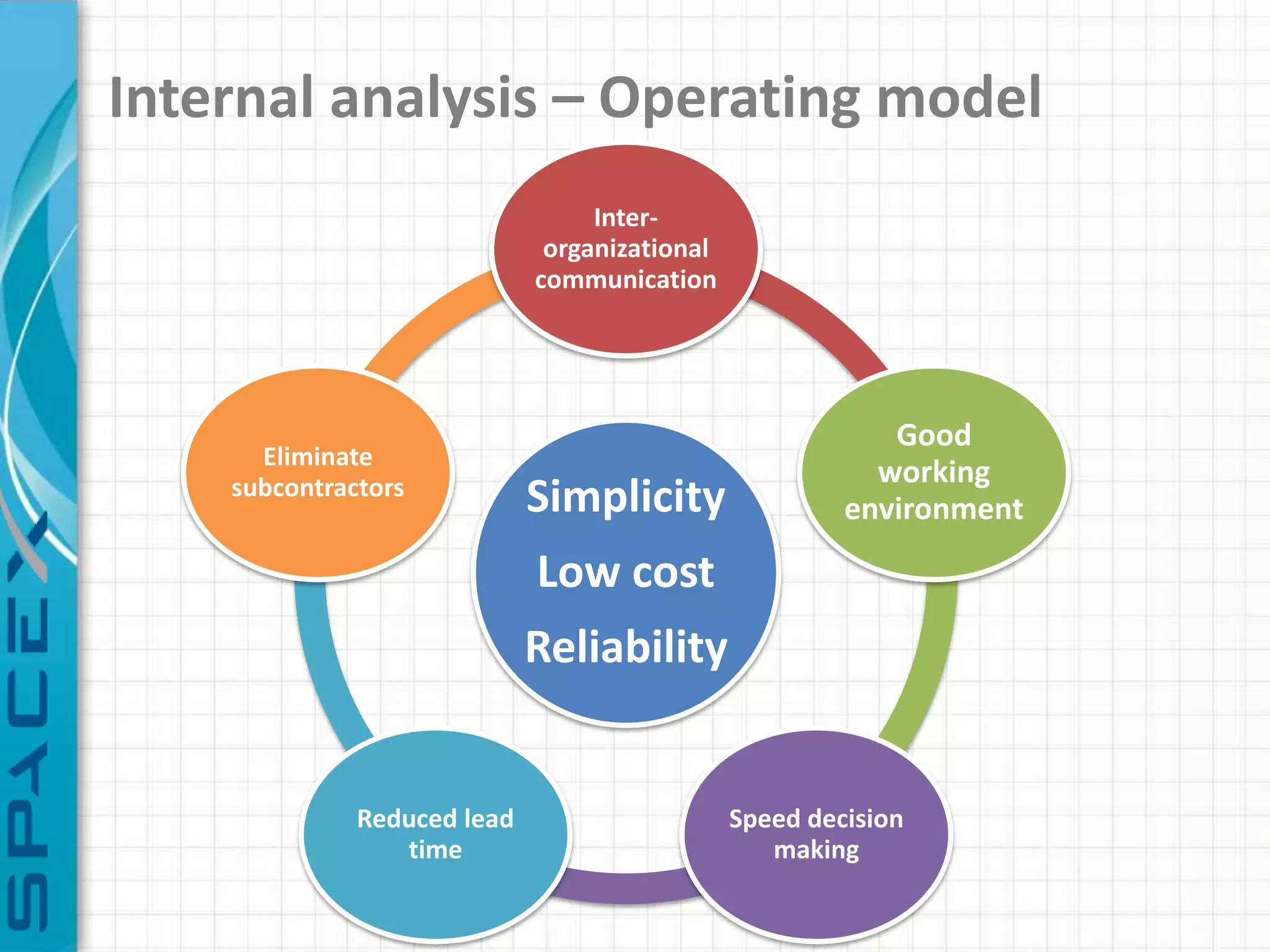
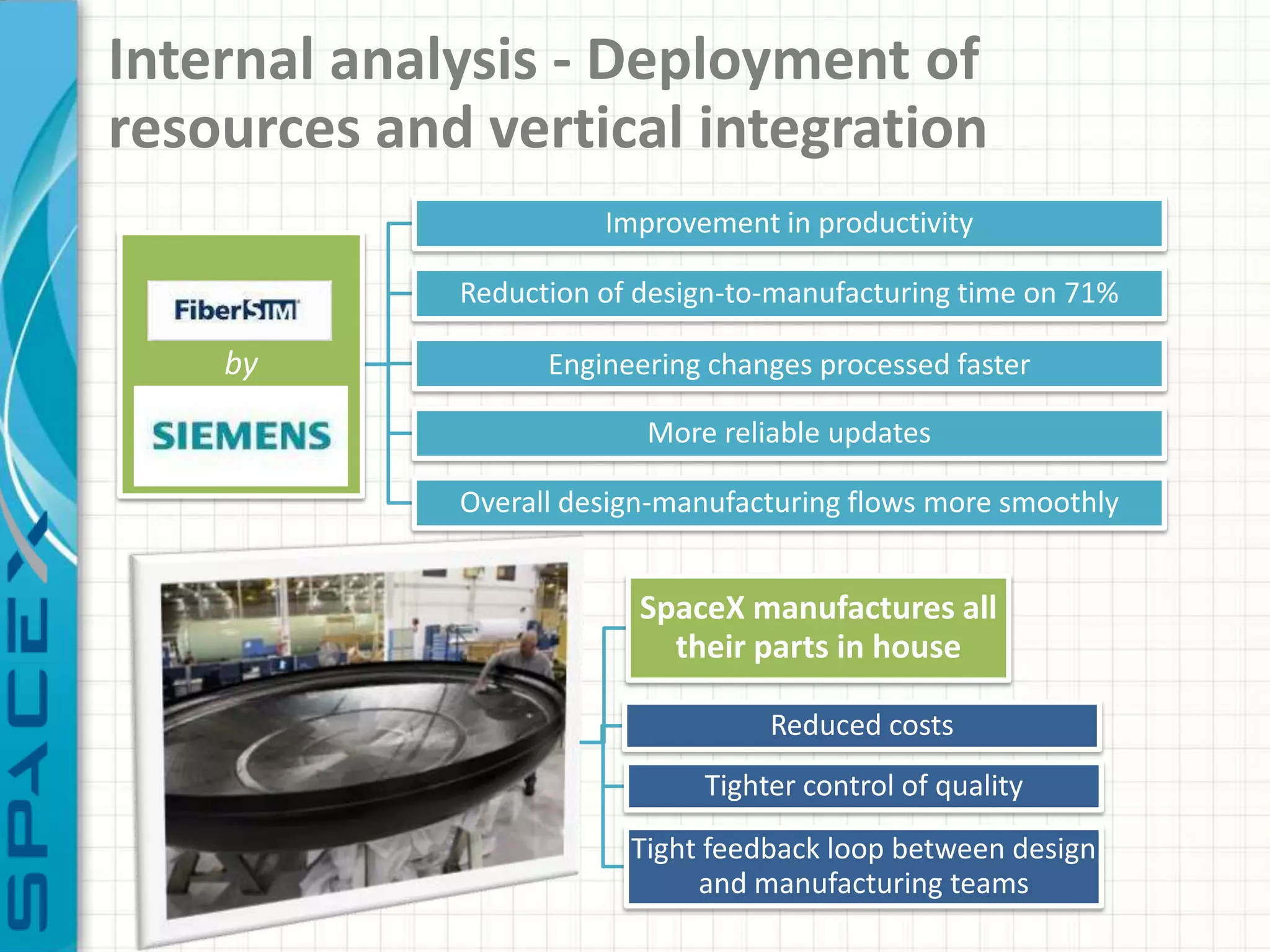
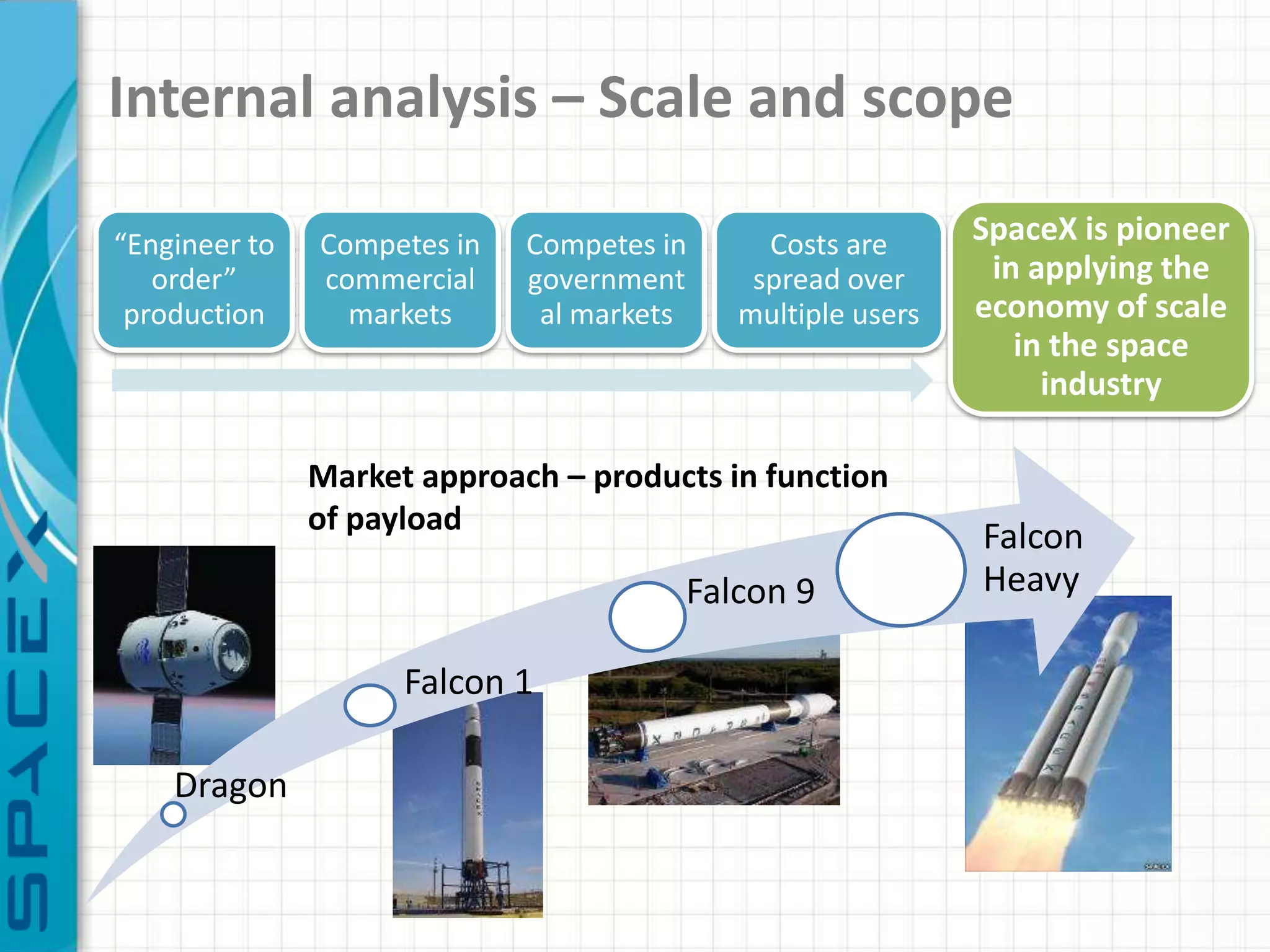
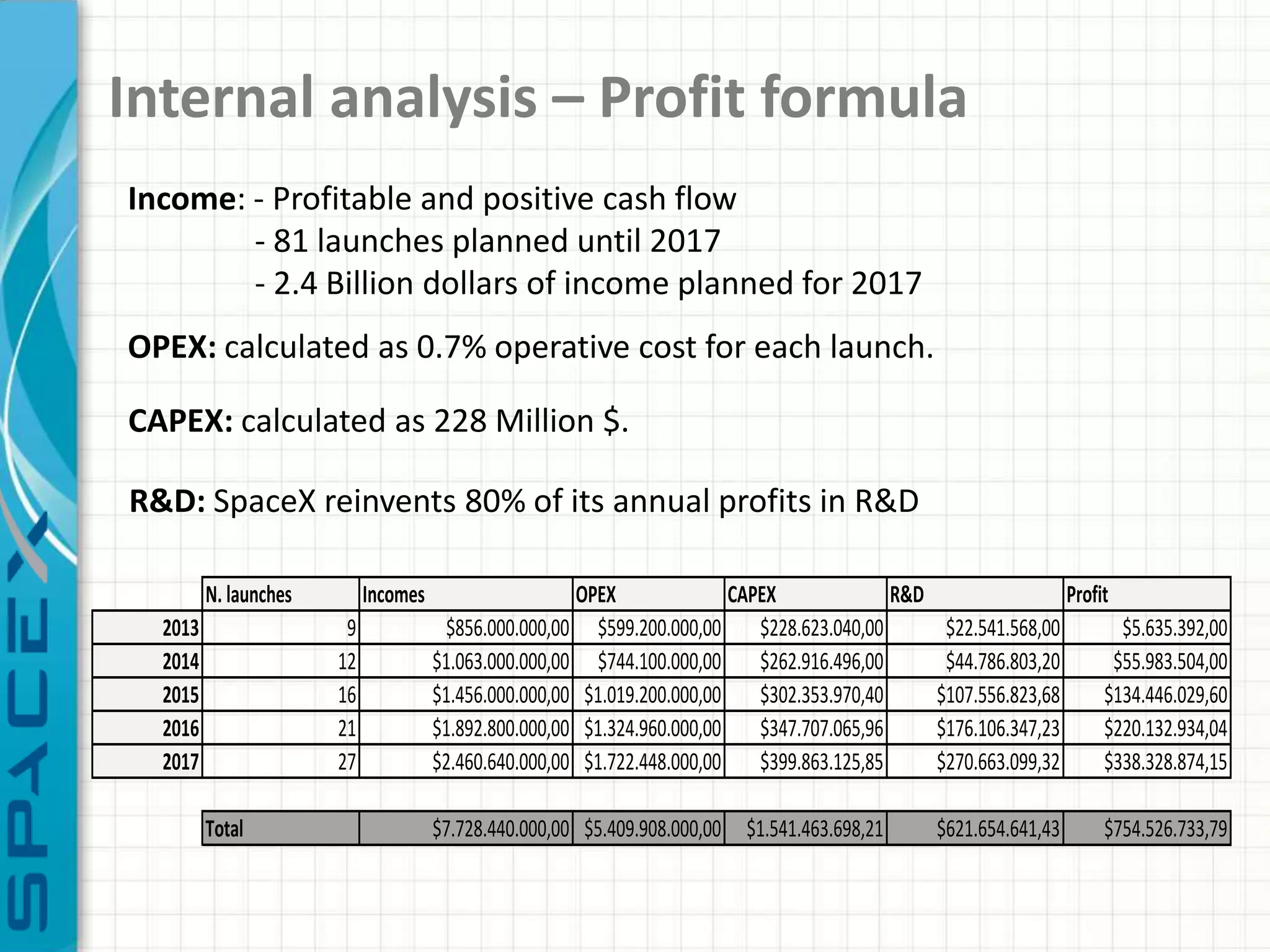
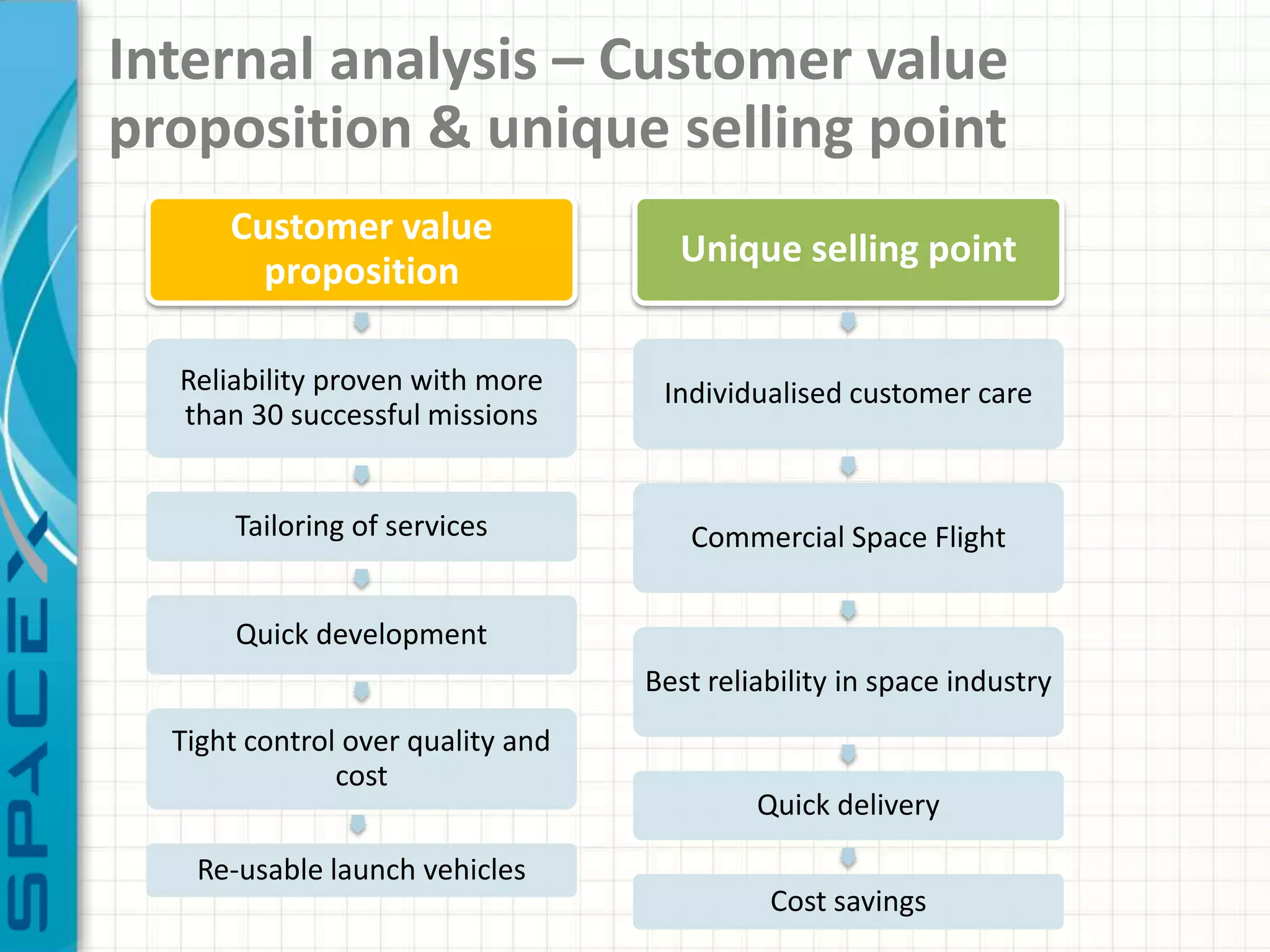
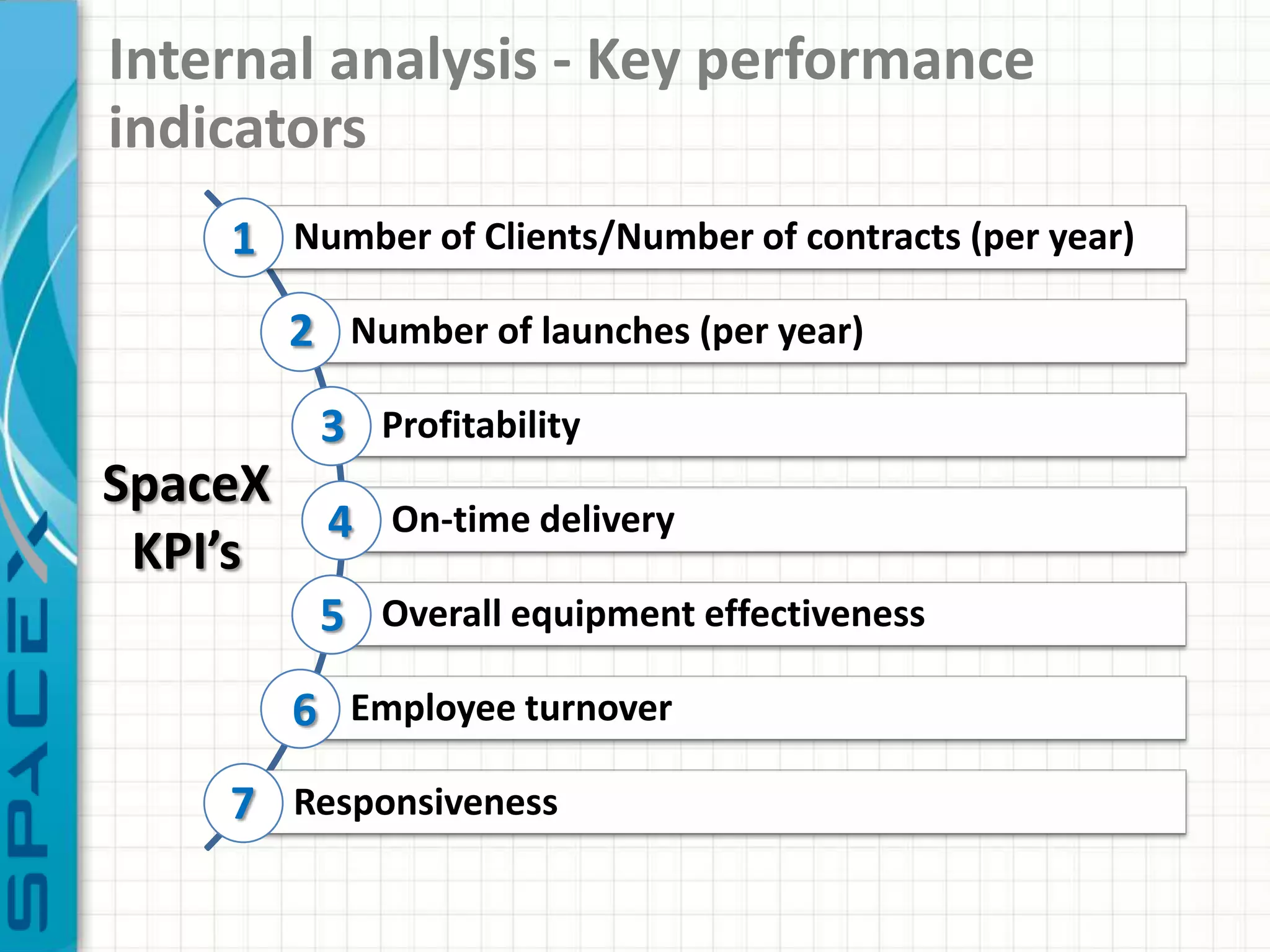
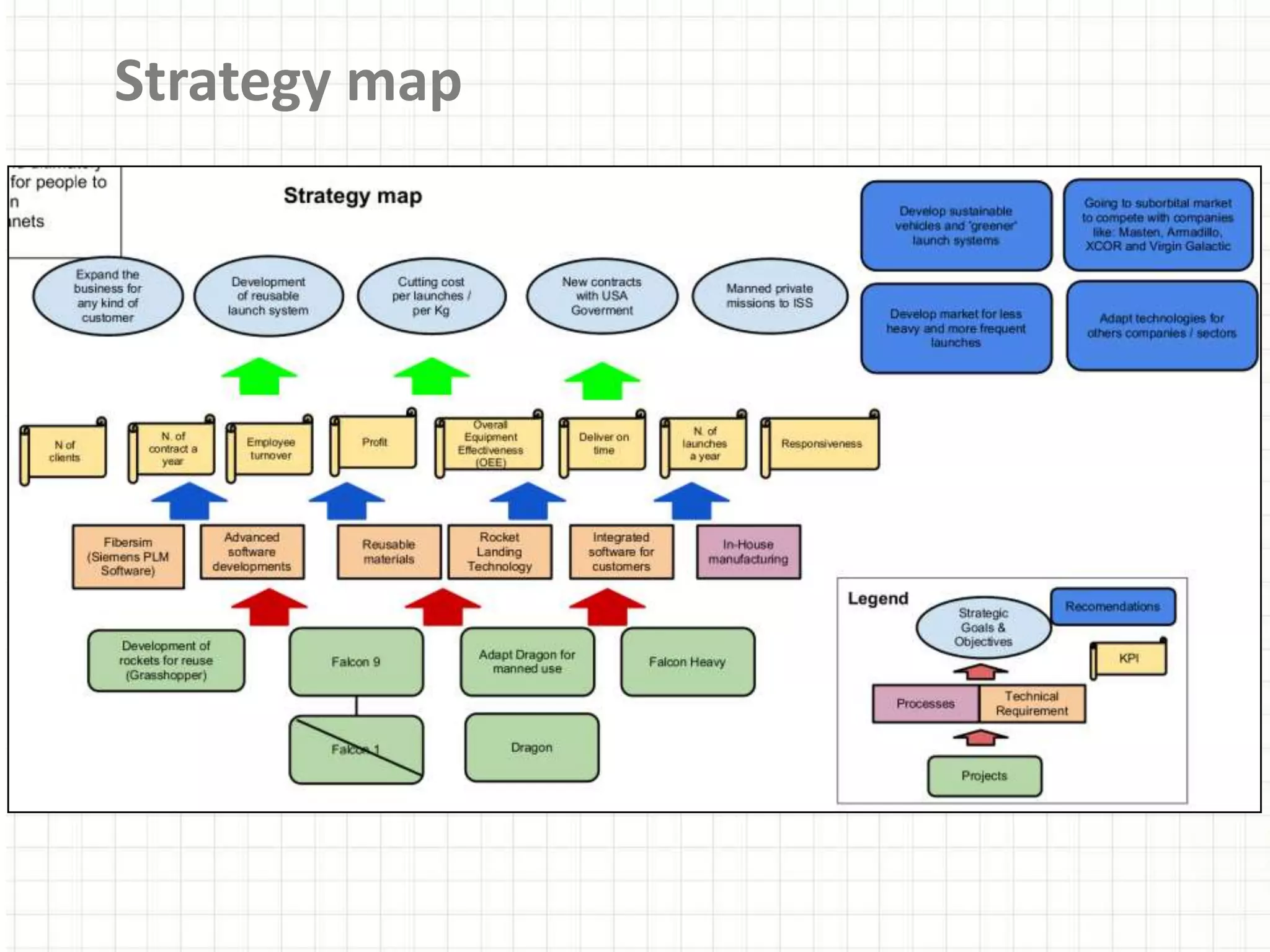
