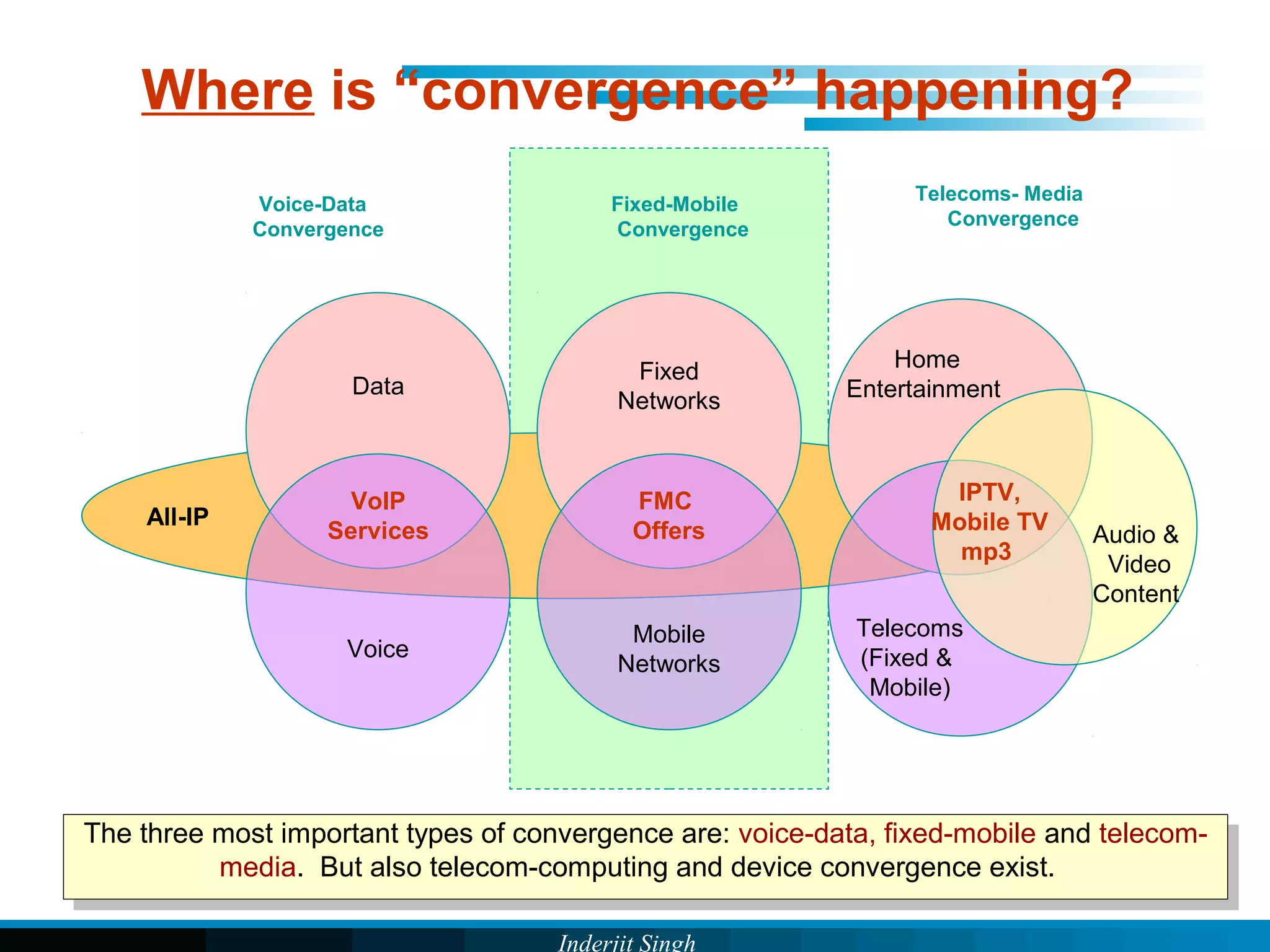
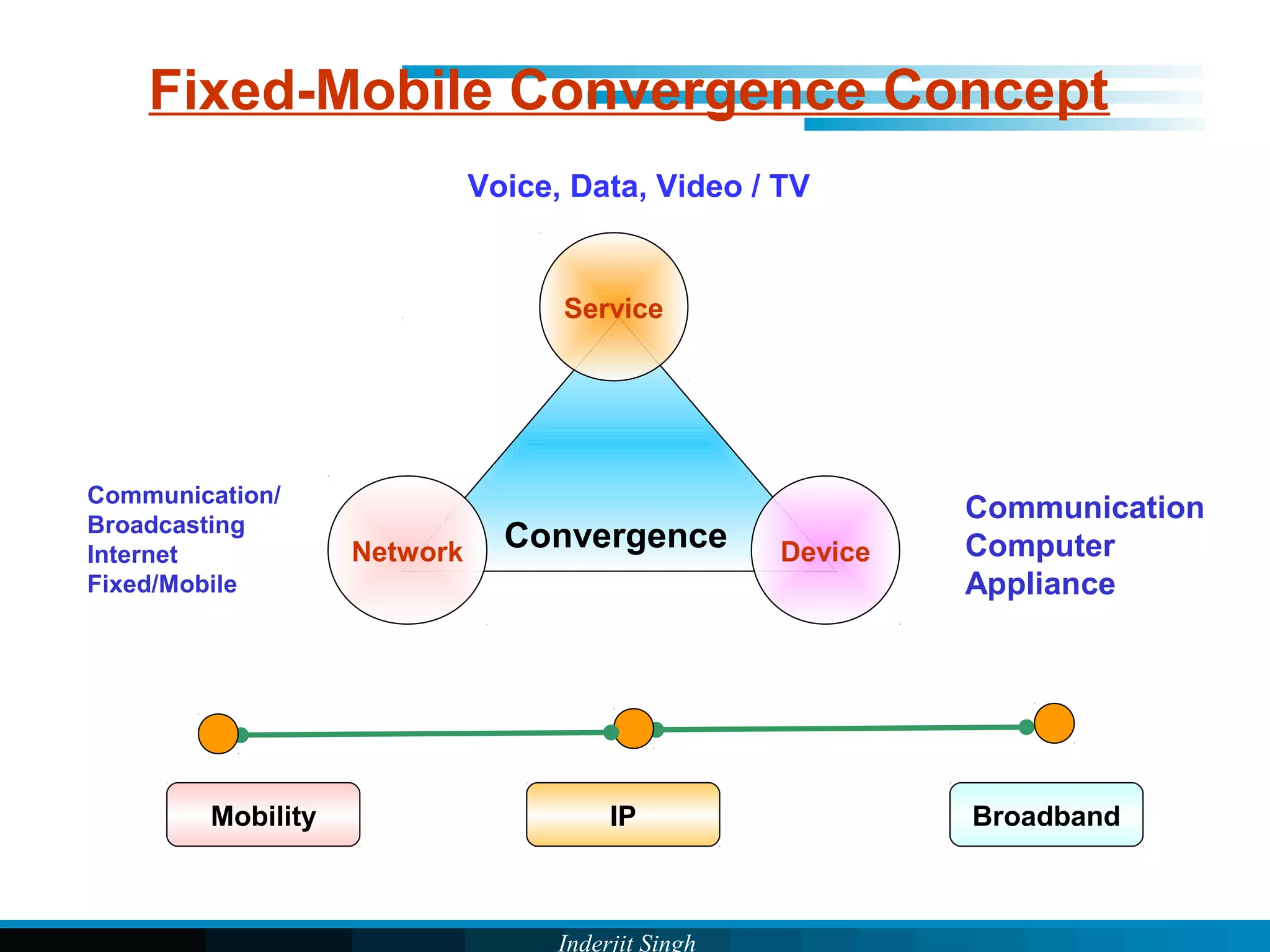
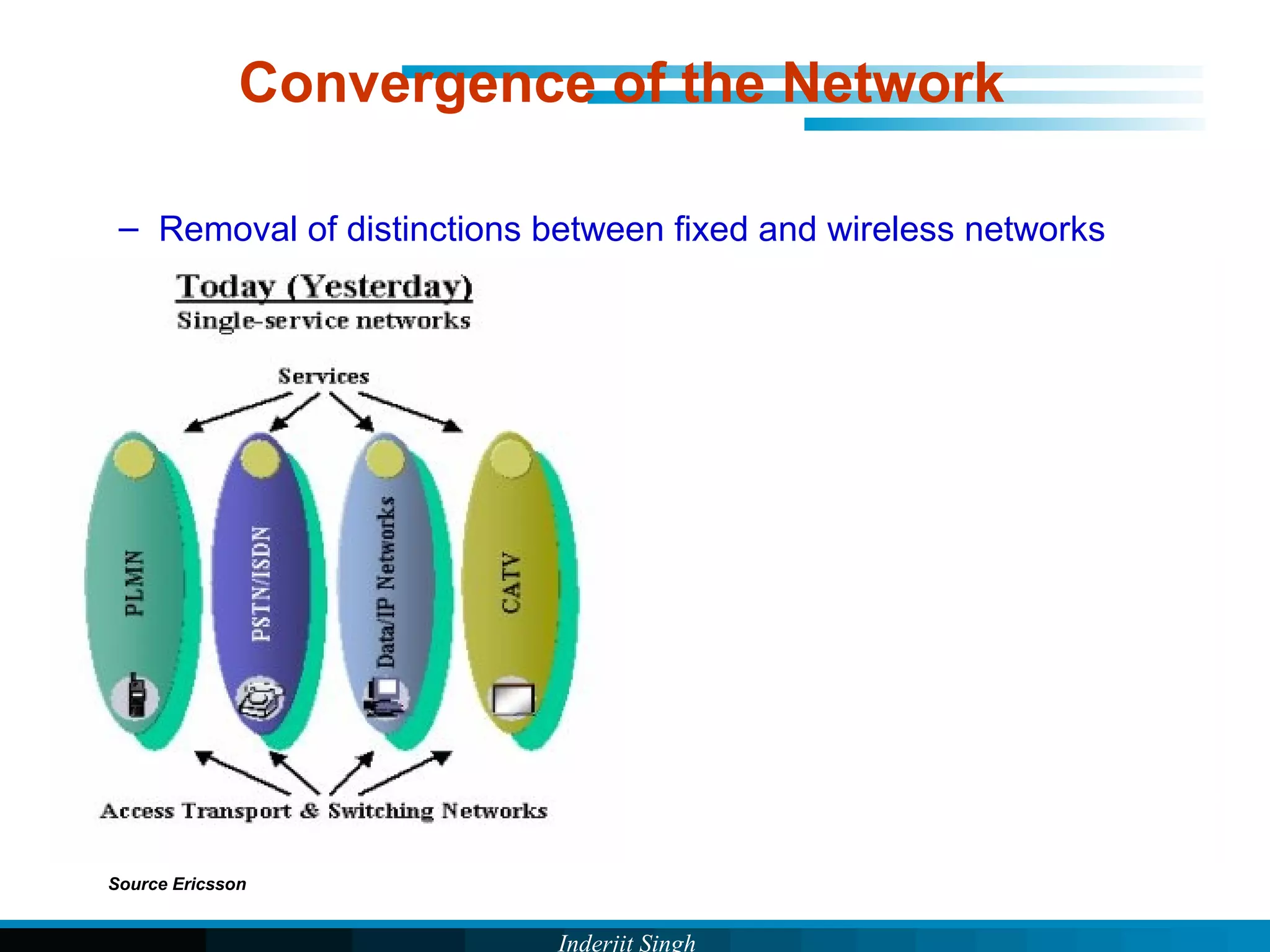
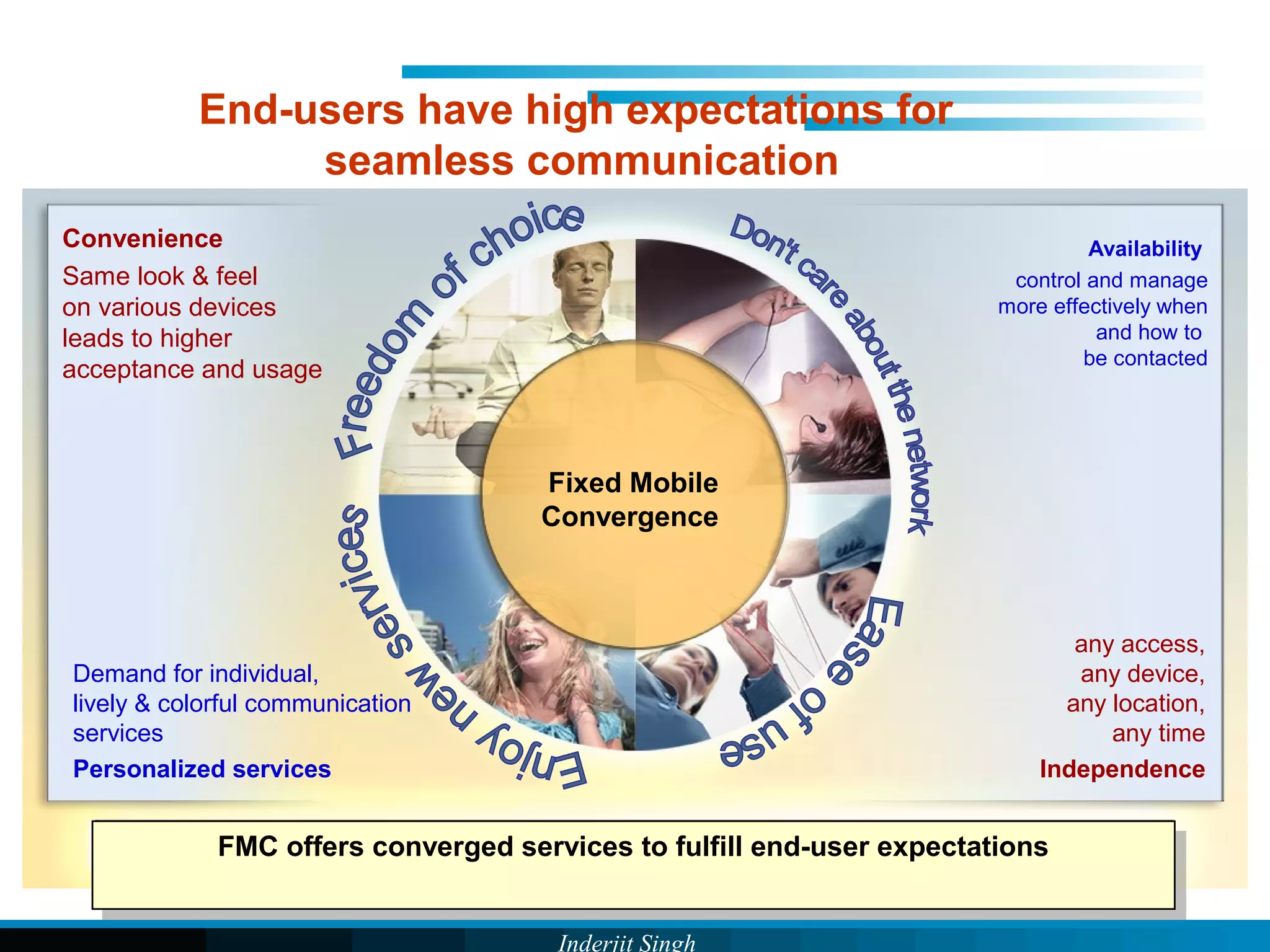
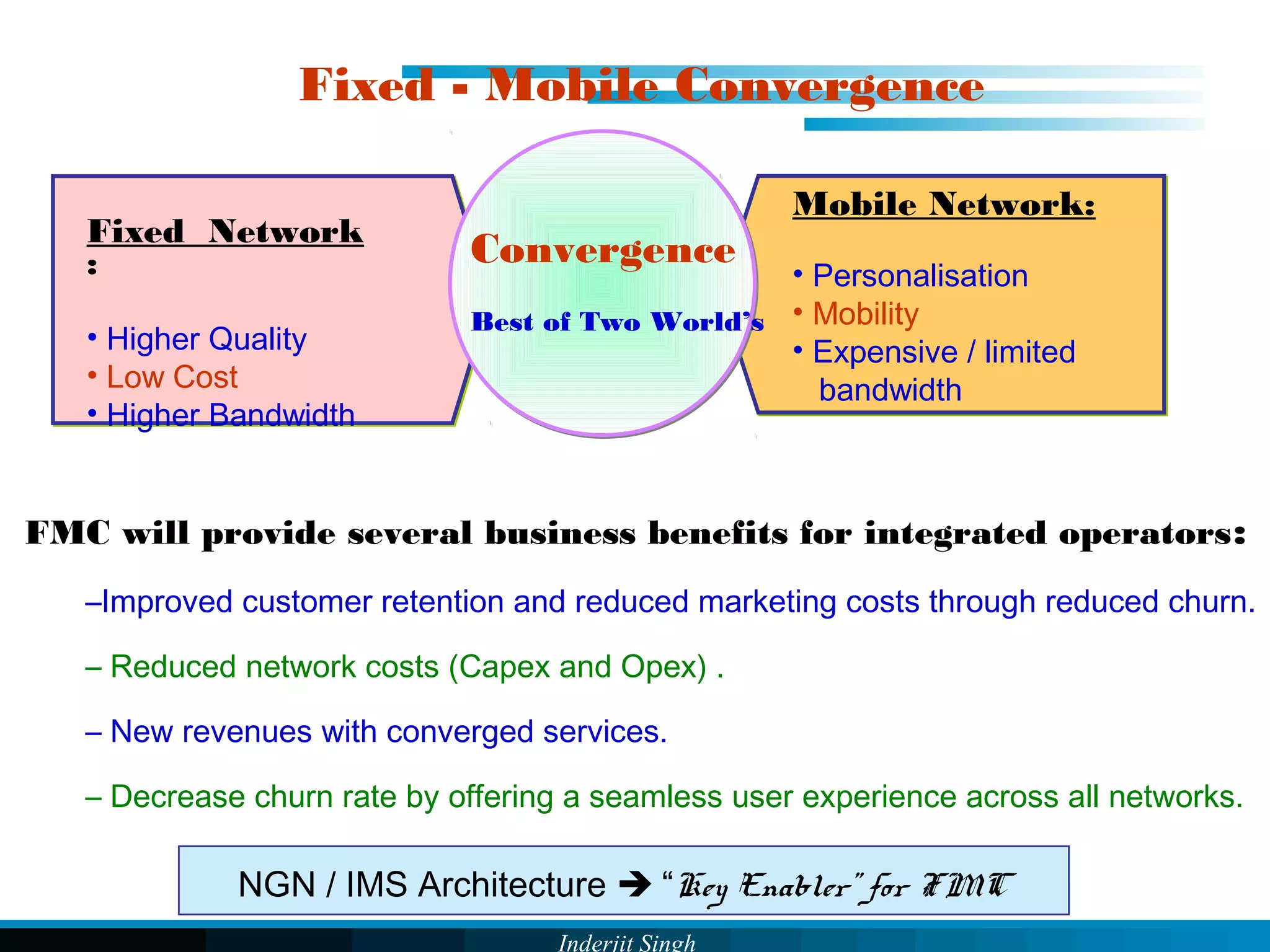
