The document discusses managing research data and digital repositories in difficult economic times. It provides an overview of policies, strategies, technologies and infrastructure used to manage research and teaching materials. It also discusses funding from JISC and other organizations for repository services and projects in the UK.

![Overview policies/strategies/technologies/infrastructure to manage research/teaching Scope Digital repositories at the level of the institution (for itself), at a level above the campus: for institutions, for UK, for much much more within the European and wider international context in support of research, learning & teaching …. and management Having voice as … a provider of common services and national infrastructure [EDINA] a user of repository software [Eprints, DSpace, IntraLibrary] a member of SONEX and indirectly of COAR and UK-CORR and focus on repository-related progress in the UK since last JISC/CNI; where is the value, how this is assessed/expressed? Size of investment in recent times Cost-effectiveness and ‘impact’ of provision Effort at institutional & inter/national level and the ‘shared services’ agenda? Wondering what Dorothea said next …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jisccni2010burnhillv4-100715140730-phpapp02/75/Repositories-Update-UK-2-2048.jpg)

![R is for Repository What are Repositories? Facility/technology to support at least three basic types of service: PUT: a service interface that allows one or more use community to deposit/issue digital content (+ metadata on that content) KEEP: a service that ensures the integrity of that content, for the life of the repository GET: a service interface that allows one or more use