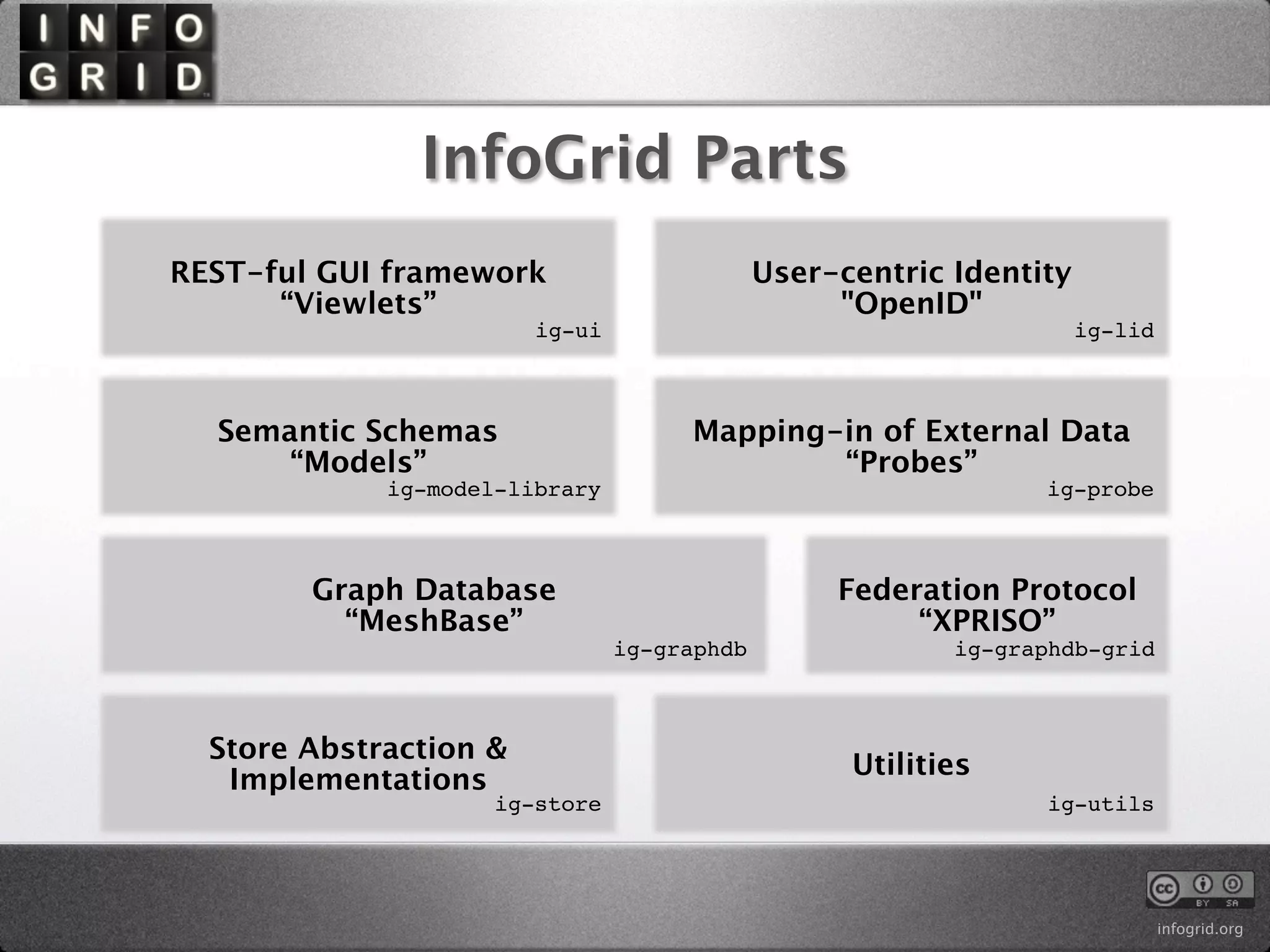
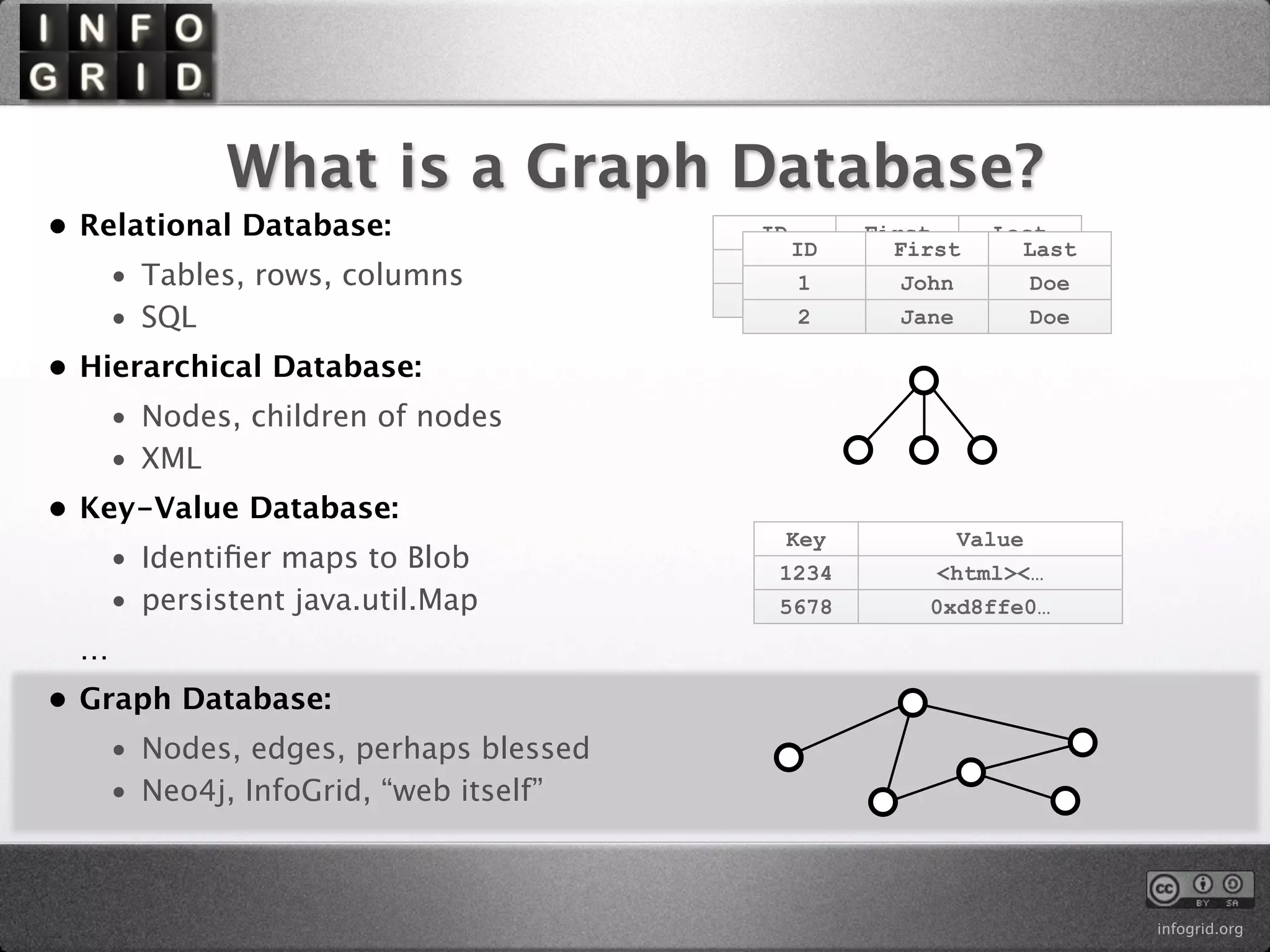