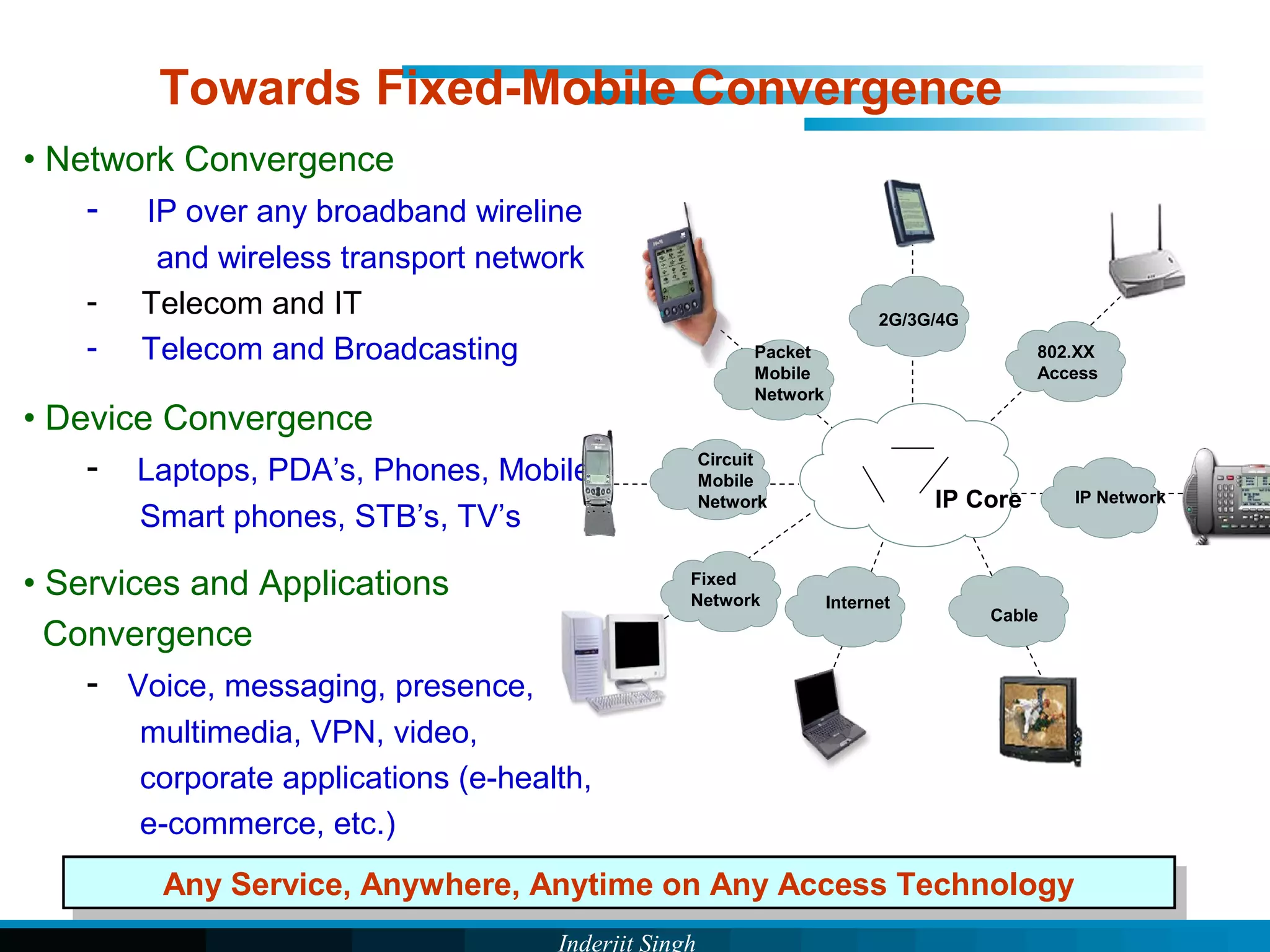
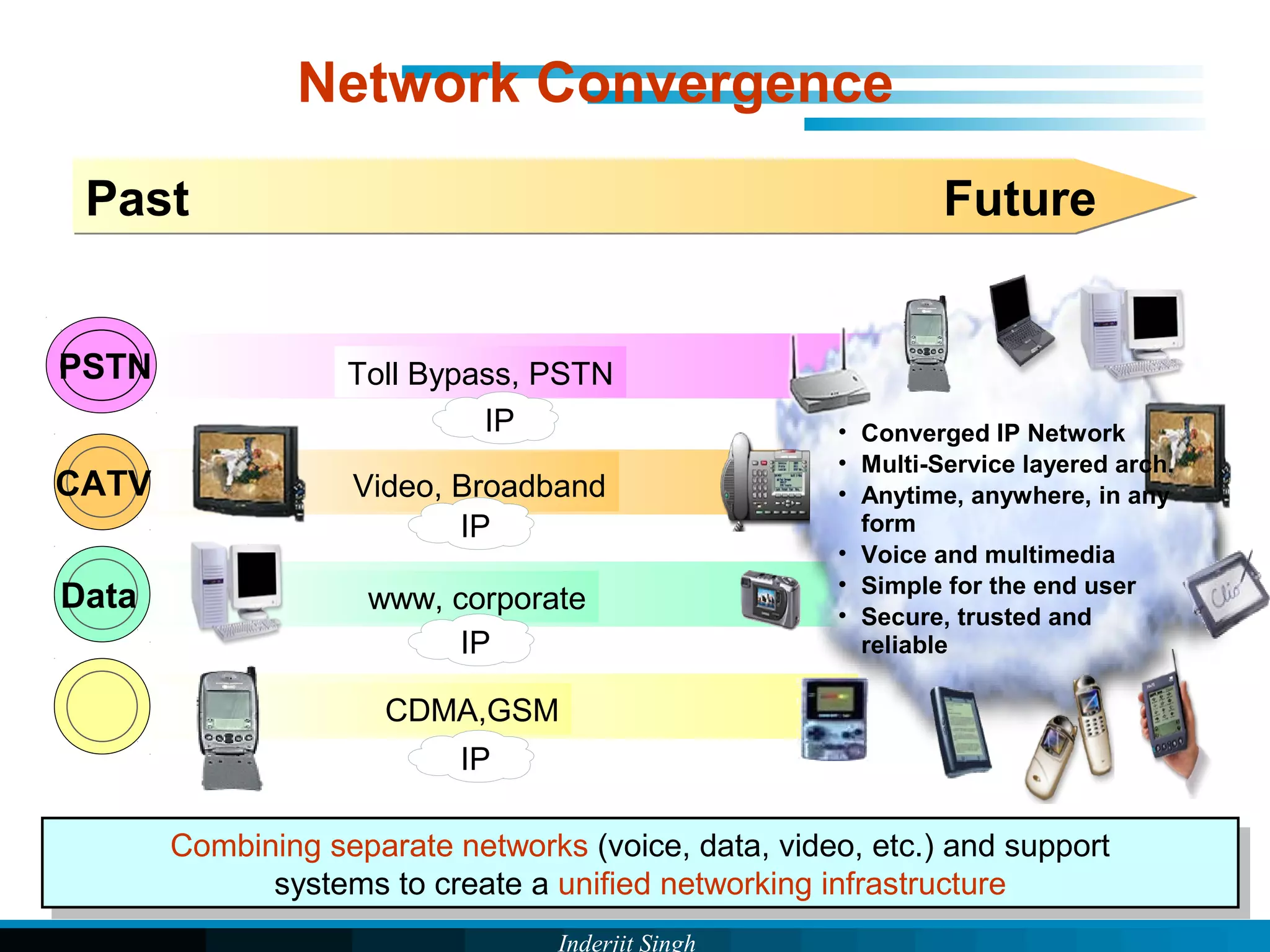
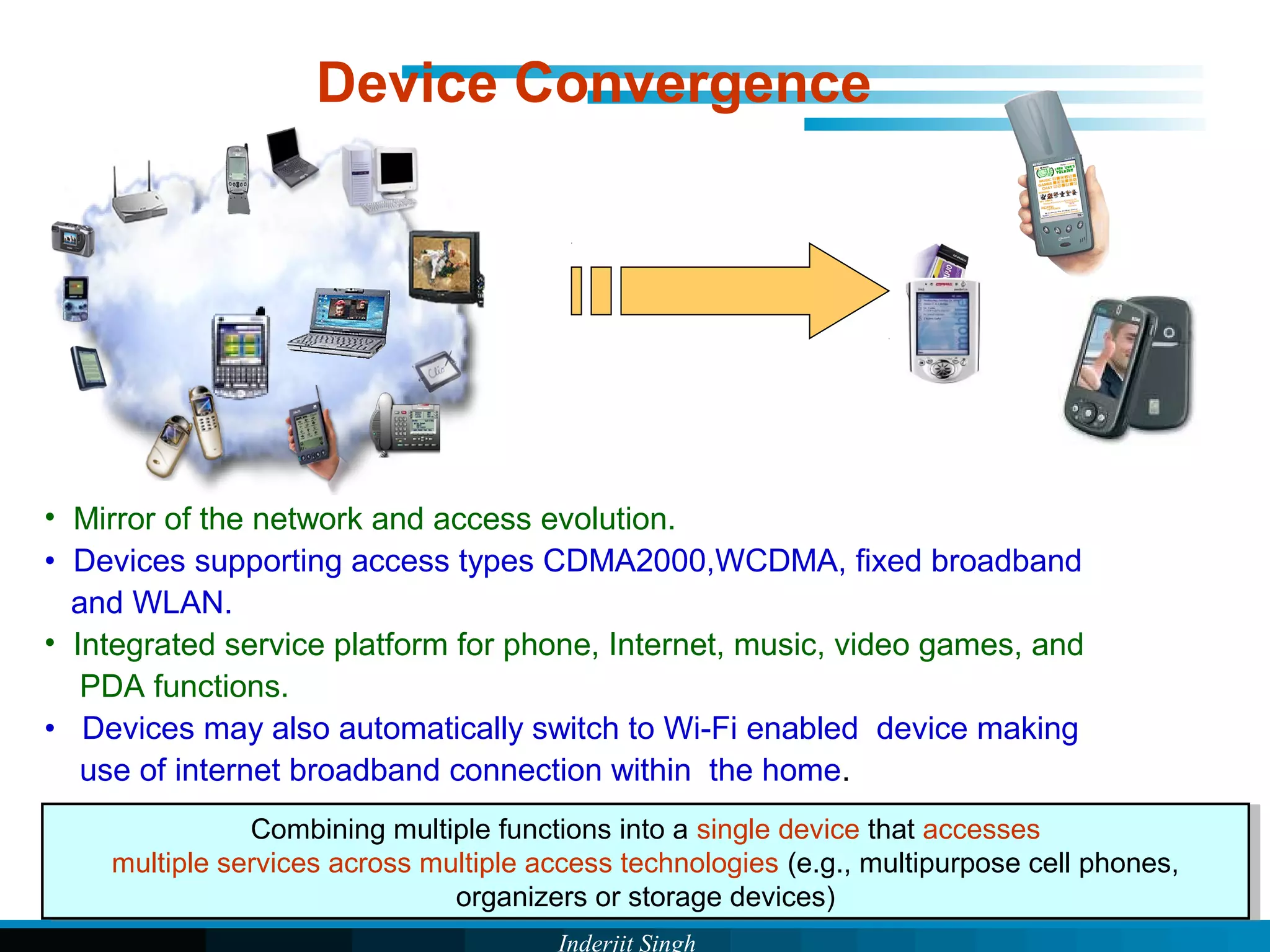
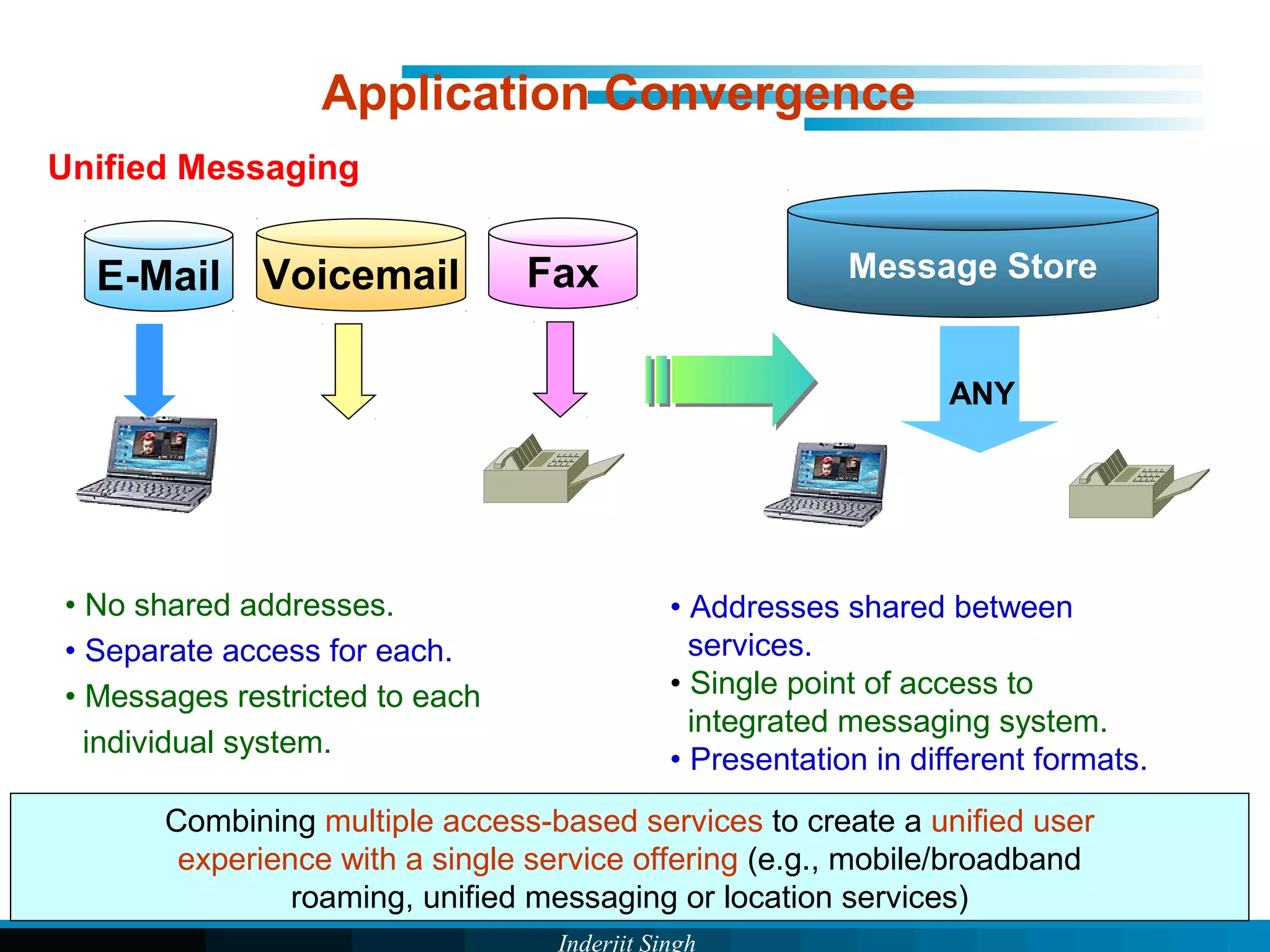