community to search/extract that content Use community: persons or machines/software; appropriate interface Digital Repositories Review (R.Heery and S.Anderson, 2005) Digital repository differs from other digital collections in that: "content is deposited, whether by content creator, owner or third party architecture manages content as well as metadata; repository offers a minimum set of basic services [put, get, search, access control] must be sustainable & trusted, well-supported & well-managed." "a university-based institutional repository is a set of services … for the management and dissemination of digital materials created by the institution and its community members. … an organizational commitment to the stewardship of these digital materials, including long-term preservation where appropriate, as well as organization and access .. ." (C. Lynch, 2003)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jisccni2010burnhillv4-100715140730-phpapp02/75/Repositories-Update-UK-4-2048.jpg)


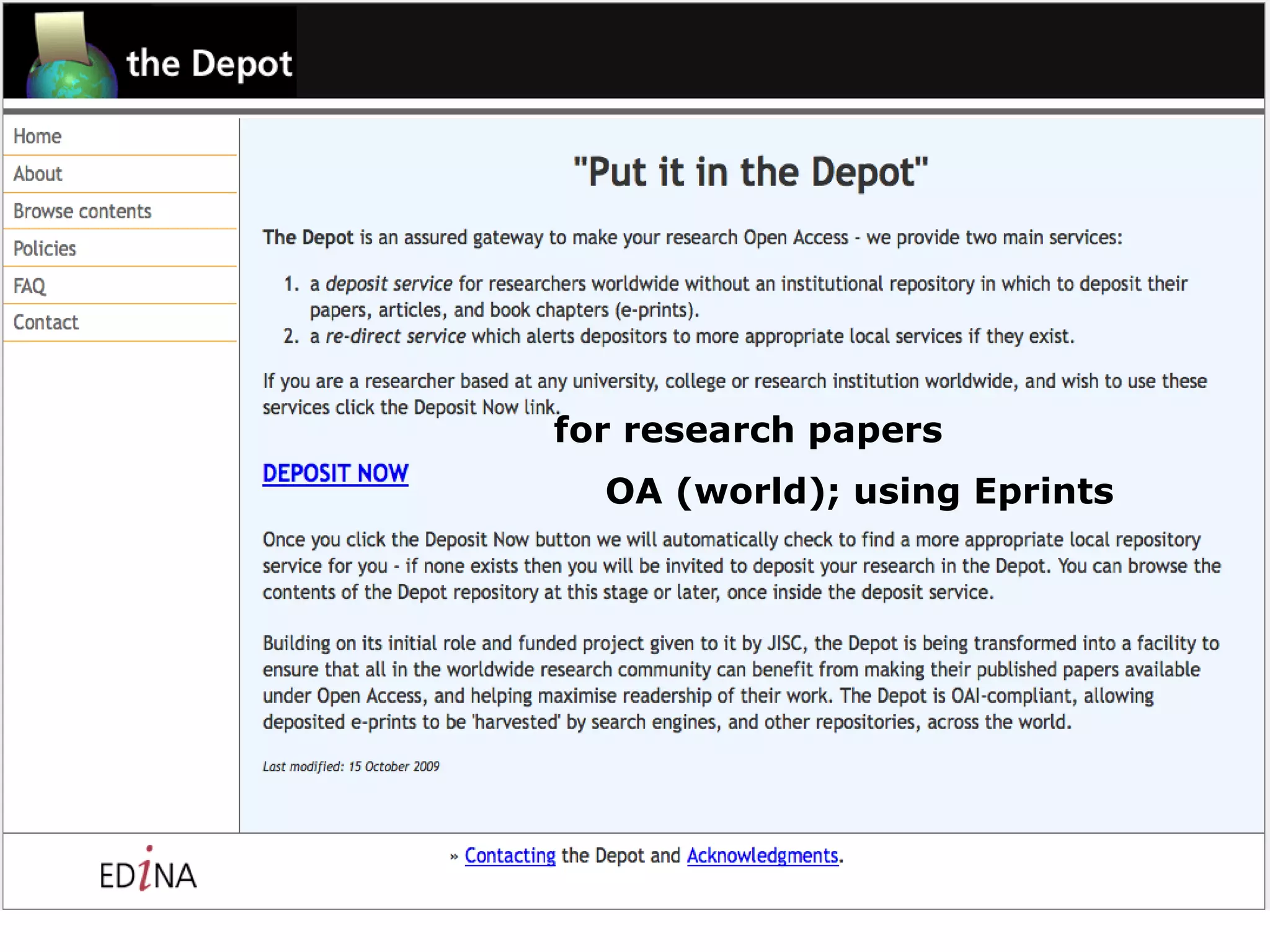
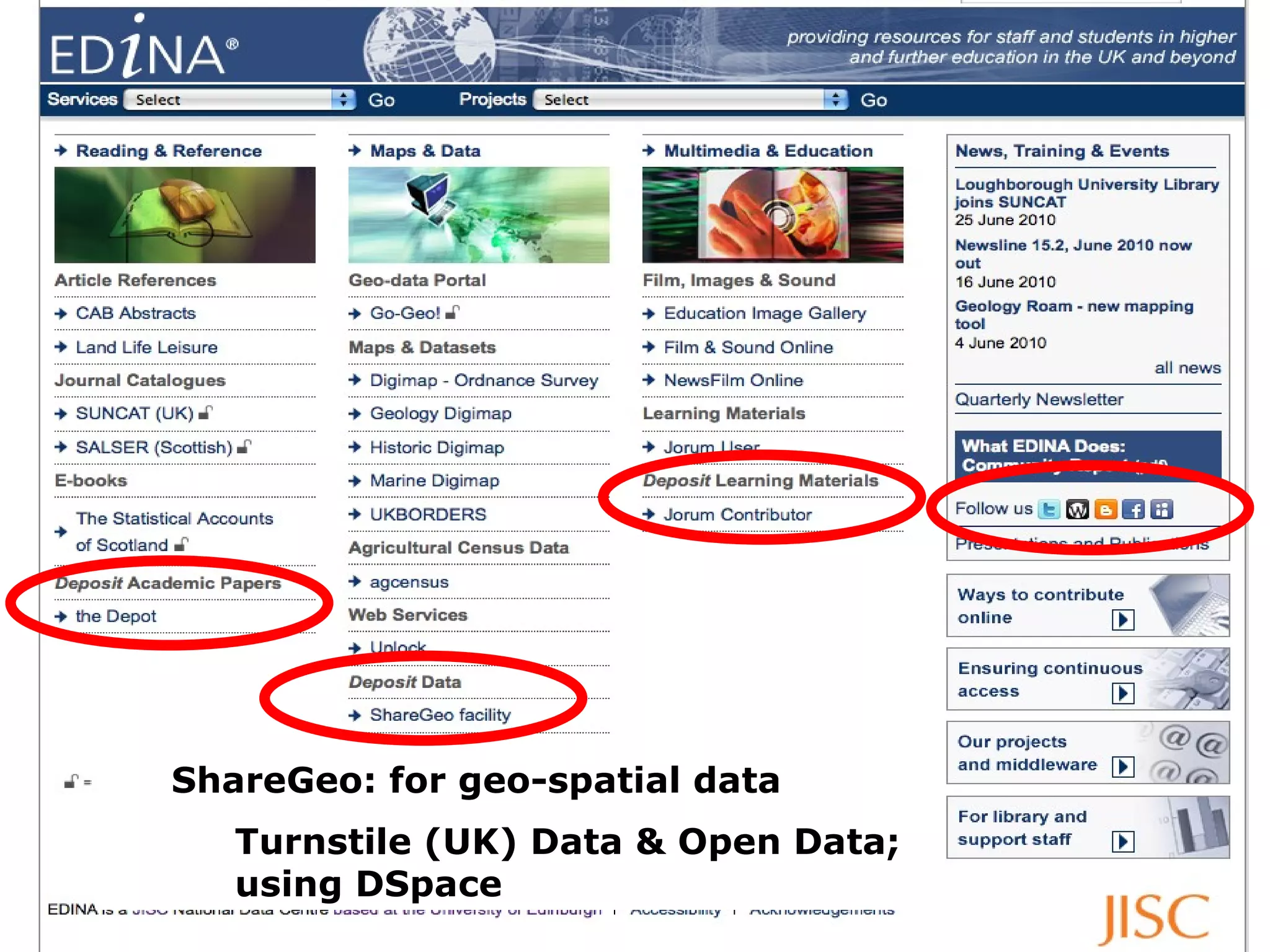
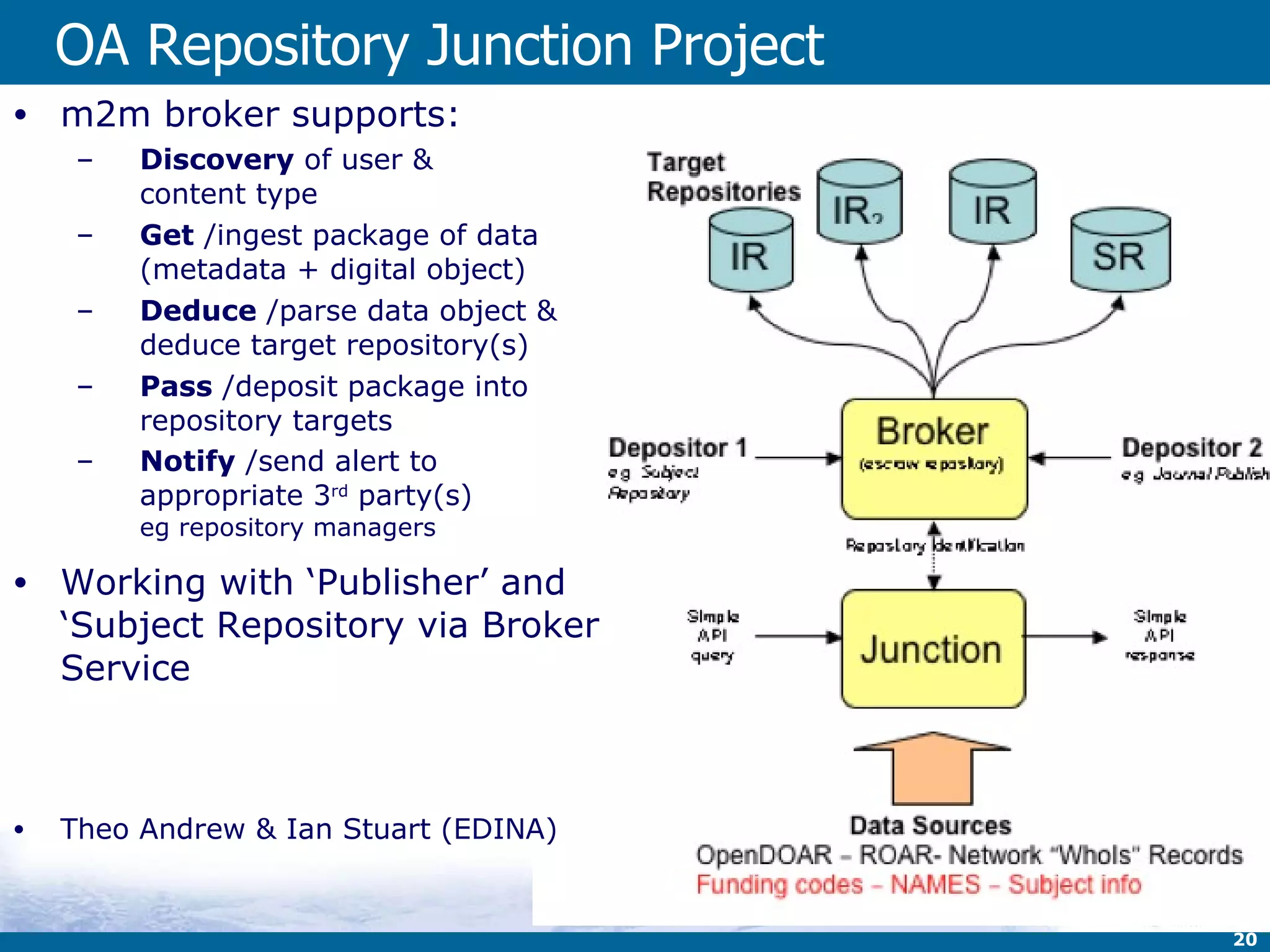
![1&2 provider of services & user of software EDINA-run repositories, with and without JISC DataShare : for research data (institutional, U of Ed) Open Data; using DSpace Jorum : for learning materials [with Mimas] OER and turnstile (UK); using DSpace & IntraLibrary OpenDepot (the Depot): for research papers OA (world); using Eprints ShareGeo : for geo-spatial data Open Data and turnstile (UK); using DSpace OA Repository Junction as shared service tool using own code and Eprints as an 'escrow' repository during the transfer process. & maybe others … depending on definition of repository](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jisccni2010burnhillv4-100715140730-phpapp02/75/Repositories-Update-UK-11-2048.jpg)
