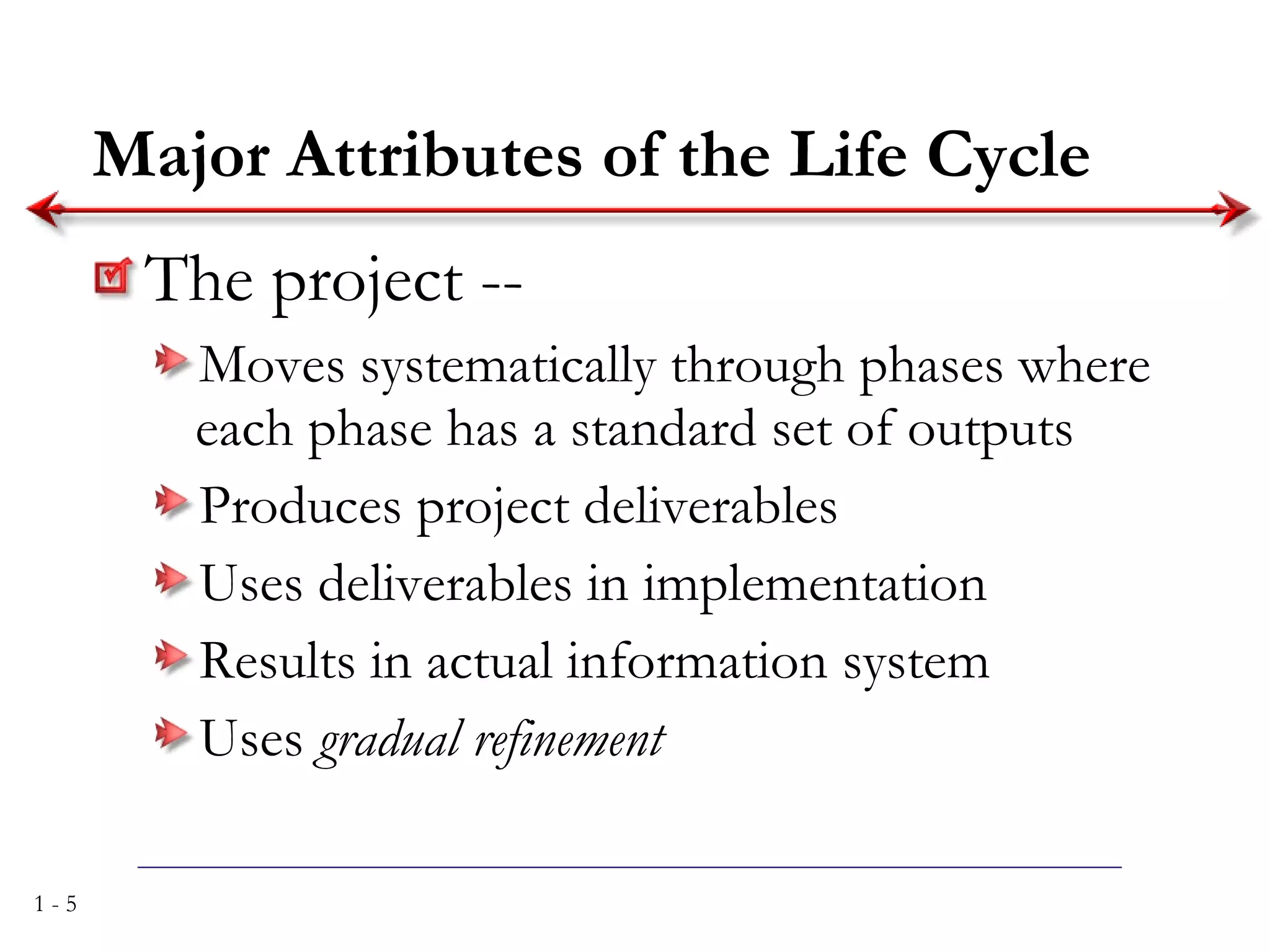
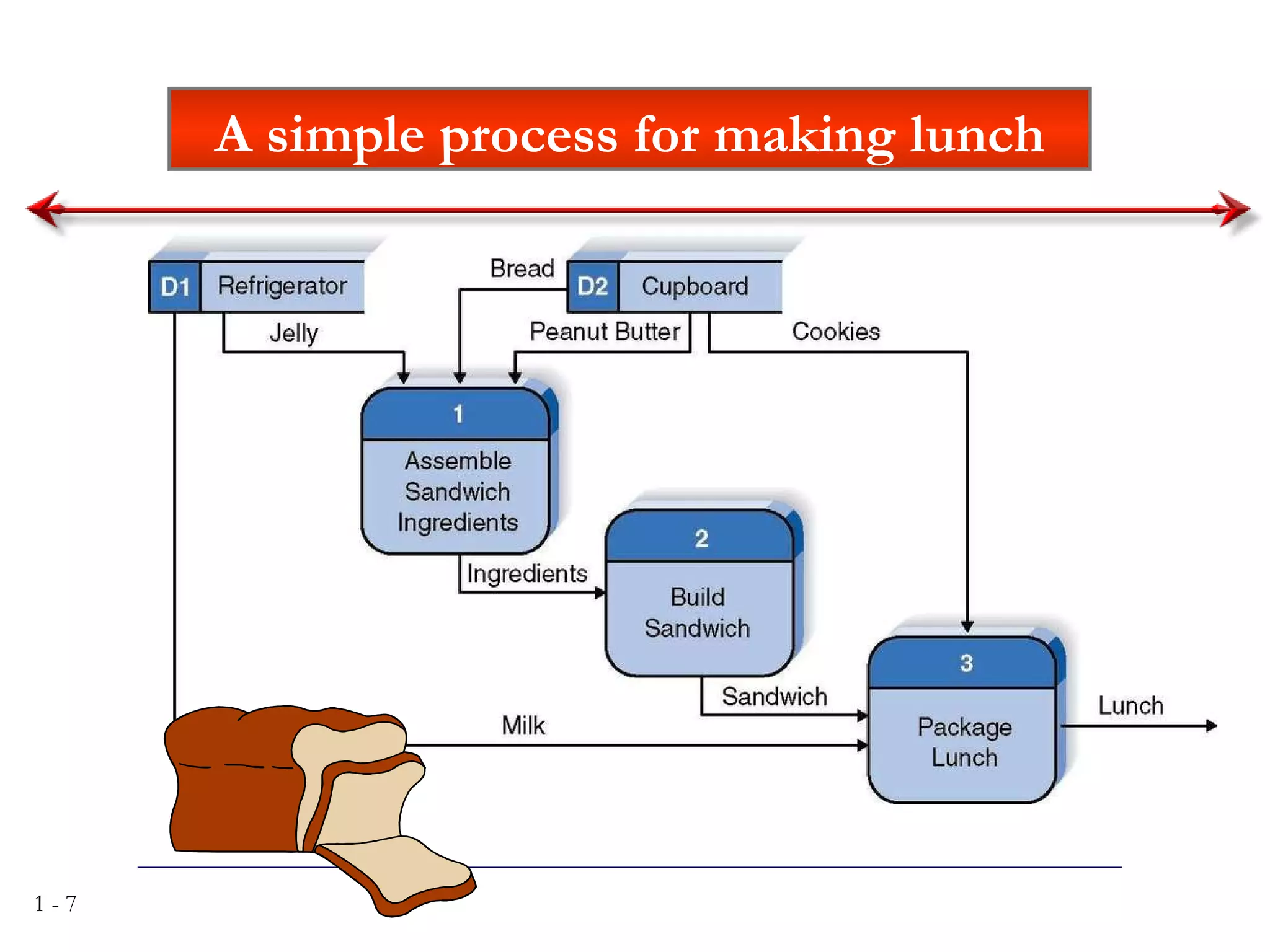
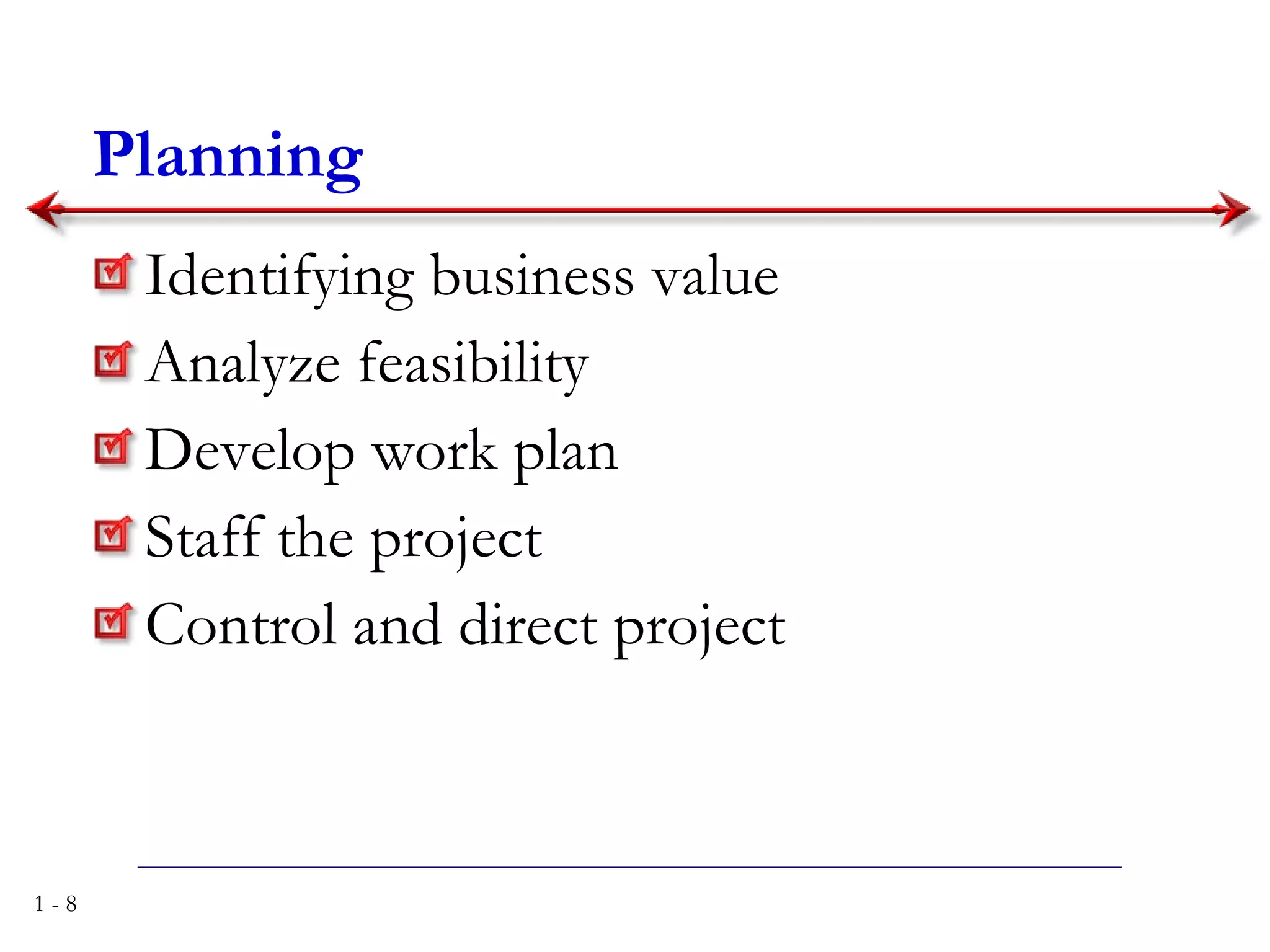
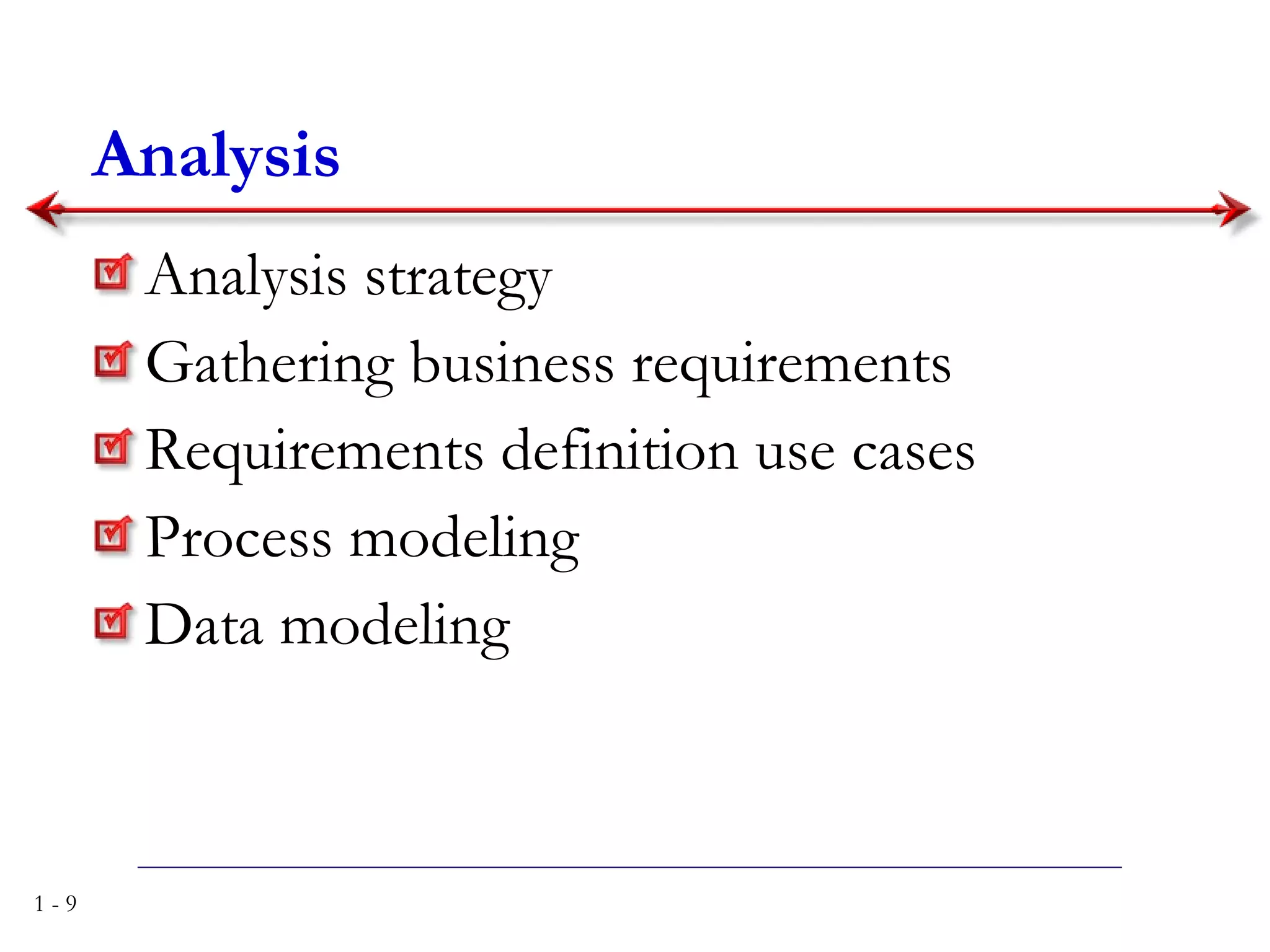
