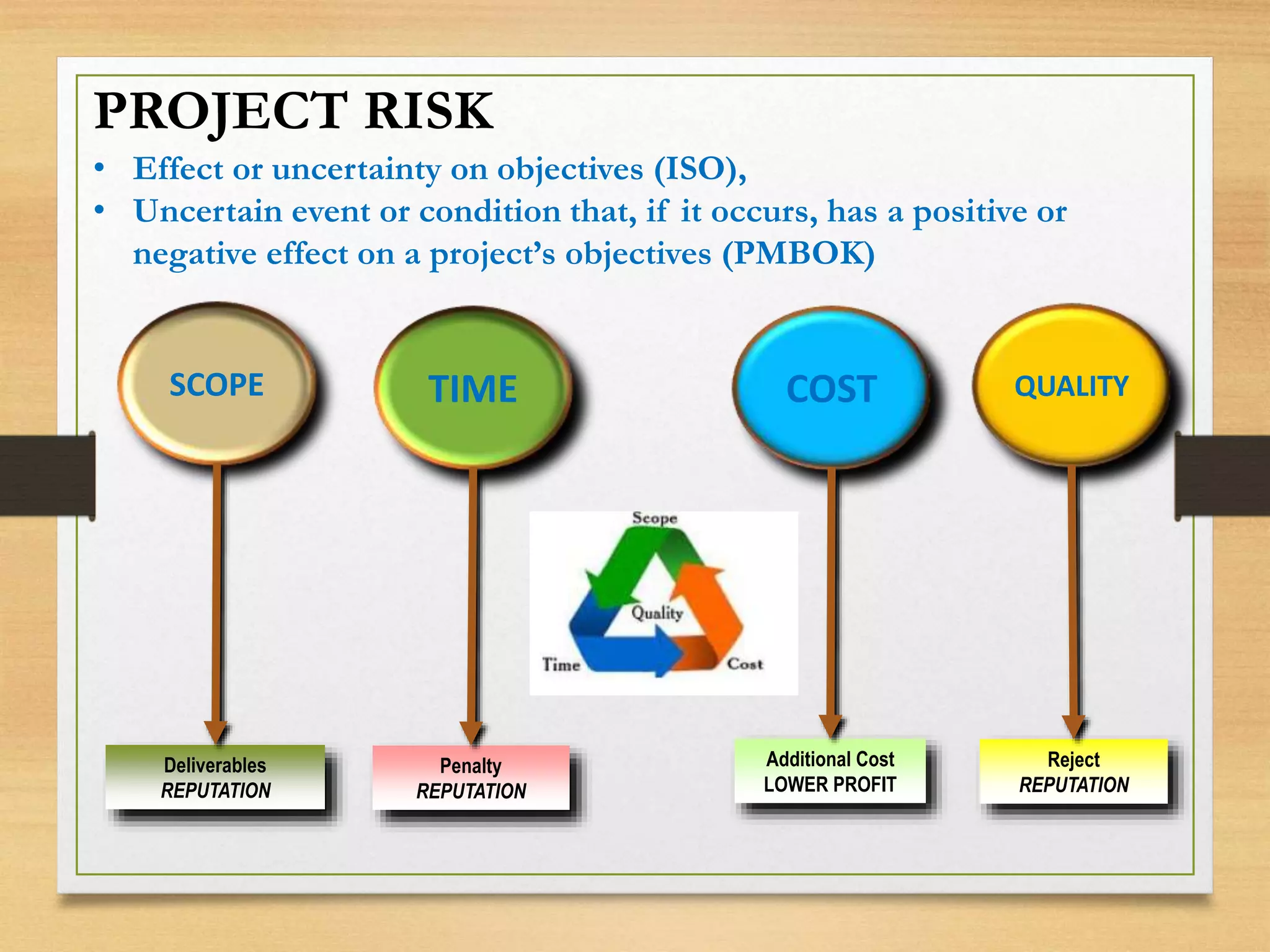
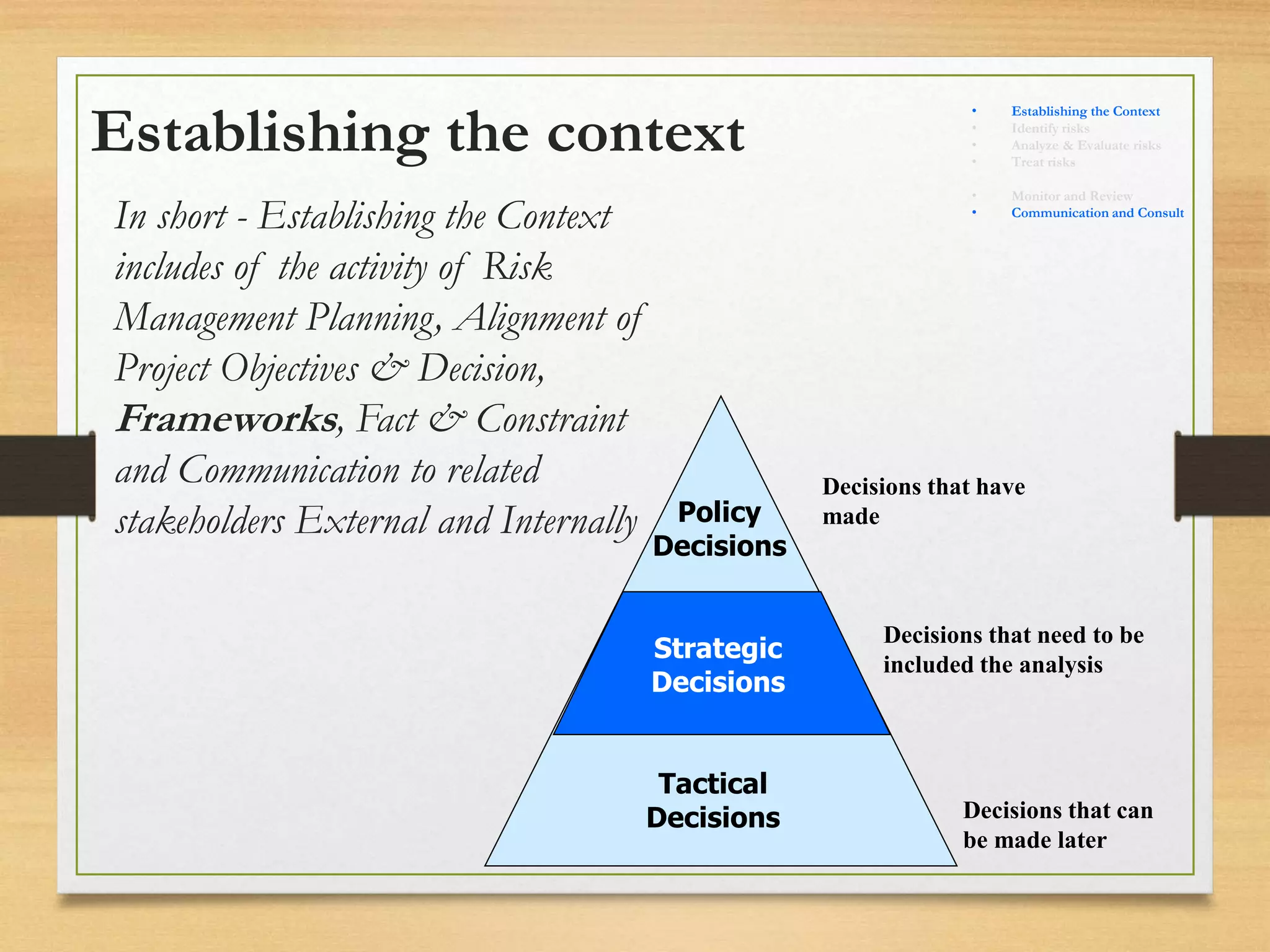
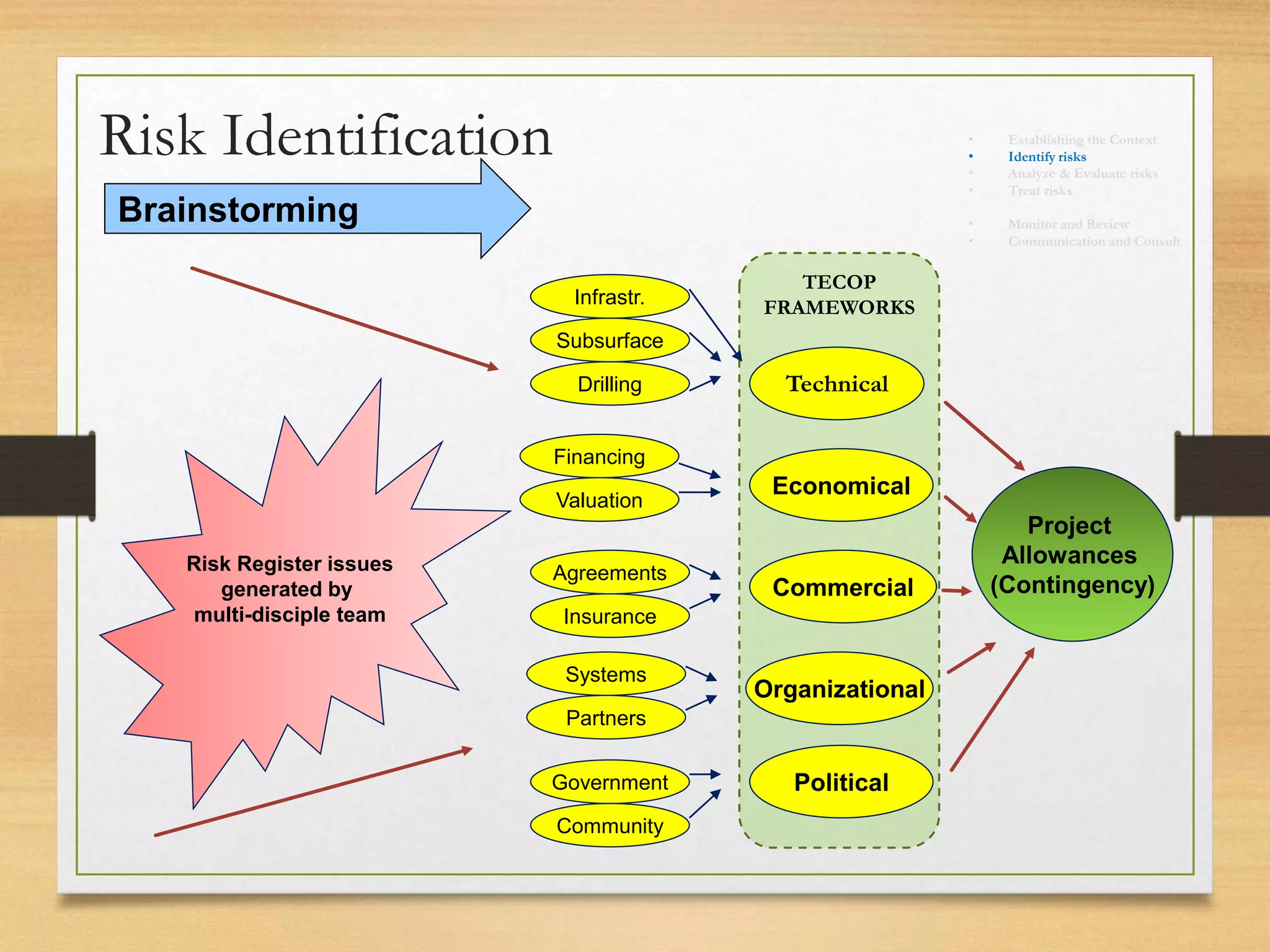