![for learning materials [with Mimas] OER and turnstile (UK); using DSpace & IntraLibrary](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jisccni2010burnhillv4-100715140730-phpapp02/75/Repositories-Update-UK-12-2048.jpg)


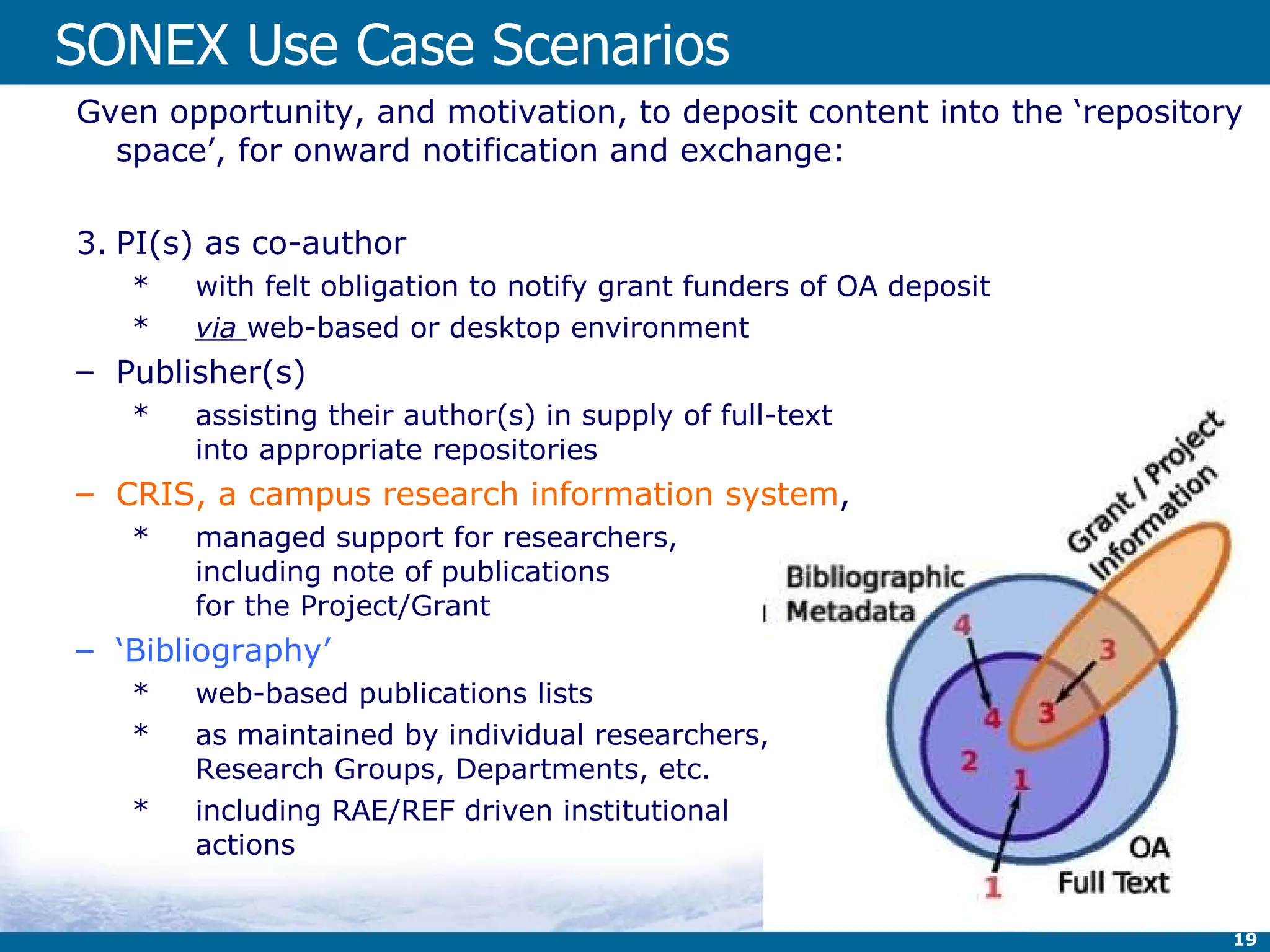
![SONEX Use Case Actors Use case Actor 1: Individual author/researcher [person] author of multi-authored article, other author(s) at other institution(s) sole author with entire career at a single institution [exception] Variant: author making deposit is the PI of funded research project(compliance with mandate from funder to deposit) Variant: author making deposit is not the PI of funded research project but work is associated with one or more funded research projects (PI) Use case Actors 2&3: Depositor is not author (Mediated deposit) Variant: support staff in research group Variant : Library’s own resources and document collections Variant: Institutional Research Support Systems (CRIS systems) [machine] Use case Actor 4: Repository Manager (RM) of an IR wishing to be notified & obtain copy from a subject (SR) or another IR Use case Actor 5: Publisher (which work is published) [machine] deposit under OA of the author's final copy (OA-RJ & PEER projects) OA of published copy Pointer supply to published copy Other Actors: Vendor of authoring or repository software](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jisccni2010burnhillv4-100715140730-phpapp02/75/Repositories-Update-UK-18-2048.jpg)