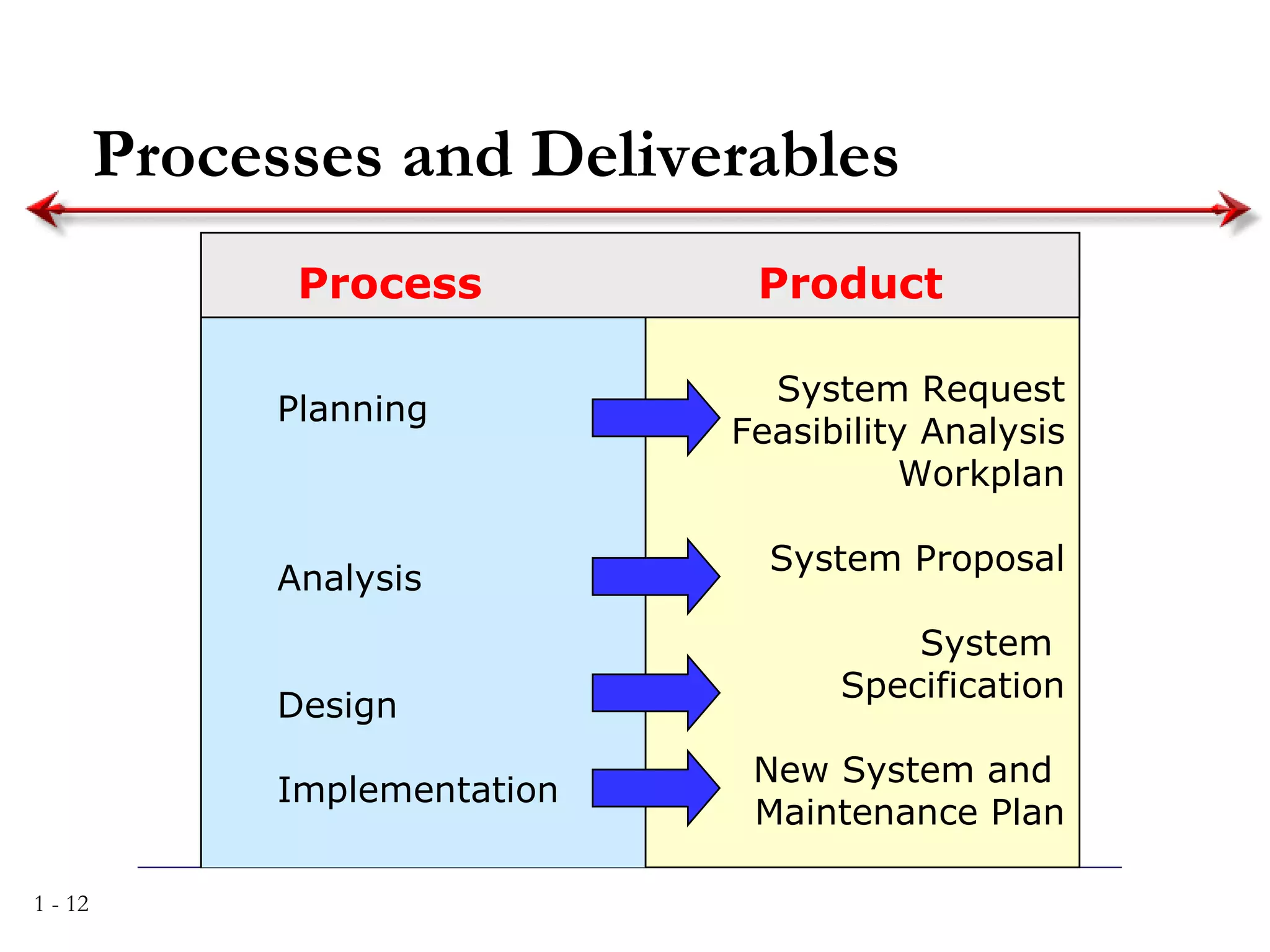
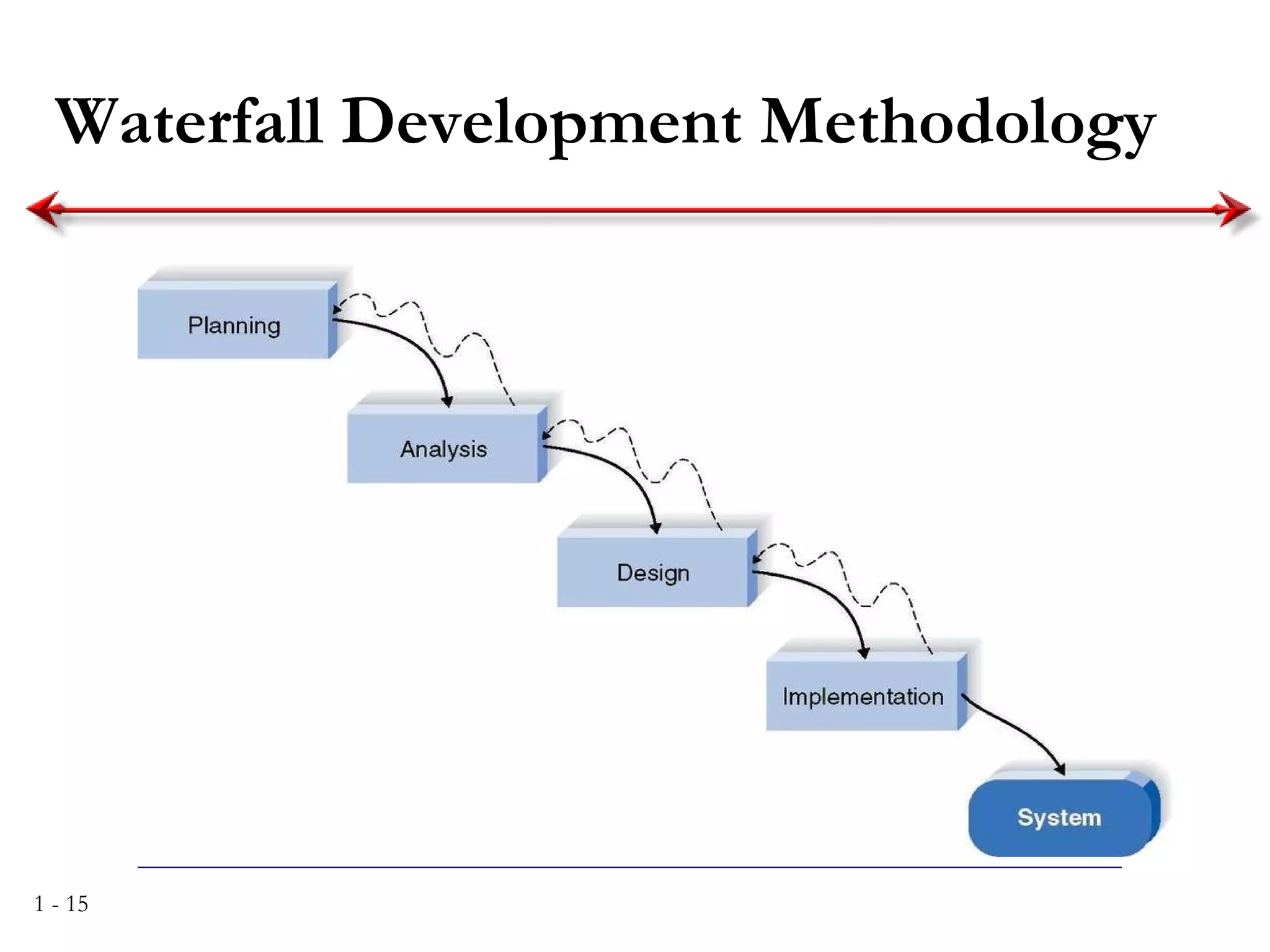
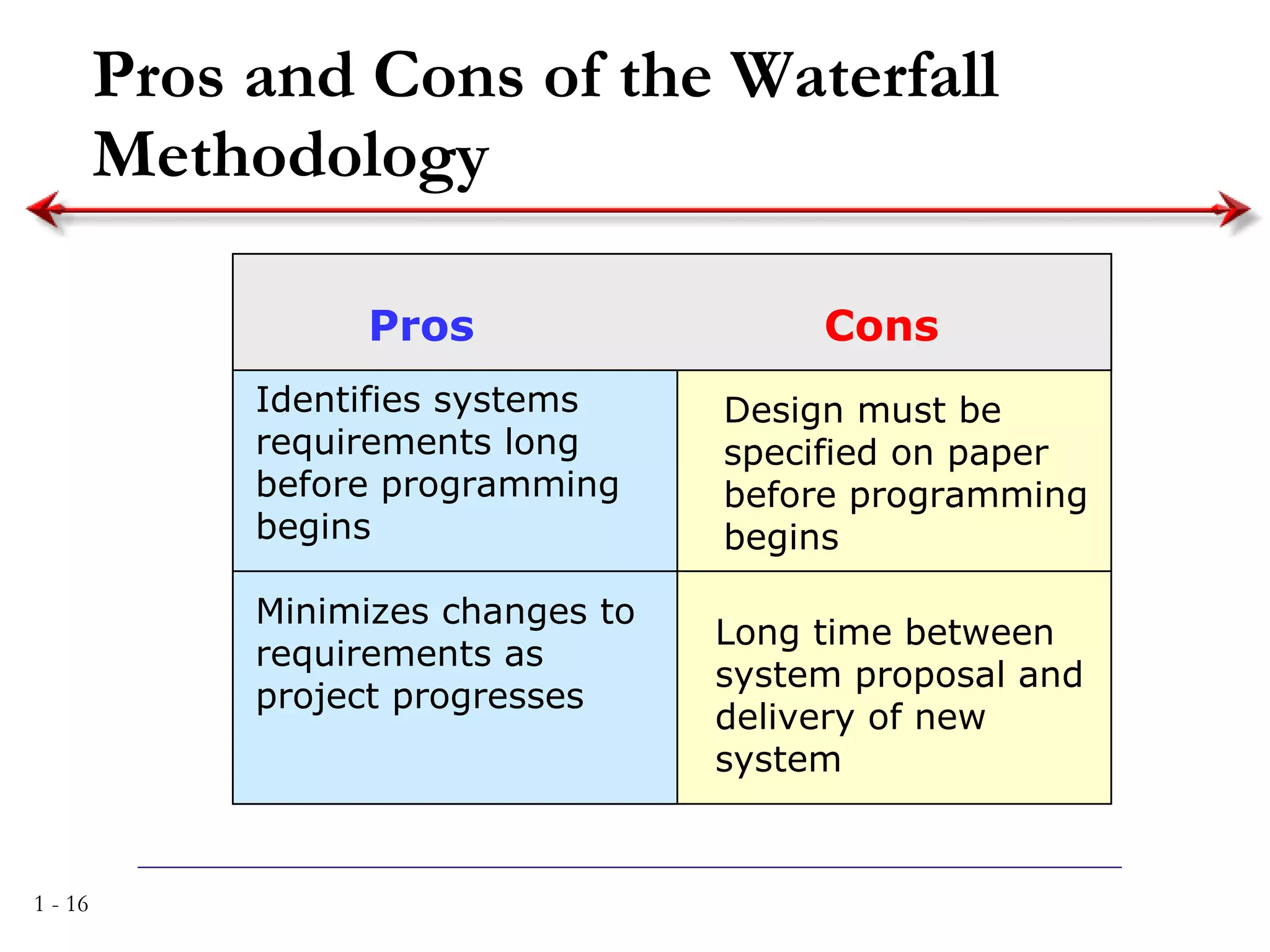
