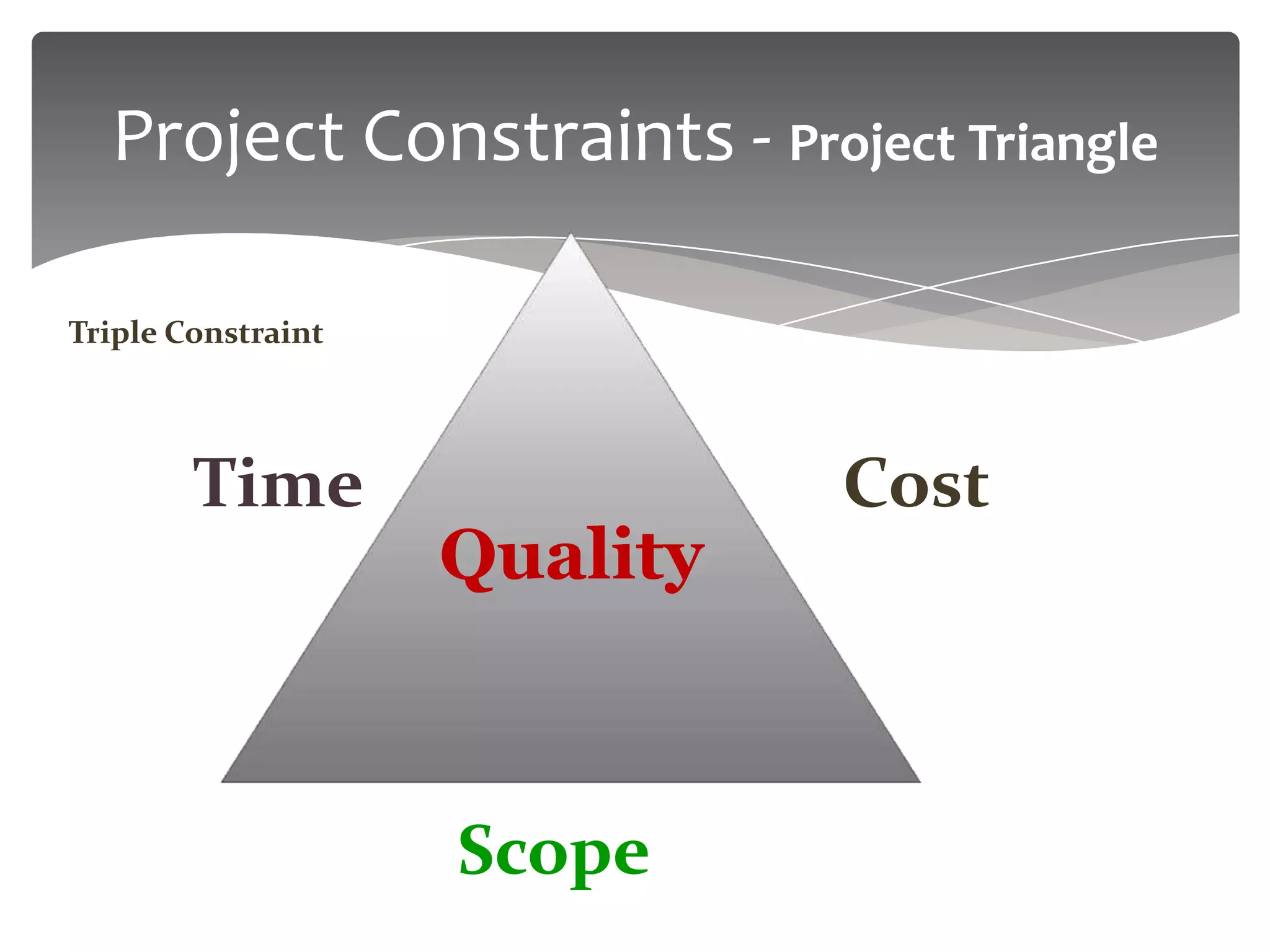
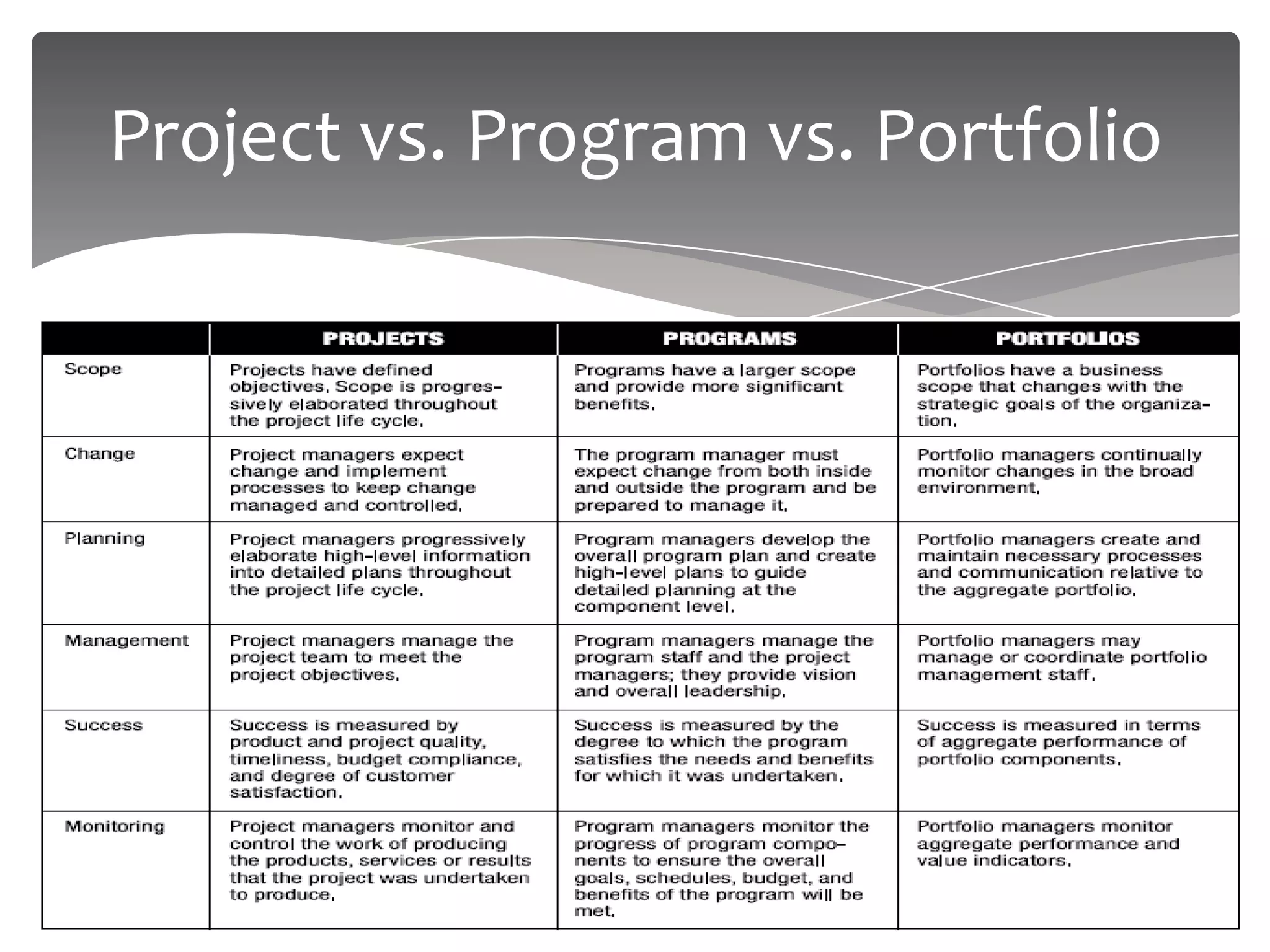
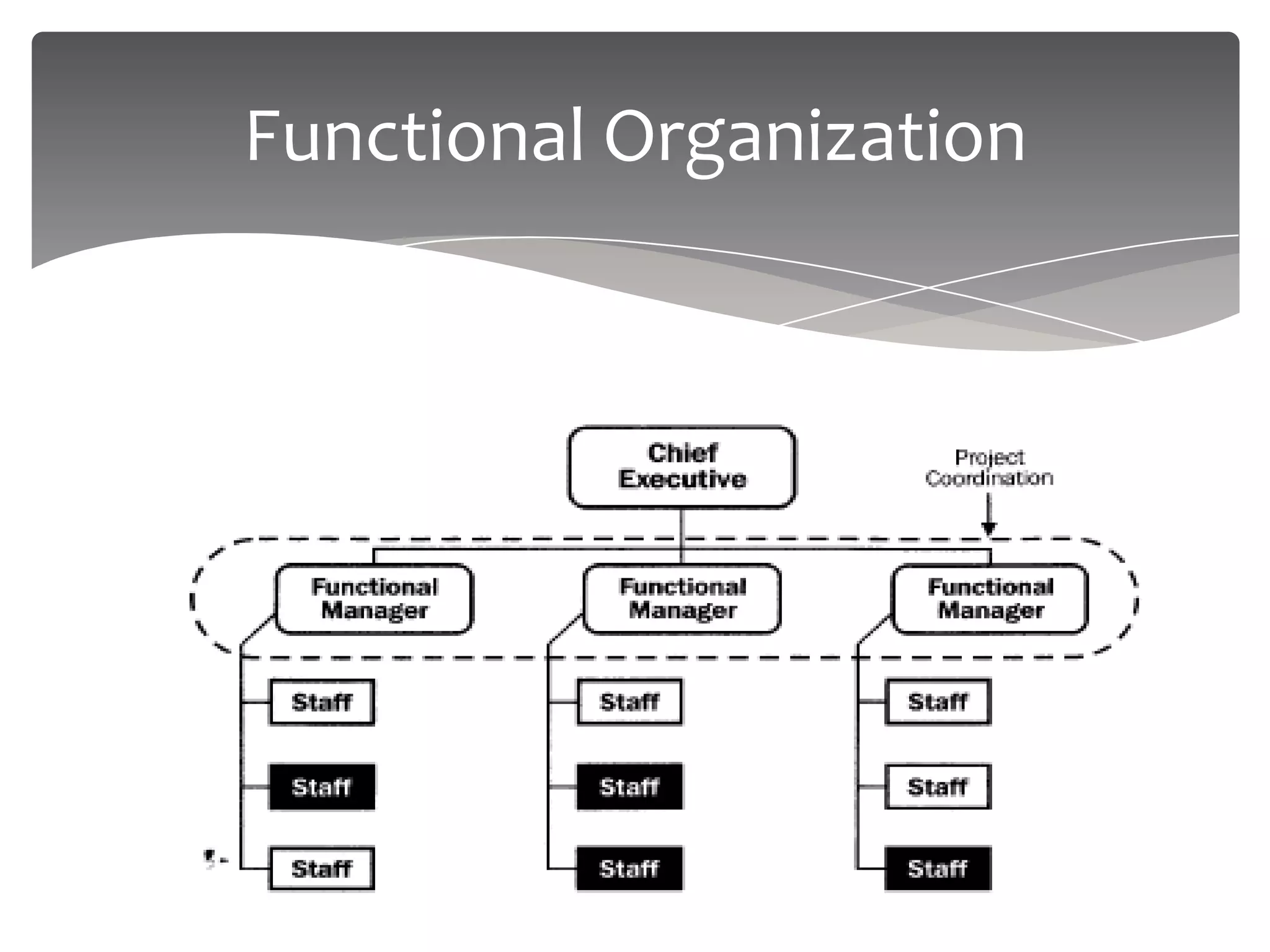
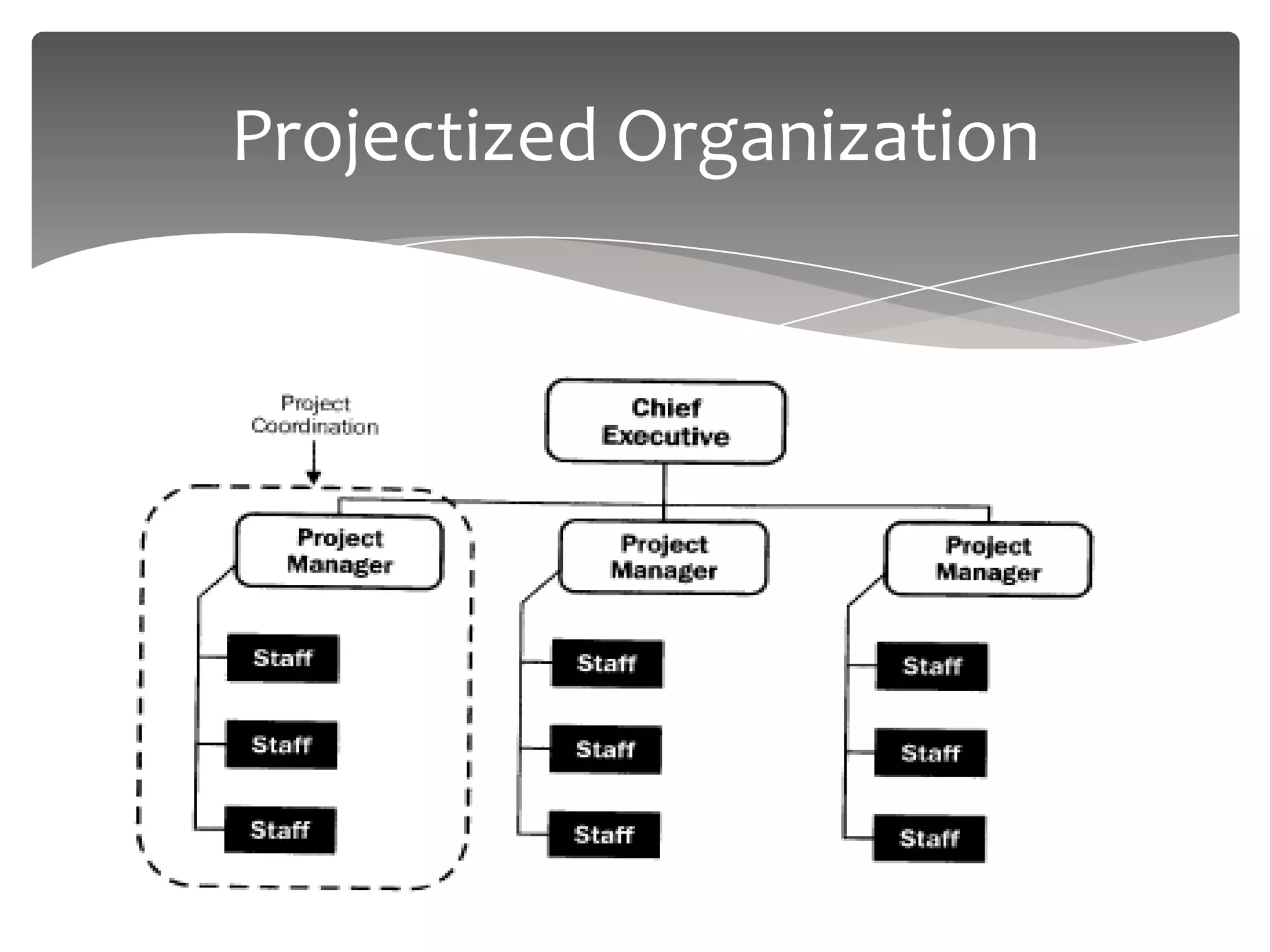