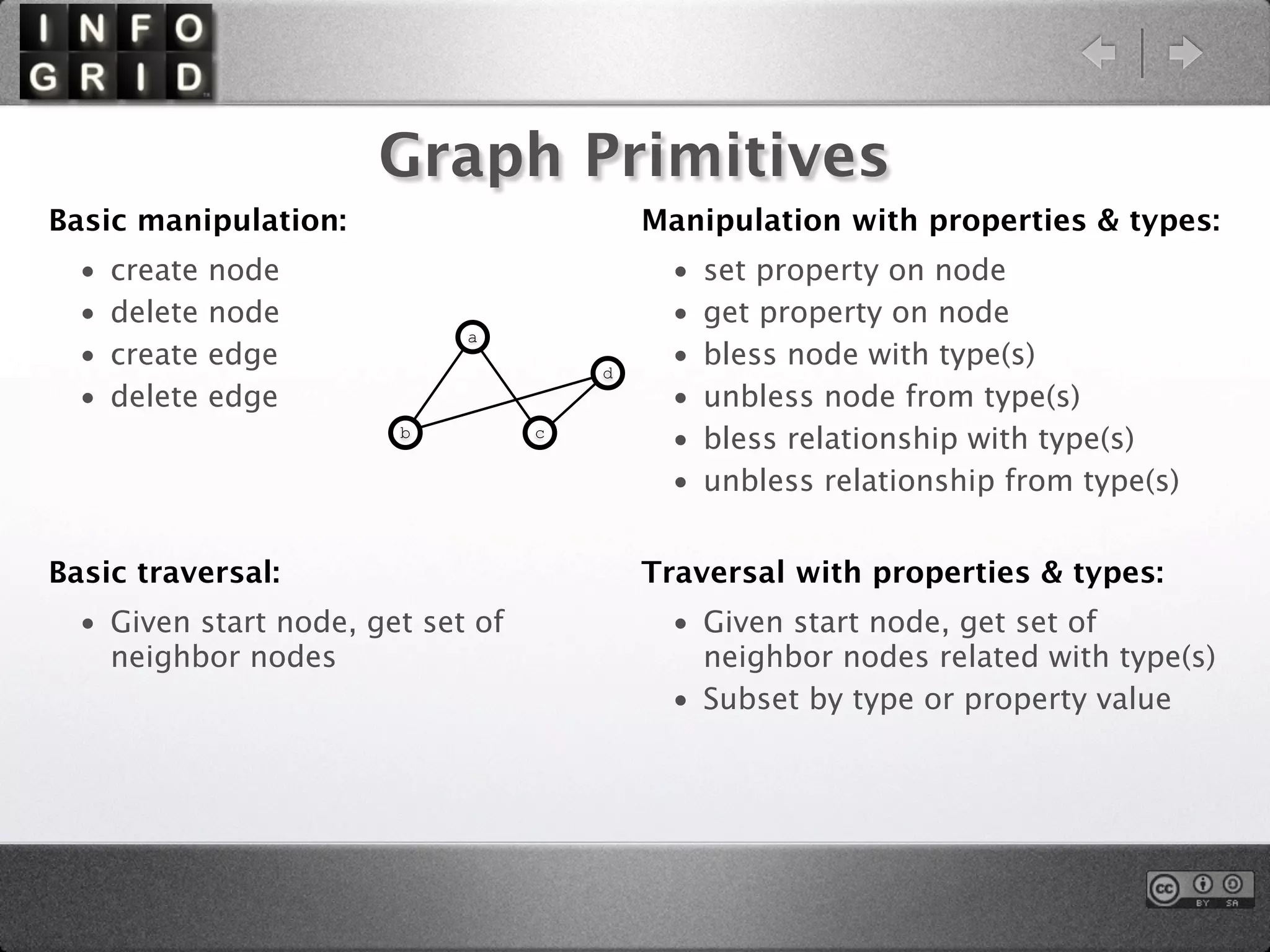
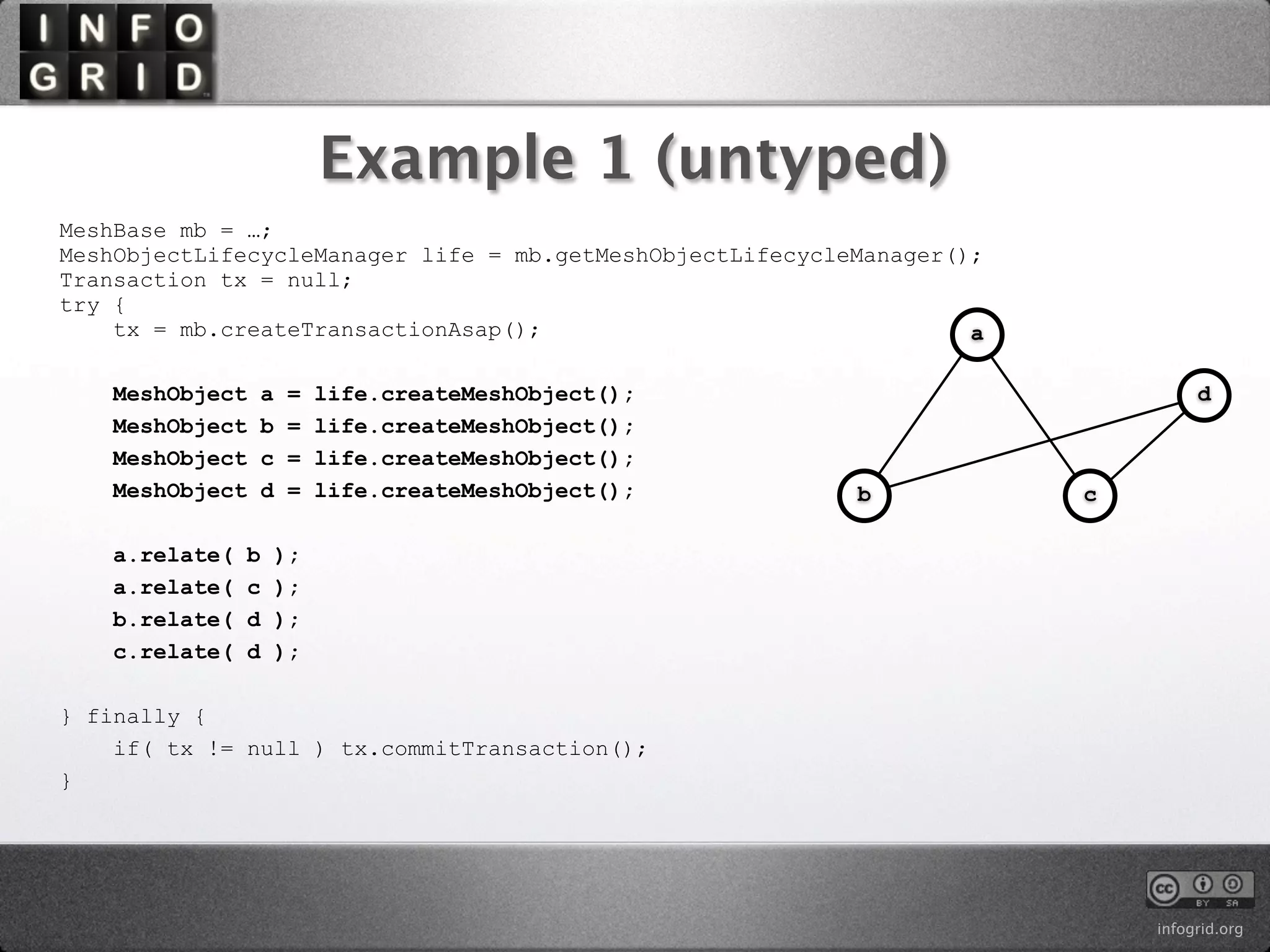
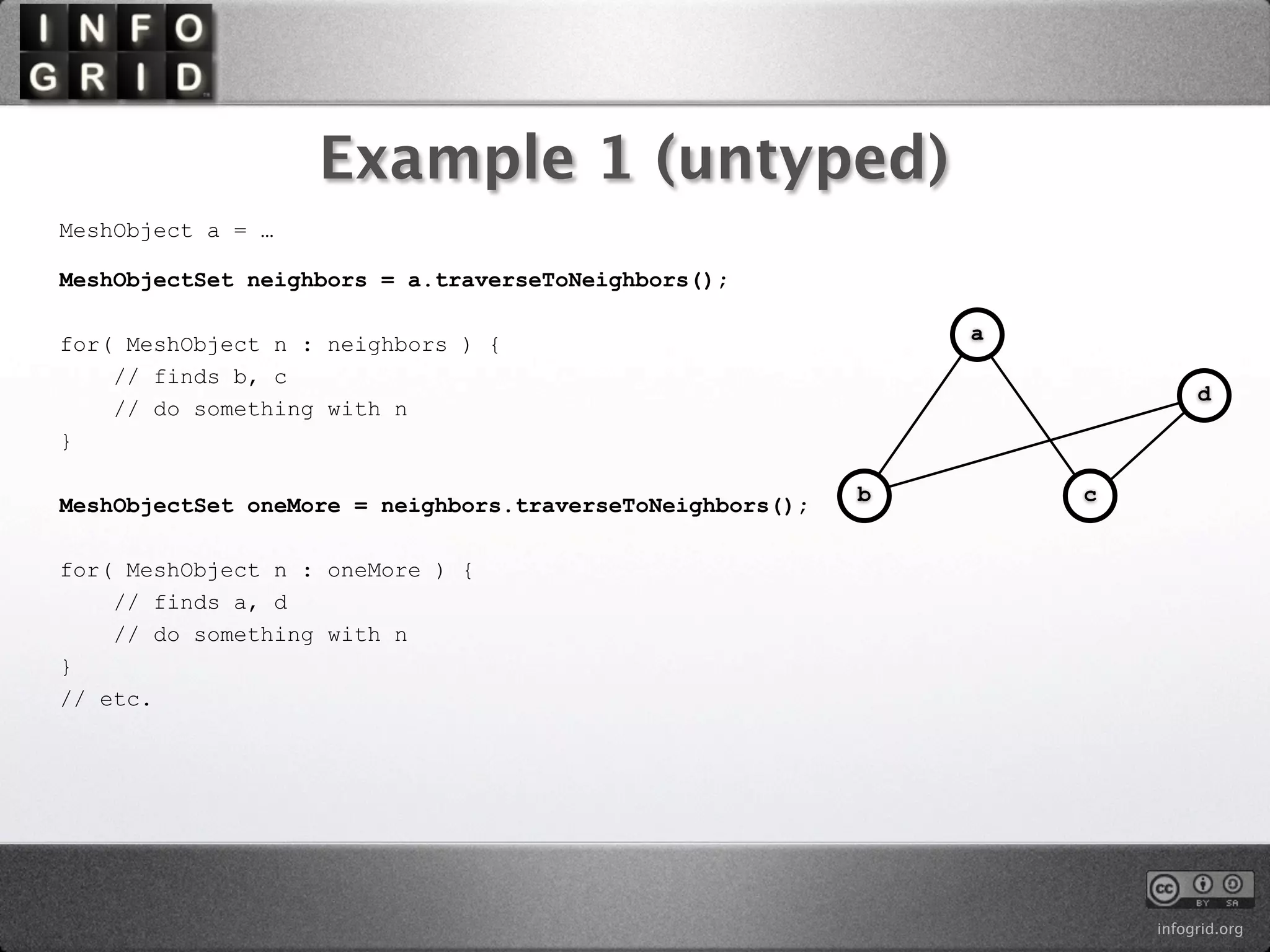