![UK-CORR: UK Council of Research Repositories individual rather than institutional, [email_address] UK has ‘rich heterogeneous repository landscape’ (C.Awre); lurk following comment from Dorothea Salo](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jisccni2010burnhillv4-100715140730-phpapp02/75/Repositories-Update-UK-25-2048.jpg)
![UK-CORR: UK Council of Research Repositories individual rather than institutional, [email_address] UK has ‘rich heterogeneous repository landscape’ (C.Awre); lurk following comment from Dorothea Salo: US mainly about OA full texts; UK mainly about … serving research assessment! Is there more to IRs than the REF: lots of bibliographic records & little full text? Should IRs only accept full text, not metadata only? in absence of a CRIS, our IR had to do REF (Lancaster & Northampton) was OA but then RAE2008, but should aim to include all (OU) motive for IR was digital preservation, with different REF system; funder mandate compliance for OA; visibility via OA (Oxford/Bodleian) RAE/REF is opportunity to engage institution-wide (Warwick) Advent of CRIS (which don’t manage outputs well) may be opportunity for IRs to have role, including use of ‘metadata only’ as lever to obtain full text (Hull) REF & research management information allows IRs to be embedded as platform for OA (Southampton) RAE/REF has different goals to OA and IRs with low % of full text may undermine OA movement (Nottingham)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jisccni2010burnhillv4-100715140730-phpapp02/75/Repositories-Update-UK-26-2048.jpg)