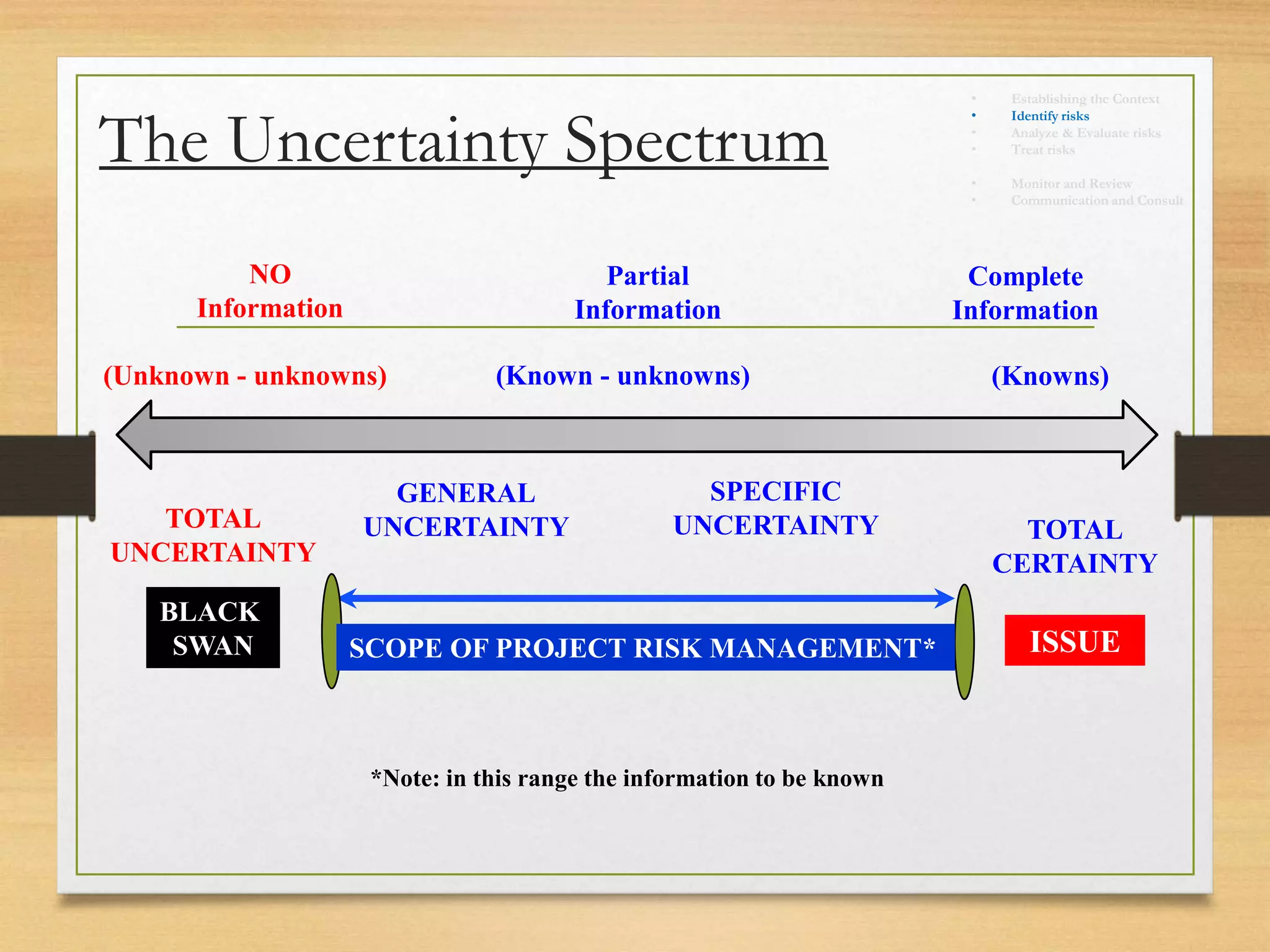
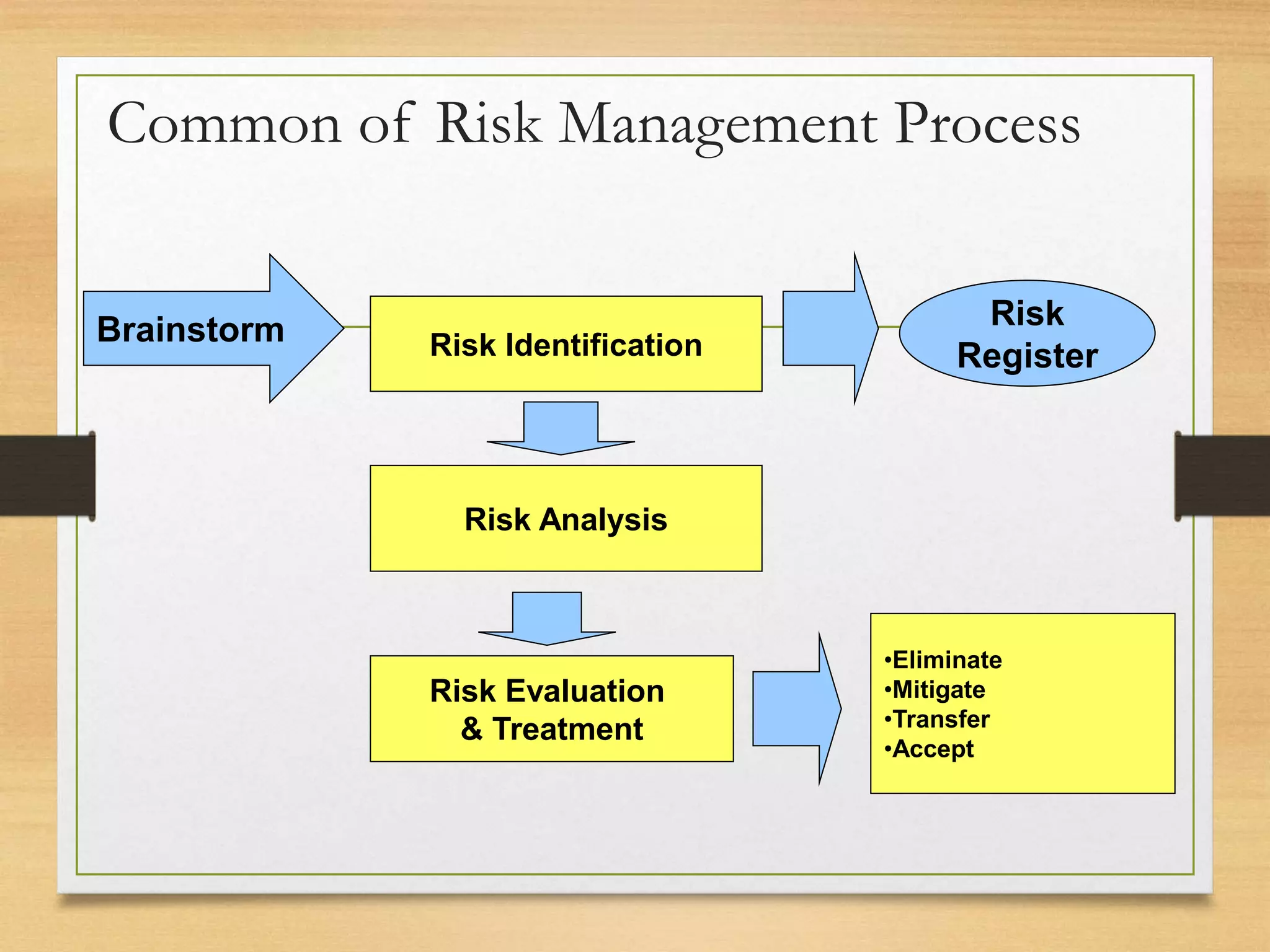
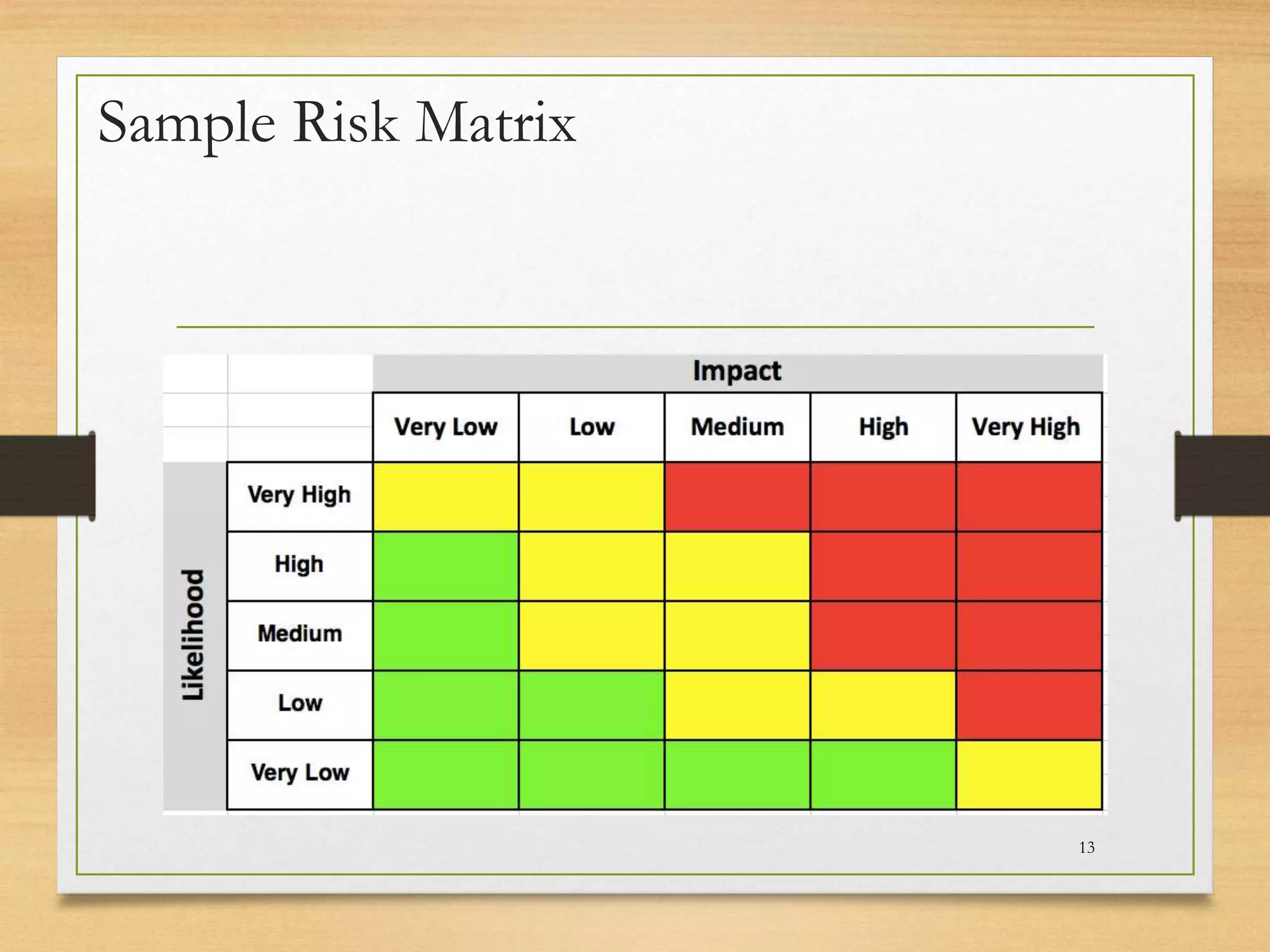