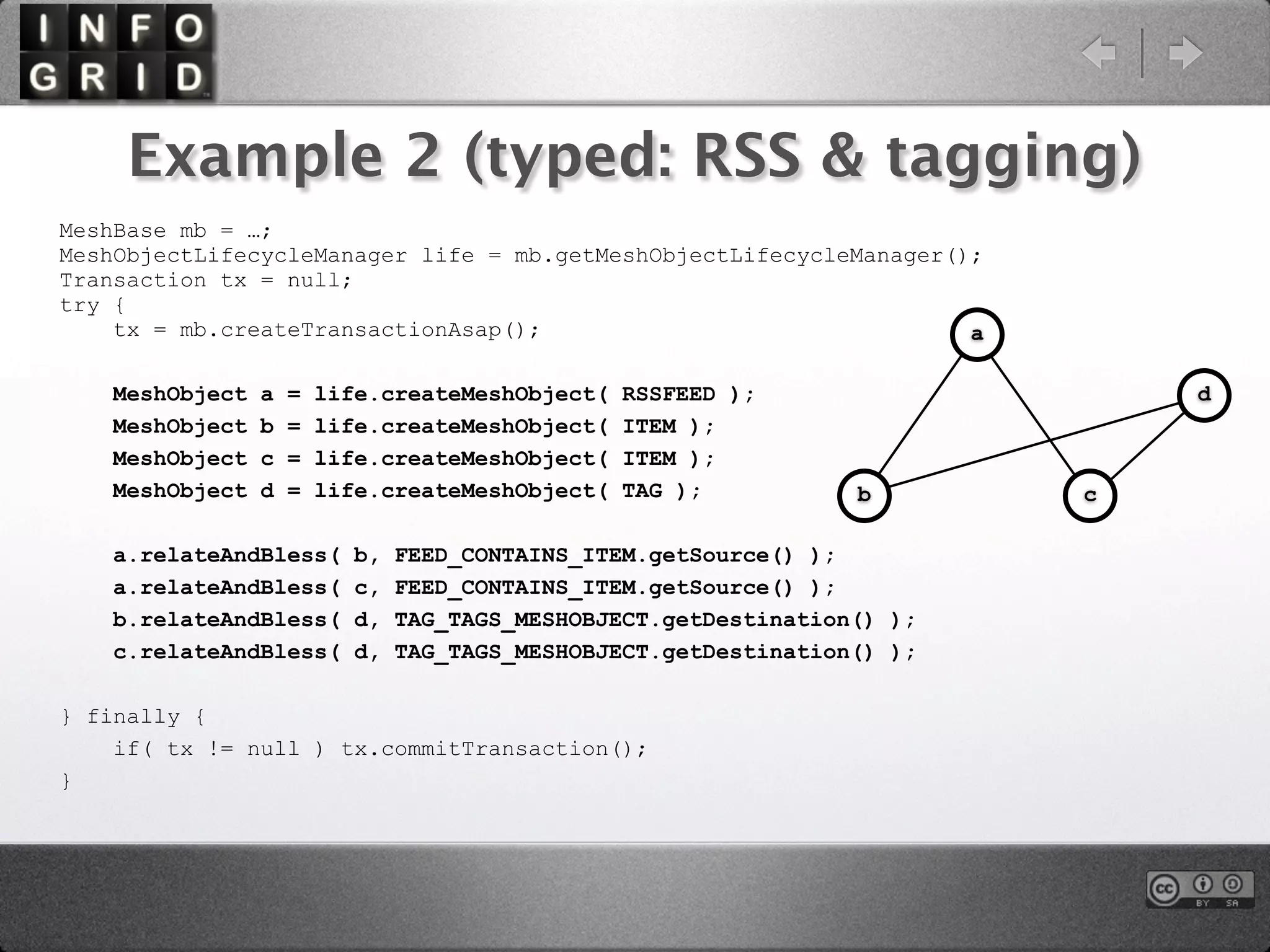
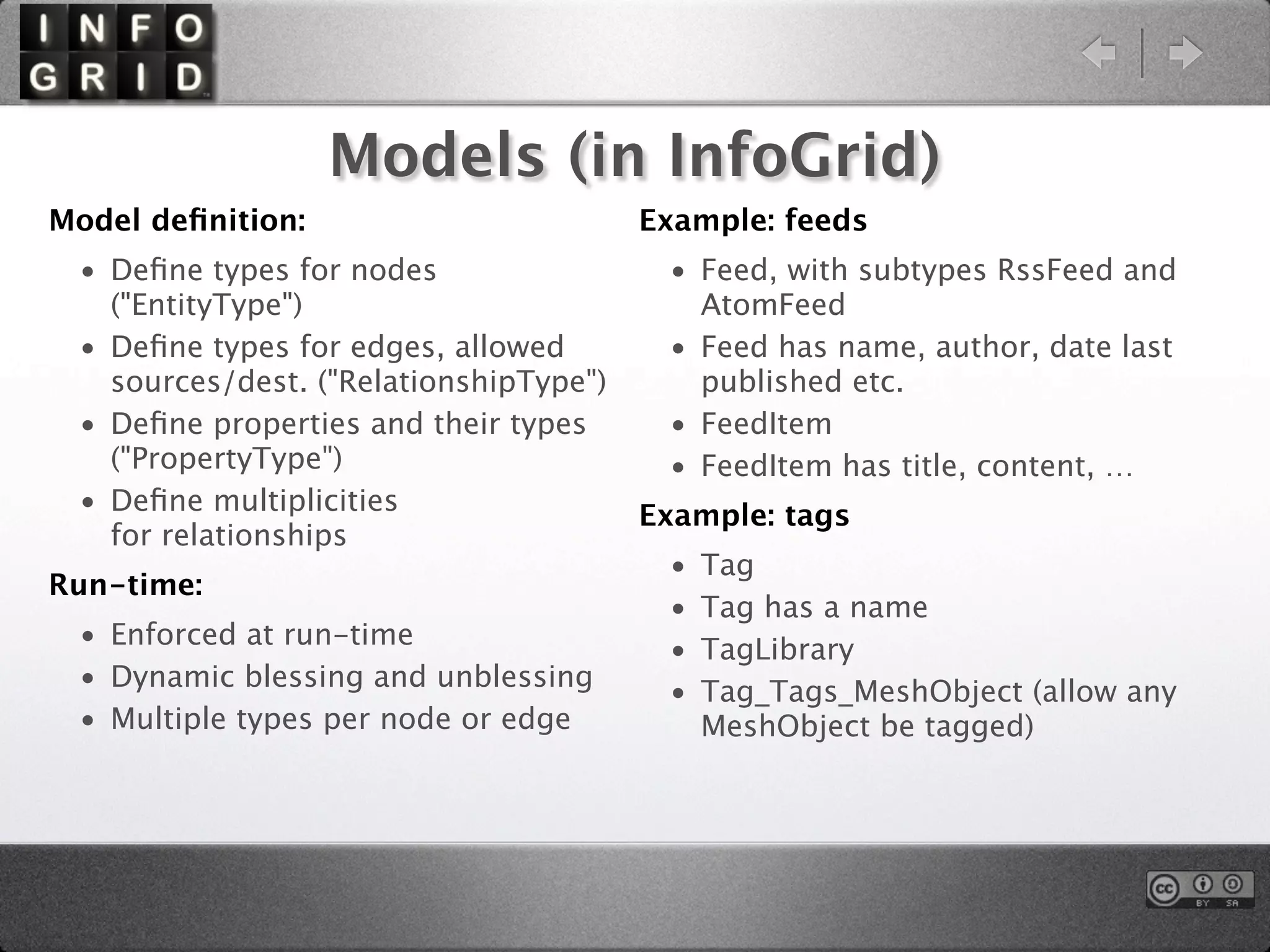
