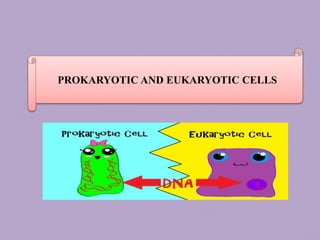
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
24 likes•18,938 views
Kingdoms of Organisms- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Two Types Of Cells - Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells

Two Types Of Cells - Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
Similar to Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Similar to Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (20)
CELL BIOLOGY LECTURE. Cells described in the purest of forms.

CELL BIOLOGY LECTURE. Cells described in the purest of forms.
Recently uploaded
Ultrasound color Doppler imaging has been routinely used for the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases, enabling real-time flow visualization through the Doppler effect. Yet, its inability to provide true flow velocity vectors due to its one-dimensional detection limits its efficacy. To overcome this limitation, various VFI schemes, including multi-angle beams, speckle tracking, and transverse oscillation, have been explored, with some already available commercially. However, many of these methods still rely on autocorrelation, which poses inherent issues such as underestimation, aliasing, and the need for large ensemble sizes. Conversely, speckle-tracking-based VFI enables lateral velocity estimation but suffers from significantly lower accuracy compared to axial velocity measurements.
To address these challenges, we have presented a speckle-tracking-based VFI approach utilizing multi-angle ultrafast plane wave imaging. Our approach involves estimating axial velocity components projected onto individual steered plane waves, which are then combined to derive the velocity vector. Additionally, we've introduced a VFI visualization technique with high spatial and temporal resolutions capable of tracking flow particle trajectories.
Simulation and flow phantom experiments demonstrate that the proposed VFI method outperforms both speckle-tracking-based VFI and autocorrelation VFI counterparts by at least a factor of three. Furthermore, in vivo measurements on carotid arteries using the Prodigy ultrasound scanner demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach compared to existing methods, providing a more robust imaging tool for hemodynamic studies.
Learning objectives:
- Understand fundamental limitations of color Doppler imaging.
- Understand principles behind advanced vector flow imaging techniques.
- Familiarize with the ultrasound speckle tracking technique and its implications in flow imaging.
- Explore experiments conducted using multi-angle plane wave ultrafast imaging, specifically utilizing the pulse-sequence mode on a 128-channel ultrasound research platform. (May 9, 2024) Enhanced Ultrafast Vector Flow Imaging (VFI) Using Multi-Angle ...

(May 9, 2024) Enhanced Ultrafast Vector Flow Imaging (VFI) Using Multi-Angle ...Scintica Instrumentation
Recently uploaded (20)
300003-World Science Day For Peace And Development.pptx

300003-World Science Day For Peace And Development.pptx
development of diagnostic enzyme assay to detect leuser virus

development of diagnostic enzyme assay to detect leuser virus
Call Girls Ahmedabad +917728919243 call me Independent Escort Service

Call Girls Ahmedabad +917728919243 call me Independent Escort Service
(May 9, 2024) Enhanced Ultrafast Vector Flow Imaging (VFI) Using Multi-Angle ...

(May 9, 2024) Enhanced Ultrafast Vector Flow Imaging (VFI) Using Multi-Angle ...
Bhiwandi Bhiwandi ❤CALL GIRL 7870993772 ❤CALL GIRLS ESCORT SERVICE In Bhiwan...

Bhiwandi Bhiwandi ❤CALL GIRL 7870993772 ❤CALL GIRLS ESCORT SERVICE In Bhiwan...
Use of mutants in understanding seedling development.pptx

Use of mutants in understanding seedling development.pptx
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
- 1. ~ PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC CELLS
- 2. INTRODUCTION • All living things are made up of cells. Cells are the smallest units that can be alive. During the 1950’s scientists developed the concept that life on earth is classified into six kingdoms and each have their own characteristic kind of cell. However the biggest division is between the cells of the Prokaryote kingdom (Eubacteria and archaebacteria and those of the other four kingdoms (animals, plants, fungi and protoctista which are all eukaryotes cells.
- 3. Characteristics • Prokaryotic Cells • Eukaryotic Cells
- 4. Prokaryote is an organism that does not have a nucleus (like bacteria), It still has DNA of course, but not enclosed in a neat little sack. Eukaryote is an organism that does have a nucleus (like me and you)
- 5. Functions • The Cell Wall • The Plasma Membrane • The Cytoplasm • The Genetic Material • The Ribosomes Prokaryotic Cell • The Cell Wall • The Plasma Membrane • The Nucleus • The Nuclear Membrane • The Nucleolus • The Mitochondria • The Chloroplast • The Endoplasmic Reticulum • The Ribosomes • The Golgi Bodies • The Lysosomes • The Vacuoles • The Cytoplasm • The Chromosomes Eukaryotic Cell Below are the organelles of each cell. Each of these organelles have specific functions.
- 6. DNA, the genetic material is located in a non-membrane bound nucleoid region in prokaryotes and a membrane- bound nucleus in eukaryotes 2. Plasma membrane, a phospholipid bilayer with proteins that separates the cell from the surrounding environment and functions as a selective barrier for the import and export of materials
- 7. 3. Cytoplasm, the rest of the material of the cell within the plasma membrane, excluding the nucleoid region or nucleus, that consists of a fluid portion called the cytosol and the organelles and other particulates suspended in it 4. Ribosomes, the organelles on which protein synthesis takes place
- 8. Connections
- 10. Reproduction Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Types, Genes and Conditions
- 11. Prokaryotic cells reproduce by a process that is called binary fission. The DNA in such cells is contained in a single circular chromosome called a plasmid within the cytoplasm. The reproductive process starts with the replication of the chromosome. Always asexual Prokaryotic Cell Reproduction
- 12. The life of eukaryotic cells is characterized by a cell cycle with two major phases: the interphase and cell division. The nucleus divides in a process called mitosis Asexual or sexual Eukaryotic Cell Reproduction
- 13. Application • The Carbon Cycles affect possible survival. • There are physical characteristics. • The temperature varies. • Environmental changes create problems.
- 14. Major Players
- 15. Biotic and Abiotic Factors Biotic Factors are; • Producers (autroph) plants • Consumers (hetertrophs) animals • Decomposers (fungi and bacteria) Abiotic Factors are; • Air • Water • Space • Temperature • Light • Soil (nutrients
- 16. Feeding Systems Feeding Systems that takes place in Prokaryotic Organisms Feeding Systems that takes place in Eukaryotic Organisms
- 17. Organisms within the Kingdoms • Prokaryotes includes several kinds of microorganisms such as bacteria and cyanobacteria. • Eukaryotes includes such microorganisms as fungi, protozoa and simple algue.
- 18. References • Rader, A. (1997) Eukaryotes – Cells with Parts. Biolgy4kids.com: Microorganisms: Eukaryotes Retrieved from www.biology4kids.com/files/micro_eukaryote.html • The Biology Project Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics. (1997) Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, & Viruses Tutorial. Retrieved from http:// www.biology.arizona.edu. www.biology4kids.com/files/micro_eukaryote.html • Understanding Evolution. From prokaryotes to eukaryotes. Retrieved from evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/_0/endosymbiosi s_03. Pg 3
