The key points of the document are:
1) Physical security assessments are important to identify security risks, vulnerabilities, and opportunities to improve protection of assets, employees, and business reputation.
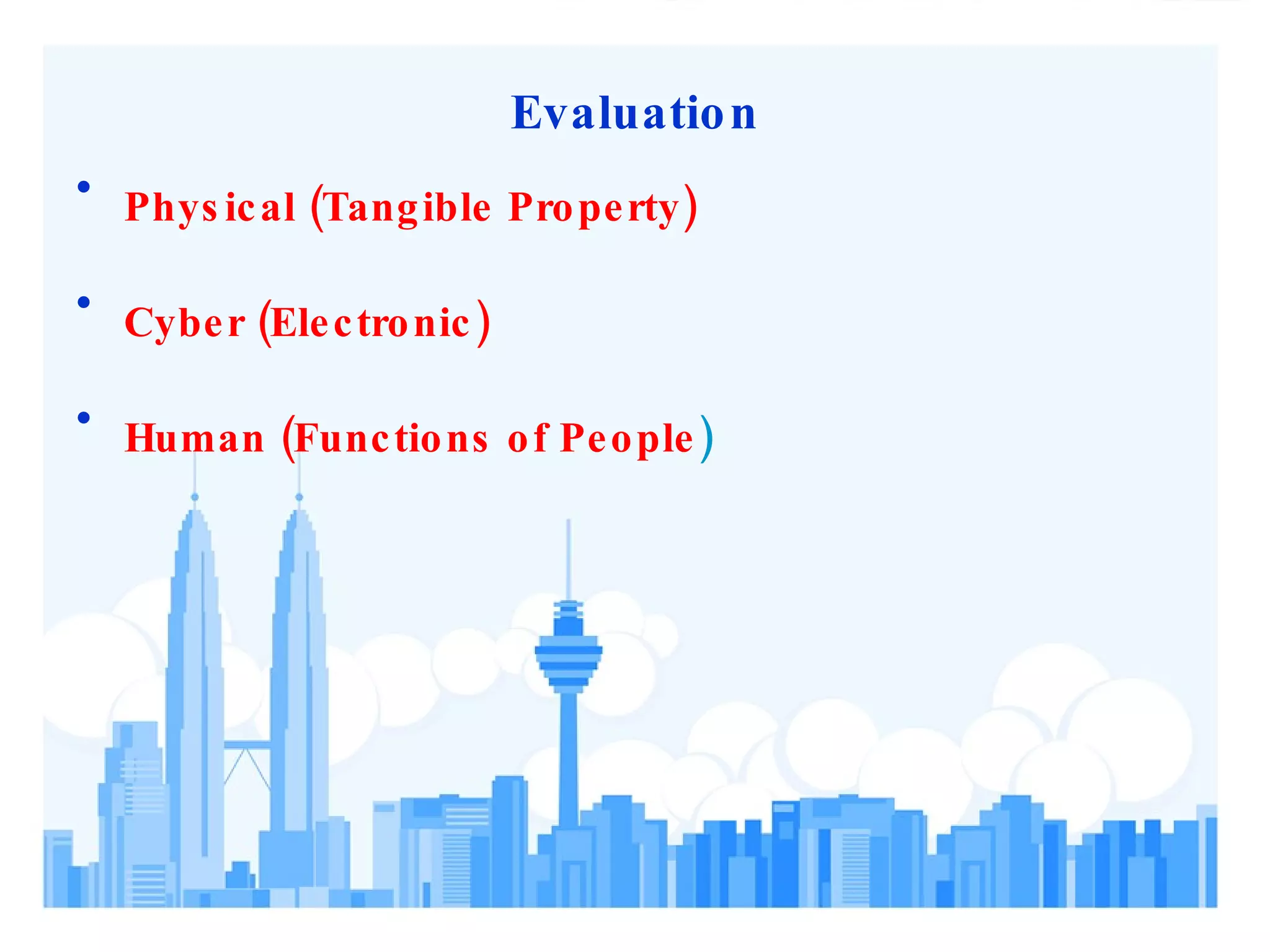
2) Assessments should evaluate physical, cyber, and human aspects of security using a risk management framework.