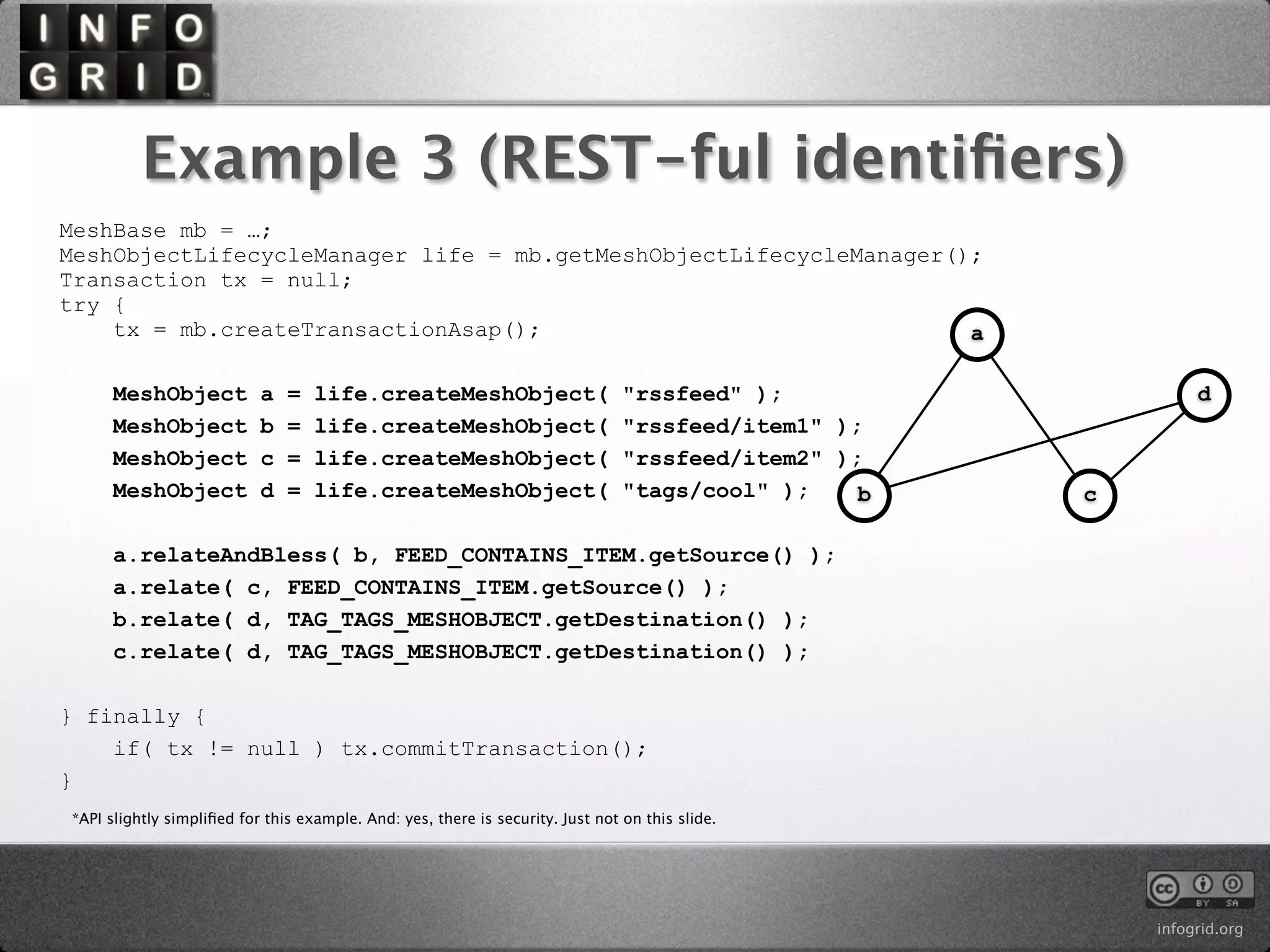
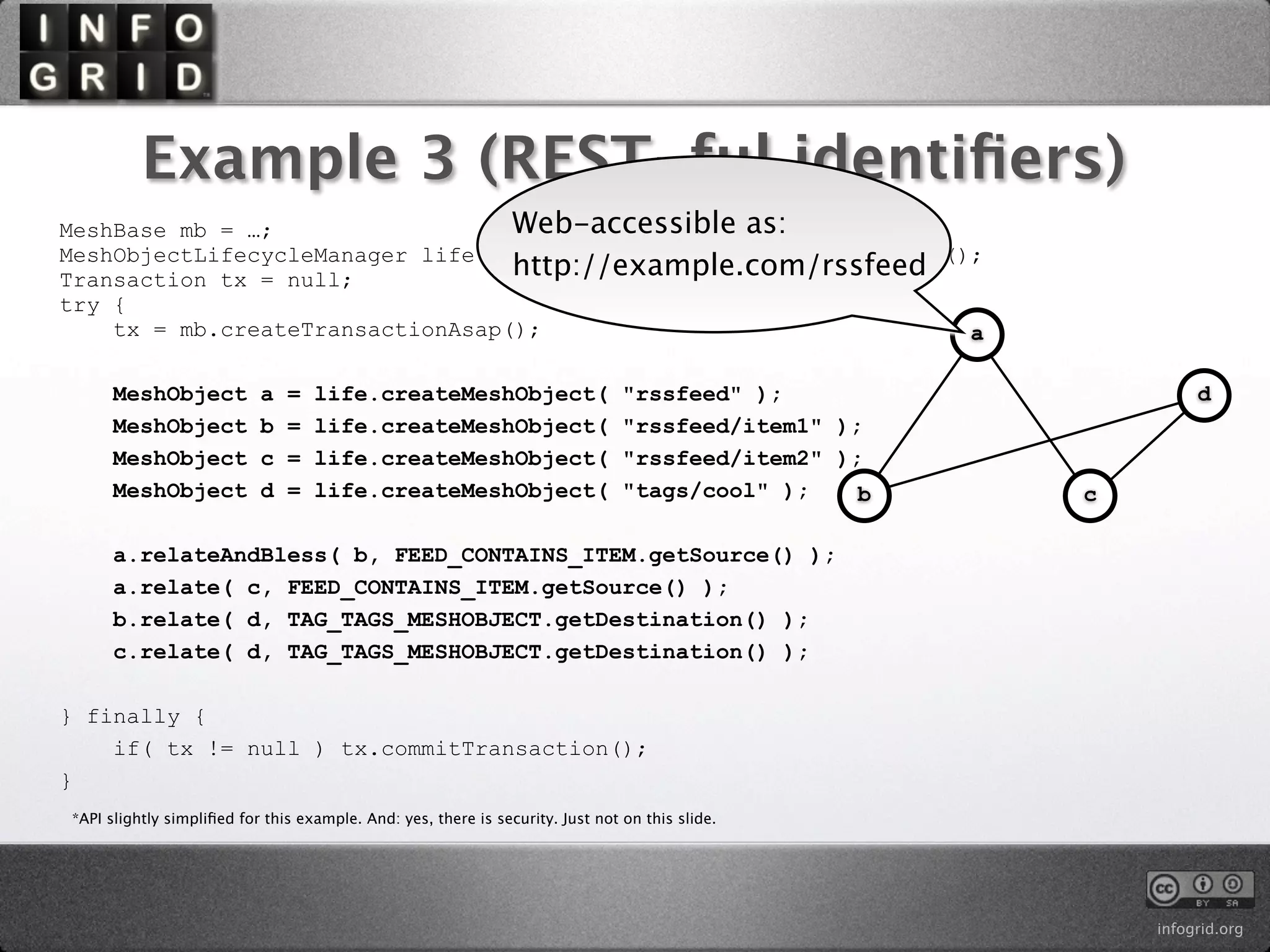
