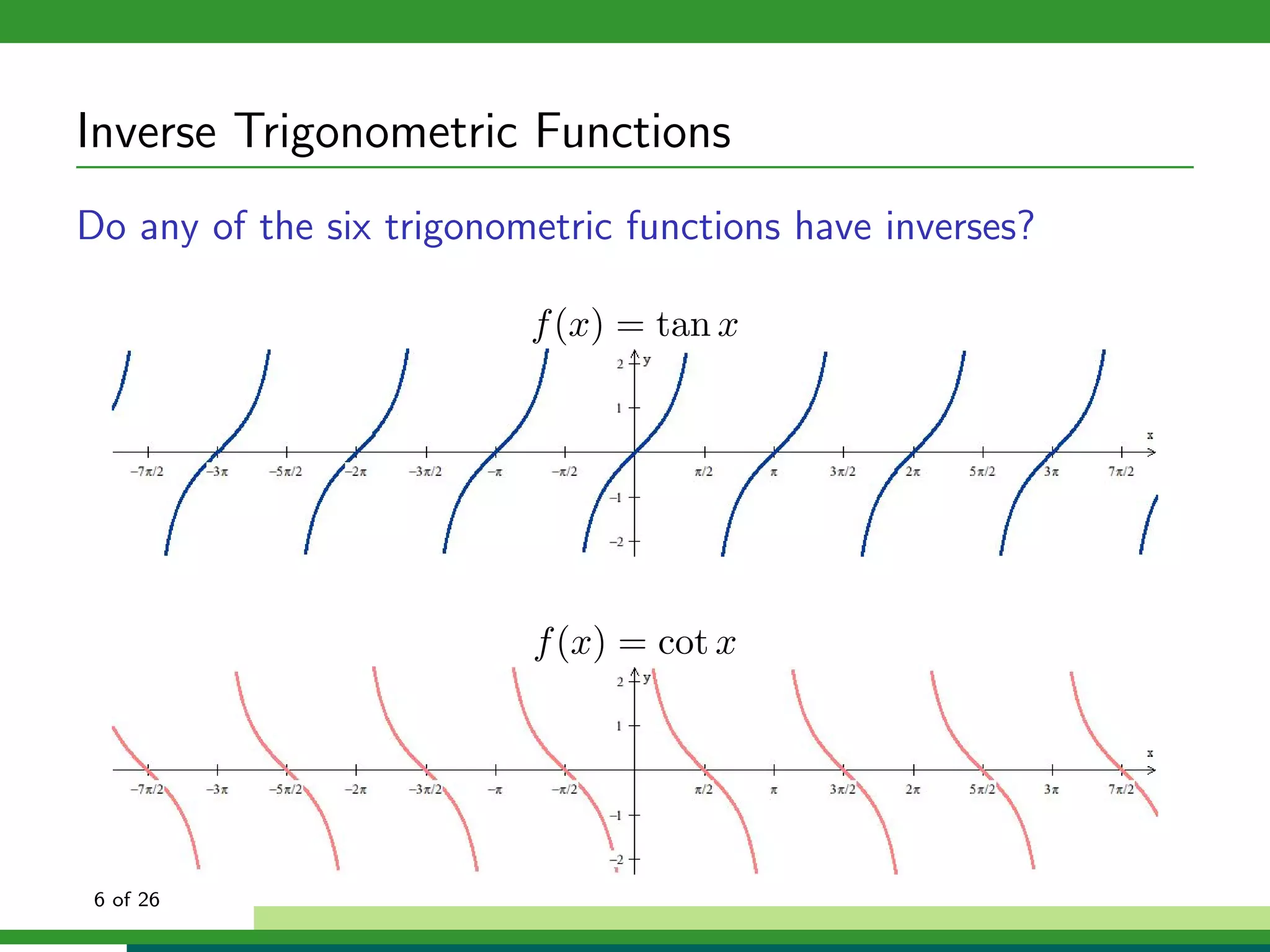
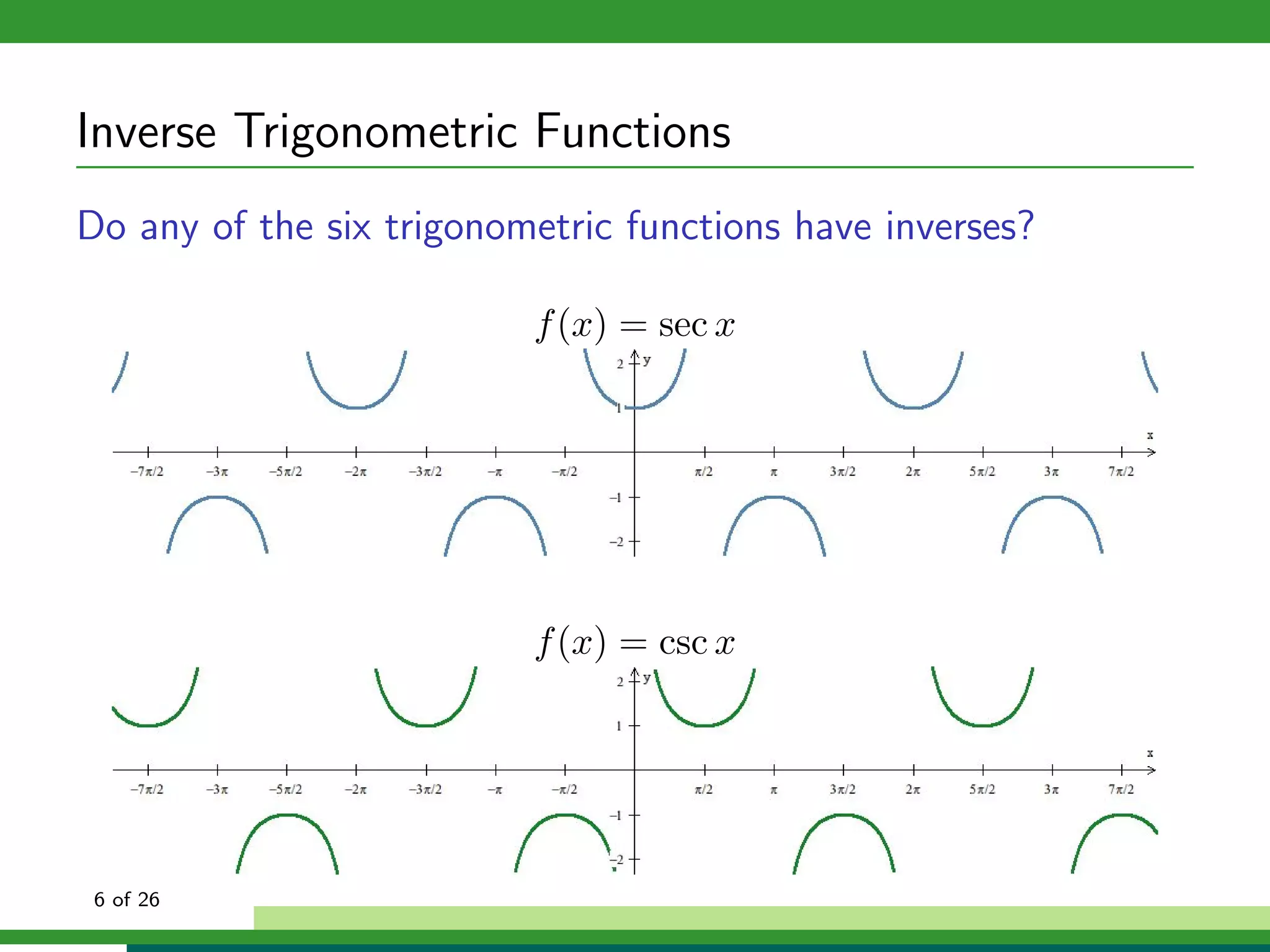
![Other Inverse Trigonometric Functions
f (x) = Cot x, x ∈ (0, π)
f (x) = Sec x, x ∈ [0, π]
f (x) = Csc x, x ∈ (− π , π )
2 2
23 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversetrigonometricfunctions-111028194453-phpapp01/75/Inverse-trigonometric-functions-80-2048.jpg)
![Other Inverse Trigonometric Functions
f (x) = Cot x, x ∈ (0, π)
f (x) = Sec x, x ∈ [0, π]
f (x) = Csc x, x ∈ (− π , π )
2 2
23 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inversetrigonometricfunctions-111028194453-phpapp01/75/Inverse-trigonometric-functions-81-2048.jpg)