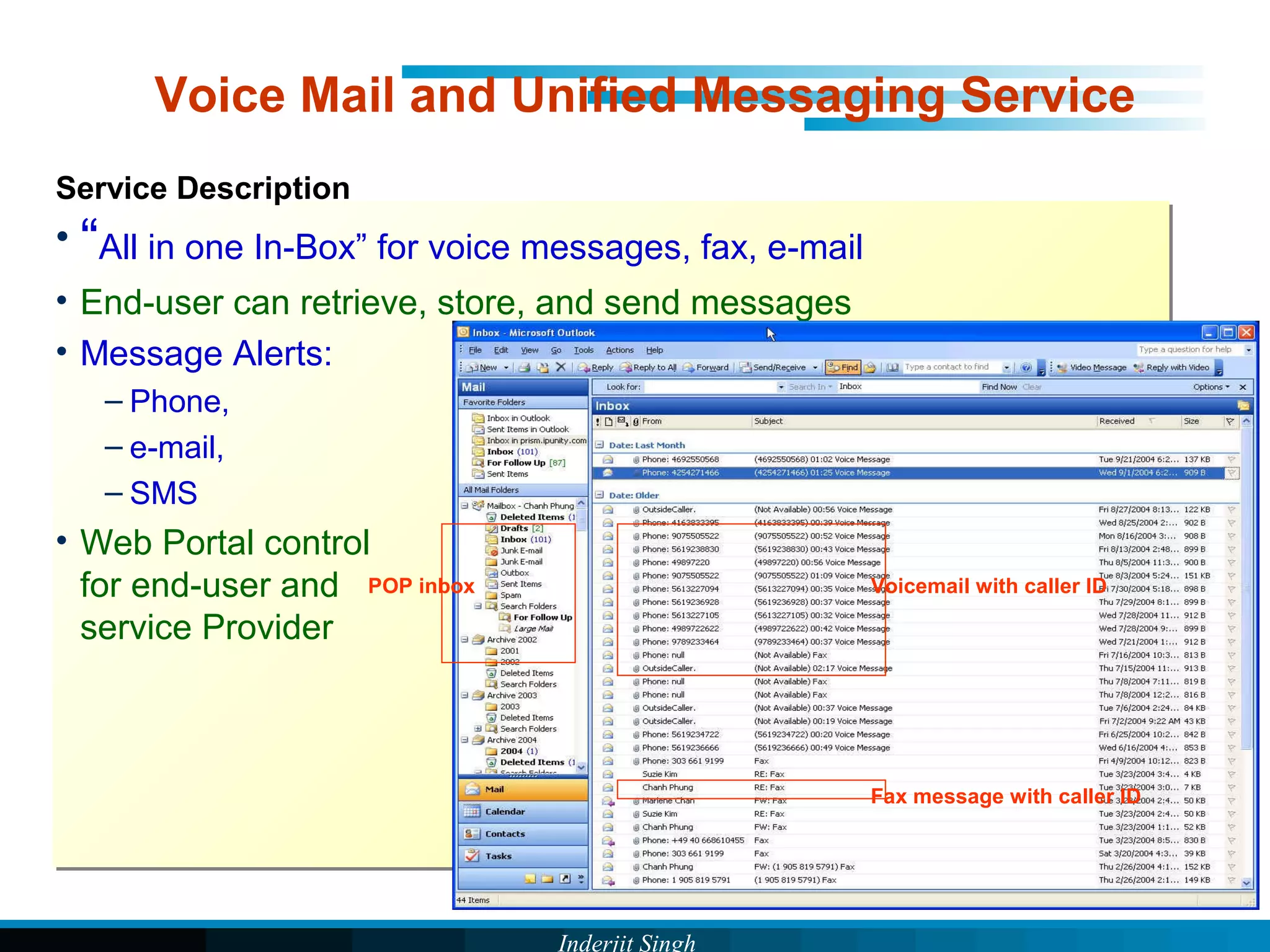
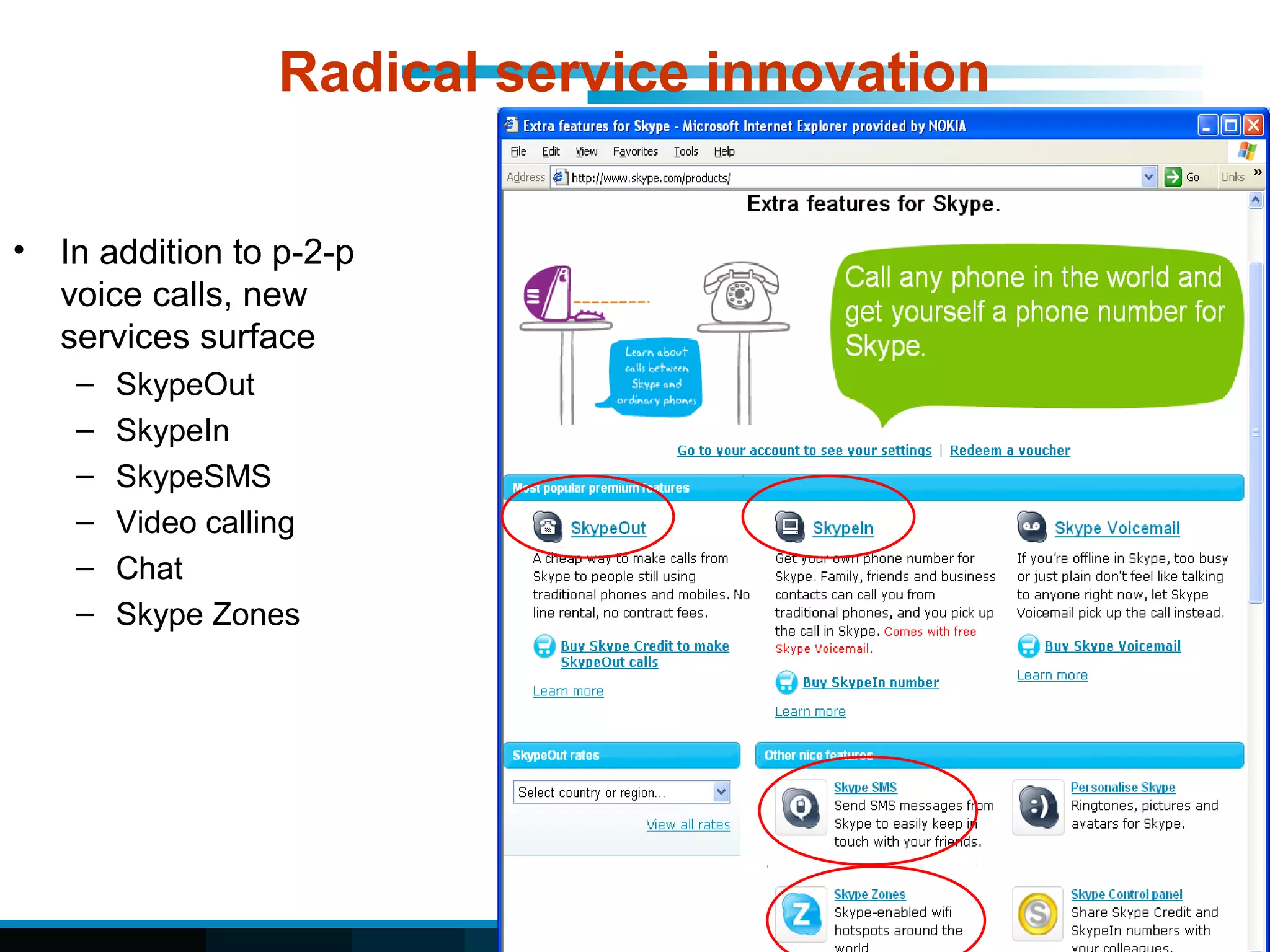
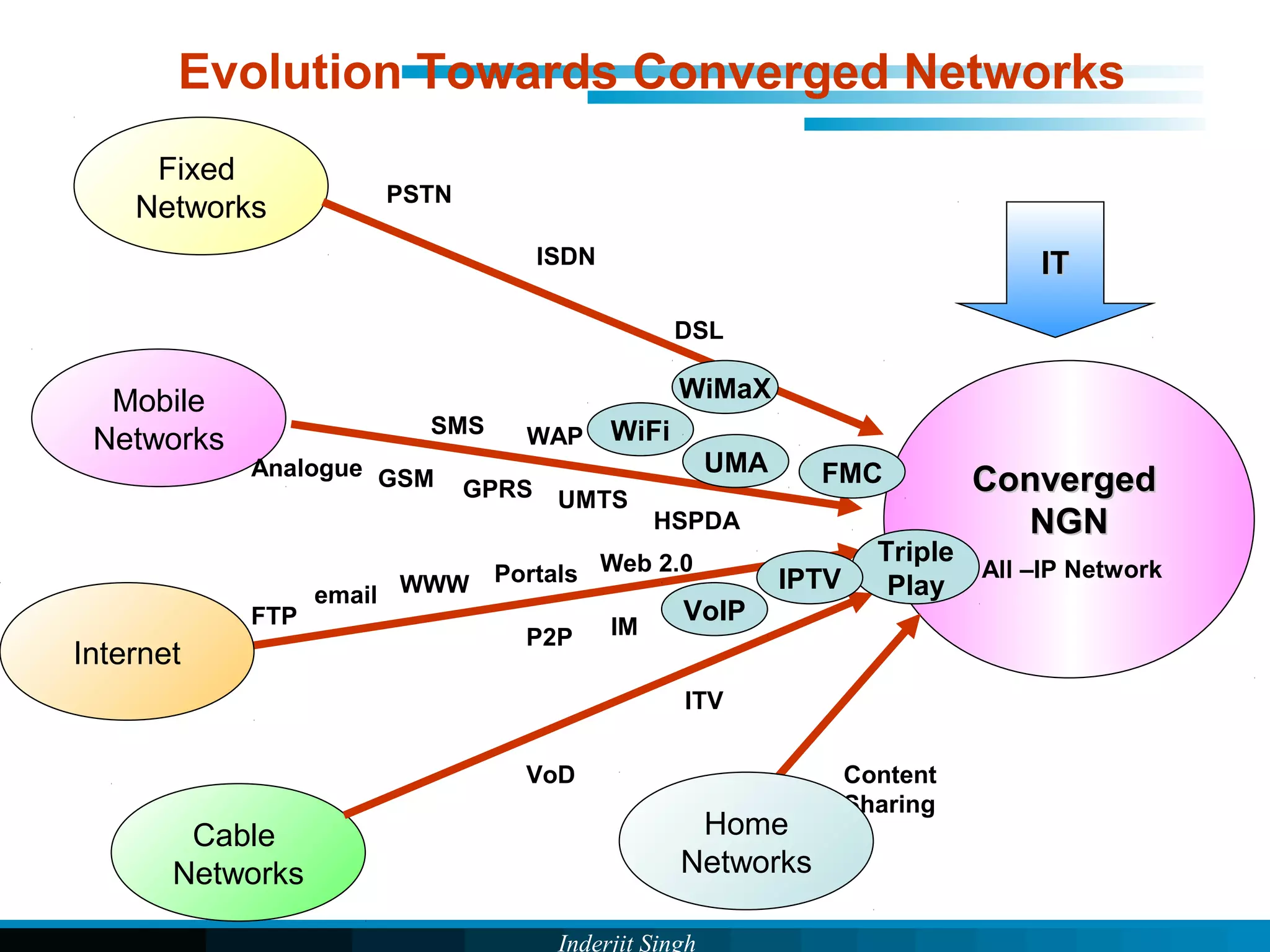
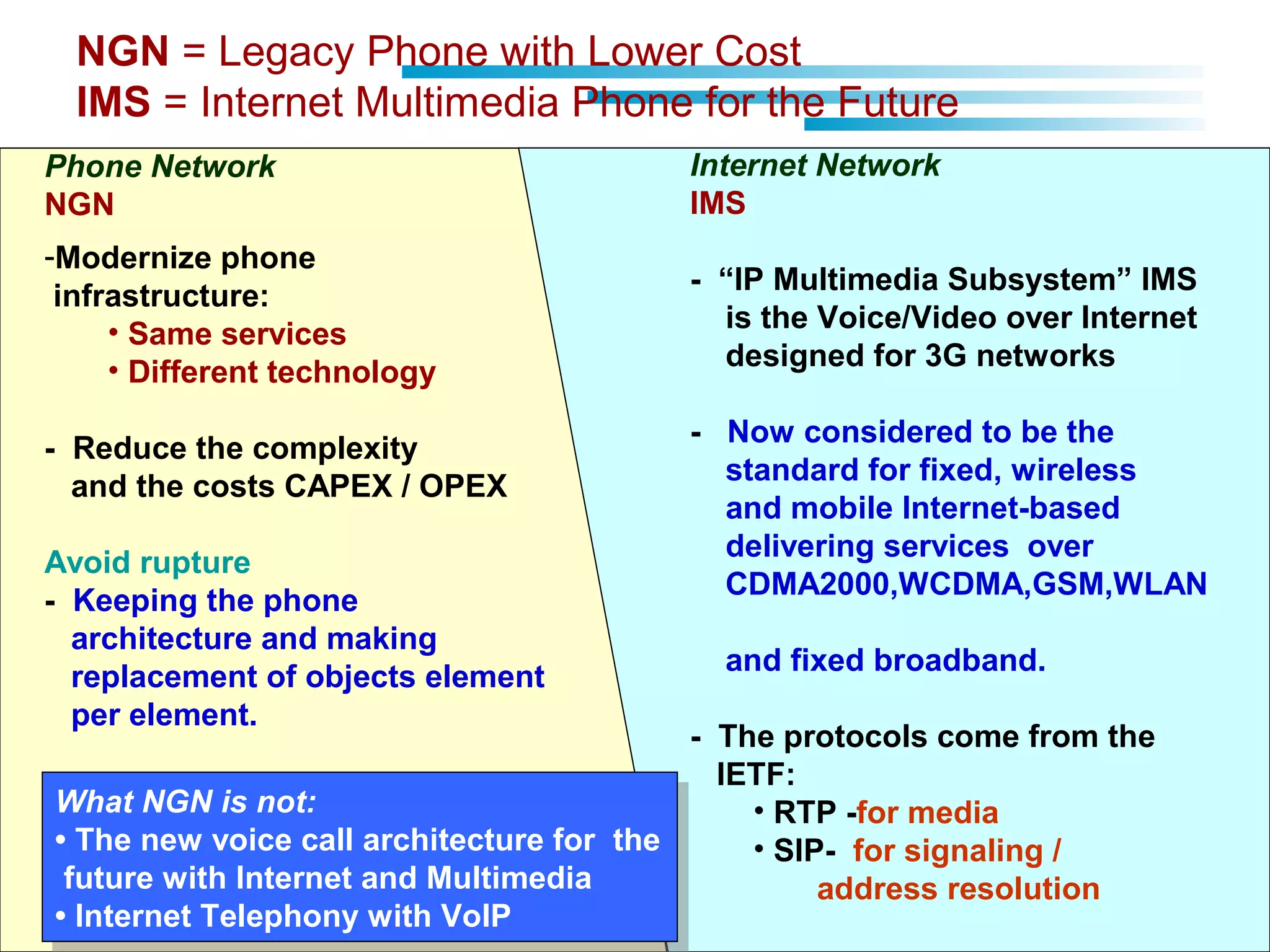
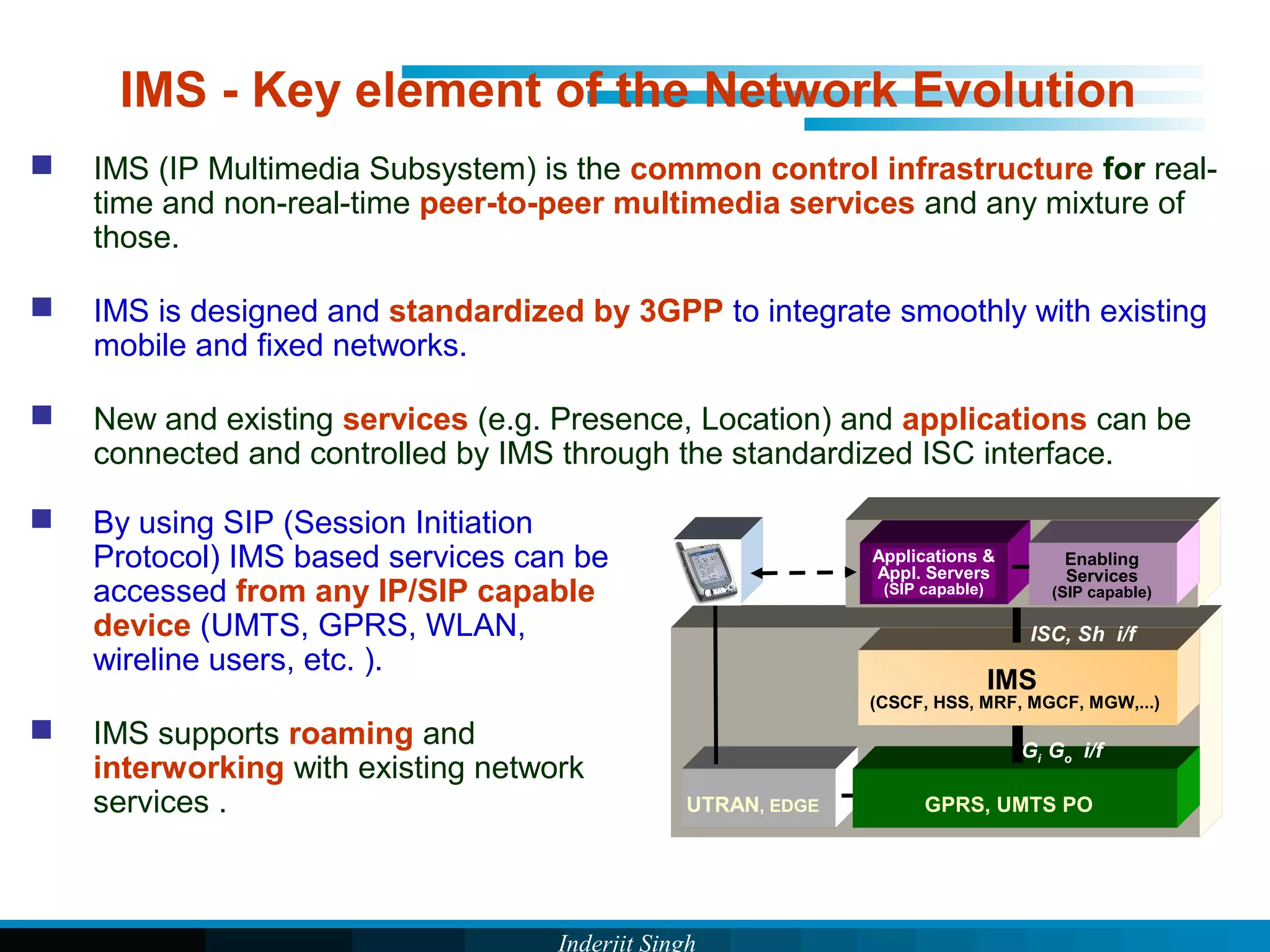
