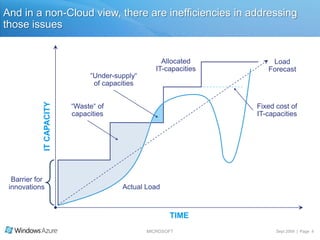
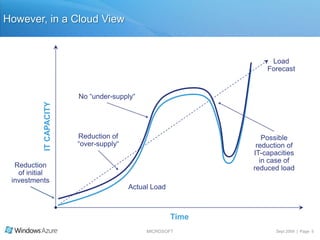
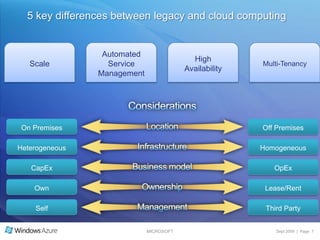
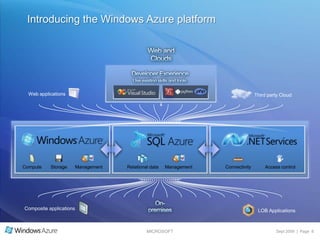
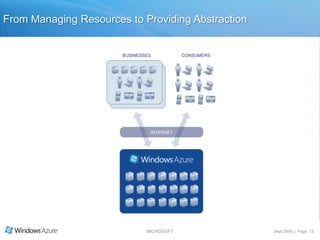
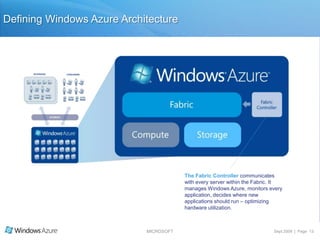
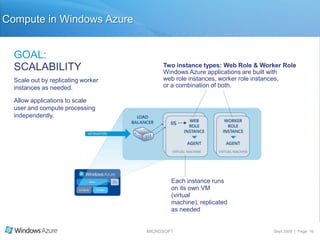
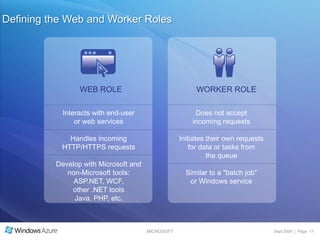
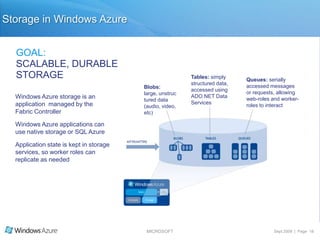
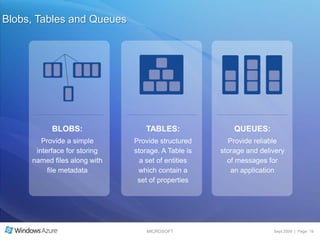
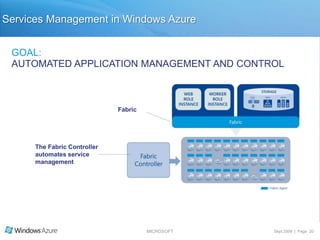
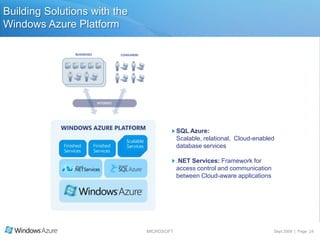
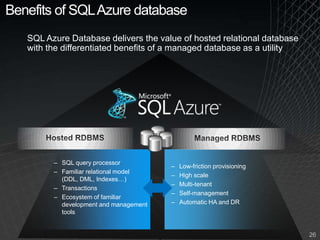
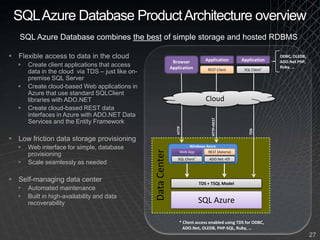
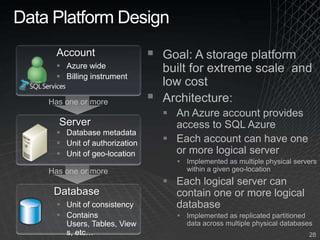
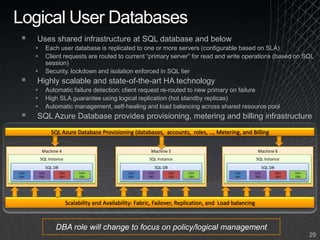
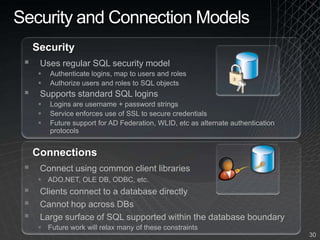
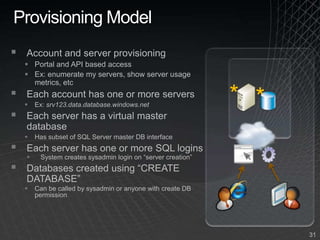
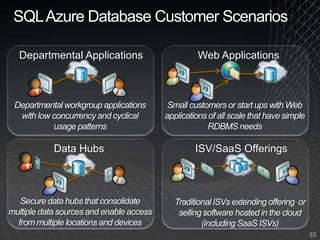
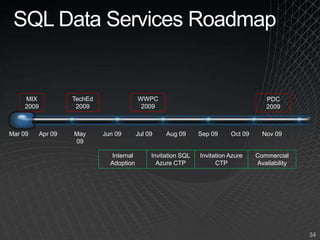
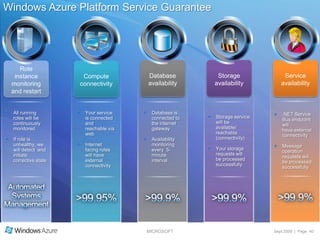
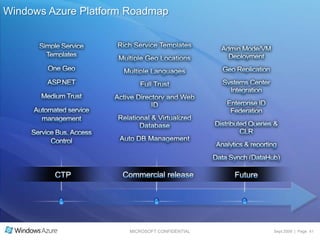
The document summarizes a presentation given by the Wisconsin .NET Users Group in September 2009. It discusses challenges facing enterprises and how cloud computing addresses issues like high infrastructure costs, limited data center capacity, and lack of a common platform. It introduces the Windows Azure platform and how it provides automated management, scalability, and a familiar development experience. Key aspects of Windows Azure including its architecture, SQL Azure, and pricing models are summarized.