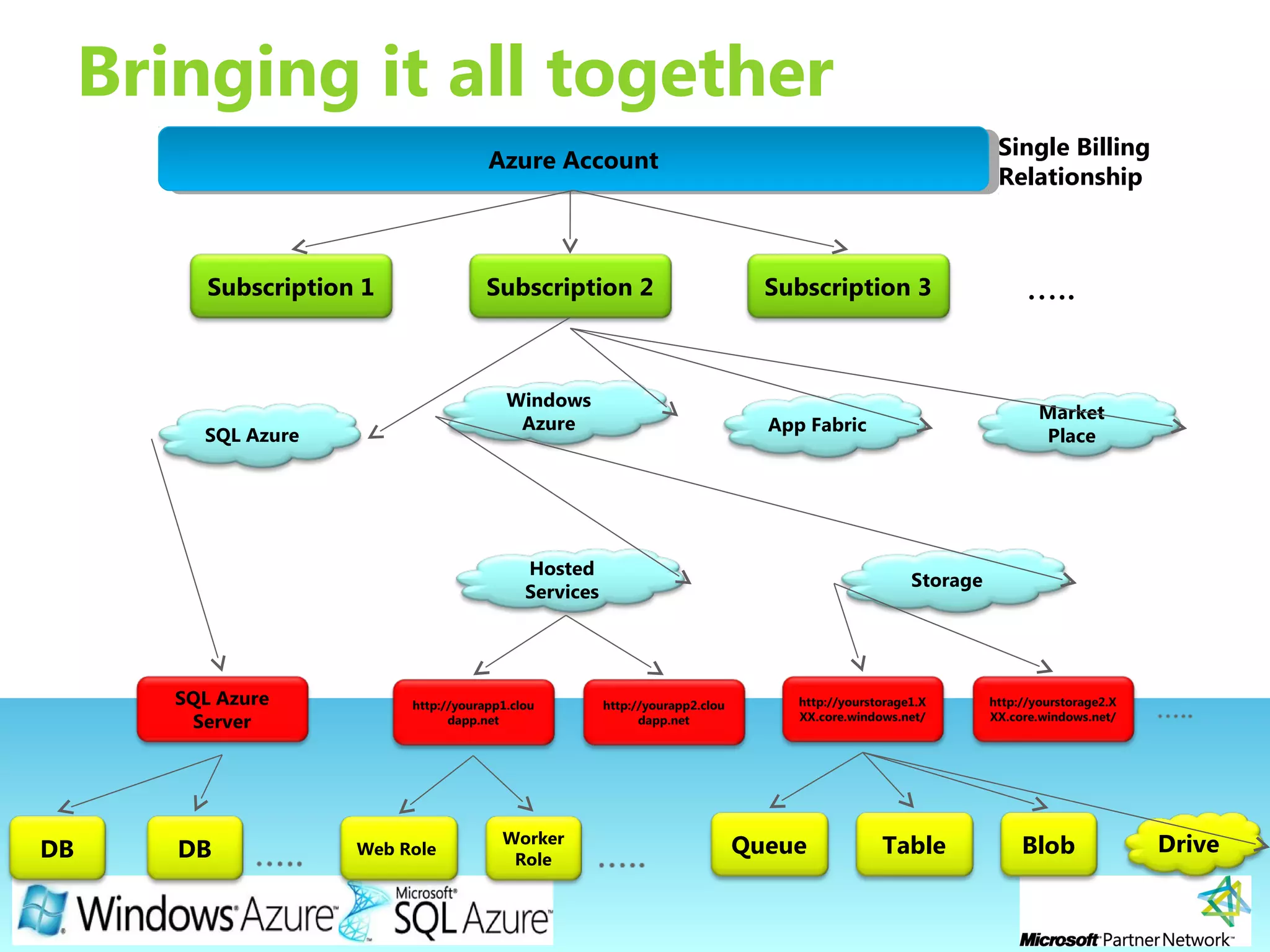
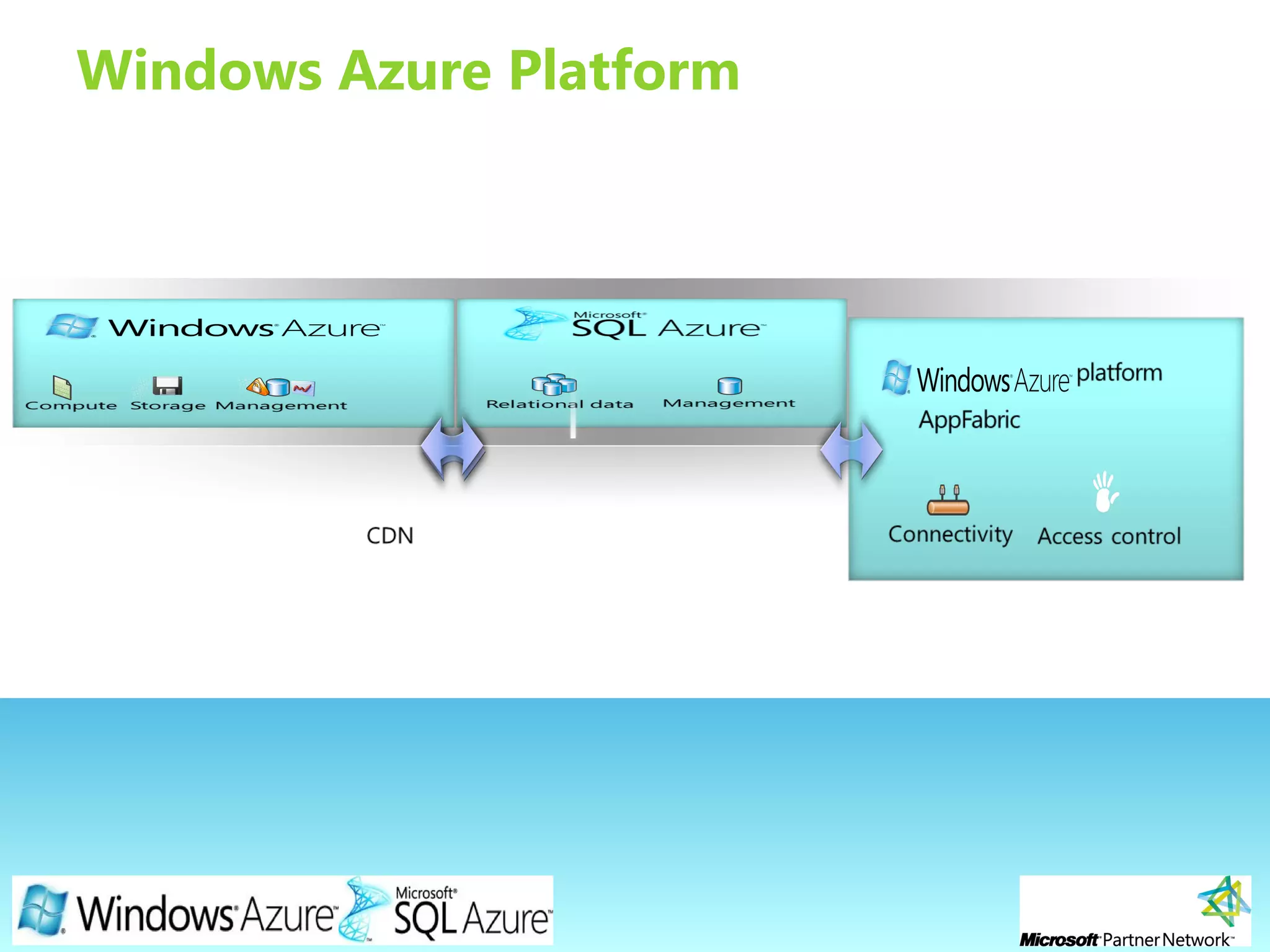
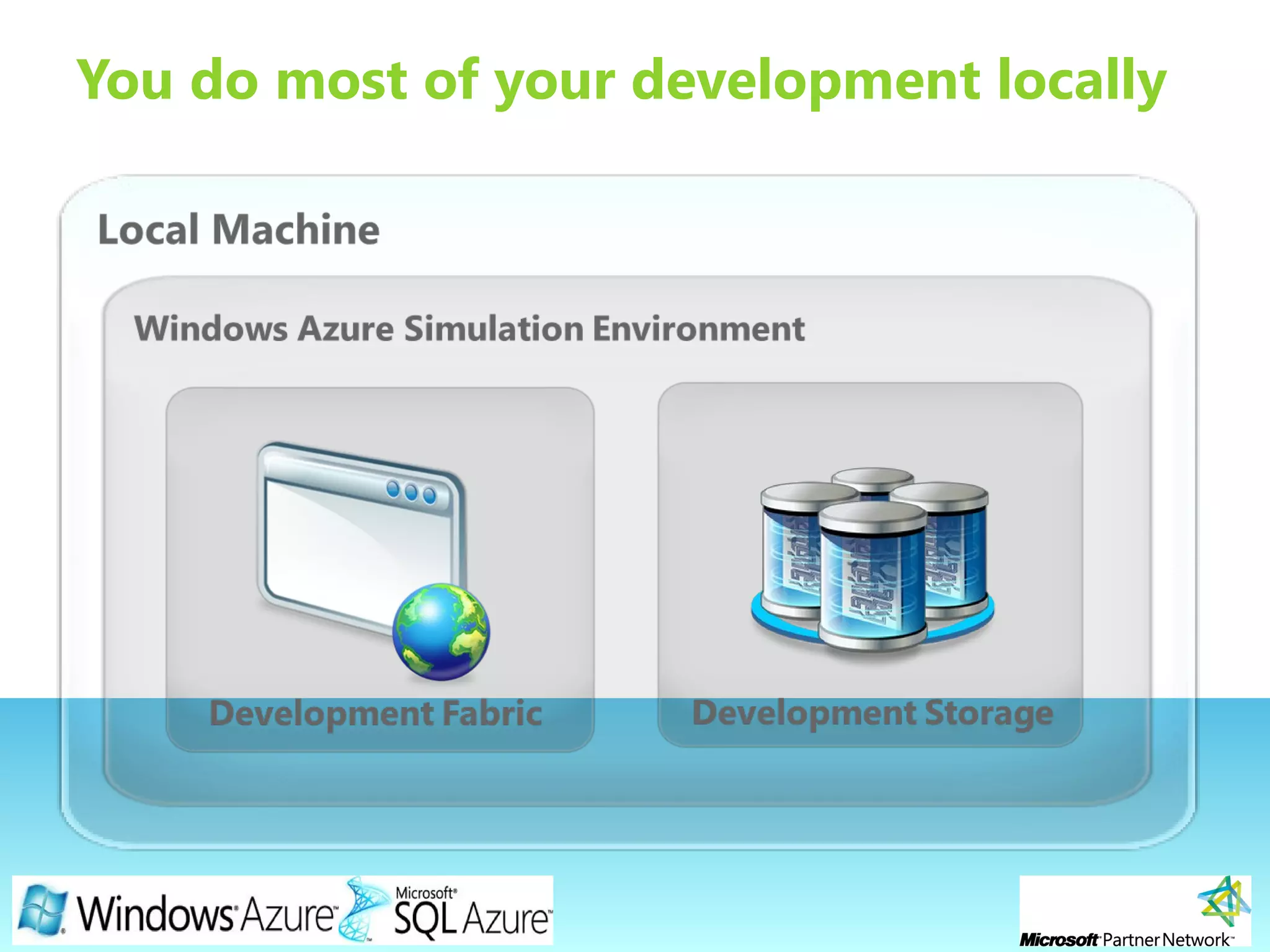