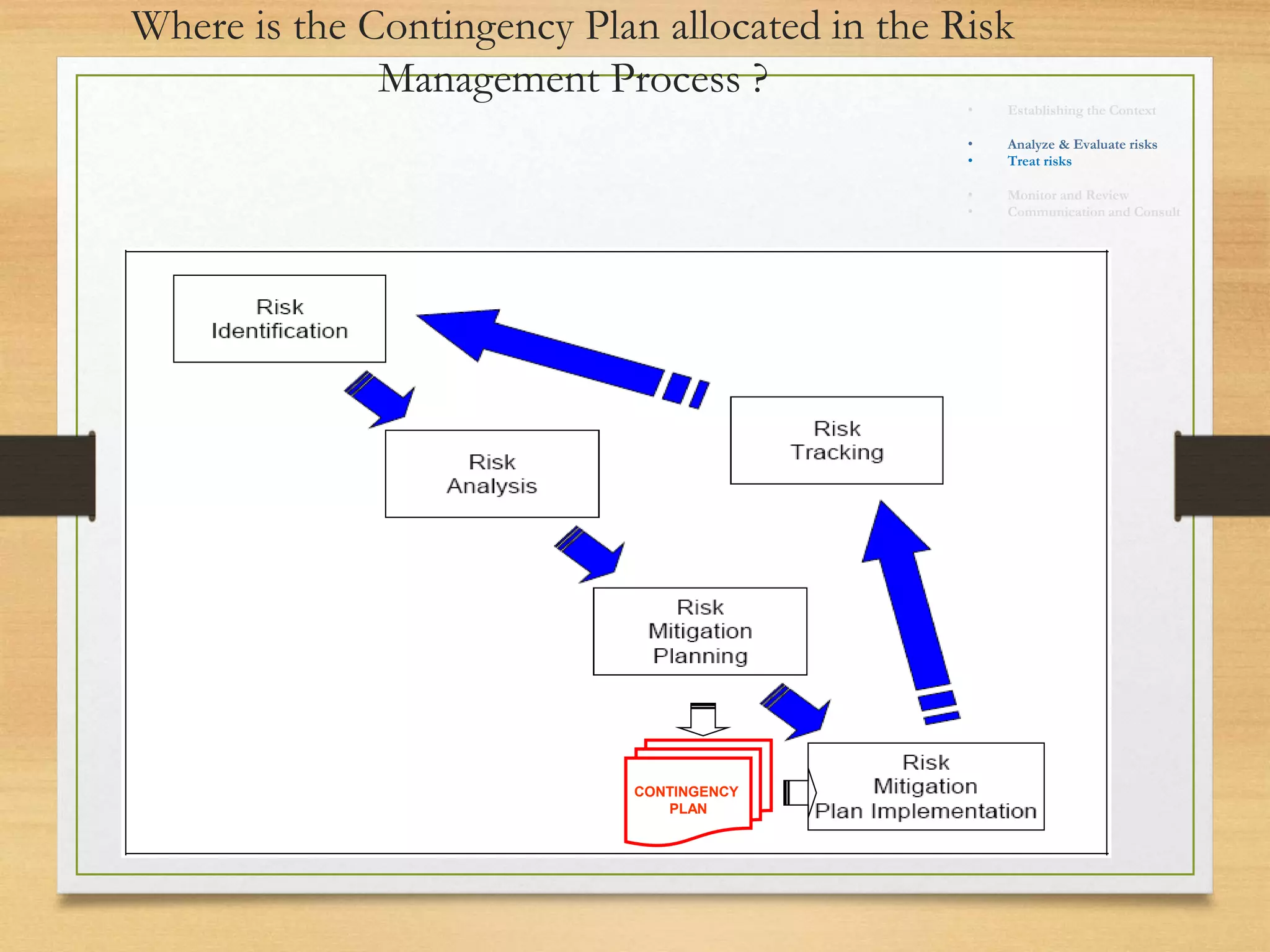
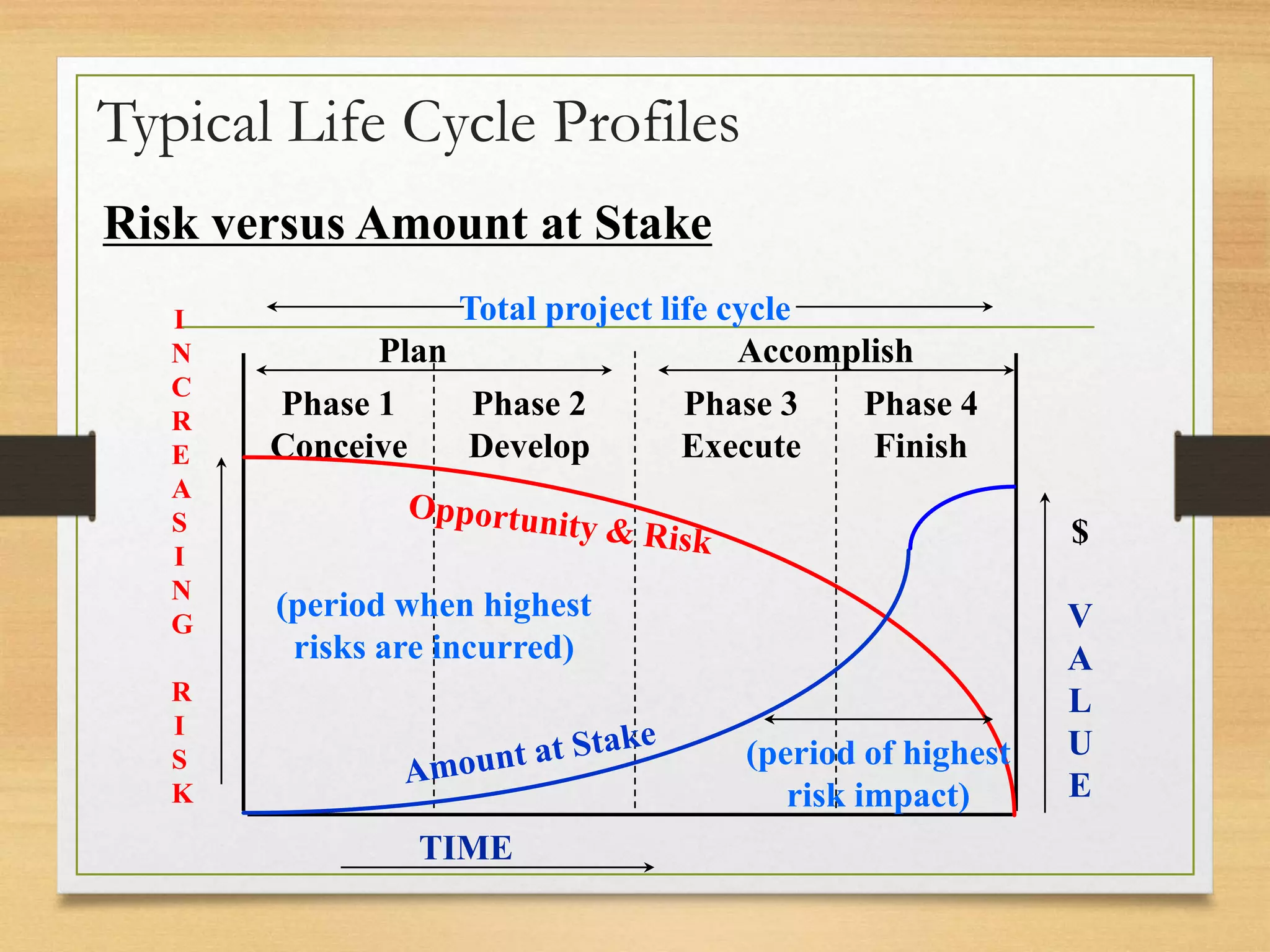
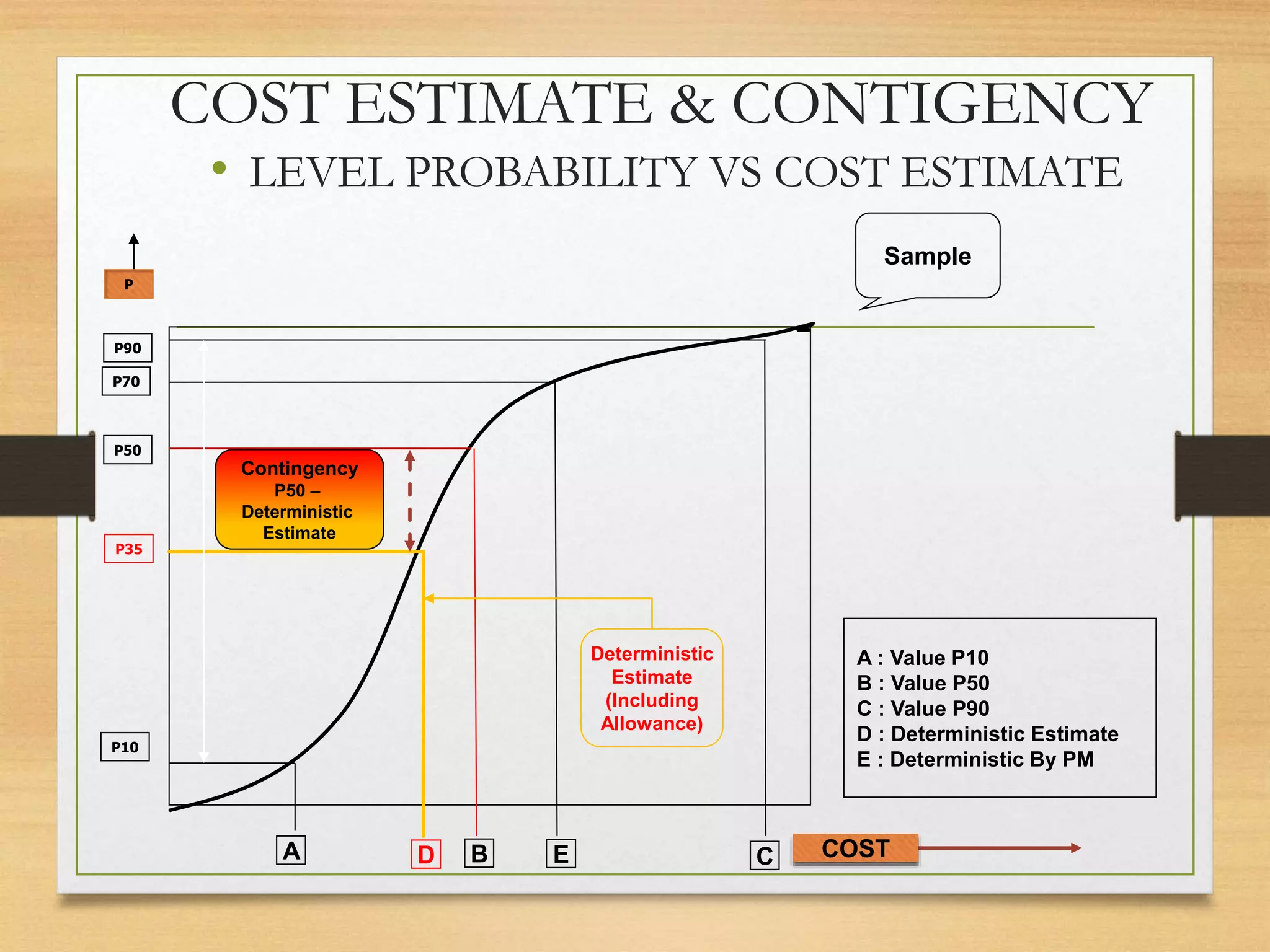
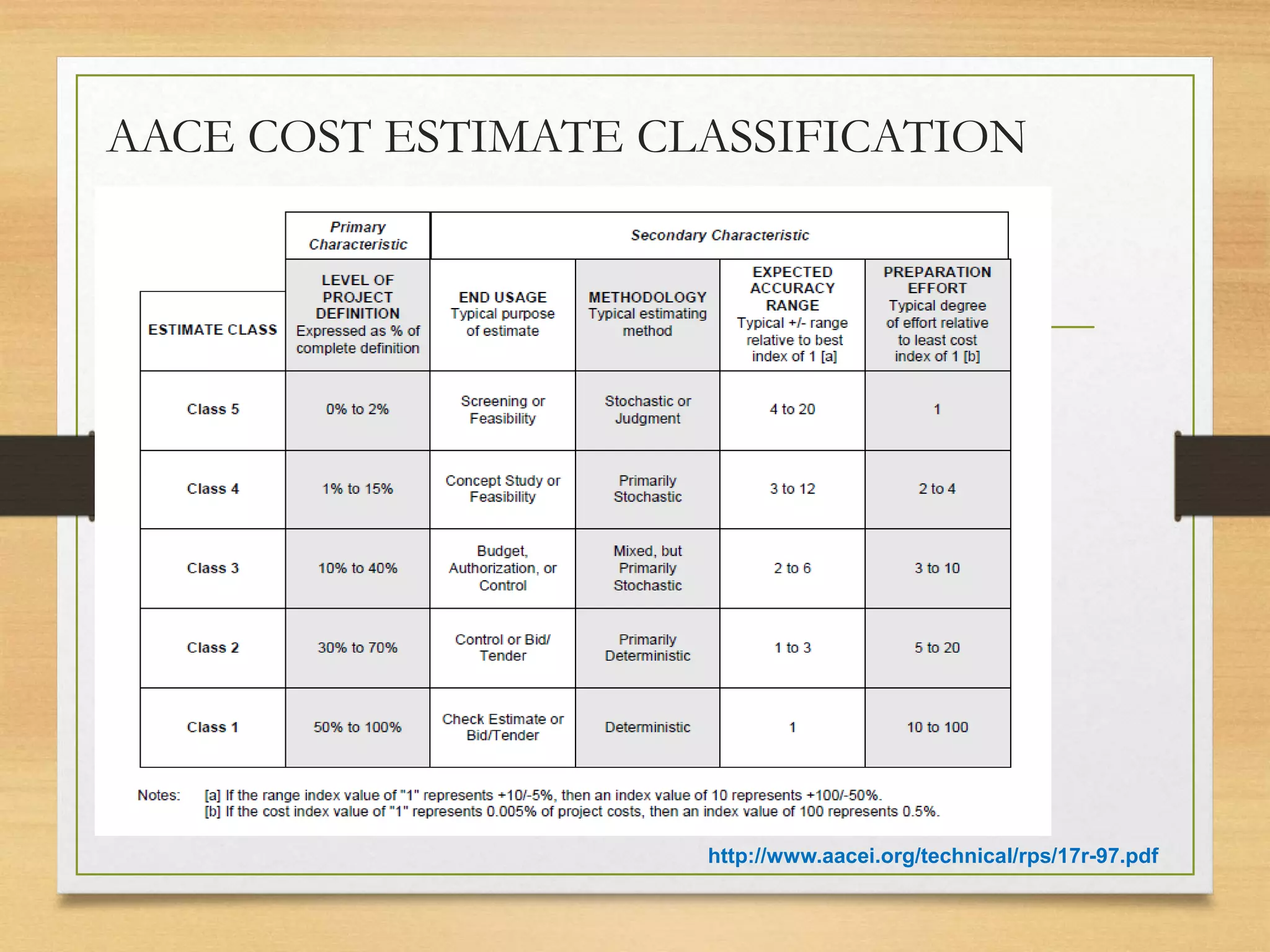