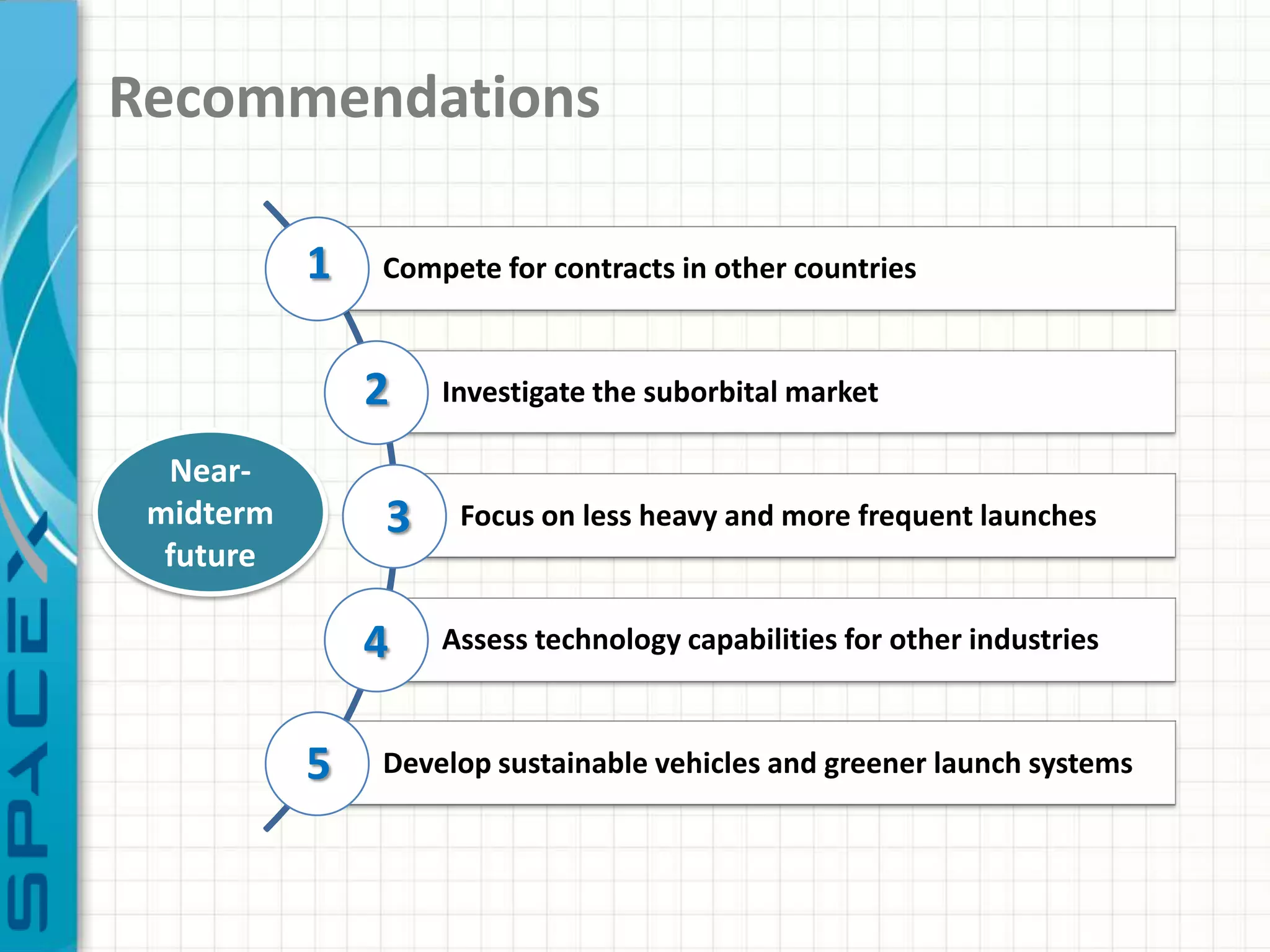
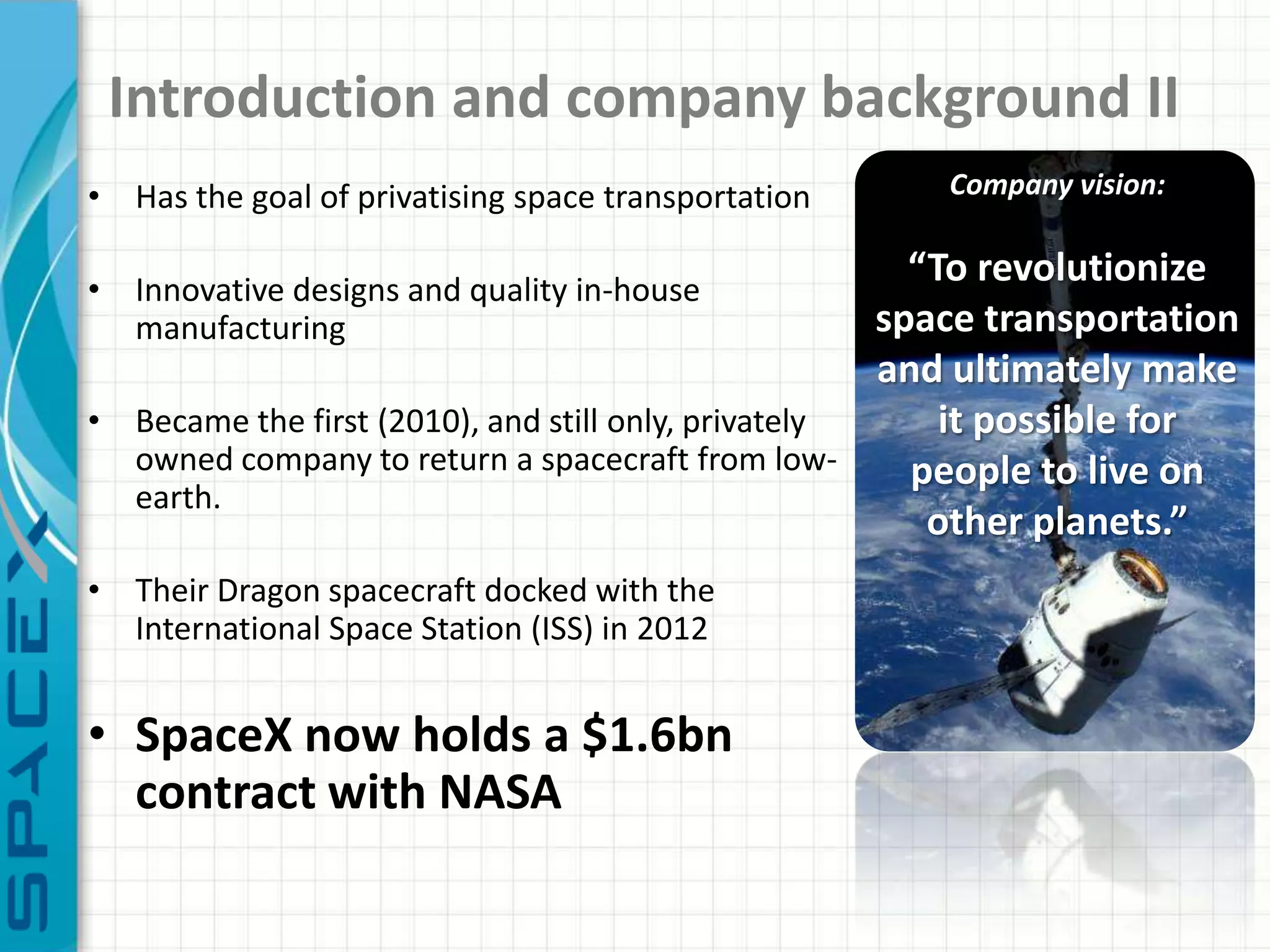
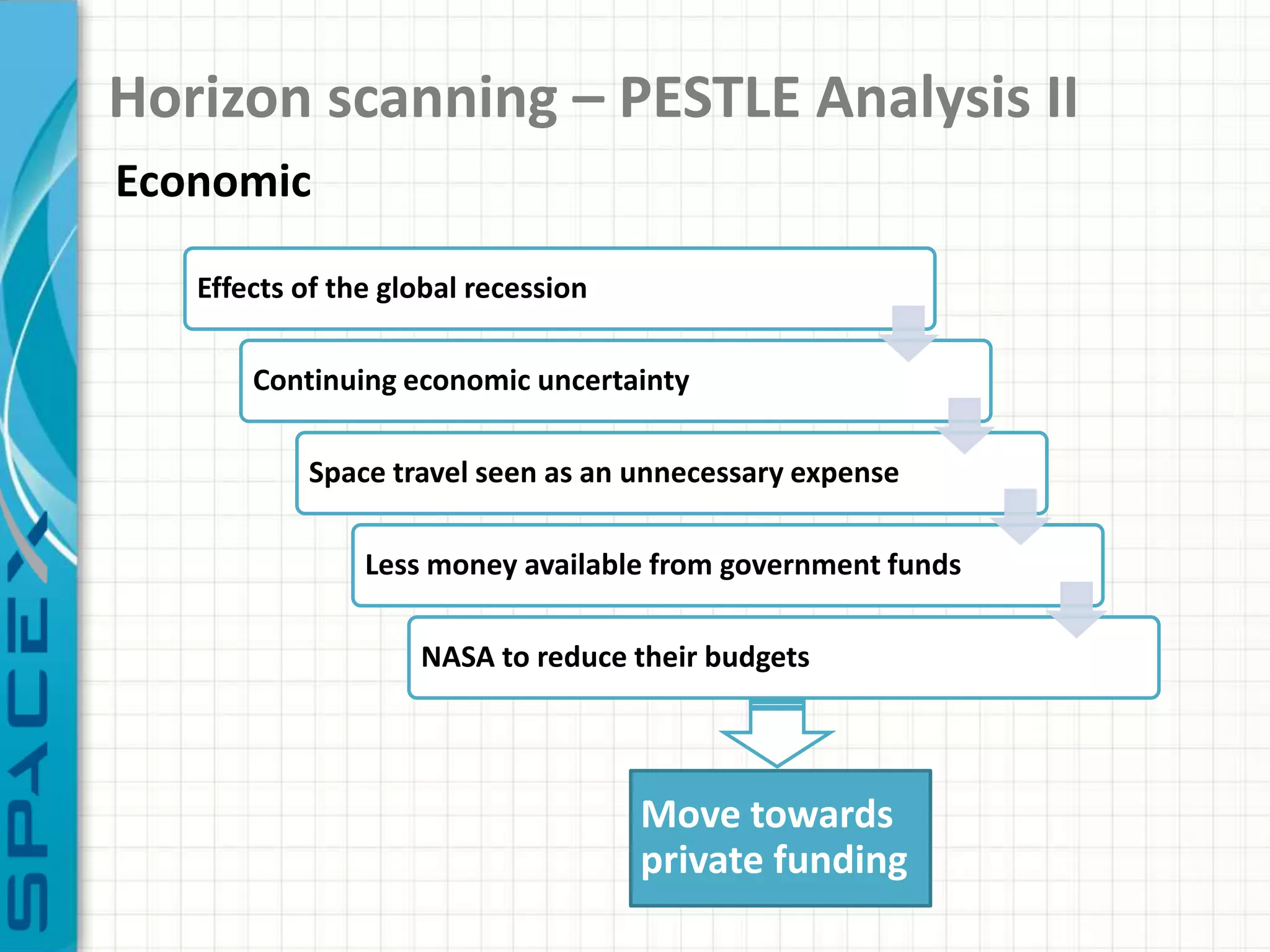
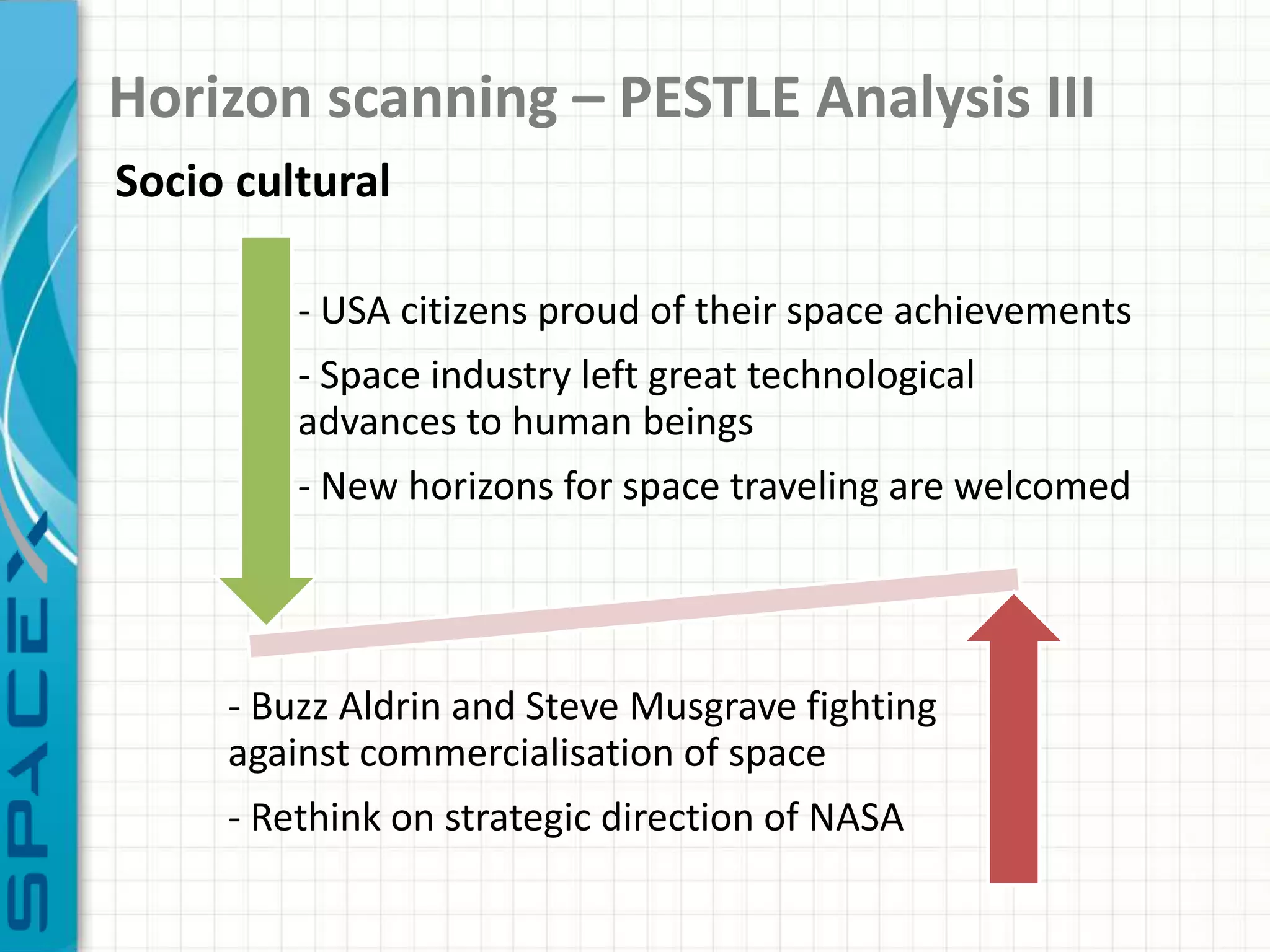
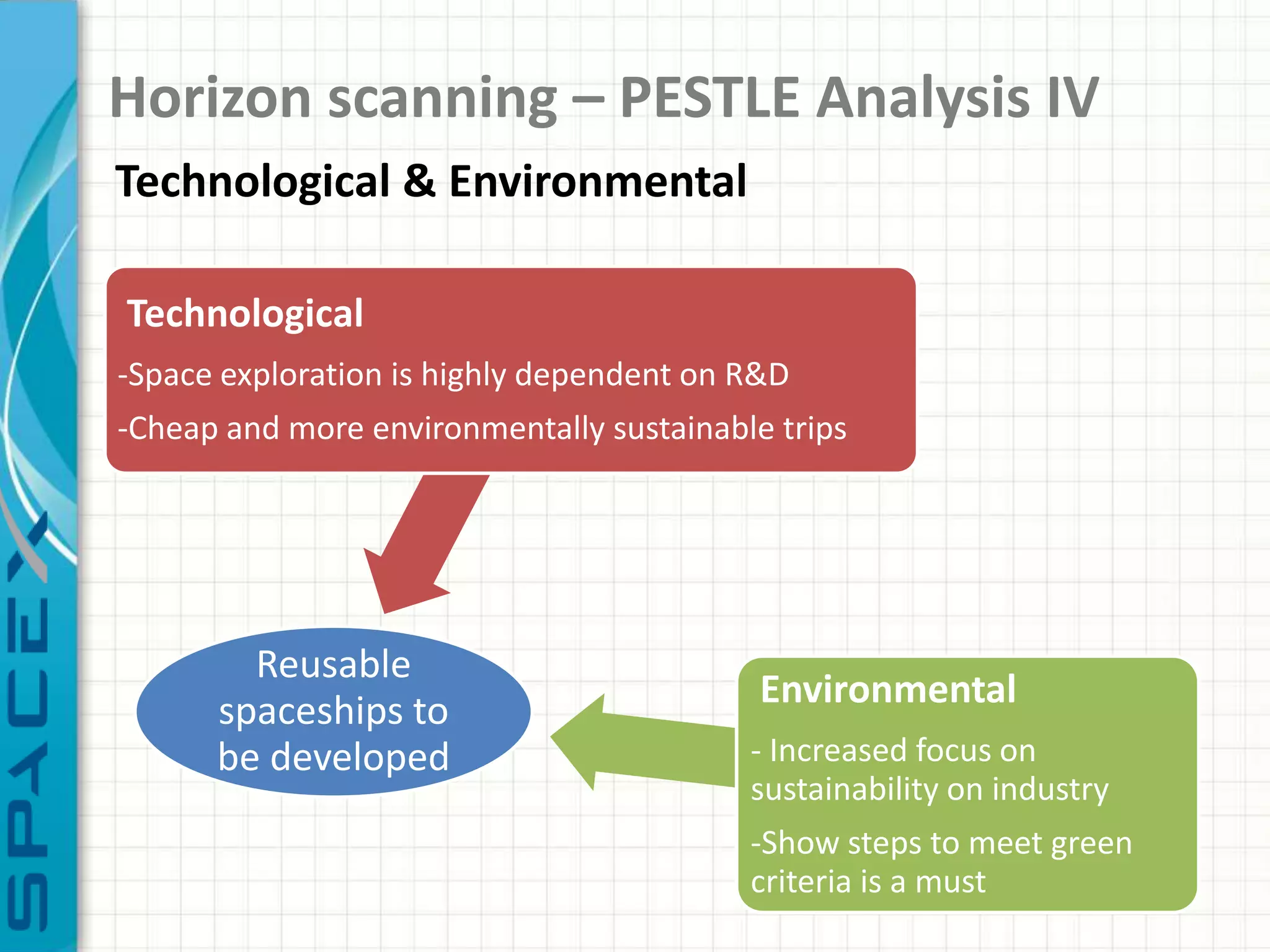
SpaceX was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the goal of reducing space