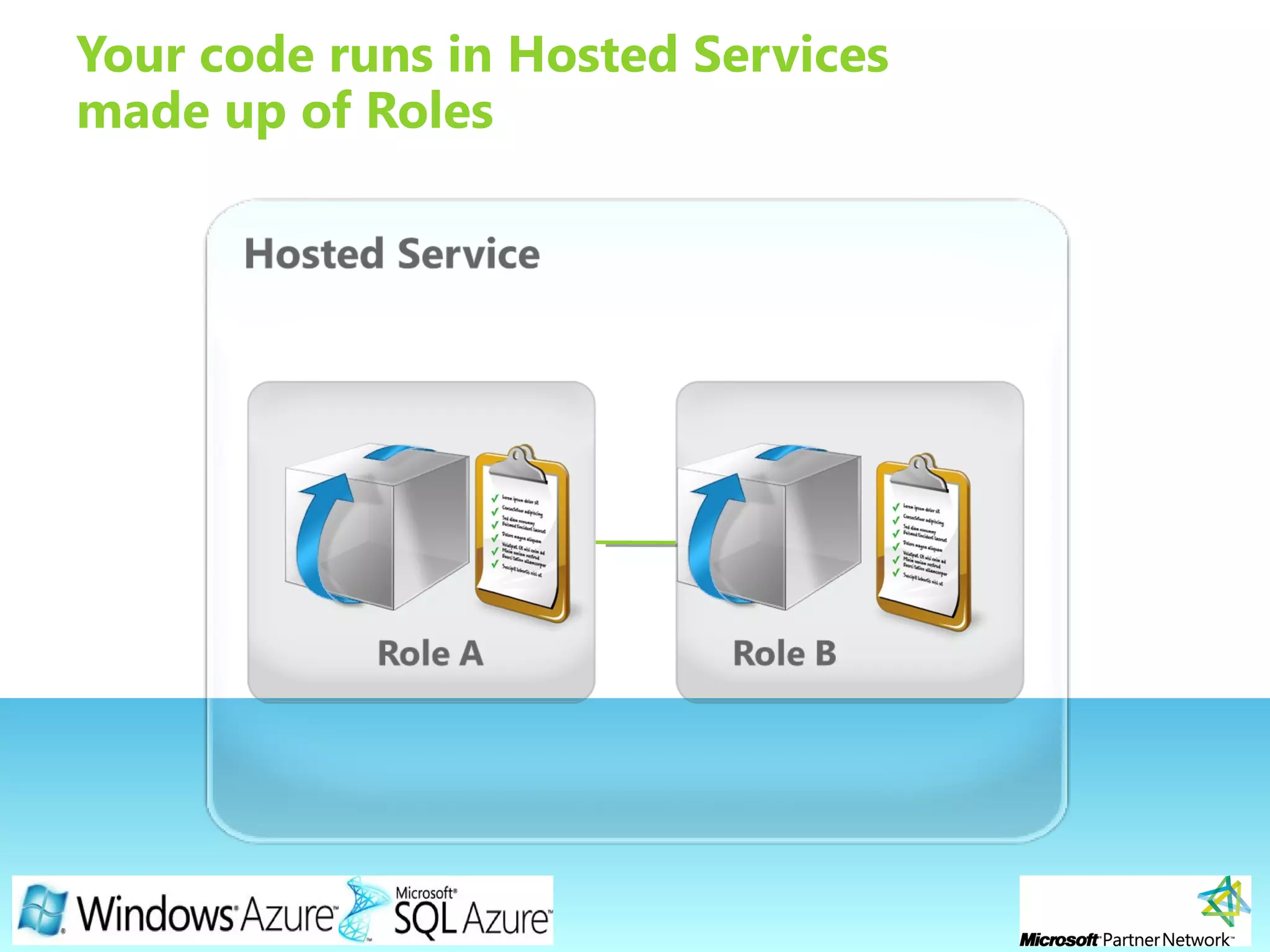
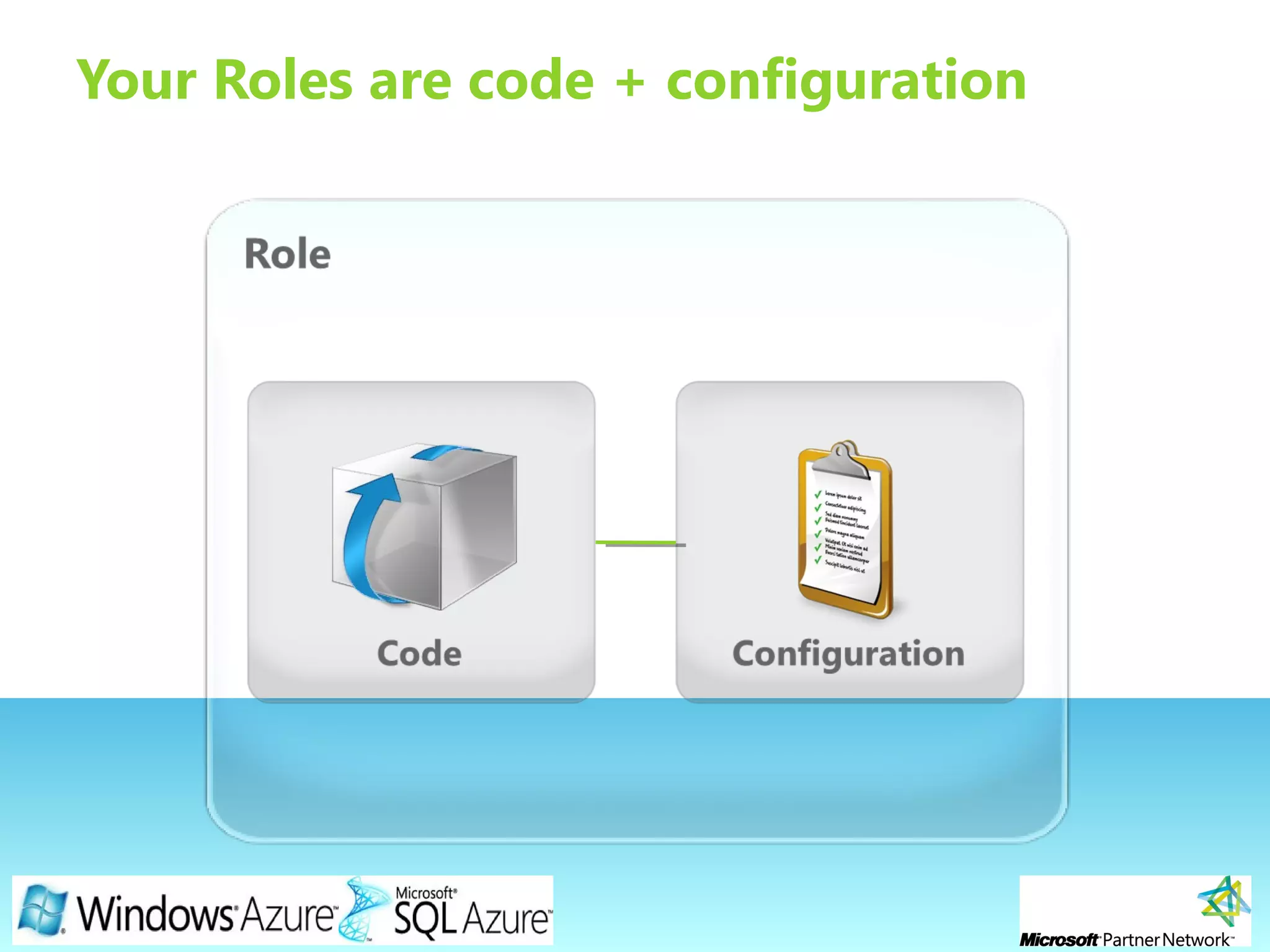
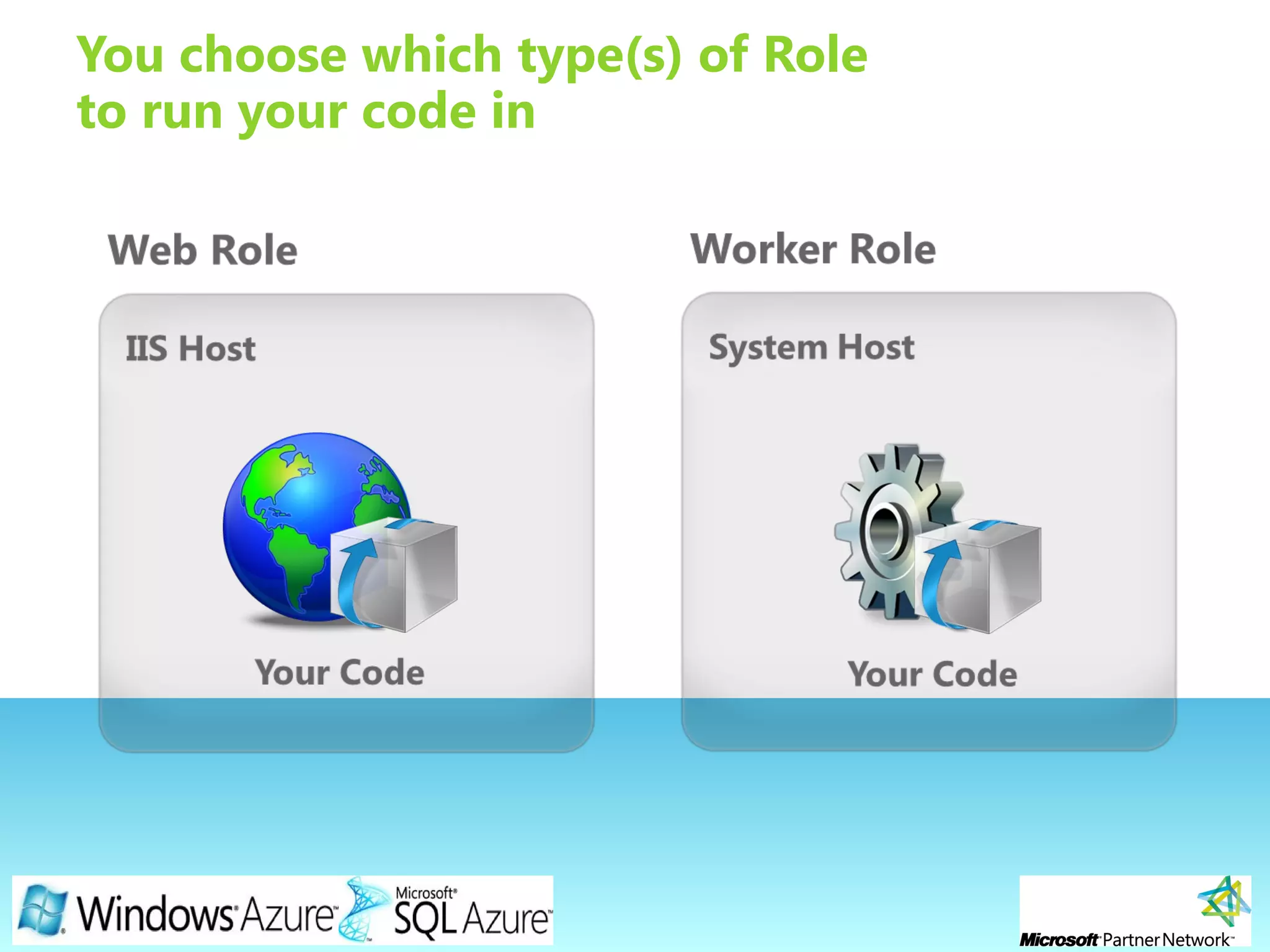