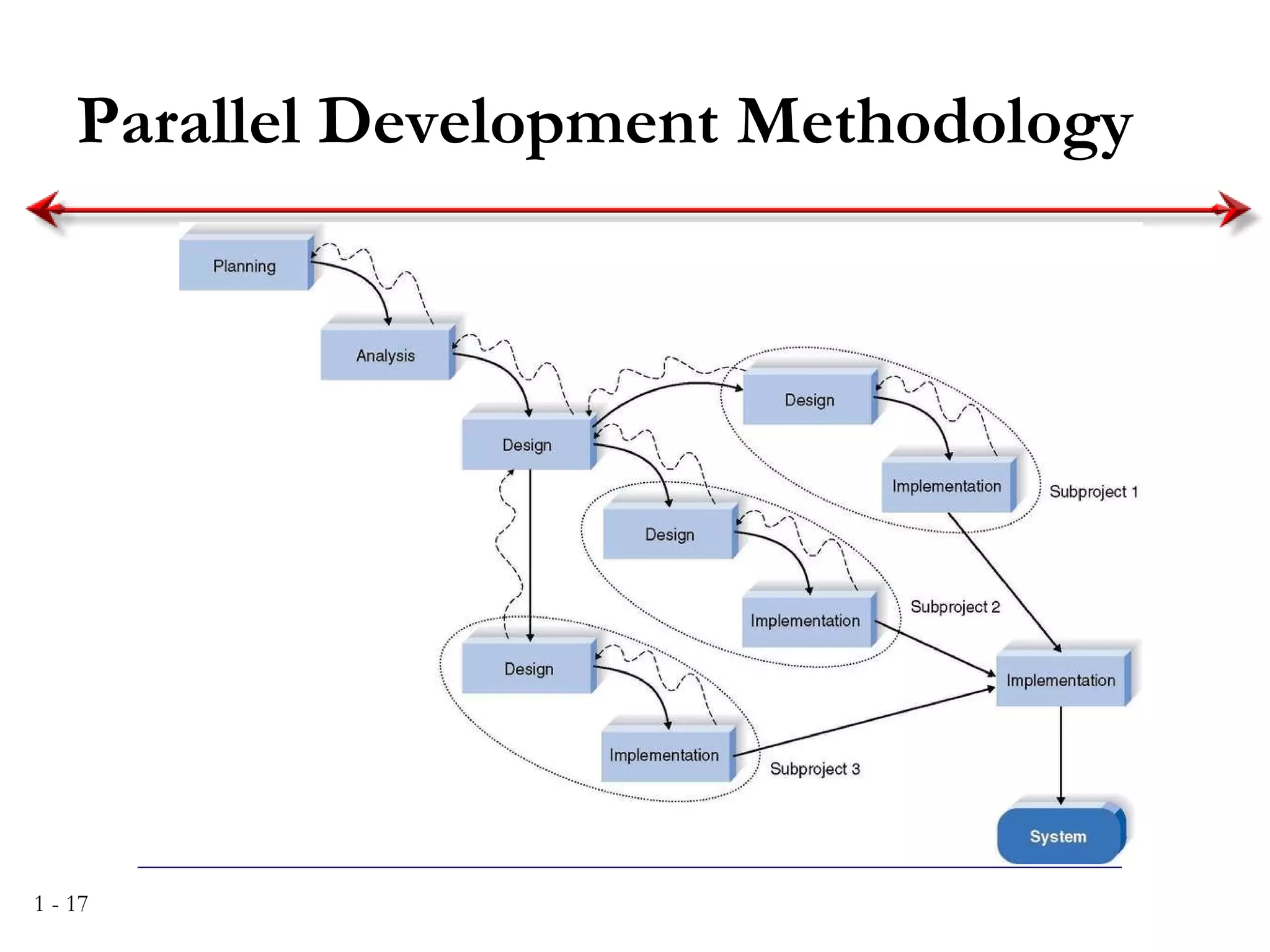
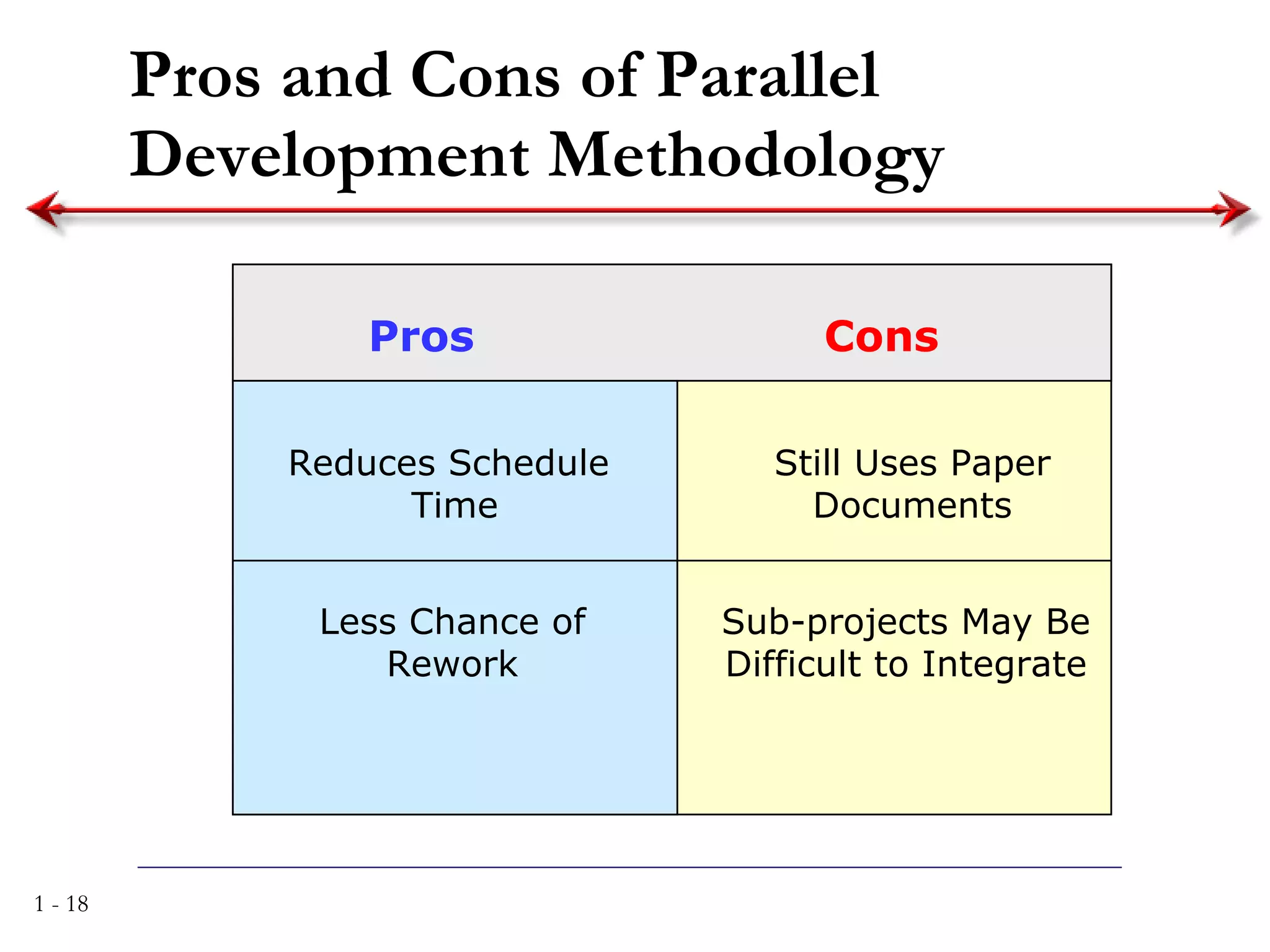
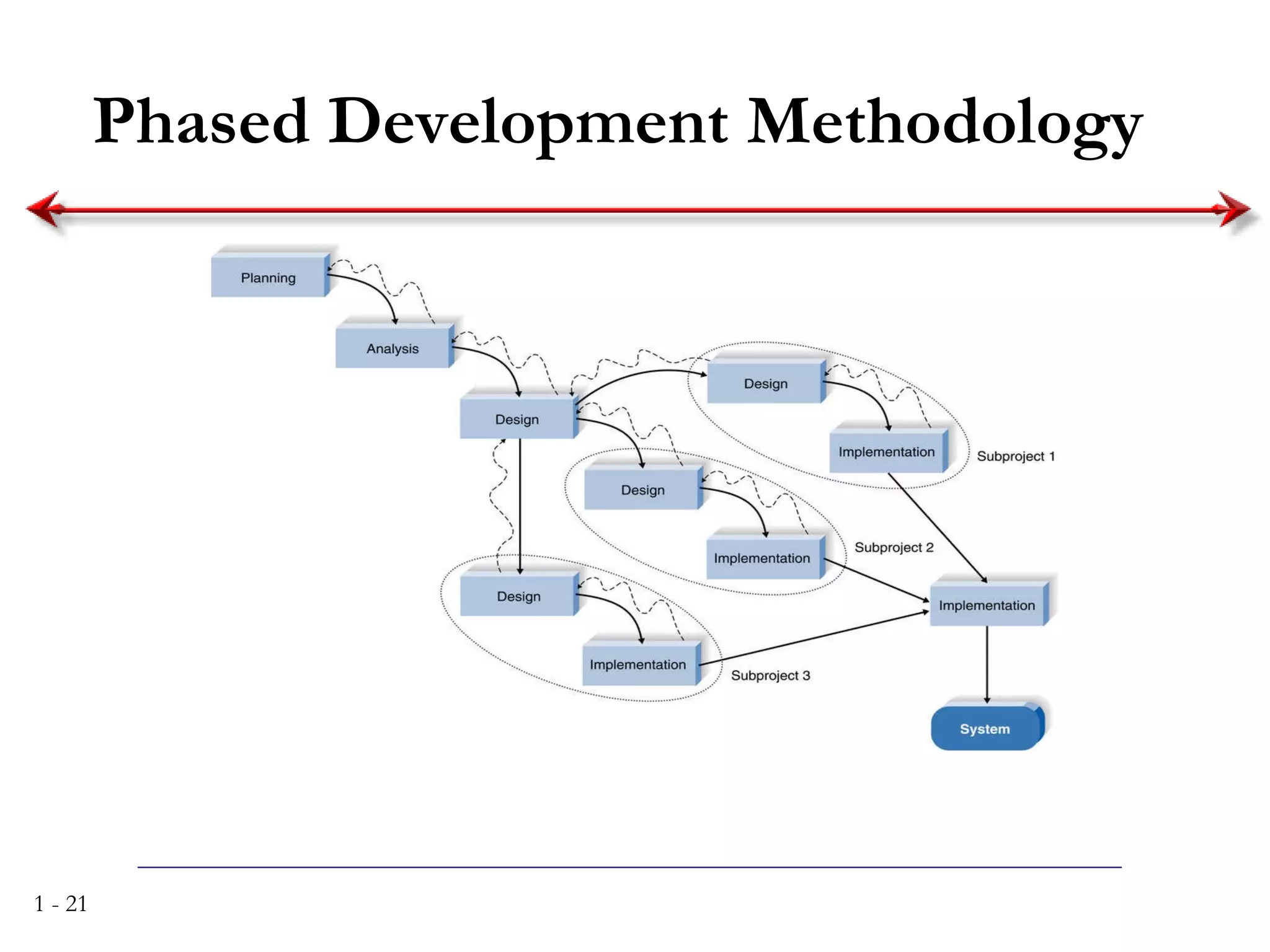
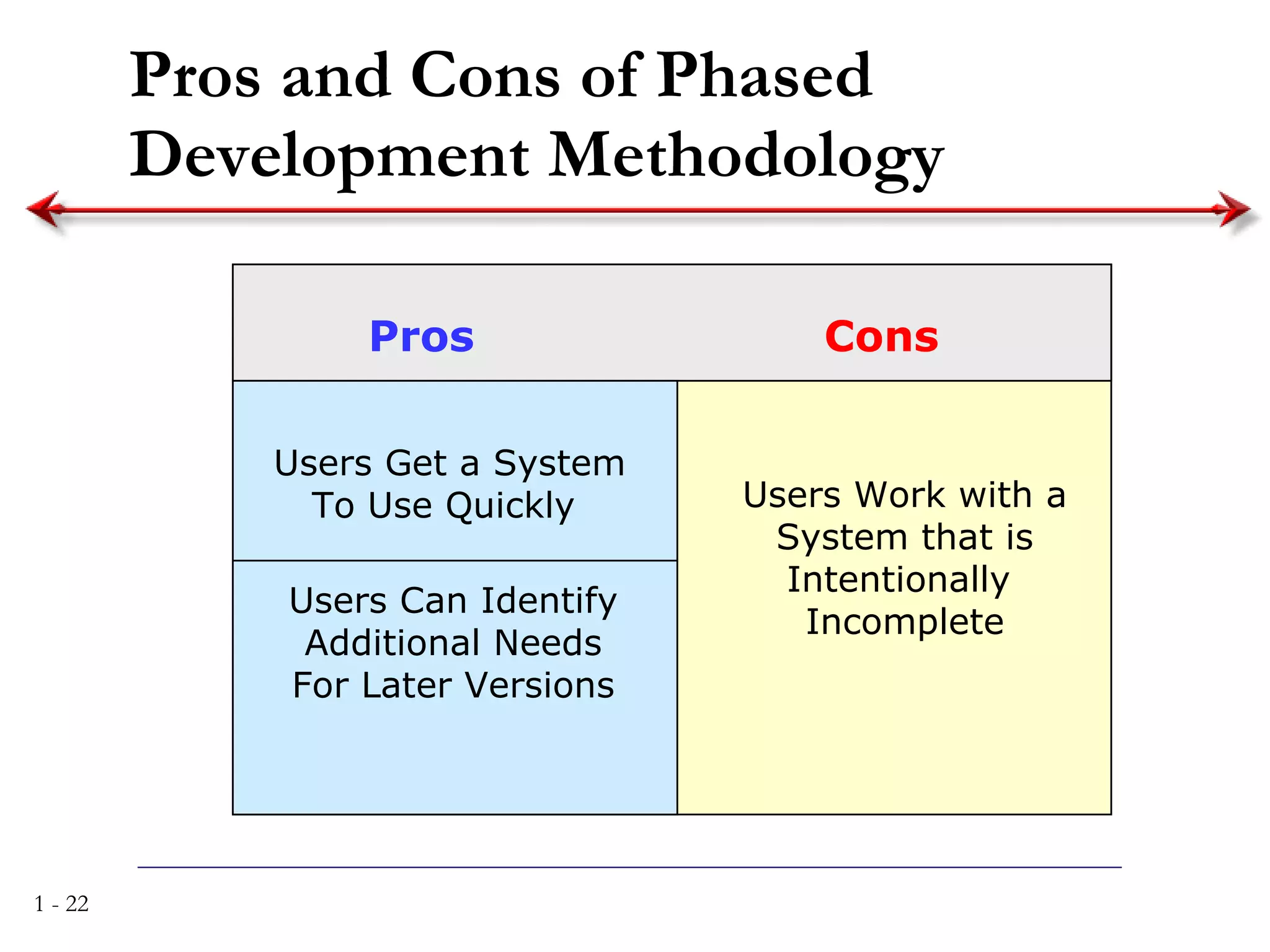