transportation costs to enable the colonization of Mars. It has achieved several firsts such as being the first privately-owned company to dock with the International Space Station. SpaceX aims to further revolutionize space travel through innovative and reusable rocket designs. A PESTLE analysis identified political support and funding as key risks. Porter's Five Forces found competition and bargaining power of suppliers as moderate threats. Internally, SpaceX utilizes vertical integration and rapid prototyping to achieve high reliability and reduce costs. Key performance metrics include number of clients, launches, profitability, and on-time delivery. Recommendations include expanding internationally, assessing other industries,



![Horizon scanning – PORTER’s 5 forces I
Industry competitors [Moderate]
Commercial Governmental Space tourism](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strategictechnologyroadmapforspacex-130414191909-phpapp02/75/Strategic-technology-roadmap-for-space-x-8-2048.jpg)
![Horizon scanning – PORTER’s 5 forces II
Threat of new entrants [Low]
- High level of capital to get started in the industry
- Fast-paced technological advanced require high investment
- Human resources are hard to find for space industry
Bargaining power of buyers [Low]
- NASA prefers American companies for supply
- SpaceX is the only American company to be approved by Congress
as a NASA supplier
Bargaining power of suppliers [Moderate]
- Very high standards of quality to be met
Threat of Substitutes [Low]
- No substitutes for space vehicles at the moment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strategictechnologyroadmapforspacex-130414191909-phpapp02/75/Strategic-technology-roadmap-for-space-x-9-2048.jpg)