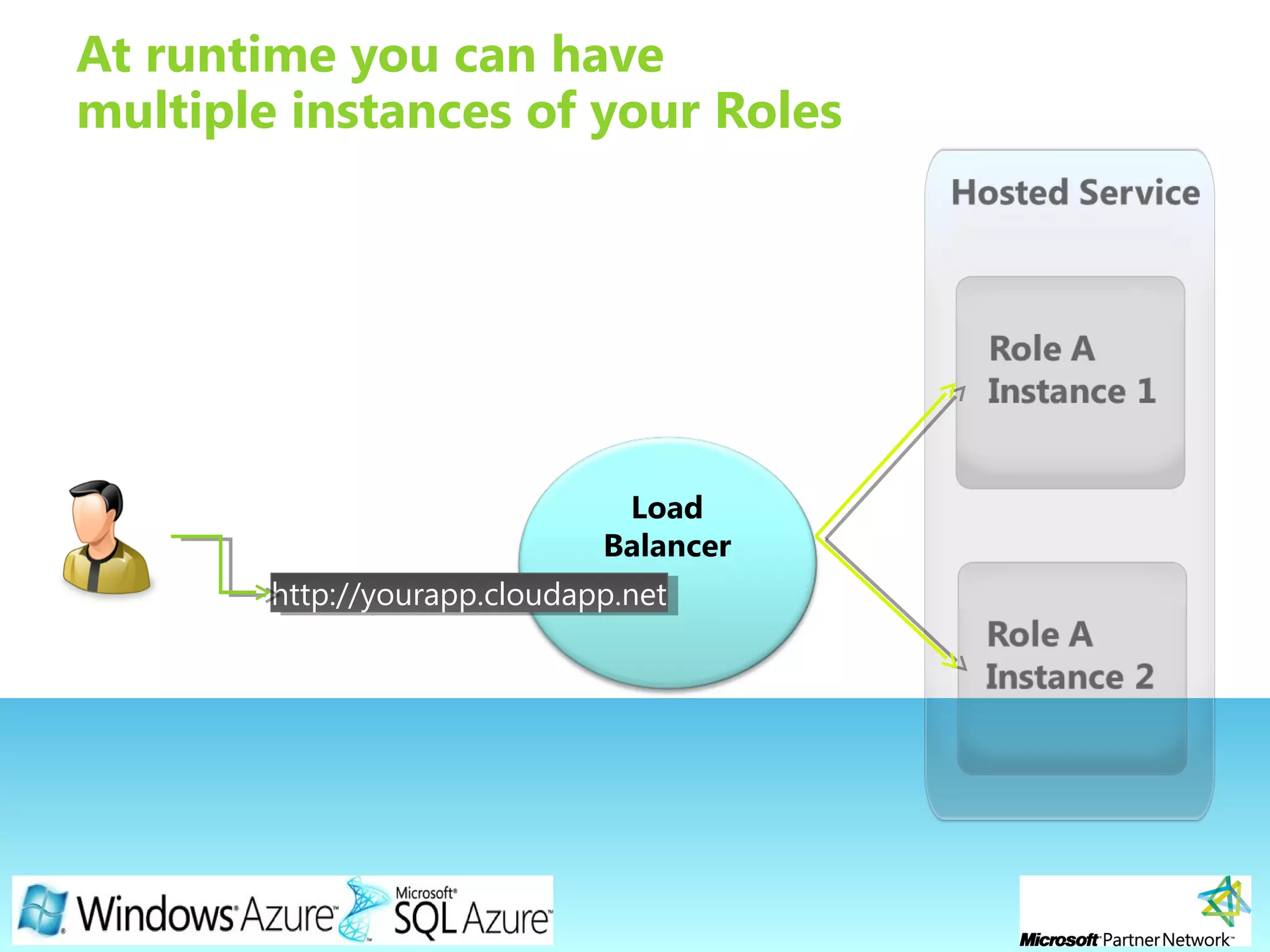
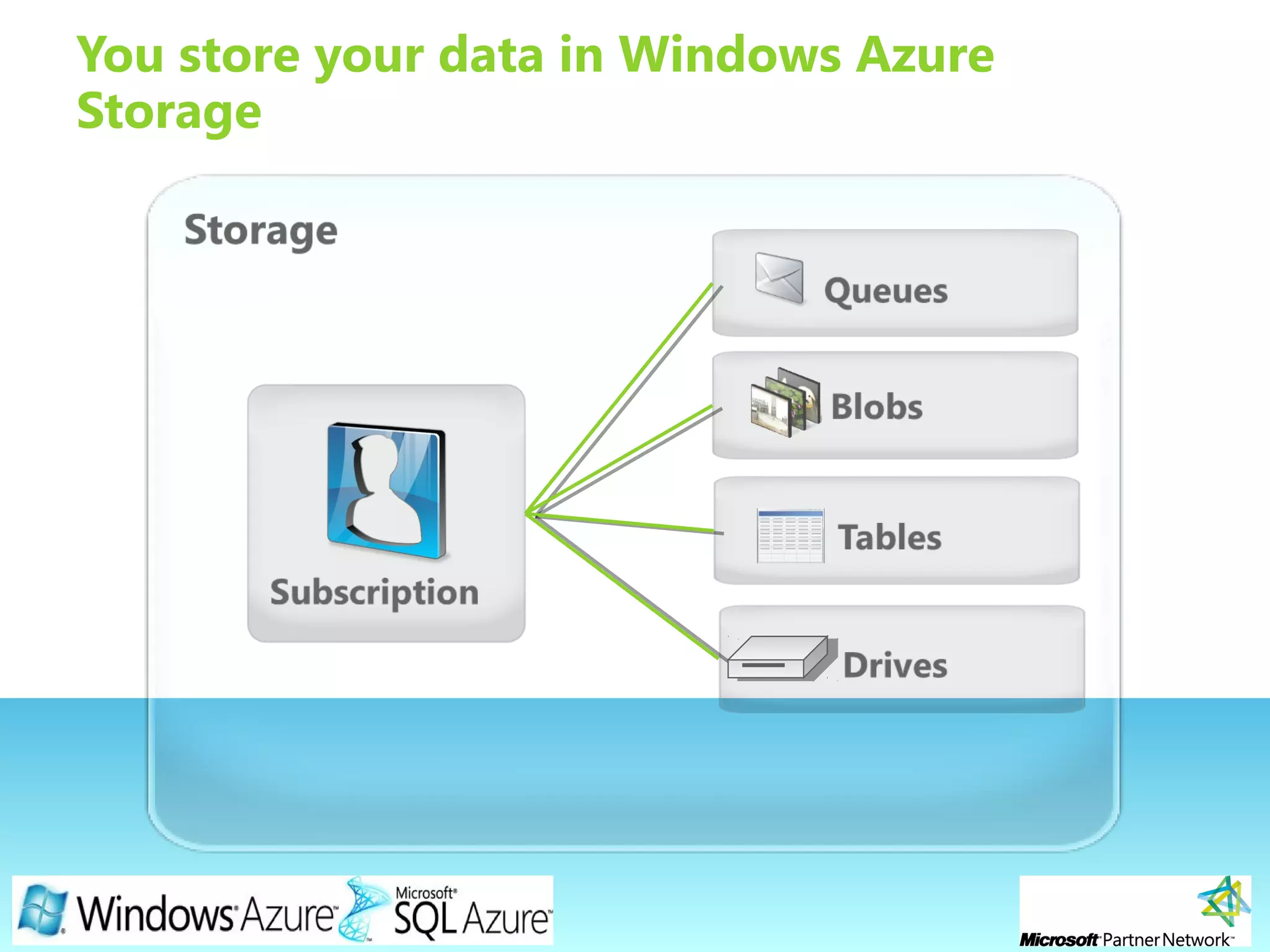
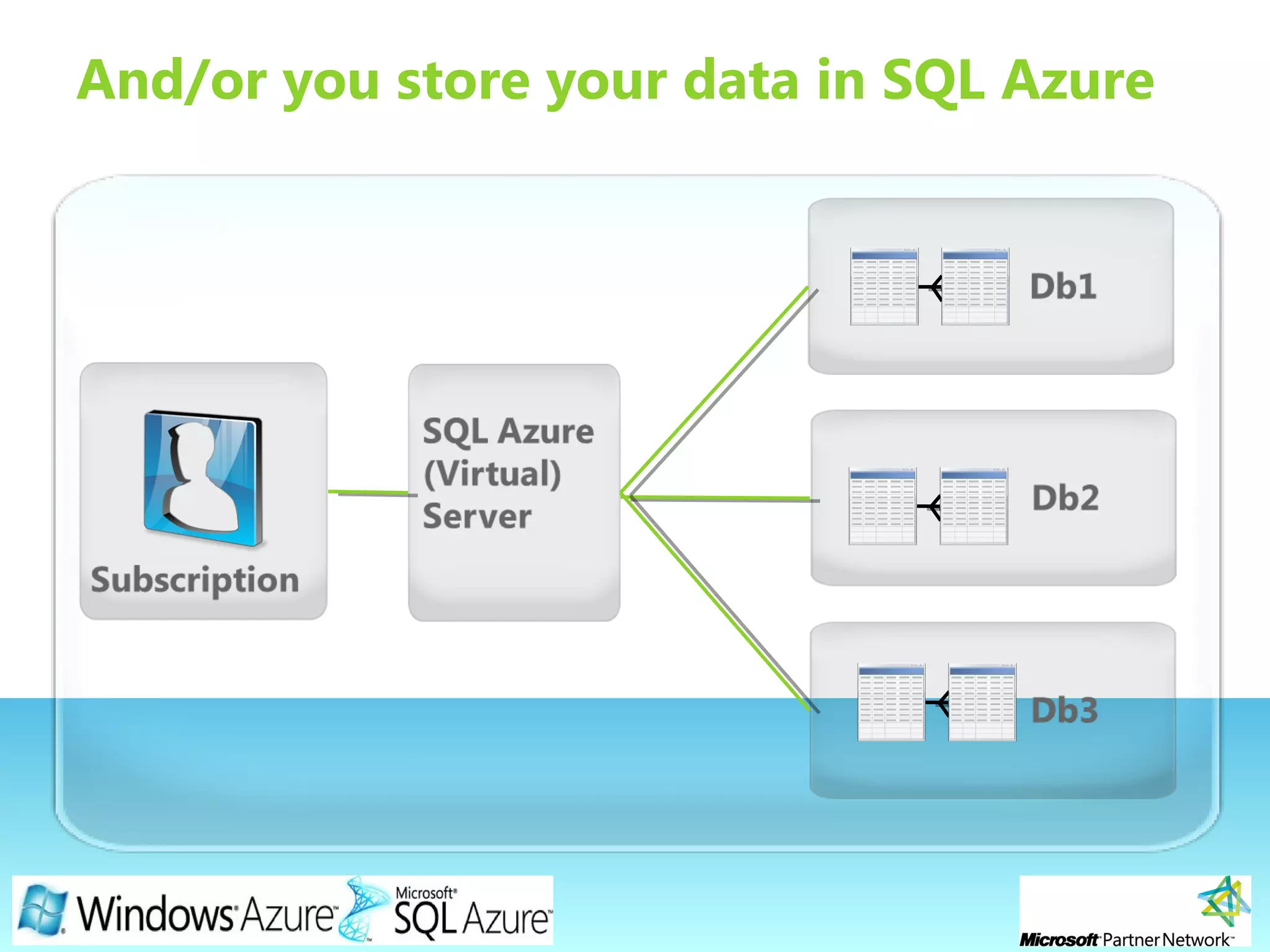
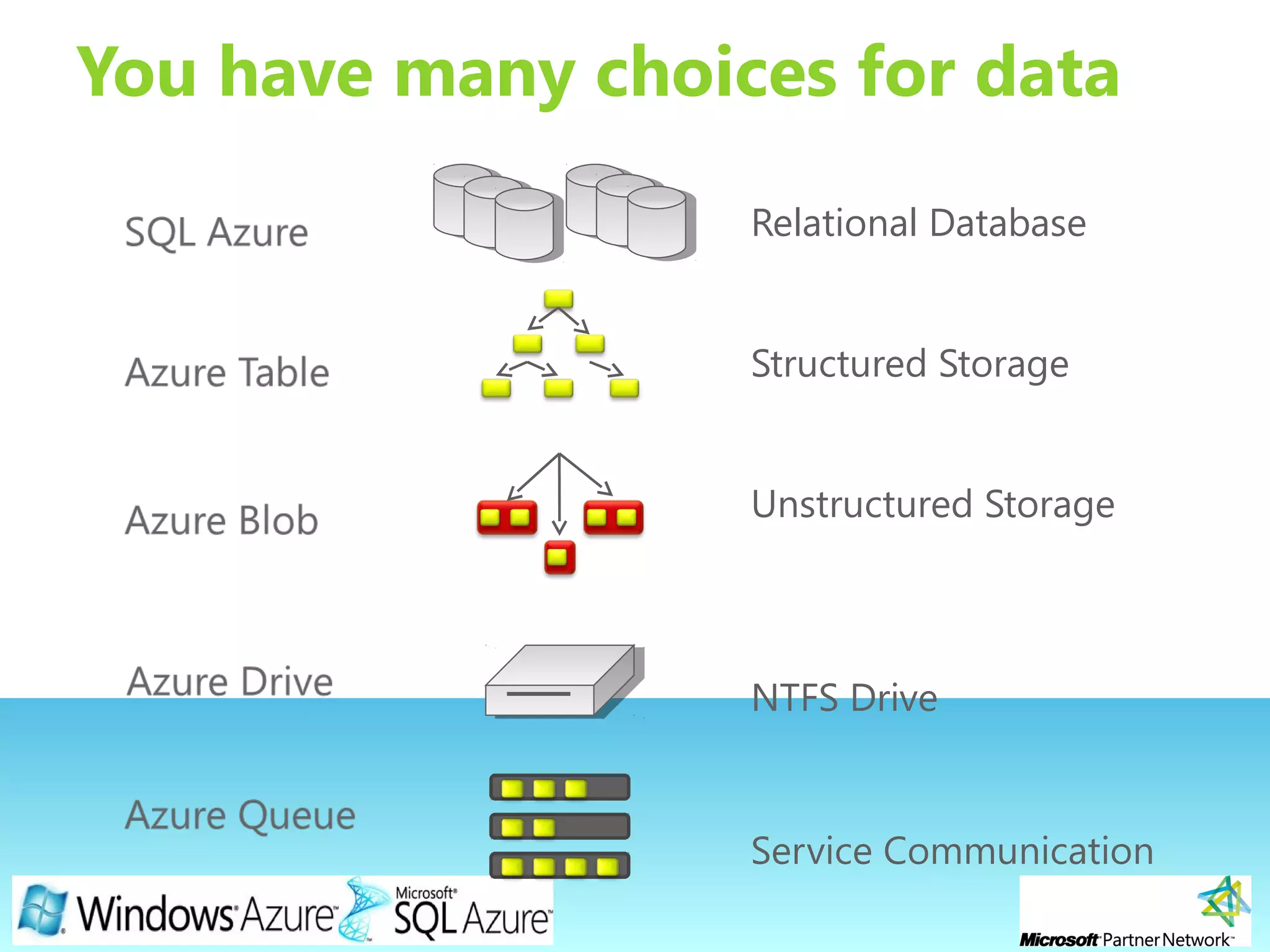
This document provides an overview of the Windows Azure platform. It discusses how developers can build applications that run code inside hosted services made up of roles. Developers can store data using Windows Azure storage options like SQL Azure, blobs, queues and tables. The document also provides a demo and recommends next steps for learning more about the Windows Azure platform.