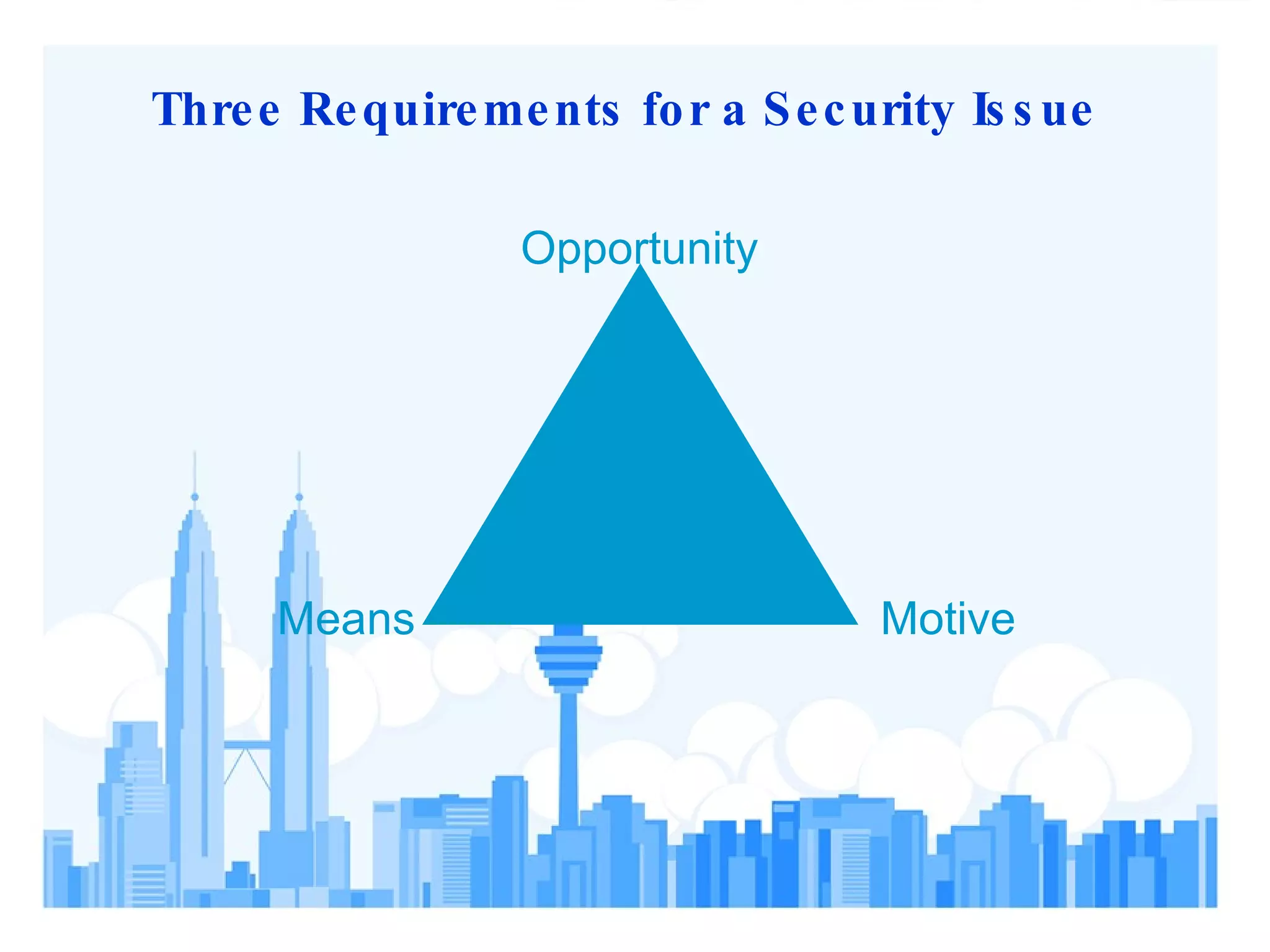
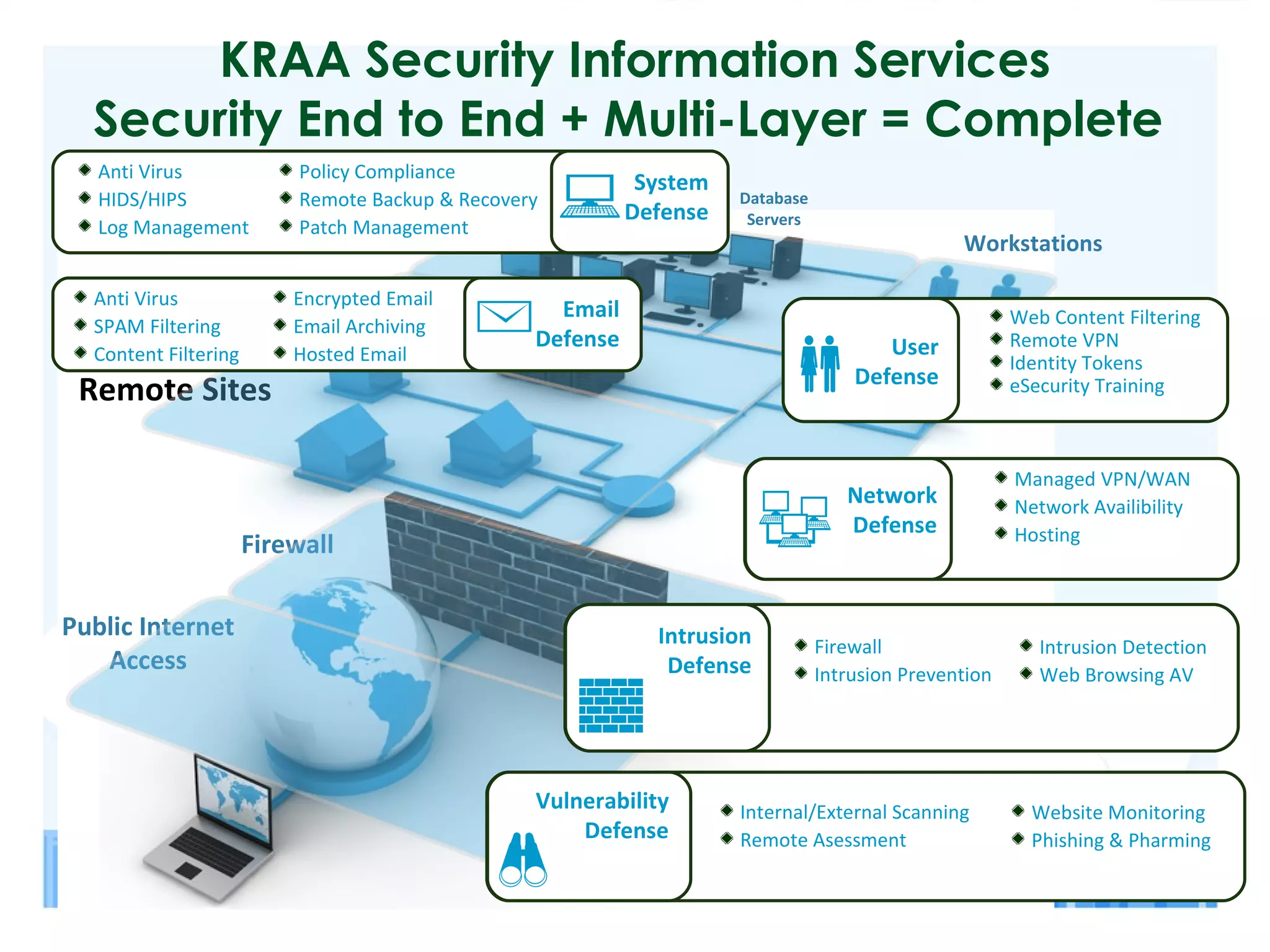
3) Effective security requires identifying assets, threats, and vulnerabilities; prioritizing risks; and implementing programs to deter threats and mitigate vulnerabilities.



































![Dan Finger Contact [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/danv3-12687623613439-phpapp01/75/Physical-Security-Assessment-39-2048.jpg)