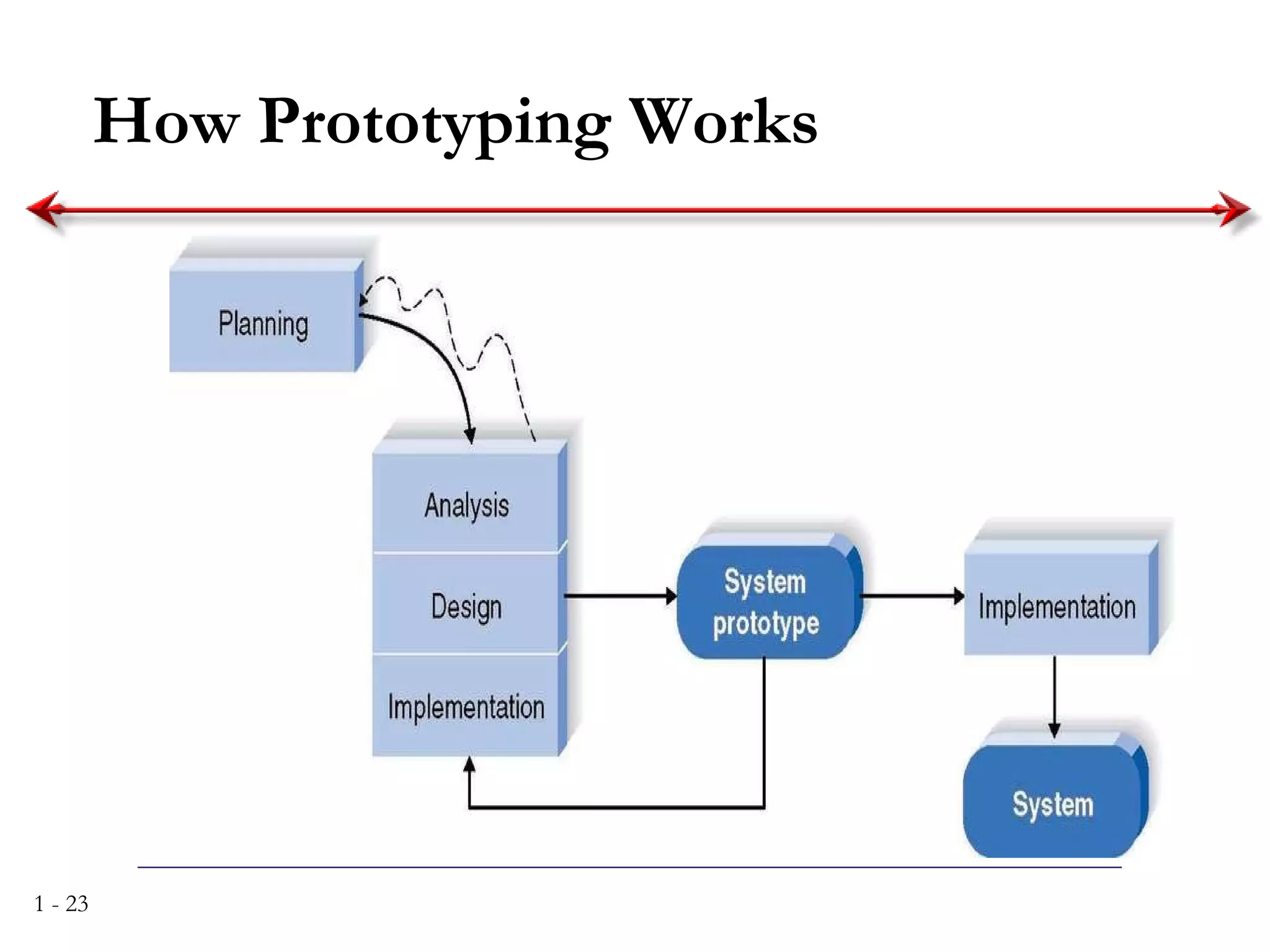
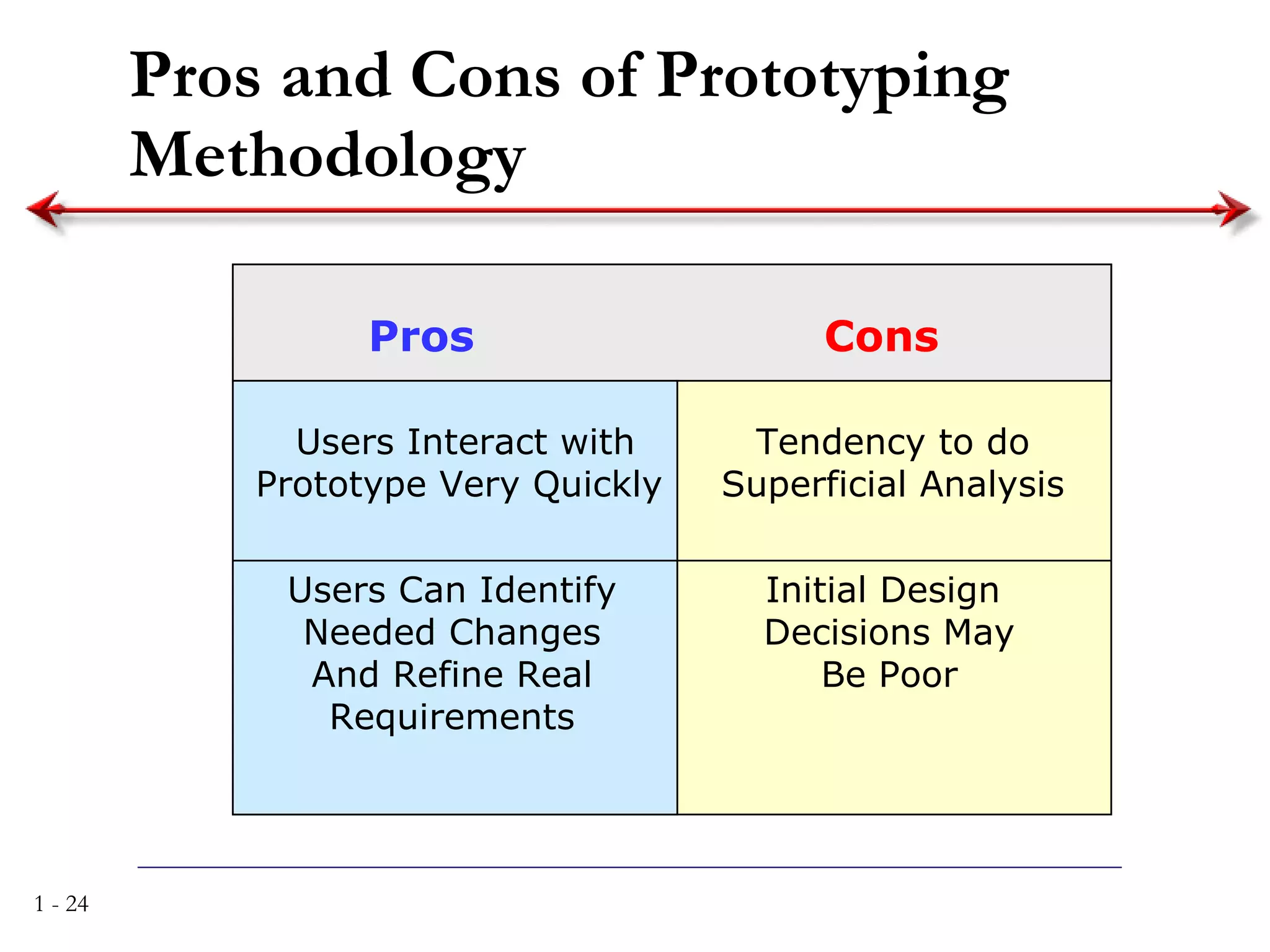
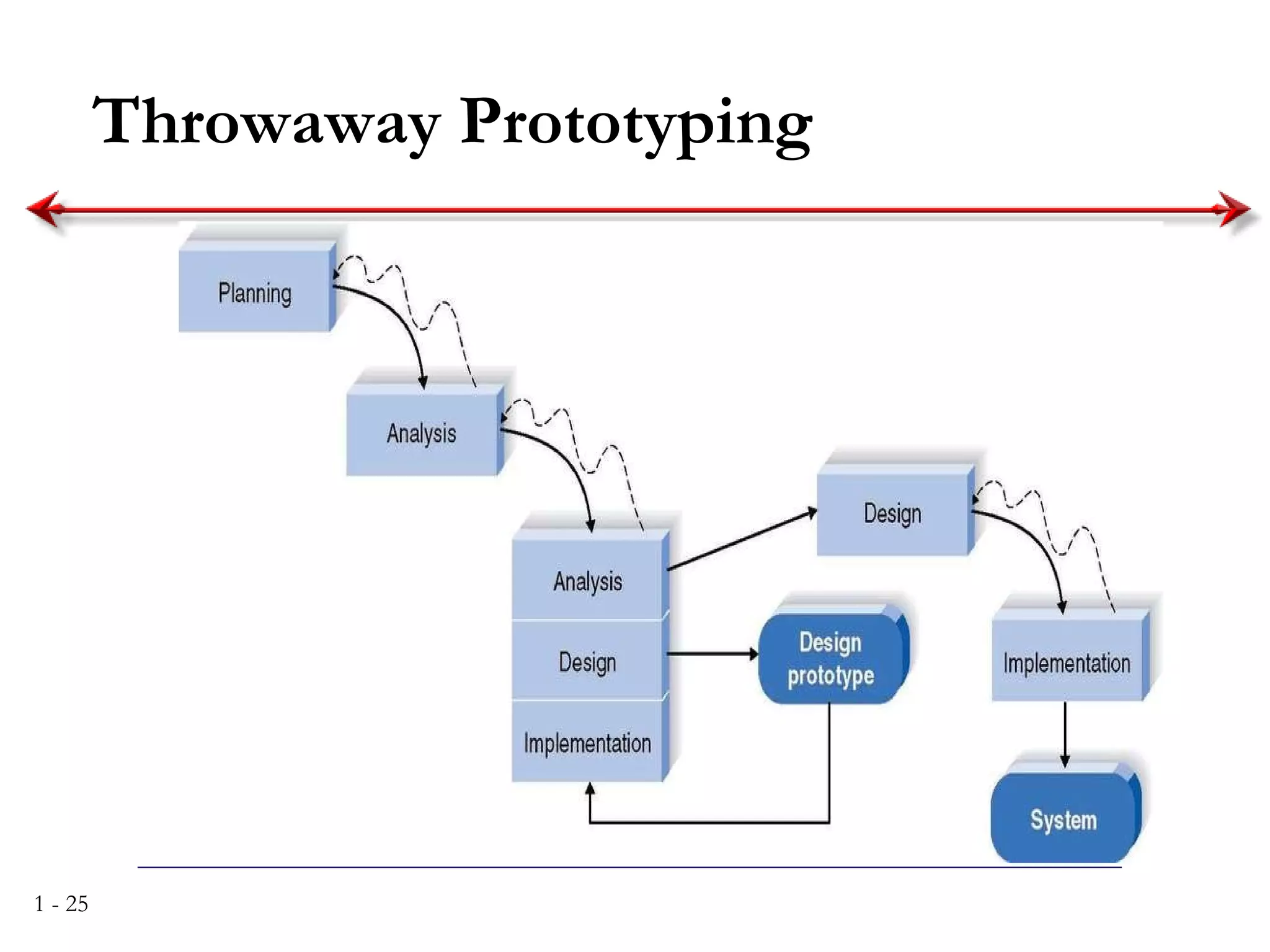
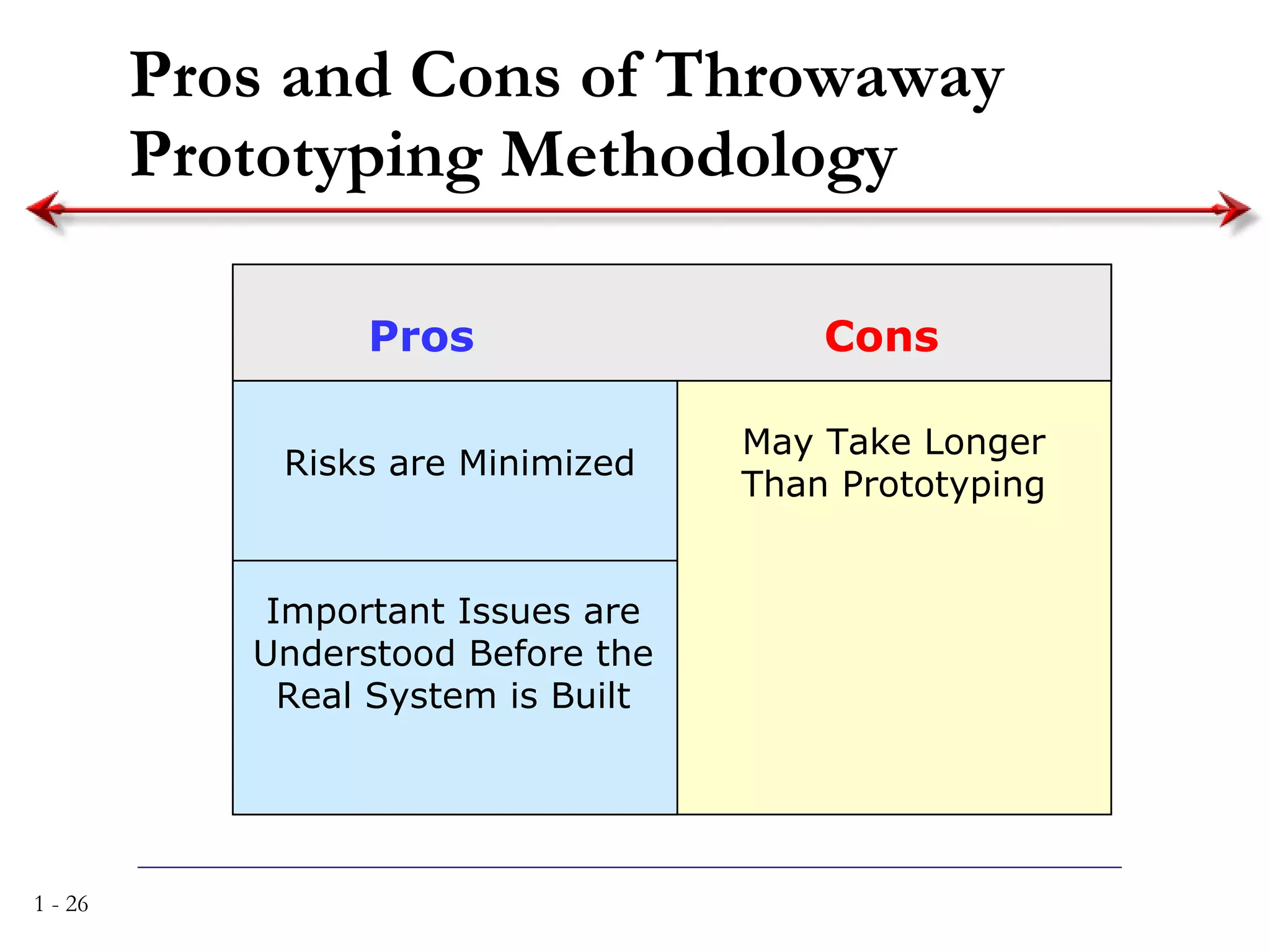