![COAR: Confederation of Open Access Repositories New: 1 st General Assembly in Madrid in March 2010 48 members drawn largely from Europe, but including both JISC & CNI, and also EDINA (University of Edinburgh) Work Plan for 2010/12, including Advocacy on behalf of OA and repositories (Rs) [both together?] Populating (OA) Rs Best practice documents Facilitate and ensure data interoperability of (across?) Rs interoperability with other systems (such as CRIS systems) Support national helpdesks Guidance on how Rs will form essential elements for global e-infrastructure Promote R manager profession Provide advice & guidance on suitable R infrastructure technologies Global (meta)data store Strategic partner other infrastructure-related initiatives worldwide](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jisccni2010burnhillv4-100715140730-phpapp02/75/Repositories-Update-UK-27-2048.jpg)
![Managing Data in Difficult [Interesting] Times End of an era? End of the R word? Embedded in domain-specific processes? Moving from technology to policy & practice: some domain-specific, some common to repositories Collection management: active curation & Linked relationships versions, data|article|learning material Collections, ‘see also’ First point of public issue (availability); Take-down regimes Institutional stewardship responsibility for its born-digital [and digitised] content "a university-based institutional repository [supports] a set of services … for the management and dissemination of digital materials created by the institution and its community members. … an organizational commitment to the stewardship of these digital materials, including long-term preservation where appropriate, as well as organization and access .. ." (C. Lynch, 2003) What of the (new) shared services imperative? Who does what, at what level/scale?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jisccni2010burnhillv4-100715140730-phpapp02/75/Repositories-Update-UK-28-2048.jpg)