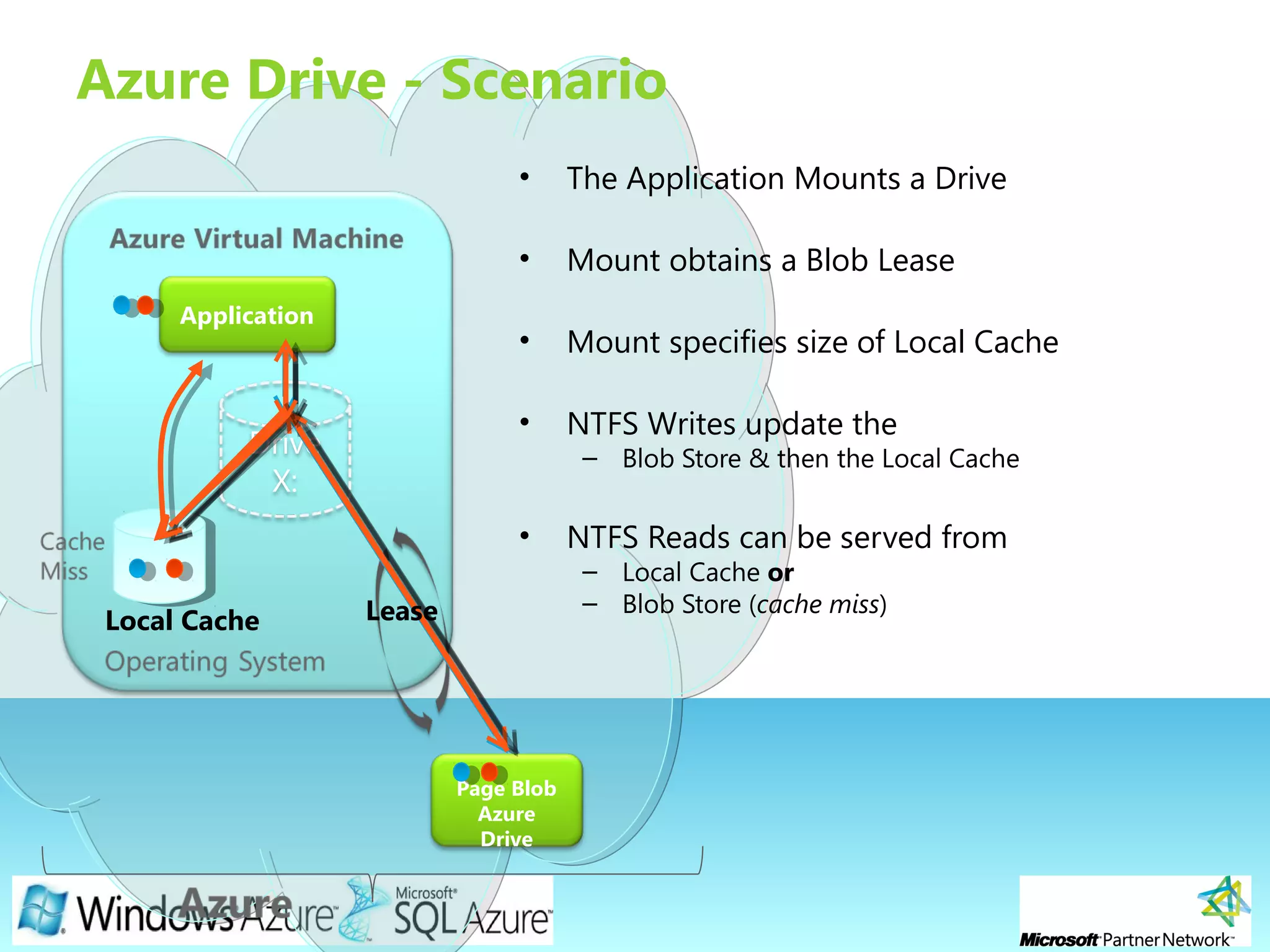
![Page 21
Azure Drive (X-Drive)
• Access to a Local Drive in Azure
• Enables existing applications using NTFS to easily migrate to the
cloud
• Essentially a Page Blob formatted as NTFS
– Remote Access via Page Blob Interface
• Durable NTFS volume [upto 1TB] for Windows Azure Applications
• Drives in the Cloud are only mountable by VMs within Cloud
– Mounted by one VM at a time for read/write
– A VM can dynamically mount up to 16 drives](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2windowsazureplatformin30mins-ericnel-101124101950-phpapp01/75/Windows-Azure-Platform-in-30mins-by-ericnel-21-2048.jpg)
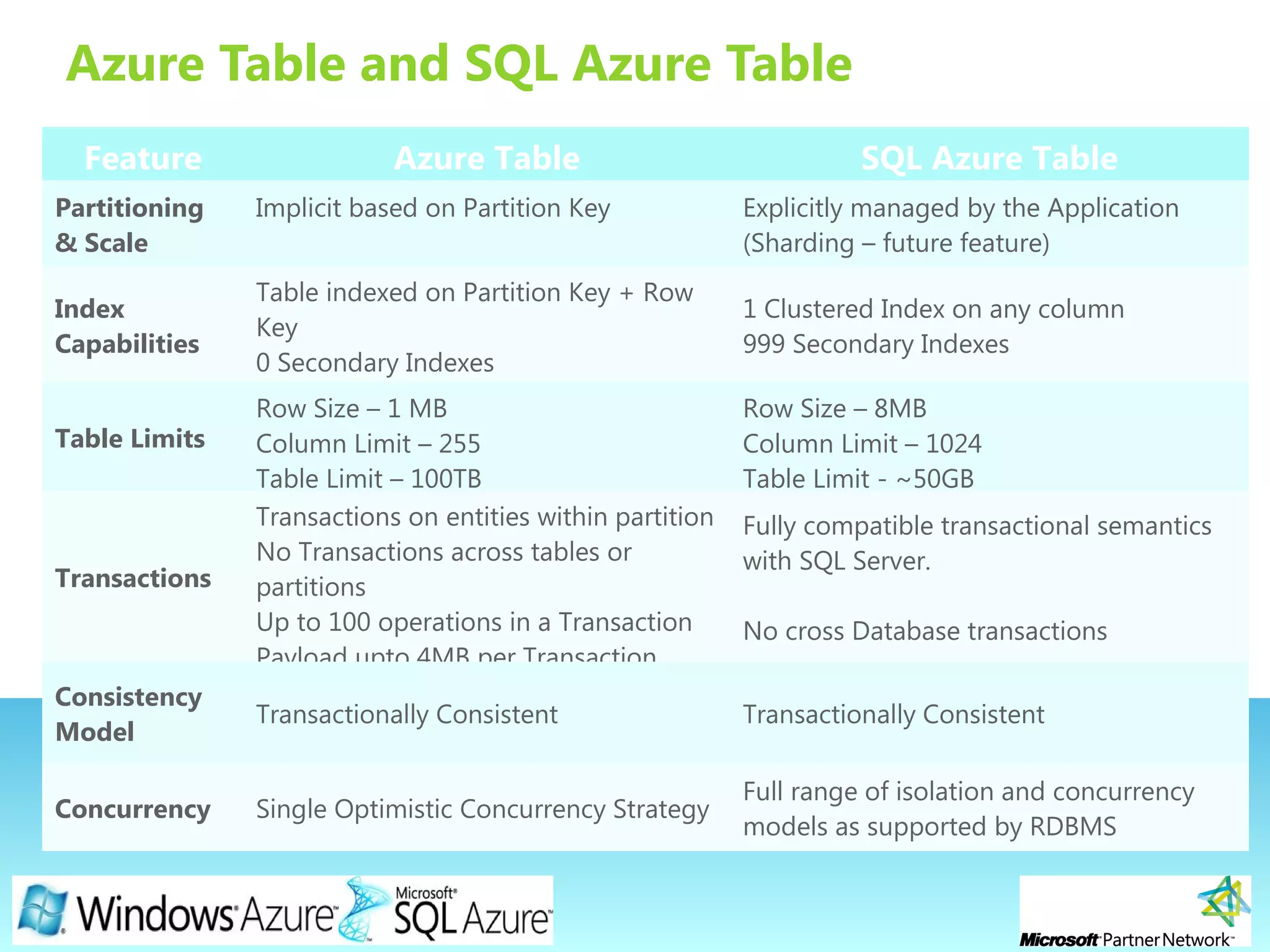
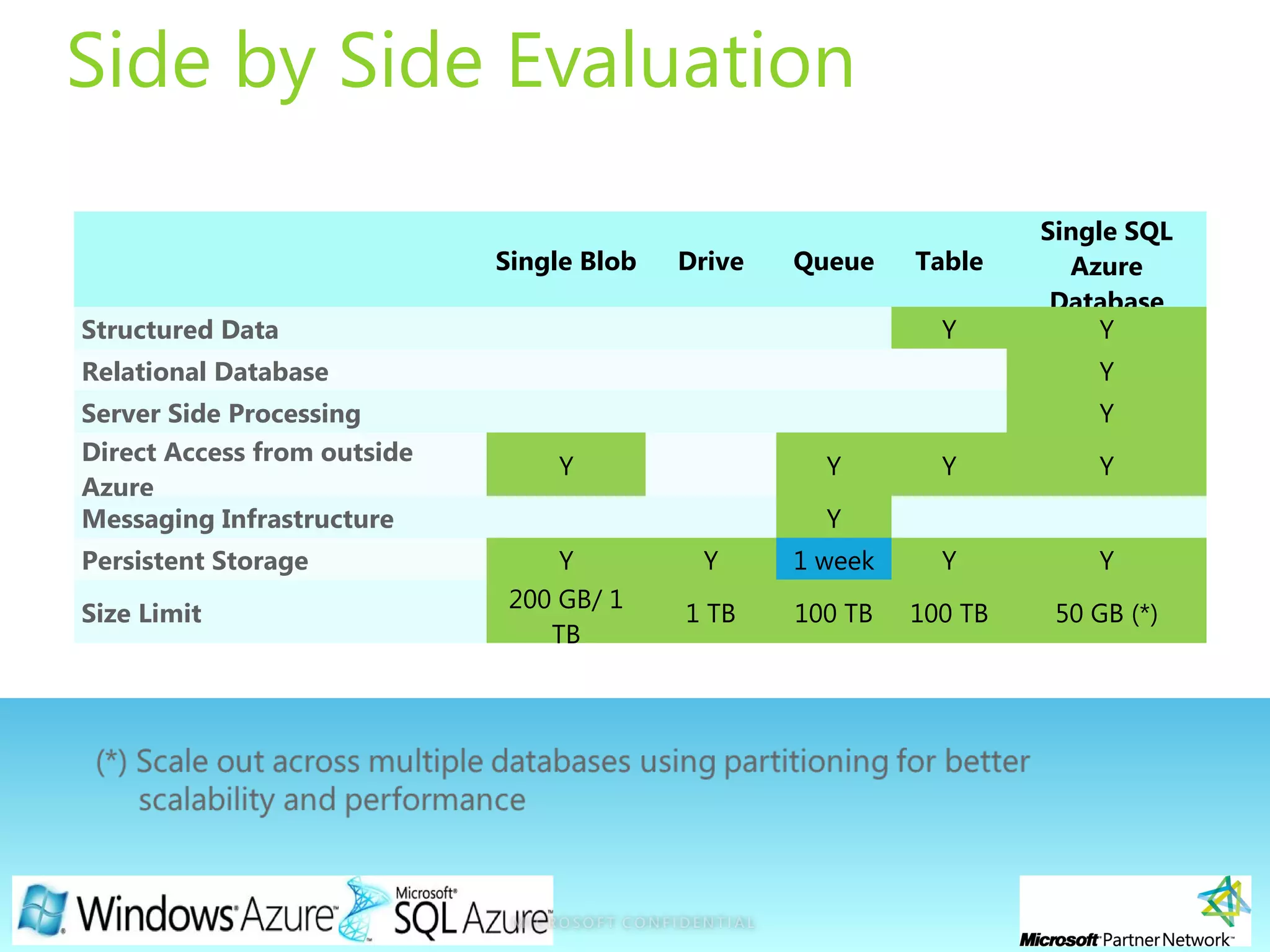
![Page 24
Azure Table and SQL Azure Table
Feature Azure Table SQL Azure
Data
Access
REST API, ADO .NET, Client Library SDK
Standard tools and APIs apply
SSMS, Visual Studio, ADO .NET, ODBC
Column
Types
Basic Types Usual SQL Server Data Types
Portability
Data portability coming with Windows Azure
Appliance
Data in SQL Azure similar to SQL Server
-Easy migration in and out of the cloud
-Use multi stream transfer to mitigate
network latency.
Queries
Upto 1000 entities [token pagination]
Beyond 5 sec – return continuation token
Queries by partition & row key are fast
No Custom Indexes Today
Non key queries are scans
Query capabilities as per standard SQL
Server database expectations
Offer Server Side Processing through
Stored Procedures and Complex
Queries
(Aggregation, Joins, Sorts, Filters, etc.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2windowsazureplatformin30mins-ericnel-101124101950-phpapp01/75/Windows-Azure-Platform-in-30mins-by-ericnel-24-2048.jpg)