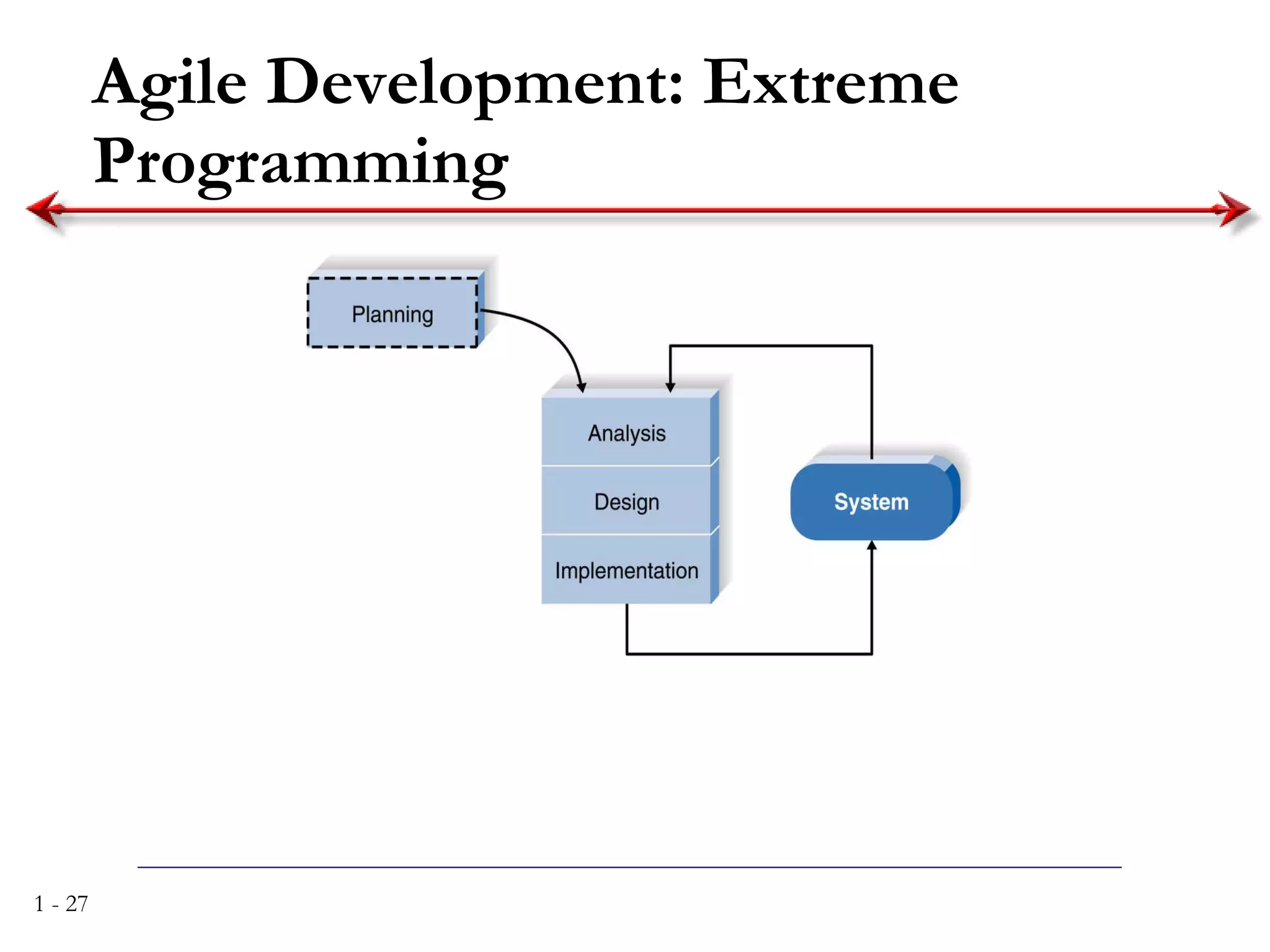
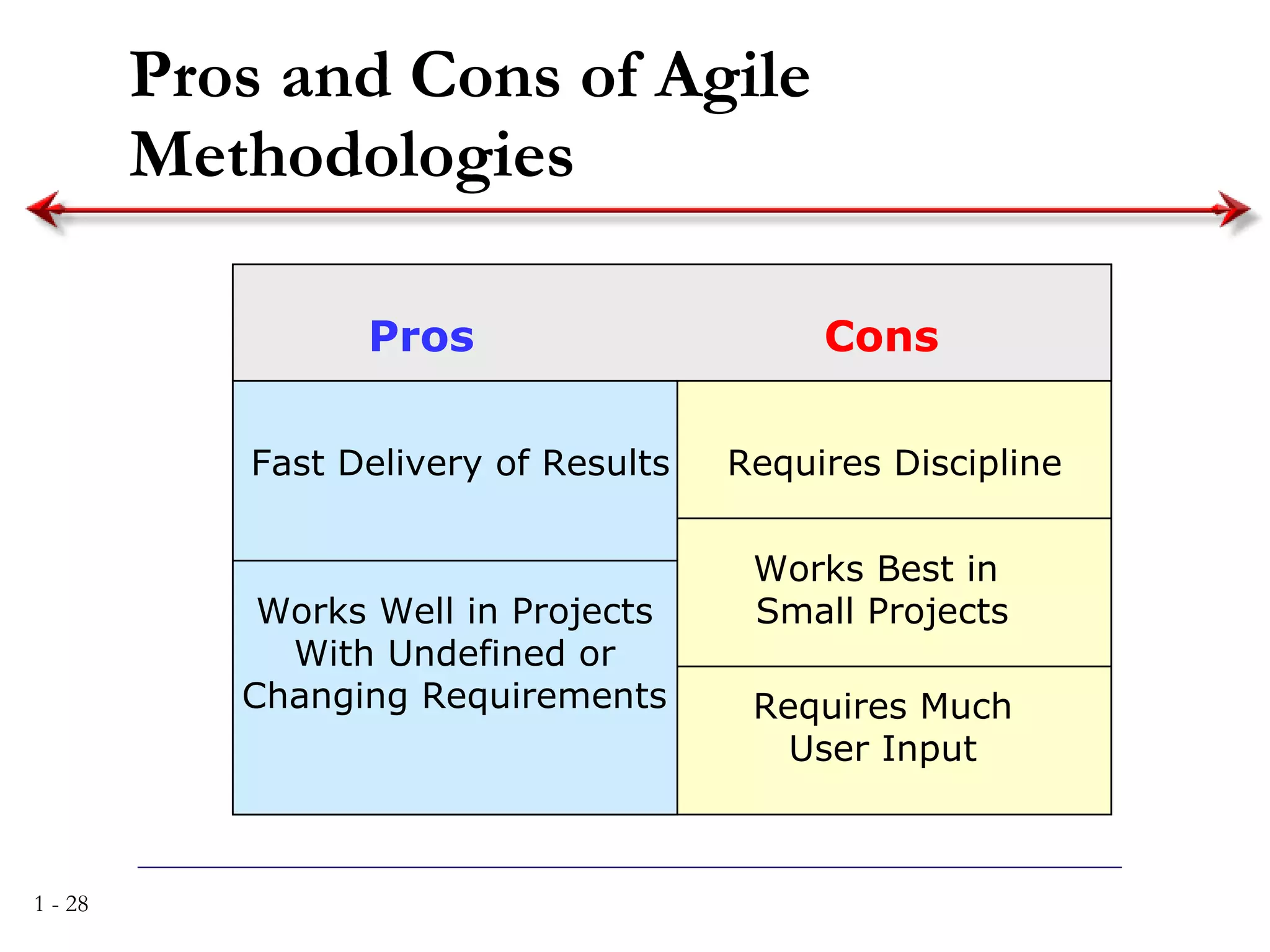
The document discusses systems analysis and design. It describes the systems development life cycle as having four phases - planning, analysis, design, and implementation. It then explains six major systems development methodologies: waterfall, parallel development, phased development, prototyping, design prototyping, and agile development. Finally, it lists five common team roles in systems development: business analyst, systems analyst, infrastructure analyst, change management analyst, and project manager.