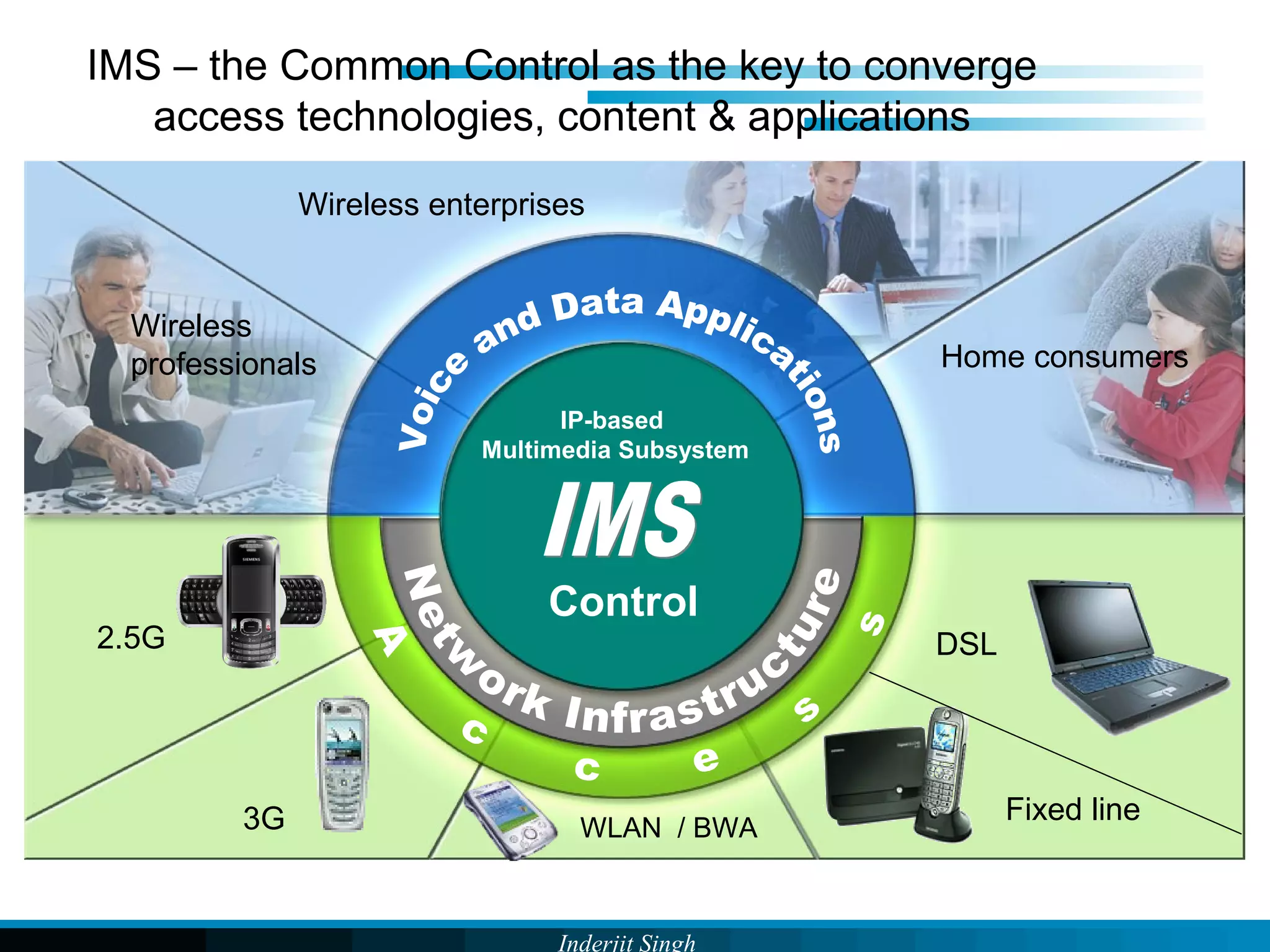
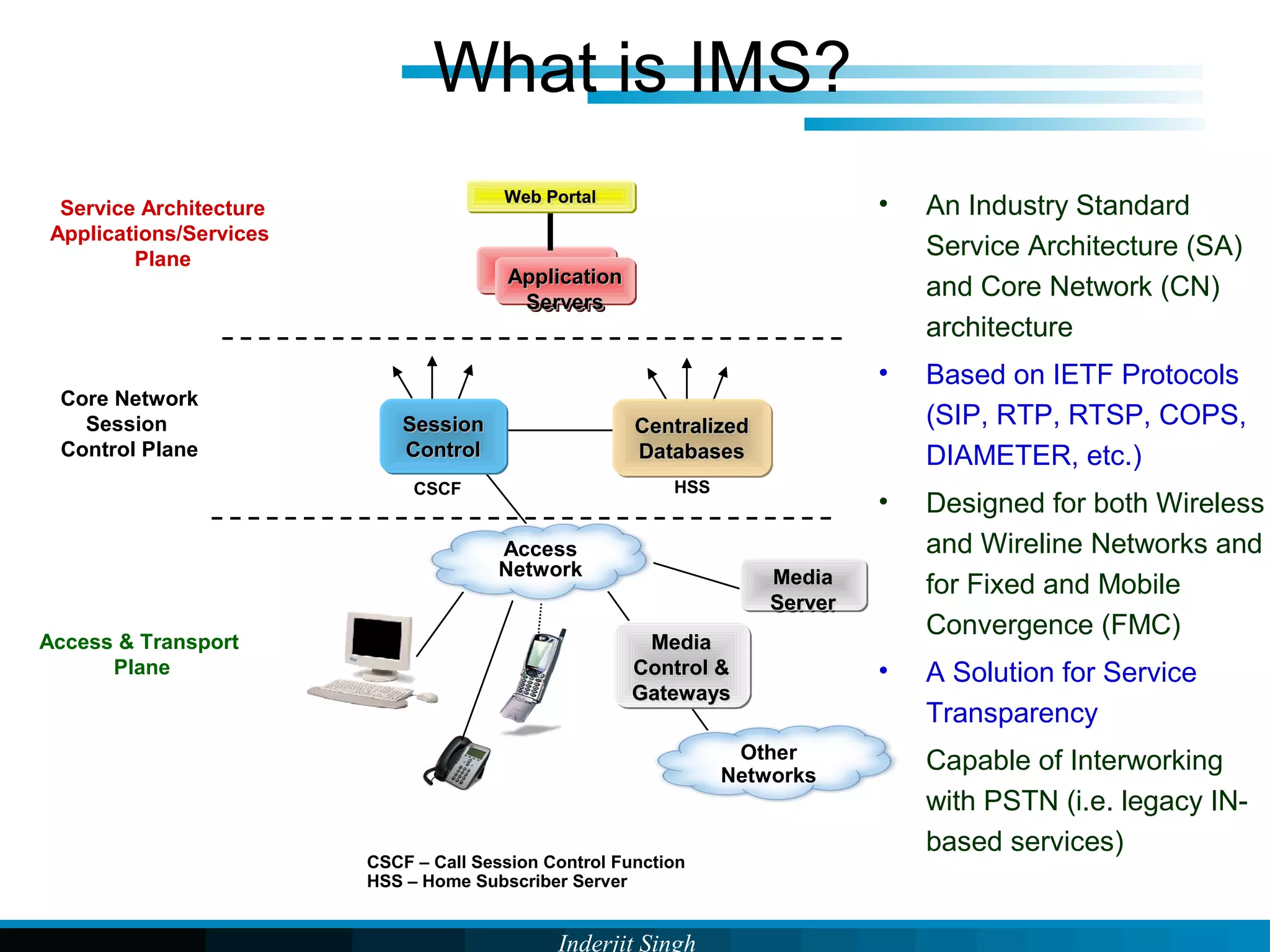
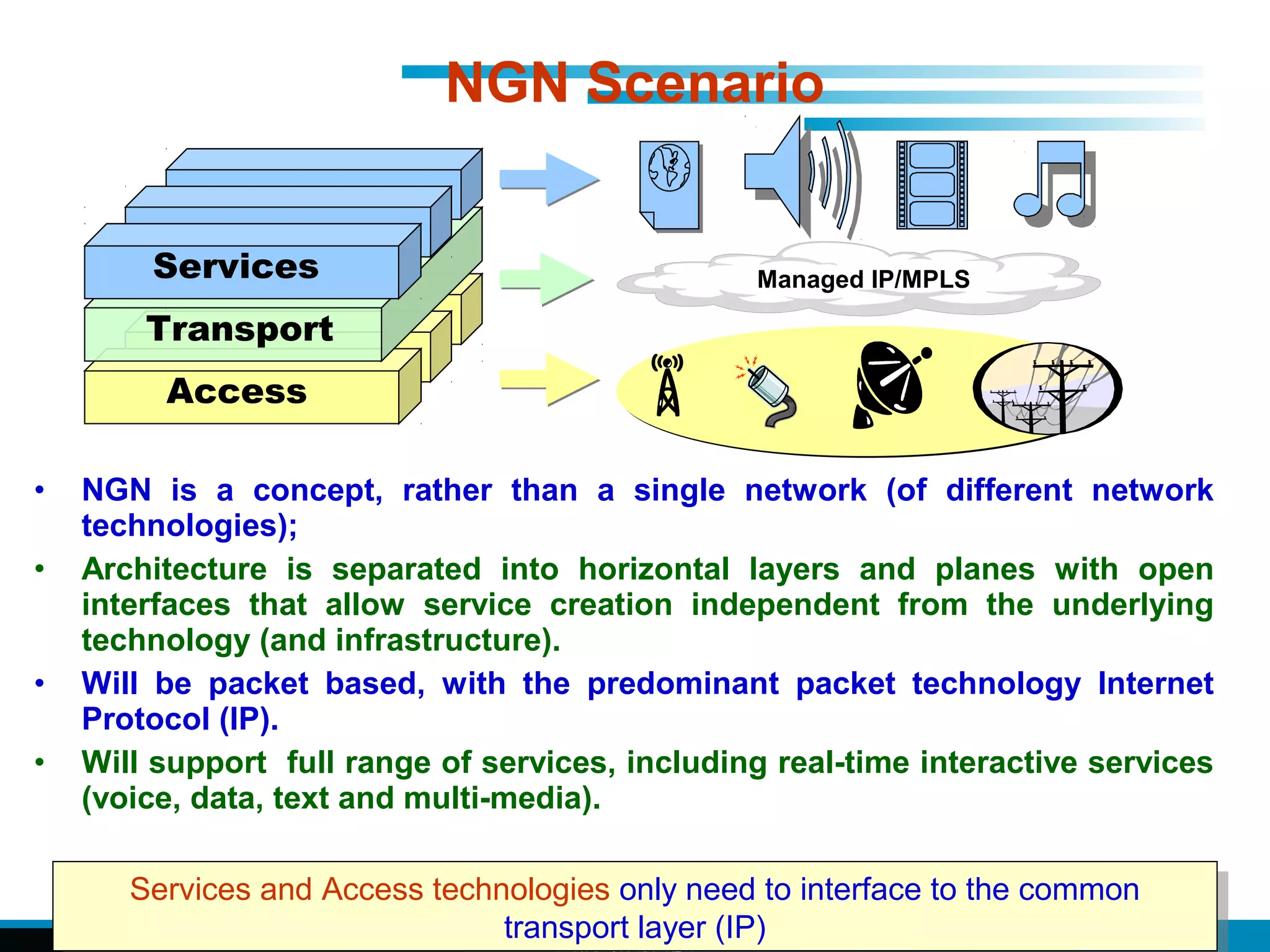
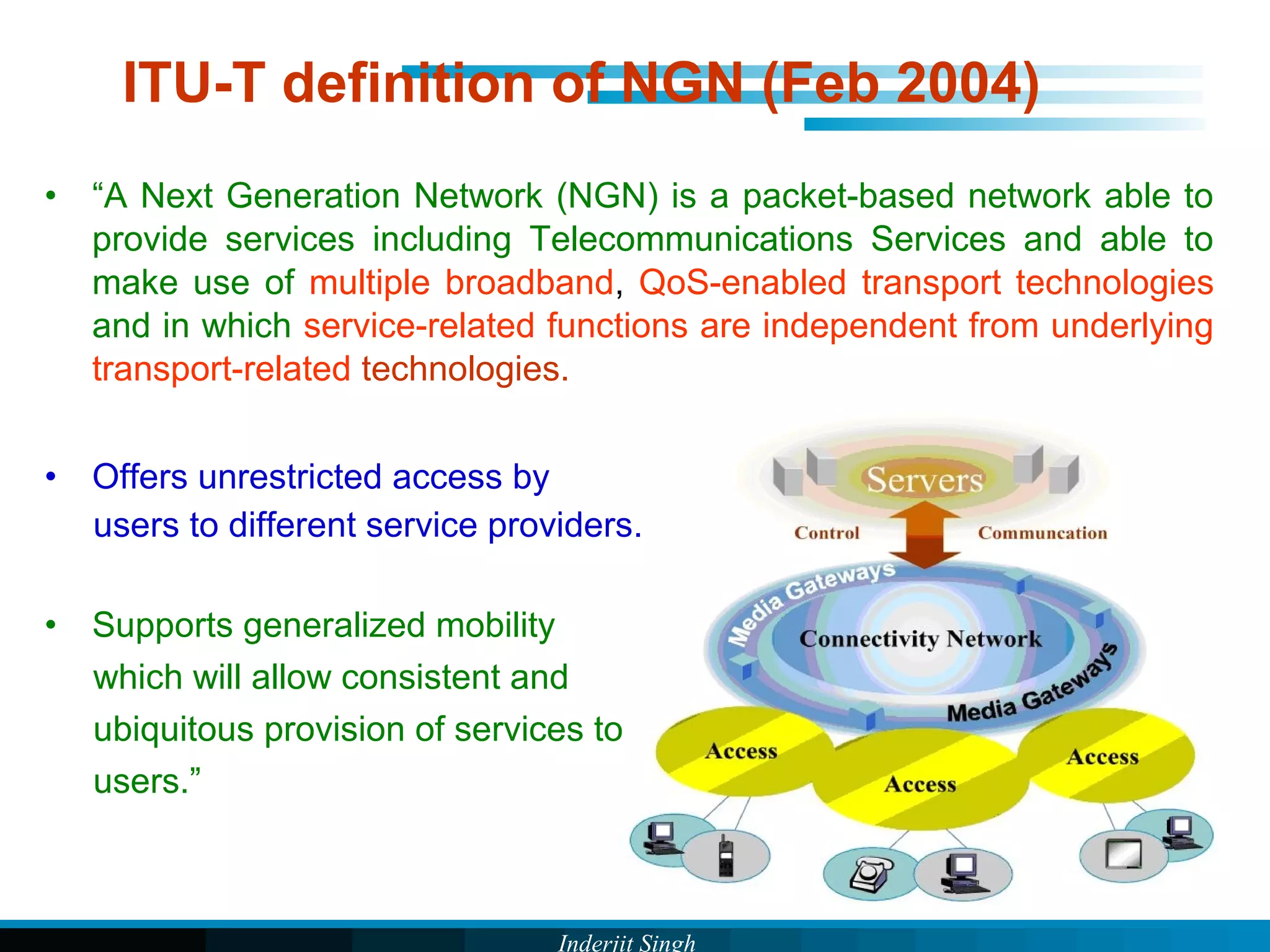
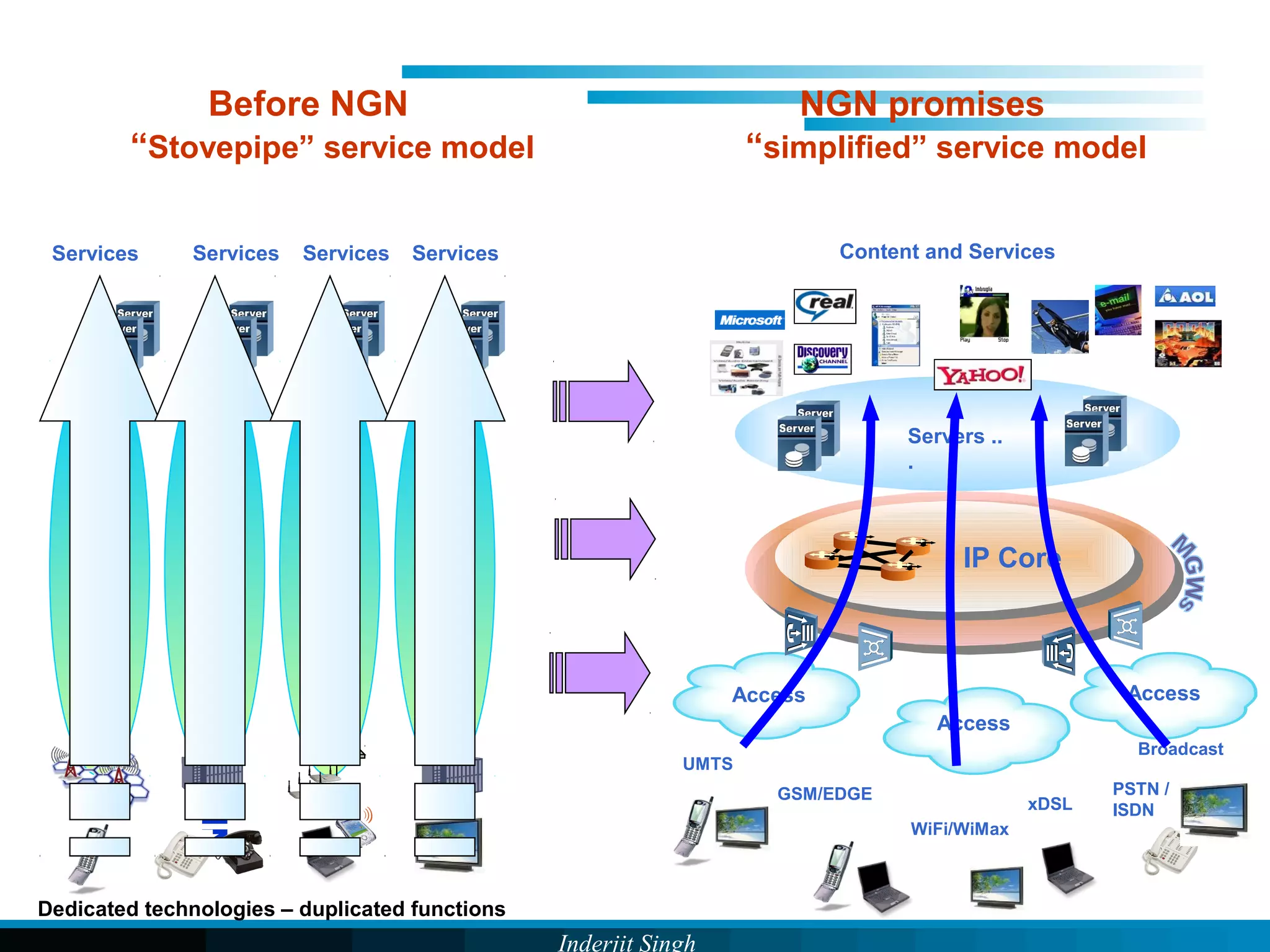