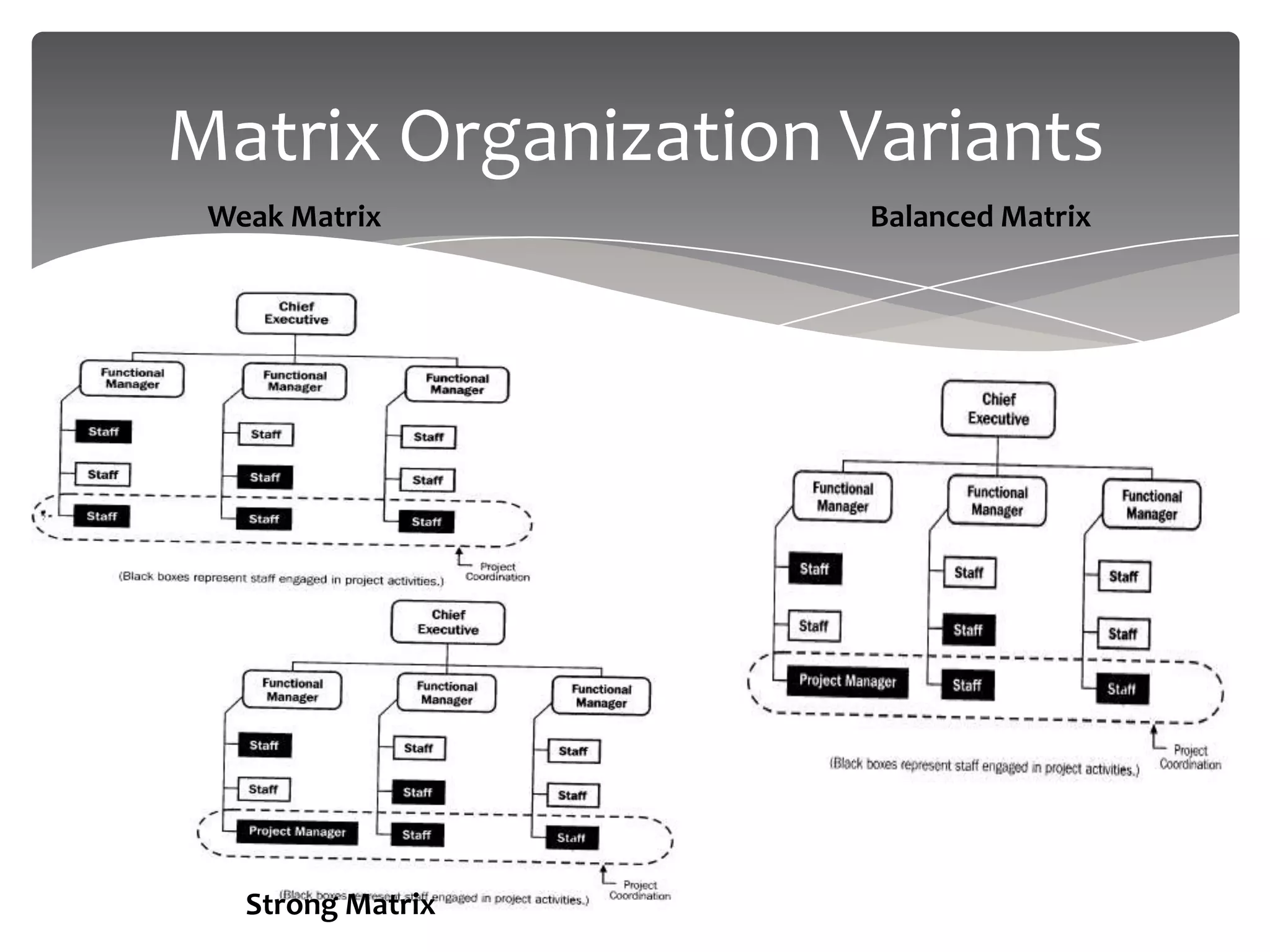
The document provides an overview of project management. It defines a project as a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product or service. It discusses project characteristics, examples of IT and non-IT projects, and compares projects to operations. The document also covers the project management triangle, stakeholders, the need for projects, project constraints, and the roles and responsibilities of a project manager. Finally, it discusses project environments, organizations, and compares functional, matrix and projectized organizational structures.