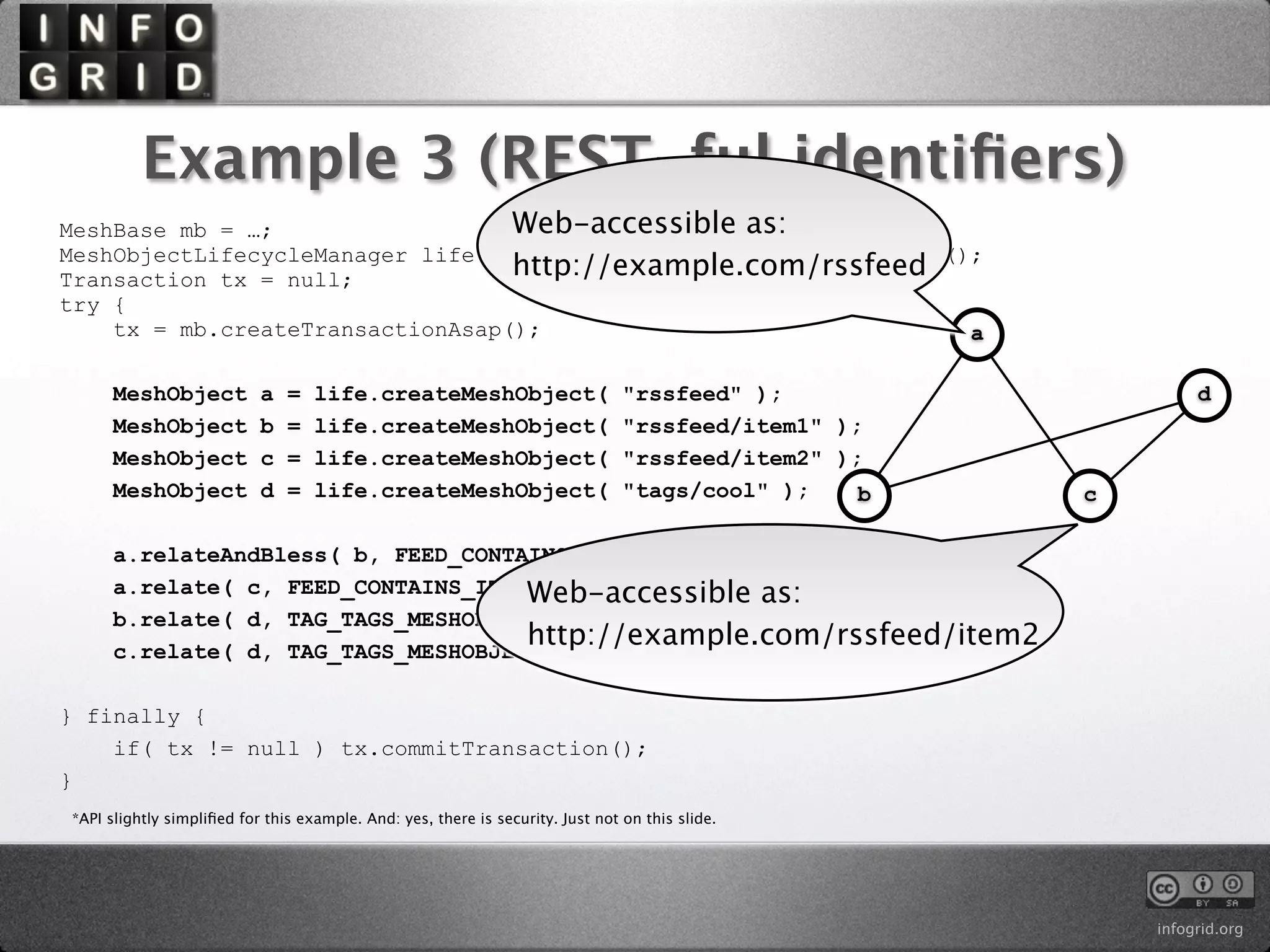
The document describes the InfoGrid graph database. It is composed of several parts including a RESTful GUI framework, semantic schemas, a graph database, and store implementations. It explains what a graph database is and how it differs from relational and other databases. Examples show how to create and relate nodes and edges in a graph using the InfoGrid API.