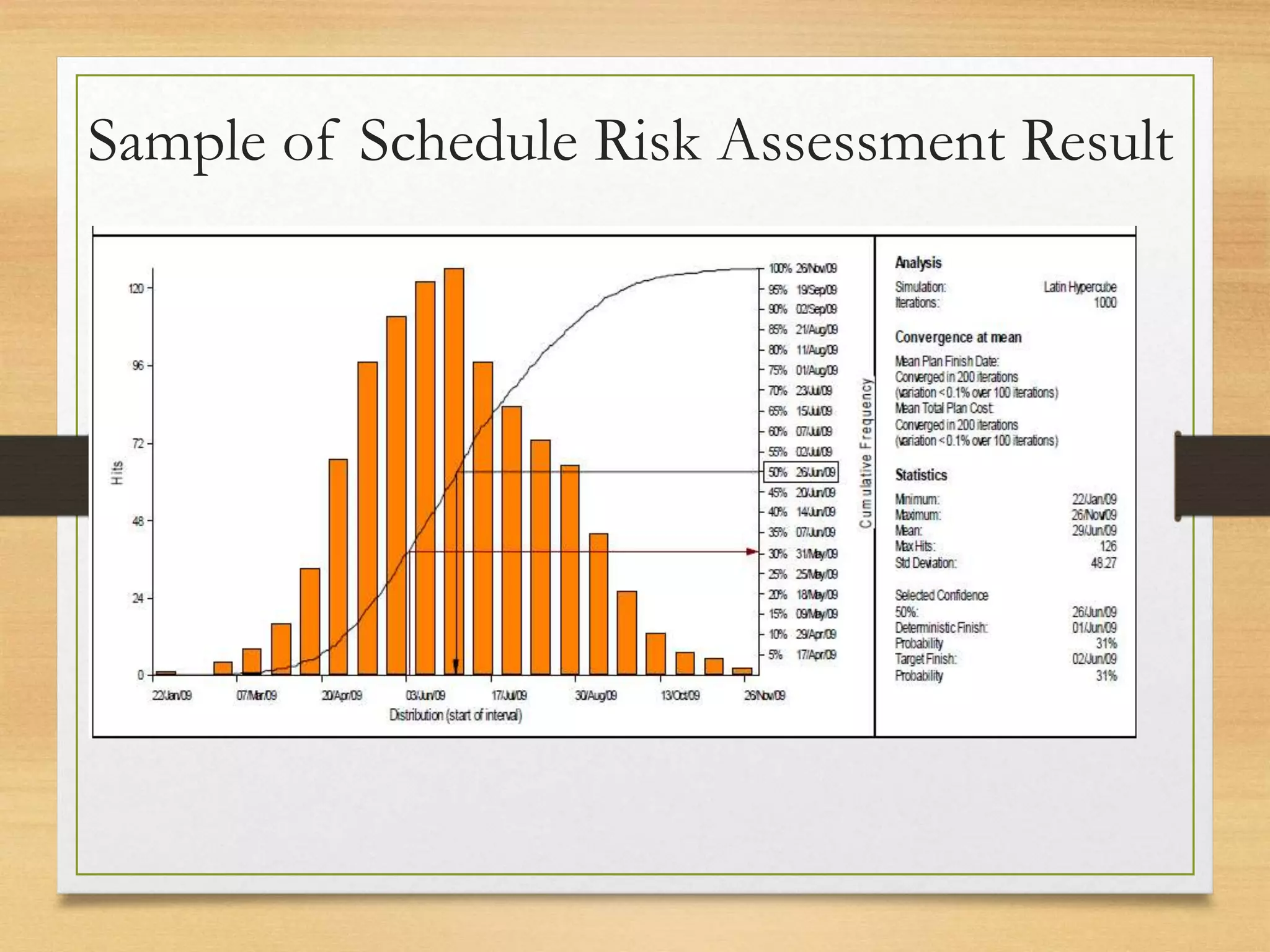
This document provides an overview of project risk management processes based on PMBOK and ISO 31000 standards. It discusses key concepts such as defining project risk, risk management, and establishing the context for risk identification. The core processes covered are identifying risks, analyzing and evaluating them based on impact and likelihood, developing treatment plans, and ongoing monitoring. Contingency planning is presented as a means to address risks through fallback options and workarounds. Various techniques are demonstrated like risk matrices and probabilistic cost estimating approaches.