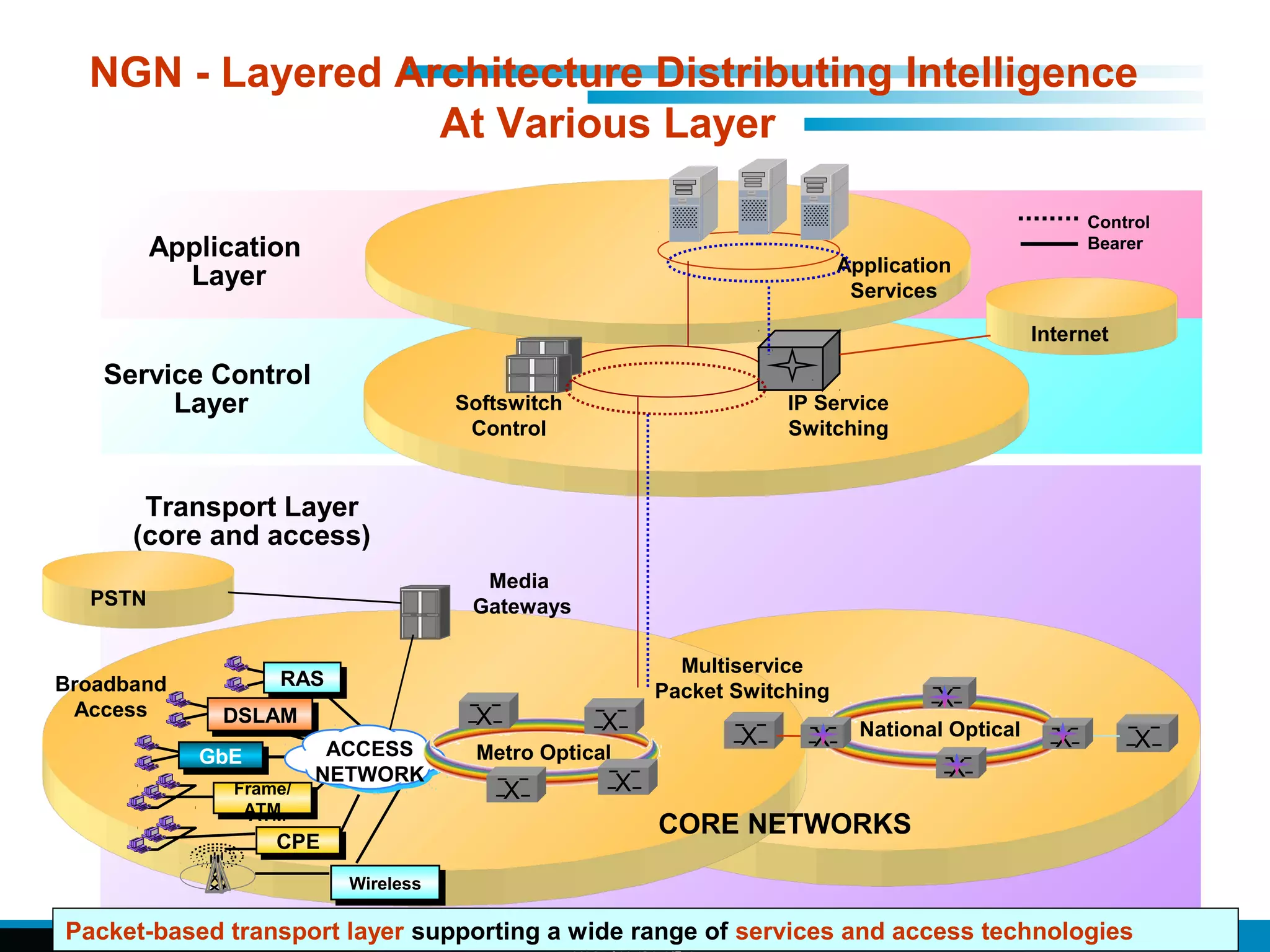
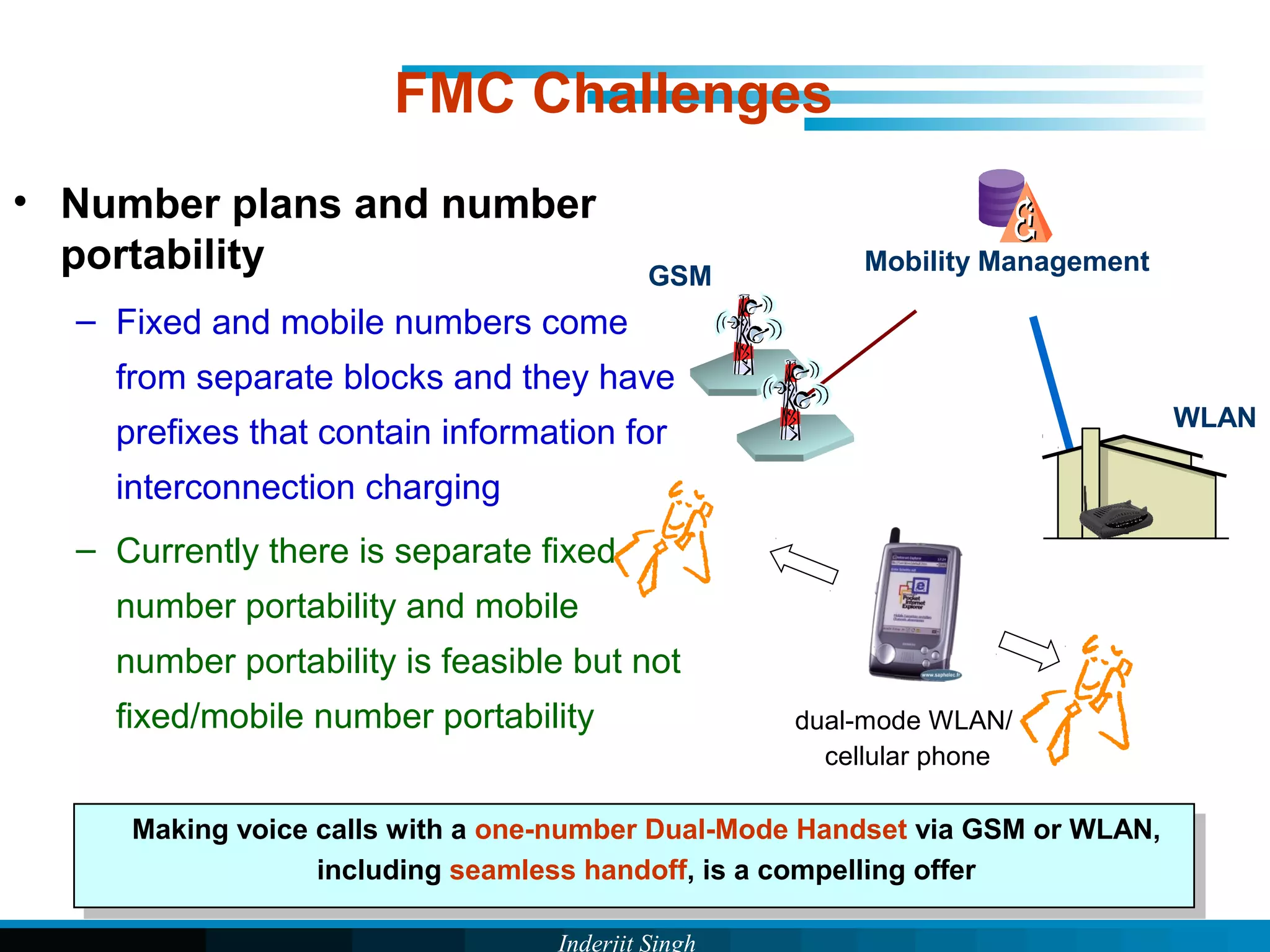
The document discusses fixed-mobile convergence (FMC), which aims to provide seamless communication services regardless of access network. FMC is enabled by converging telecom networks on an all-IP infrastructure using IMS. This allows any service to be accessed from any device over either fixed or mobile networks. However, FMC faces challenges regarding number plans, directory services, spectrum allocation and interconnection charges between networks. Overall, FMC has the potential to offer users integrated communication services with the benefits of both fixed and mobile networks, but also requires new investments and standards to address complex network integration issues.